Chapter 12 Infrastructure: Lifting Potential Growth
The Union Government increased capital expenditure nearly three-fold in FY24 compared to FY20 to boost infrastructure. Beneficiaries include roads and railways. Reforms like PPPs, the National Infrastructure Pipeline, and PM-GatiShakti facilitated execution. Improved physical, digital connectivity, and social infrastructure enhanced quality of life. Sustained growth requires viable PPP projects and periodic asset assessments.
Introduction
India aims to develop resilient, world-class infrastructure by 2047 to become ViksitBharat. Recent studies highlight investment gaps in various sectors. This chapter examines FY24 developments, focusing on financing infrastructure, balancing private and public investments, and addressing sectoral challenges. It discusses government efforts to reduce infrastructure bottlenecks, excluding financial and social infrastructures. The chapter concludes by outlining challenges, opportunities, and the way forward for infrastructure development.
Infrastructure Financing: Public Expenditure Push
Capital expenditure by the Union and State Governments have the central role in funding of large-scale infrastructure projects. Capital expenditure of the Union Government increased by 2.2 times from FY21 to FY24 (PA) while that of the State governments increased by 2.1 times during the same period.
| Union Government’s capital expenditure and its support for CPSEs and State Governments expands considerably | State Governments’ combined capital spending* also expands robustly |
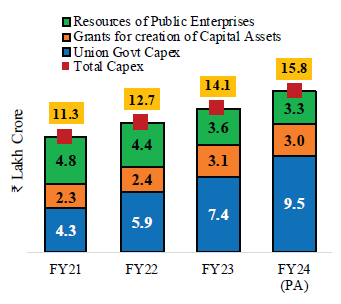 |
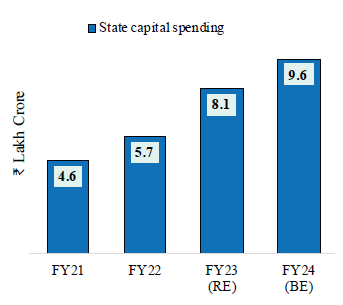 |
The support of the Union Government for capital expenditure of the State Governments
and instititions increased by 31.6 per cent during FY21 and FY24
| FDI equity inflows to infrastructure sectors during FY24 |
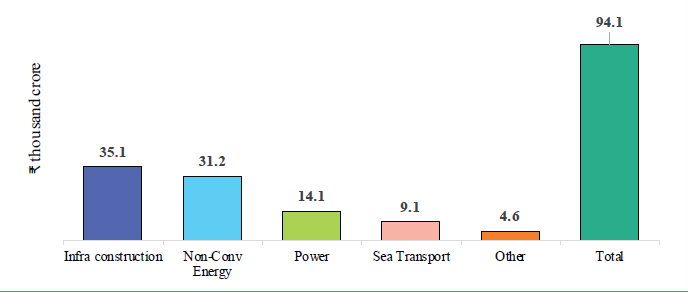 |
| Major Mechanisms for fostering Public Private Partnership (PPP)) |
|
National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP)
NMP was announced in August 2021 on the principle of ‘asset creation through monetisation’ i.e., tapping private sector investment for new infrastructure creation. The aggregate monetisation potential under NMP was estimated at ₹6.0 lakh crore through core assets of the Government, over four-years from FY22 to FY25.
DEVELOPMENTS ACROSS INFRASTRUCTURE SECTORS
This section discusses the progress in key infrastructure sectors along with outlook and challenges, including covering physical connectivity, electricity, water and sanitation, urban strategic and digital infrastructure. An attempt has been made to present only the details relating to infrastructure development in this chapter, leaving the discussion on infrastructure-related services to chapter on services.
Physical Connectivity Infrastructure
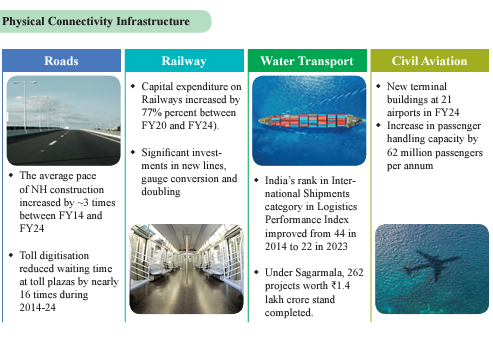
Road Transport:
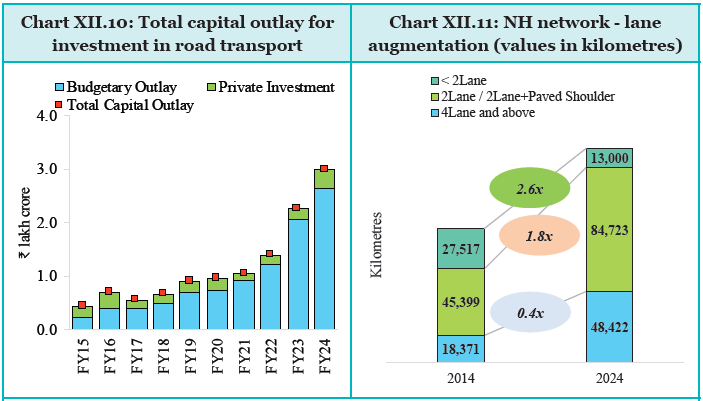
Strategic planning and increased public and private investment have upgraded India’s road network. Capital investment rose from 0.4% of GDP in FY15 to 1.0% in FY24, attracting record private investment and asset monetisation revenues. National highways expanded, construction efficiency tripled, and logistics efficiency improved, evidenced by a higher World Bank Logistics Performance Index ranking.
