Yatharth January Magazine 2025
History
1. Deciphering Indus Valley Script
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

Overview of the Indus Valley Civilisation
- The IVC, also called the Harappan Civilisation, existed during the Bronze Age (3000-1500 BCE).
- Spanning over 1.5 million square kilometers, it covered parts of modern-day India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan.
- It was geographically larger than the Egyptian and Mesopotamian civilisations combined.
- Renowned archaeologist Ahmad Hasan Dani noted that the IVC lay across ancient migration routes linking Central and Western Asia to India.
Stalin’s Offer and the Indus Script Mystery
- Tamil Nadu Chief Minister M.K. Stalin’s $1 million prize for deciphering the Indus Valley script aims to address a historical enigma while reinforcing his position as a defender of Tamil and Dravidian heritage.
- The move aligns with recent findings linking the Indus script and Tamil Nadu’s ancient graffiti, strengthening claims of cultural continuity.
The Study Behind the Announcement
The study titled “Indus Signs And Graffiti Marks of Tamil Nadu – A Morphological Study” by K. Rajan and R. Sivananthan documents over 15,000 graffiti marks from Tamil Nadu and compares them with 4,000 Indus Valley artefacts. Key findings include:
- Identification of 42 base signs, 544 variants, and 1,521 composite forms.
- Nearly 60% of Tamil Nadu signs show parallels with the Indus script.
- The study posits cultural exchanges between the Copper Age Indus and Iron Age South India, suggesting a shared or evolved symbolism rather than a lost script.
About the Indus Script:
- The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), one of the most advanced ancient urban cultures, left behind an enduring mystery in its undeciphered script.
- Since its discovery in the 1920s, scholars have made numerous attempts to decode this enigmatic script, often sparking debates over its linguistic and cultural implications.
- Recent research by Bahata Ansumali Mukhopadhyay offers fresh perspectives, suggesting that the script primarily served commercial purposes.
Significance of the Findings
- Excavations at Keeladi, Sivagalai, and Thulukarpatti yielded graffiti marks that resonate with Indus symbols.
- This underscores the possibility of cultural contact or continuity, challenging established Aryan-centric historical narratives.
- The Tamil Nadu study’s morphological, non-linguistic approach highlights the evolution of these symbols rather than their disappearance.
Conclusion
- Stalin’s prize announcement and the Tamil Nadu study advance both historical and political agendas.
- They seek to resolve the enduring mystery of the Indus script while asserting the importance of Tamil culture and identity, challenging mainstream historical narratives with scientific and cultural evidence.
- Deciphering the Indus script necessitates more comprehensive archaeological exploration and analysis.
- Expanding the dataset, uncovering multilingual artefacts, and identifying the language linked to the script are critical steps.
- Only with these breakthroughs can scholars hope to unravel one of the greatest enigmas of ancient history.
| Indus Valley Script and Challenges in Deciphering the Script |
Absence of Multilingual Inscriptions
Unknown Language
Limited Material Evidence
|
| PYQ: To what extent has the urban planning and culture of the Indus Valley Civilization provided inputs to the present-day urbanization? Discuss.(150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2014 |
Art and Culture
1. This tribe prefers to live and let ‘live-in’
| Context |
|
Location and Population of the Konda Reddi Tribe:
- The Konda Reddi Tribe primarily resides in the hilly and forested regions of Andhra Pradesh.
- The tribe is primarily concentrated in the districts of East Godavari, West Godavari, Khammam, and Srikakulam.
Economic Activities:
- The tribe primarily practices shifting cultivation.
- Key commercial crop: Annatto, used in lipstick-making.
- Red soil from the region is used for constructing traditional mud-walled houses.
Marriage Traditions:
- Live-in Relationships: Increasingly preferred due to the financial burden of traditional weddings.
- Traditional Weddings: Ritualistic ceremonies lasting four days, involving feasts with mandatory chicken and mutton dishes.
- Laagudu Tradition: The bride is “abducted” by the groom’s family, followed by wedding negotiations.
Community and Cultural Changes:
- The tribe is experiencing gradual cultural shifts, such as intermarriage with non-tribals.
- Disputes within the community are traditionally resolved by village elders.