Outlook: The development of expressways and corridors, along with the adoption of transformative initiatives to promote user convenience and environmental sustainability, have been the highlight of the recent road sector growth journey. However, continuous ribbon development along developed NHs is posing a challenge for the construction of a new parallel road/bypass.
Rail Transport:
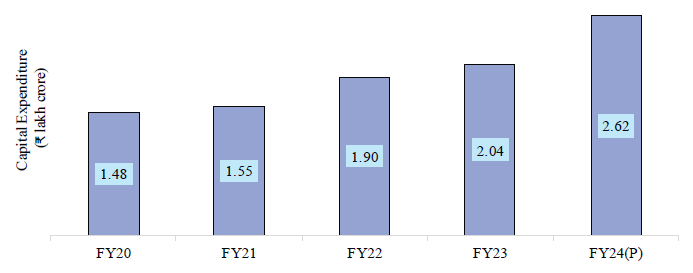
Indian Railways, with over 68,584 route km (as of 31st March 2024) and 12.54 lakh employees (as of 1st April 2024), is the fourth largest network in the world under single management. Capital expenditure on Railways has increased by 77 per cent over the past 5 years (₹2.62 lakh crore in FY24) with significant investments in the construction of new lines, gauge conversion, and doubling.
| Capital expenditure on railways |
 |
- Railways achieved its highest-ever production for both locomotives and wagons I FY24. Fifty one pairs of Vande Bharat have been introduced until March 2024.
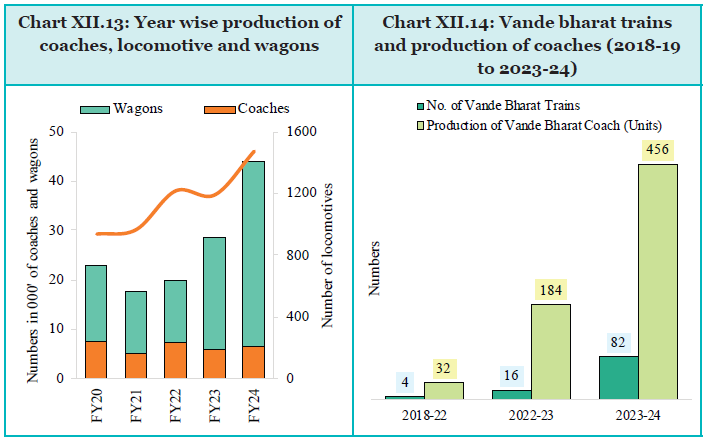
Key focus areas for Railways include capacity augmentation, modernisation, service quality, and energy efficiency. Investments target freight corridors, high-speed rail, modern passenger services, and renewable energy. Projects aim to reduce logistics costs and carbon footprint, with plans to install 30 GW of renewable capacity by 2029-30 and transition to electric traction.
Water Transport
- Indian ports have nearly doubled capacity since 2014, enhancing global competitiveness through improved connectivity and public-private partnerships. India’s World Bank Logistics Performance Index rank improved to 22nd in 2023. The Sagarmala programme has undertaken 839 projects worth ₹5.8 lakh crore, boosting port efficiency, connectivity, and coastal development.