2. A giant palm unearthed amid ASI excavation
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

Objective of the Excavations
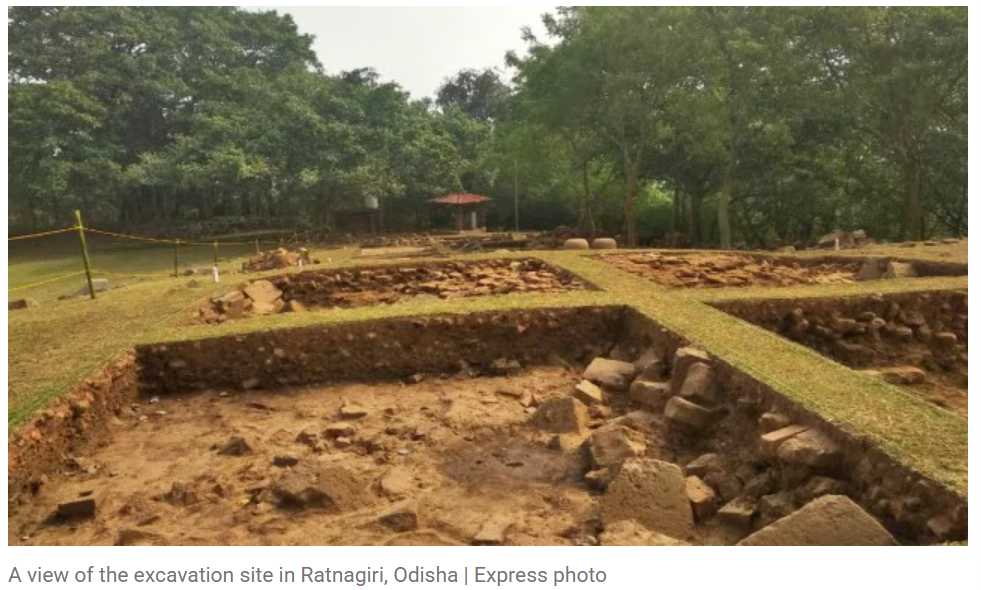
- In December, the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) resumed excavations at the 5th-13th century Buddhist site in Ratnagiri, Odisha, after a 60-year hiatus.
- Led by D. B. Garnayak, the team aimed to further uncover the Buddhist complex and investigate its links to Southeast Asian culture.
Key Discoveries
- The team unearthed significant artifacts, including a colossal Buddha head (3-4 feet tall), a massive palm (5 feet), ancient walls, and inscribed Buddhist relics, estimated to date back to the 8th-9th century AD.
- These findings underscore Ratnagiri’s historical and cultural importance as a Buddhist center.
Historical Significance of Ratnagiri
- Located 100 km northeast of Bhubaneswar and part of Odisha’s “Diamond Triangle,” Ratnagiri was first documented in 1905.
- Earlier excavations (1958-61) uncovered numerous relics, including a brick stupa, monastic complexes, and votive stupas, establishing its reputation as Odisha’s most excavated Buddhist site.

Odisha’s Role in Buddhism and Southeast Asia
- Odisha’s maritime trade with Southeast Asia historically facilitated the spread of Buddhism.
- The Baliyatra festival commemorates these 2,000-year-old trade links with regions like Bali, Java, Sumatra, and Burma.
- Mauryan Emperor Ashoka’s conversion to Buddhism after the Kalinga War further elevated the state’s Buddhist prominence.
Ratnagiri as a Learning Center
- Between the 7th and 10th centuries, Ratnagiri rivaled Nalanda as a hub for Buddhist learning, especially for Mahayana and Tantrayana (Vajrayana) sects.
- Scholars believe the site was visited by Hiuen Tsang during 638-639 AD and played a pivotal role in the region’s intellectual and religious history.
3. Study moots inclusion of 179 groups on SC, ST, and OBC lists
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The Anthropological Survey of India (AnSI) and Tribal Research Institutes (TRIs) conducted a three-year-long ethnographic study.
- The study categorized 268 denotified, semi-nomadic, and nomadic tribes that were previously unclassified, including tribes like Banjara, Gonds, Kanjar, Dhangar, Saharia, and Rajputs.
- Of these, 46 communities are recommended for OBC status, including Banjara and Gonds, 29 for SC status, including Saharias and Dhangars, and 10 for ST status, including Gonds and Kanjar.
- Uttar Pradesh had the highest number of fresh additions, with 19 communities recommended for inclusion, such as Saharias, Dhangars, and Kanjar.
- 63 communities were classified as “not traceable,” indicating possible assimilation or migration.
- The study’s findings are under scrutiny by the NITI Aayog panel.
- The report may impact the debate over caste-based quotas and the inclusion of these communities in the next Census.
4. President Murmu’s invite for Republic Day
| Context |
|

Kalamkari Paintings
- Kalamkari is a traditional hand-painted or block-printed textile art.
- The paintings often depict mythological themes and nature-inspired motifs.
- Nimmalakunta artisans, known for their intricate work, create these paintings.
- They are made using natural dyes and a painstaking, detailed process.
Ikat-Pochampalli Cover
- Ikat is a resist-dyeing technique used to create unique patterns on fabric.
- Pochampalli is a renowned weaving tradition from Telangana.
- The cover is crafted with bright, geometric patterns typical of this art form.
- The fabric is durable and reusable, promoting sustainability.
- The Ikat-Pochampalli cover adds elegance and cultural significance to the box.
Ganjifa Art Magnet
- Ganjifa art originates from Mysore and is inspired by traditional playing cards.
- It features intricate designs and motifs, often hand-painted.
- The art depicts cultural and mythological themes in vibrant colors.
- It showcases the artistic heritage of Karnataka.
Kanjeevaram Silk Pouch
- Kanjeevaram silk is a traditional handwoven silk from Tamil Nadu.
- Known for its vibrant colors and rich textures, it is widely admired.
- The silk is woven using pure mulberry silk and gold zari threads.
- It represents the exceptional craftsmanship of Tamil Nadu.
Etikopakka Dolls
- Etikopakka dolls are traditional wooden toys made in Andhra Pradesh.
- They are crafted using soft wood and lacquer derived from natural dyes.
- These toys are eco-friendly and safe for children.
- Each doll is handcrafted with attention to detail and design.
- They are a reflection of Andhra Pradesh’s artisan heritage.
Screwpine Leaf Bookmark
- Screwpine leaves are woven to create fine handicrafts in Kerala.
- The craft involves drying, slicing, and weaving the leaves into intricate patterns.
- Artisans create durable and sustainable products using this material.
- It symbolizes Kerala’s rich tradition of natural fiber weaving.
5. Chinese New Year 2025
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Lunisolar Calendar System
- Unlike the Gregorian calendar, the Chinese follow a lunisolar system, integrating both solar and lunar cycles.
- The year starts with the second or third new moon after the winter solstice, requiring adjustments like an extra 13th month every three years to align with seasonal changes.
Fortune-Telling and Zodiac Signs
- The Chinese calendar follows a 60-year cycle, combining Heavenly Stems, Earthly Branches, Five Elements, Yin-Yang forces, and the 12 zodiac animals. 2025 marks the Year of the Wood Snake, symbolizing wisdom, transformation, and personal growth.
Mythical Origins and Legends
- The festival’s origins trace back to the legend of Nian, a beast that terrorized villages until people discovered its fear of loud noises and the color red—leading to traditions of fireworks, red decorations, and festive lights.
- The zodiac’s origin story comes from a race held by the mythical Jade Emperor, determining the order of the 12 animals.
New Year Celebrations
- The festival, observed between January 21 and February 20, involves house cleaning to remove bad luck, family feasts, symbolic foods like dumplings (wealth) and fish (abundance), and the exchange of red envelopes (hóngbāo) for prosperity.
- Superstitions like avoiding negative words and not sweeping on New Year’s Day are strictly followed.
Global Celebrations
- Chinese New Year is observed worldwide, including in Vietnam (Tết) and Korea (Seollal), with major celebrations in cities like San Francisco, Melbourne, and Singapore, uniting over two billion people in cultural festivities.
6. Revised Iron Age Timeline
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

Key Discoveries and Dates
- Earliest Evidence: Sivagalai yielded dates as early as 3345 BCE from charcoal and potsherds.
- Milestone Sites: Mayiladumparai samples were dated to 2172 BCE, while a burial at Kilnamandi was dated to 1692 BCE.
- Global Context: These findings redefine Tamil Nadu as an innovator in metallurgy, showcasing a trajectory distinct from the northern Copper Age.
Technological Sophistication
The study identified advanced iron-smelting techniques across Tamil Nadu:
- Furnace Innovation: Sites like Kodumanal featured circular furnaces capable of reaching 1,300°C, enabling the production of sponge iron.
- Metallurgical Expertise: The mastery of high-temperature smelting (1,200°C to 1,400°C) reflects an advanced understanding of pyro-technology.
Implications for Indian and Global Archaeology
- The findings suggest that Tamil Nadu’s Iron Age coincided with the Copper Age of northern India, marking a parallel but unique cultural development.
- This challenges assumptions about the global origins of iron technology and aligns with reports of iron from Harappan sites like Lothal.
7. Dinosaur highway: where dinos walked
| Context |
|
A Dinosaur highway:
- A limestone quarry in Oxfordshire, UK, is known as a “dinosaur highway” due to numerous dinosaur footprints found there.
- In 1997, more than 20 dinosaur footprints, some extending 180 meters, were discovered at Dewars Farm Quarry.
- The footprints date back to the Jurassic period.
- On January 4, 2024, over 200 new footprints were uncovered by a team from the University of Birmingham and the University of Oxford.
- The footprints, from the Middle Jurassic period, were made by sauropods (cetiosaurus) and a carnivore (megalosaurus).
- The discovery includes five trackways, with evidence that the dinosaurs were walking, not running.
8. Maha Kumbh Mela 2025
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Key Takeaways
Spiritual Significance
- The Maha Kumbh Mela is deeply rooted in Hindu beliefs, offering devotees the opportunity to absolve sins and attain Moksha (liberation).
- It is considered auspicious due to planetary alignments that enhance spiritual energy, making it a transformative event for spiritual practices.
Historical Foundations
- The festival is tied to ancient mythology, particularly the Samudra Manthan (churning of the ocean) story, where drops of Amrita (nectar) fell at the four Kumbh Mela sites.
- References in the Mahabharata and Puranas add a mythical charm to its origins.
Cultural Relevance
- The Sangam (confluence) of the Ganga, Yamuna, and Saraswati rivers at Prayagraj is the festival’s focal point.
- Rituals performed here are believed to cleanse sins and grant spiritual freedom, fostering unity among diverse communities.
Modern Relevance
- Beyond its religious importance, the Kumbh Mela remains a symbol of cultural heritage, spirituality, and universal harmony, bringing together people across backgrounds for shared pursuits of peace and devotion.
Key Rituals
- Shahi Snan (Royal Bath): Led by ascetic groups like Naga Sadhus, this ceremonial dip in holy rivers is the highlight, symbolizing spiritual purification.
- Sankirtan and Bhajans: Devotional songs and chants create a vibrant spiritual ambiance.
- Yoga and Meditation: Visitors engage in practices for physical and mental well-being.
- Spiritual Discourses: Renowned saints deliver teachings on philosophy and spirituality.
9. Pravasi Bharatiya Divas
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Why January 9?
- Pravasi Bharatiya Divas is celebrated annually on January 9 since 2003 to honor the contributions of the Overseas Indian community to India’s development.
- The date commemorates Mahatma Gandhi’s return to India from South Africa in 1915, marking the beginning of his pivotal role in India’s freedom struggle. Since 2015, the event has been held biennially.
Historical Background
- The initiative stemmed from the recommendations of a High-Level Committee on Indian Diaspora led by LM Singhvi in 2002.
- The committee emphasized the need to strengthen ties with the Indian diaspora and proposed the establishment of a Pravasi Bharatiya Bhavan for networking and preserving the diaspora’s history.
- The first PBD was held in 2003 to implement these ideas.
PBD 2025 in Odisha
- The 18th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas Convention is scheduled from January 8–10, 2025, in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, under the theme “Diaspora’s Contribution to a Viksit Bharat”.
- The event celebrates India’s bond with its global diaspora and showcases Odisha’s economic opportunities, especially in the ASEAN and Indo-Pacific regions.
- Known for its strengths in mining, steel manufacturing, marine economy, IT, and sports, Odisha will leverage the event to attract investments and partnerships.
Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Award (PBSA)
The PBSA is the highest honor for Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) and Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs). It recognizes contributions to India’s global image, local Indian communities’ welfare, and promoting India’s causes abroad.
- 2025 Awards: 27 individuals and organizations from countries like the US, Fiji, Mauritius, and Russia will be honored.
- Conferment: President Droupadi Murmu will present the awards during the valedictory session.
10. Tyagaraja’s guidance
| Context |
|
More About Tyagaraja:

- Born in Tiruvarur, Tamil Nadu, he belonged to the Telugu Brahmin Mulakanadu sect of the Kakarla vamsa.
- His aradhana (commemoration) is observed worldwide by musicians and devotees.
- He emphasized that devotion to God, particularly through chanting the name of Rama, is the way to attain divinity.
- Tyagaraja led a simple, disciplined, and austere life, focusing on spiritual practice rather than elaborate rituals.
- At 18, he was instructed by a sage to chant Lord Rama’s name 96 crore times, leading to divine visions.
- It is believed that Tyagaraja received divine blessings, including the grace of Narada, in his spiritual journey.
11. Where did dinosaurs first evolve?
| Context |
|
Species in news – Mbiresaurus Raathi

- Species: Mbiresaurus raathi is a species of dinosaur discovered in Zimbabwe.
- Size: It was about one meter tall and weighed approximately 30 kilograms.
- Tail: The dinosaur had a long tail, which was typical for early dinosaurs.
- Habitat: It lived in what was likely a hot, dry environment with seasonal wildfires.
- Discovery: Its remains were found in 2019 in the northern part of Zimbabwe.
- Era: The fossils date back to around 230 million years ago, during the Late Triassic period.
- Significance: Mbiresaurus provides insights into early dinosaur evolution.
- Mbiresaurus is one of the oldest-known dinosaur species.
Indian Society
1. The impact of classifying denotified tribes
| Context |
|
Comprehensive Categorization of Tribes

- The Anthropological Survey of India (AnSI) and Tribal Research Institutes (TRI) have classified 268 denotified, semi-nomadic, and nomadic tribes for the first time.
- This study included 1,559 individuals across South and Southeast Asia and recommended the inclusion of 179 communities in the Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST), and Other Backward Classes (OBC) lists.
- Among these, 85 communities were classified for the first time.
- However, 63 communities could not be traced, suggesting they may have assimilated or migrated.
Why the Study Was Needed?
- After the repeal of the Criminal Tribes Act in 1949, many tribes were denotified, but their classification remained incomplete.
- Various commissions, including the Kalelkar, Lokur, Mandal, Renke, and Idate Commissions, have tried to address this but faced difficulties.
- The Idate Commission in 2017 found over 1,200 tribes but also highlighted the lack of classification for 267 tribes.
- A Special Committee formed in 2019 gave the task of classification to AnSI and TRIs, who submitted their report in 2023.
Need for Categorization
- The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Social Justice and Empowerment stressed the urgency of categorizing these communities for better welfare access.
- Misclassification in previous censuses has led to confusion regarding tribes and castes.
- Some communities remain unclassified, making it difficult for them to avail welfare schemes.
Impact of the Study
- The classification of these tribes is creating political debate, especially regarding reservations for SC, ST, and OBC categories.
- Activists and experts are discussing whether these tribes should be classified separately or included under existing categories.
- The study could ease the process of including these communities in welfare programs.
Next Steps
- The Special Committee is reviewing the report and will prepare a final report for government action.

| PYQ: Why are the tribals in India referred to as the Scheduled Tribes? Indicate the major provisions enshrined in the Constitution of India for their upliftment. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2016) |
2. Origins of Nicobarese people
| Context |
|
Early Human Migration
- More than 500,000 years ago, human ancestors began migrating beyond Africa in search of food and better living conditions.
- Over time, humans spread to all habitable parts of the world, but some migration stories are still unclear.
New Genetic Findings
- The research team analyzed 1,559 DNA samples from South and Southeast Asia.
- The Nicobarese share a genetic link with the Htin Mal community from the Laos-Thailand region.
- They have also retained their Austroasiatic language roots, belonging to the Khmuic branch.
Revised Migration Timeline
- Earlier studies suggested the Nicobarese arrived 11,500 years ago, but new genetic research shows they migrated around 5,000 years ago.
- DNA mutations, which occur due to environmental changes, helped researchers refine the migration timeline.
Differences Between Andamanese and Nicobarese
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are separated by the Ten Degree Channel (150 km wide).
- Despite their proximity, the Andamanese and Nicobarese have distinct physical features and genetic histories.
- A 2005 study found Andamanese tribes like Onge and Great Andamanese preserved two ancient maternal genetic lineages M31 and M32, dating back 50,000–70,000 years.
Future Research Plans
- The Nicobarese live in isolation, which has preserved their genetic identity without much mixing with other populations.
- Their lifestyle differs greatly from genetically similar Southeast Asian groups.
- Scientists aim to study how natural selection and environmental factors have shaped their immunity and survival strategies.
- Their isolation from pathogens makes them vulnerable to infections from the outside world.
| Nicobarese Tribe |
|
| PYQ: Why are the tribals in India referred to as the Scheduled Tribes? Indicate the major provisions enshrined in the Constitution of India for their upliftment. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2016) |
Geography
1. Artesian Well
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
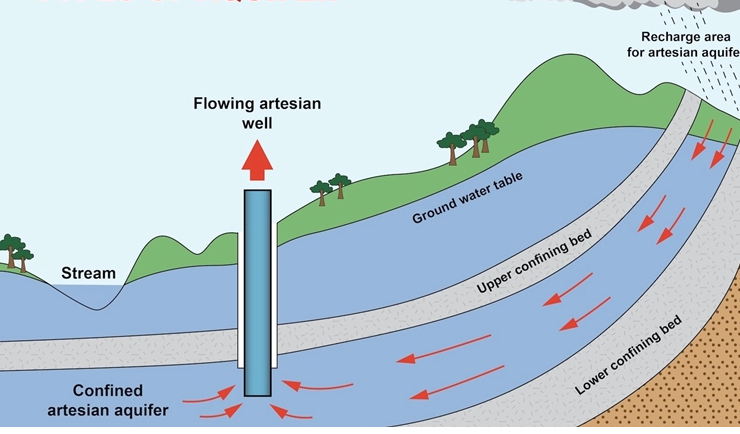
Artesian Well
The Event
- In Rajasthan’s Jaisalmer district, a rare phenomenon occurred in Taranagar village on December 27, 2023, when water began gushing out uncontrollably from underground after a farmer drilled a tube well.
- The high-pressure water flow created a large pit, inundating nearby land. Accompanying the water was a small amount of non-inflammable gas.
- The flow ceased on its own on December 29, drawing significant attention and speculation.
Claims and Scientific Explanation
- Some linked the event to the ancient Saraswati river mentioned in the Rig Veda, but scientists dismissed this and attributed it to artesian conditions.
- Artesian aquifers store water under pressure between impermeable geological layers, like sandstone in this case.
- When these layers are punctured, the pressure forces water to flow upward naturally, unlike traditional wells where external force is required.
What Are Artesian Conditions?
- Artesian water is confined below impermeable rock layers under pressure. When ruptured, the water rises to the surface without mechanical intervention.
- The phenomenon, named after Artois, France, where such wells were first identified, occurs in specific geological conditions.
Why in Jaisalmer?
- In desert regions like Jaisalmer, artesian aquifers lie beneath layers of sandstone.
- The drilling ruptured this layer, releasing water under immense pressure. Similar events have been recorded in Mohangarh and Nachana areas, as well as in deserts of Australia and Africa, but the intensity in Taranagar was unprecedented.
Broader Significance
- This incident highlights the unique geology of Rajasthan’s desert regions and underscores the importance of careful groundwater management.
- It also dispels myths linking such occurrences to ancient rivers, emphasizing the role of scientific inquiry in understanding natural phenomena.
2. Severe Winter Storm in the US
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Impact of the Winter Storm in the United States
- A severe winter storm has caused widespread disruptions across the United States, leading to the loss of at least five lives, mass school closures, hazardous road conditions, and power outages.
- Approximately 60 million people across 30 states are under weather alerts, with seven states declaring emergencies: Maryland, Virginia, West Virginia, Kansas, Missouri, Kentucky, and Arkansas.
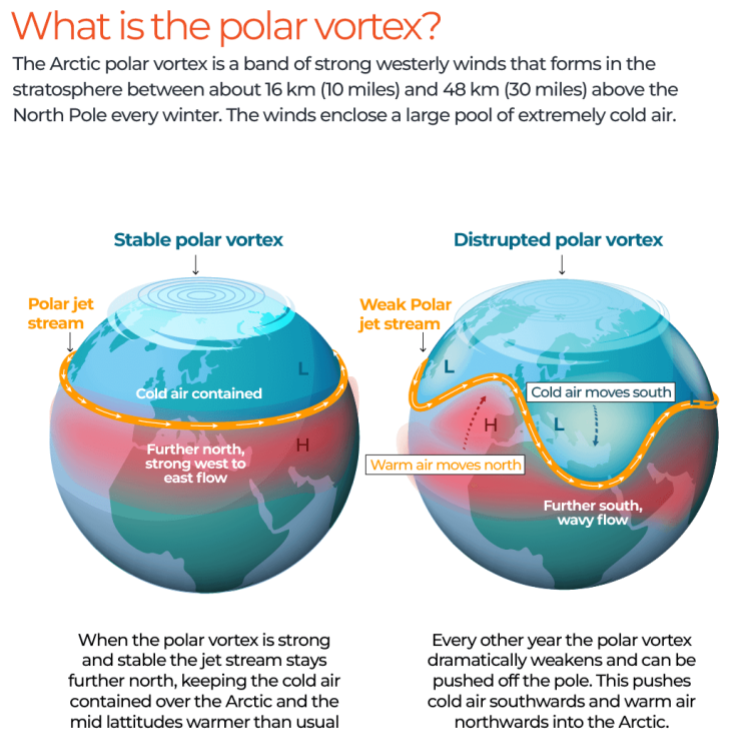
What is the Polar Vortex?
The polar vortex is a large, low-pressure system of cold air swirling around the Earth’s polar regions. It exists in two forms:
- Tropospheric Polar Vortex: Found in the lowest layer of the atmosphere (up to 15 km), where most weather phenomena occur.
- Stratospheric Polar Vortex: Located 15–50 km above the surface, strongest in autumn and disappears in summer.
Extreme cold occurs when the polar vortex weakens, allowing arctic air to travel southward, disrupting weather patterns and leading to cold spells even in regions as far south as Florida.
Role of the Jet Stream in Weather Disruptions
- The jet stream, a strong wind band in the upper atmosphere, typically keeps cold air confined to the poles.
- When the polar vortex weakens, the jet stream becomes wavy and unstable, enabling cold air to spill southward.
- This interaction is a key factor in creating extreme weather conditions during polar vortex disruptions.
Climate Change and the Polar Vortex
- Research is ongoing to determine the exact link between climate change and the polar vortex.
- However, some scientists argue that the accelerated warming of the poles weakens the polar vortex and jet stream, making them more prone to disruptions.
- As global temperatures rise unevenly, the imbalance further destabilizes the system, leading to more frequent and intense cold spells in mid-latitude regions.
3. Wildfires in Los Angeles
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
What Are Wildfires?
Wildfires are uncontrolled fires that spread rapidly across forests, grasslands, or urban areas, fueled by dry vegetation and wind.
- While they are natural occurrences in ecosystems, human activities and climate change have amplified their frequency and severity.
The Escalating Wildfire Crisis in Los Angeles
- Wildfires raging across Los Angeles have caused significant devastation, including the loss of 10 lives, evacuation of over 130,000 people, and destruction of numerous properties, including celebrity homes.
- These fires, occurring unusually in winter, have disrupted life, including delays in events like the Oscars nominations announcement.
Unusual Weather Patterns: From Wet to Dry
- Los Angeles has experienced extreme weather fluctuations in recent years. The unusually wet winters of 2022 and 2023 promoted abundant vegetation growth.
- This year’s exceptionally dry winter has turned this vegetation into highly flammable material.
- With negligible rainfall since October, the region has recorded its driest start to the water year since 1944, intensifying the wildfire risk.
Impact of Santa Ana Winds
- The Santa Ana winds, a seasonal phenomenon, are unusually strong this year.
- Originating from high-pressure systems in the Great Basin, these winds blow westward, descending the Sierra Nevada and Santa Ana mountains.
- As they lose humidity, gain speed, and heat up, they fuel and spread fires rapidly across Southern California, exacerbating the crisis.
Role of Climate Change
- Climate change has intensified California’s wildfire season. Rising global temperatures have led to warmer springs and summers, early snow melts, and longer dry seasons.
- These conditions increase moisture stress on vegetation, creating an ideal environment for wildfires.
- Studies have shown that the state’s wildfire season is not only longer but also more intense than in previous decades.
Conclusion:
- The wildfires in Los Angeles are the result of a confluence of factors, including extreme weather variations, strong seasonal winds, and climate change.
- Addressing this crisis requires urgent measures to mitigate climate change, improve disaster preparedness, and manage vegetation growth to reduce wildfire risks.
| Measures to Mitigate Wildfires |
|
Indian Polity
1. The nature of dissent in the Indian judiciary
| Context |
|
Dissent in Democracies: A Comparative Overview:
Role of Dissent in Democracy
- Dissent is an essential component of a vibrant democracy, including in the judiciary.
- While both the Indian and U.S. Supreme Courts feature powerful judicial dissents, the underlying reasons differ between the two countries.
Dissents in the U.S. Supreme Court (SCOTUS)
- SCOTUS dissents are often influenced by the political leanings of the appointed judges.
- Example: Justice Stephen Breyer (appointed by Democrats) supported pro-affirmative action, anti-capital punishment views, as seen in his dissent in Glossip v. Gross (2015).
- Example: Justice Samuel Alito (appointed by Republicans) opposed same-sex marriage and abortion rights, as demonstrated in his dissent in Obergefell v. Hodges (2015).
Political Dissent in the Indian Supreme Court
- Unlike the U.S., Indian judges are selected by a collegium of senior judges, reducing political influence in decisions.
- Example: ADM Jabalpur (1976) – Justice H.R. Khanna dissented against suspending fundamental rights during the Emergency, a stance that later became law through a constitutional amendment.
- Example: P.V. Narasimha Rao (1998) – Justices Agarwal and Anand dissented on parliamentary immunity regarding accepting bribes, a stance later overruled in Sita Soren (2023).
Social Dissent in the Indian Supreme Court
- Dissent can reflect different social views on legal issues, particularly when they touch on personal or religious matters.
- Example: Shayara Bano (2017) – Justices Khehar and Nazeer dissented from the majority opinion that struck down triple talaq, arguing it was an integral part of Sunni personal law.
- Example: Aishat Shifa (2022) – Justices Gupta and Dhulia had different views on whether the hijab ban in schools infringed upon secularism.
Intellectual Dissent in the Indian Supreme Court
- Some dissents are rooted in intellectual debates over constitutional interpretation.
- Example: Lalta Prasad Vaish (2024) – Justice Nagarathna dissented on the interpretation of “intoxicating liquor” in the Constitution, focusing on textual clarity.
Conclusion
- Dissent serves as a critical tool for maintaining judicial independence and shaping legal precedents in democracies.
- It fosters deeper engagement with legal principles and societal values.
2. Gujarat’s Banaskantha district bifurcated
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Creation of Vav-Tharad District
- The Gujarat government has decided to bifurcate Banaskantha district, creating a new district named Vav-Tharad with its headquarters at Tharad.
- This decision was made during the state cabinet meeting chaired by Chief Minister Bhupendra Patel.
- With this move, Gujarat will now have 34 districts.
Rationale Behind the Decision
- Banaskantha is Gujarat’s largest district in terms of talukas and the second largest by area.
- The division is aimed at improving accessibility and ensuring better public services.
- By creating Vav-Tharad, people in remote villages will no longer have to travel an additional 35-85 km to reach administrative facilities.
Structural Details of the New Districts
Vav-Tharad District:
- Talukas: Vav, Bhabhar, Tharad, Dhanera, Suigam, Lakhni, Diodar, and Kankrej.
- Area: 6,257 sq km.
- Municipalities: Bhabhar, Tharad, Thara, and Dhanera.
Banaskantha District:
- Talukas: Palanpur, Danta, Amirgadh, Dantiwada, Vadgam, and Deesa.
- Area: 4,486 sq km.
- Municipalities: Palanpur and Deesa.
The division ensures both districts will have approximately 600 villages each for balanced administration.
Anticipated Benefits
- Ease of Access: Reduced travel time for residents, enhancing connectivity to government offices.
- Resource Allocation: The new district will receive increased funds and government grants, fostering infrastructure development.
- Human Development: Enhanced focus on health, education, and public facilities, improving living standards in the newly formed district.
This strategic move is expected to bring long-term benefits by ensuring more equitable governance and development.
3. Arunachal Pradesh Revives 1978 Act
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
What is the Arunachal Pradesh Freedom of Religion Act?
- The Arunachal Pradesh Freedom of Religion Act, enacted in 1978, prohibits religious conversion through force, inducement, or fraudulent means.
- Violators face up to two years of imprisonment or a fine of ₹10,000.
- The Act mandates reporting all conversions to the Deputy Commissioner of the district.
- Despite its enactment, the Act remained dormant for 46 years due to the lack of implementation rules.
Why Was the Act Introduced?
- The Act aimed to protect the diverse indigenous faiths and cultures of Arunachal Pradesh’s ethnic communities, such as the Monpas, Sherdukpens, and Tani tribes, from perceived threats posed by religious conversions.
- The steady growth of Christianity, from 0.79% of the population in 1971 to 4.32% in 1981, sparked debates on proselytization and its impact on indigenous practices, leading to demands for legal safeguards.
Why Has the Act Remained Dormant?
- Opposition from Christian groups like the Arunachal Christian Forum, which view the Act as discriminatory and prone to misuse, has hindered its implementation.
- Christianity, now the state’s largest religion, comprising 30.26% of the population in 2011, has grown significantly, creating vocal resistance to the Act.
- Political reluctance to alienate these groups further stalled the framing of rules.
Why Is the Act Being Revived Now?
- In 2022, a PIL filed in the Gauhati High Court highlighted the state government’s failure to frame rules for the Act.
- The court’s recent directive to finalize draft rules within six months has reignited discussions.
- Proponents, like the Indigenous Faiths and Cultural Society of Arunachal Pradesh (IFCSAP), argue that the Act is vital to preserve indigenous traditions and counter the rising conversion rates.
Concerns and Diverging Views
- Critics, particularly Christian organizations, see the Act as a tool for curbing religious freedom and fostering discrimination.
- In contrast, advocates view it as essential for cultural preservation. The involvement of the RSS and its affiliates in institutionalizing indigenous faiths adds complexity, as their activities are seen as supportive of traditional practices without direct conversion efforts.
Conclusion
- The revival of the Arunachal Pradesh Freedom of Religion Act underscores tensions between safeguarding cultural identity and ensuring religious freedom.
- Its implementation will require careful balancing to address diverse perspectives and uphold constitutional rights.
4. Decoding the National Anthem controversy
| Context |
|
Raj Bhavan’s Allegations
- The Tamil Nadu Raj Bhavan claimed that “the Constitution of Bharat and the National Anthem were once again insulted in the Tamil Nadu Assembly.”
- It emphasized that respecting the National Anthem is a fundamental duty enshrined in the Constitution.
Tamil Nadu’s Practice Regarding Anthems
- In Tamil Nadu, the State anthem, ‘Tamil Thai Vazhthu,’ is played at the beginning of the Governor’s address, and the National Anthem is played at the end.
- This practice was introduced in July 1991 during the AIADMK government led by Jayalalithaa and Governor Bhishma Narain Singh.
- Prior to this, the Governor would enter the House, deliver the address, and leave without playing either anthem.
Practice in Other States
- Different states follow varying conventions. In Nagaland, the National Anthem was played for the first time in February 2021 during Ravi’s tenure as Governor.
- Similarly, Tripura first played the National Anthem in March 2018.

| Constitutional Provisions and Legal Practices: |
|
5. Should voter IDs be linked with Aadhaar?
| Context |
|
Background of the Proposal
- In February 2015, the Election Commission (EC) launched the National Electoral Rolls Purification and Authentication Program (NERPAP) to remove duplicate entries by linking voter IDs (EPIC) with Aadhaar. Over 300 million voters were linked in three months.
- The Supreme Court intervened in August 2015, ruling that Aadhaar could only be used for welfare schemes and PAN linking, halting the NERPAP.
- In December 2021, Parliament amended the Representation of the People Act, 1950, allowing the linking of Aadhaar with EPIC, making it voluntary.
- If voters don’t have Aadhaar, they can provide alternate documents like PAN cards or bank passbooks.

| Potential Implications: |
Challenges and Concerns
Pros and Cons
Way Forward
|
6. Does ‘blood money’ have a legal standing?
| Context |
|
| What is ‘Blood Money’? |
|
Contemporary Use of ‘Blood Money’
- Several Islamic countries follow ‘blood money’ laws, with variations in how compensation is calculated.
- In Saudi Arabia, for example, ‘blood money’ is mandated in traffic accidents, and a prison term is also imposed on the perpetrator.
- ‘Blood money’ laws in Saudi