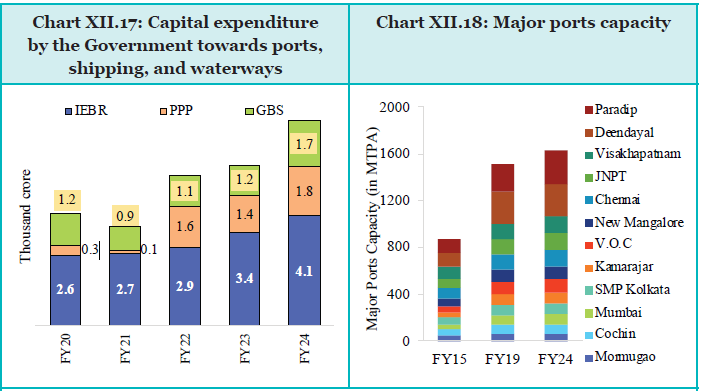
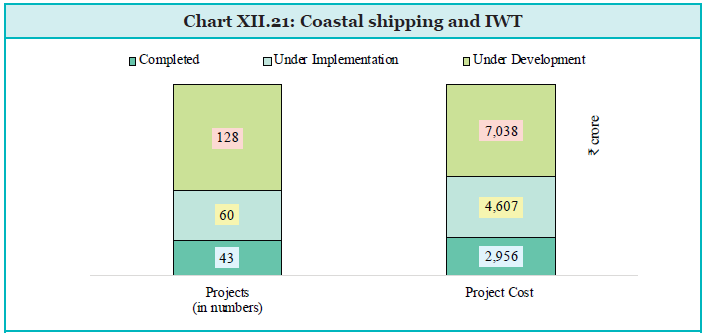
Coastal Shipping and Inland Water Transport
The Government’s focus on coastal shipping increased gross tonnage from 1.19 million GT (846 vessels) in 2014 to 1.72 million GT (1039 vessels) in 2024. Inland waterways, spanning 14,500 km, saw modernization through the Inland Vessels Act 2021 and significant capital expenditure. Key projects like Jal Marg Vikas and Indo-Bangladesh Protocol have enhanced navigation and cargo handling.
Civil Aviation
India is amongst the fastest-growing aviation markets globally. The Government has a capital expenditure plan of more than ₹26,000 crore for the period FY20 to FY25 to develop, upgrade and modernise airports to meet international standards.
Energy Infrastructure

Power Sector:
India’s unified power grid, with a 1,18,740 MW transfer capability, expanded to 4,85,544 circuit kilometers and 12,51,080 MVA by March 2024. Peak electricity demand rose 13% to 243 GW in FY24. The government boosted electricity generation, especially from renewables. Since October 2017, 2.86 crore households were electrified under Saubhagya. Implementation of the 2022 Electricity Rules settled ₹8.1 lakh crore of bills by April 2024.
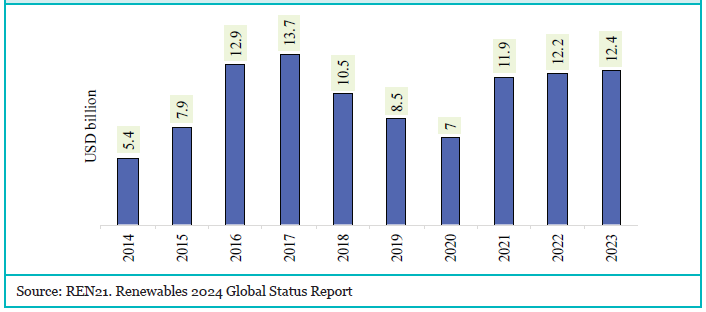
Renewable Sector
India’s updated nationally determined contributions aim for 50% of electric power from non-fossil fuels by 2030. The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy targets 500 GW of non-fossil capacity by 2030. By March 2024, 190.57 GW of renewable energy capacity was installed, representing 43.12% of total installed generation capacity.
| Investment in Renewables |
 |
Social and Economic Infrastructure

Sports Sector
Major Programmes, Projects, and Initiatives in Sports Sector
- Khelo India Programme: 323 infrastructure projects sanctioned at ₹3,073.7 crore; 38 new projects sanctioned and 58 completed in FY24.
- National Sports Development Fund: Ten projects sanctioned in FY24 (seven sports infrastructure, three sports promotion).
- Sports Authority of India: Nine infrastructure projects approved and 13 completed in FY24.
- National Sports University, Imphal: Development ongoing with ₹611.74 crore sanctioned; 56% physical progress.
- Model Concession Agreement (MCA): Drafted to promote private participation in sports infrastructure development on a DBFOT basis, enabling faster onboarding of private players by States/UTs and Union Government departments.
Water & Sanitation Sector
- The year 2024 marks 10 years of Swachh Bharat Mission – Grameen (SBM-G), Phase I which was launched in October 2014 to make India open defecation free (ODF) After achieving ODF, SBM-G Phase II has been launched to achieve Sampoorn Swachhata, i.e., sustaining the ODF status, managing solid and liquid waste by 2024-25 and transforming all the villages from ODF to ODF Plus Model. The total estimated outlay of SBM-G Phase-II is ₹1.4 lakh crore.
- The Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) launched in August 2019 to provide a tap water connection to every rural household by 2024 with a total outlay of ₹3.6 lakh crore.
Water Resource Management Sector
- The Namami Gange programme – National Mission on Clean Ganga (NMCG) launched in 2014-15 is a flagship integrated conservation mission focusing on pollution abatement, conservation, and rejuvenation of river Ganga. The budget for the programme has increased from ₹20,000 crore (2014-2020) to ₹22,500 crore (2021-2026)
| Major Programmes Water Resource Sector |
|
Urban Sector
Housing for All: The vision being pursued by the implementation of Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U) since 2015 to provide pucca houses with basic amenities to all eligible beneficiaries in urban areas.
Affordable Rental Housing Complexes (ARHCs) initiative is being taken up for the
first time in the country to improve living conditions and obviate urban migrants/ poor from
staying in slums, informal settlements or peri-urban areas.
Metro and RRTS: At present, 945 km of metro rail or regional rapid transit system (RRTS) lines are operational, and 939 km are under construction in a total of 27 cities.
Smart city Mission: SCM was launched in June 2015 to promote cities that provide core infrastructure, clean and sustainable environment and give a decent quality of life to their citizens through the application of ‘smart solutions’. A total number of 100 cities have been selected for development as smart cities. As on 20 June 2024, 100 SPVs have undertaken 8,011 multi-sectoral projects worth around ₹1.64 lakh crore.
Swatch Bharat Mission Urban (SBM-U): The objectives of SBM-U are to make the urban areas open defecation free (ODF) and achieving garbage free status for all cities. SBM-U achievement includes the construction of 63.07 lakh individual household latrine (IHHL) units surpassing the target by reaching 113.75 per cent and 6.37 lakh community and public toilets, exceeding the target by nearly 128 per cent.ar
Tourism Sector
Under the PRASHAD scheme which caters to the augmentation of tourism infrastructure at pilgrimage and heritage sites, 29 new sites have been identified for development.ties
Strategic Infrastructure
Space sector
- String of Space exploration missions has been conducted viz. Mars Orbiter Mission (2014), ASTROSAT (2015), Chandrayan-2 Orbiter (2019) and subsequently, Chandrayaan-3 landing on the Moon (2023) & Aditya – L1 mission (2023).
Digital Infrastructure
In recent years, various aspects of infrastructure development have been integrated with technology to improve the efficiency of infrastructure plans, designs, and assets. Some of the most significant uses of technology have been through:
- PM GatiShakti, Bhuvan, BharatMaps,
- Single Window Systems, PARIVESH portal,
- National Data Analytics Platform, Unified Logistics Interface Platform
- Pro-Active Governance and Timely Implementation (PRAGATI)
- India Investment Grid (IIG) and many similar dashboards and data stacks for almost all ministries
Telecommunication Sector
Government has also initiated the project for saturation of 4G mobile services with a total cost of ₹26,316 crore in 24,680 uncovered villages in remote and difficult areas. 6,279 villages having only 2G/3G connectivity shall be upgraded to 4G.
Electronics & Information Technology Sector:
The India AI programme aims to leverage transformative technologies for social impact through AI in governance, innovation, systems, data, skilling, and ethics. India, a founding member of GPAI, supports responsible AI development. Major initiatives include AIRAWAT, a top-ranked AI supercomputer, and Digital India, providing citizen-centric services via NSSO, DigiLocker, and UMANG.
Infrastructure Development and Challenges
- Land-Related Issues: Delays in land acquisition and digital land record integration hinder connectivity and energy infrastructure projects. Greenfield airport projects face time-intensive site selection and approvals.
- Skill Demands: Aviation sector requires technical skills for MRO operations and manufacturing. Effective public-private participation is essential.
- Private Participation: Limited due to capital investment, risk management, clearance delays, lack of independent regulators, and contractual disputes.
- Climate Compliance: Aviation sector must comply with CORSIA by 2027, facing high costs for sustainable aviation fuel and carbon credits.
- Financial Flows Aggregation: Complex financing structures involve multiple stakeholders with inconsistent reporting formats and definitions, complicating data aggregation and analysis.
FACILITATION AND ADDRESSING THE BOTTLENECKS
National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP)
NIP centralizes major infrastructure projects for tracking and investment opportunities. With a projected ₹111 lakh crore investment for FY20-25, it includes over 9,666 projects, predominantly in transportation and energy sectors.
Project Monitoring Group (PMG)
PMG resolves issues in projects over ₹500 crores, aiding 1,443 projects worth ₹46.1 lakh crore.
PM GatiShakti National Master Plan (PMGS-NMP)
PMGS-NMP integrates multimodal infrastructure planning across 43 Ministries, enhancing logistics efficiency with 1,530 data layers and 533 projects planned.
CONCLUSIONS AND OUTLOOK
India’s infrastructure has grown significantly, focusing on connectivity, sanitation, and digital assets, primarily led by public sector investment. Increasing private sector financing is crucial, requiring policy support and innovative funding approaches. Improved data capture and reporting mechanisms are needed for better resource allocation and tracking infrastructure demand and utilization.






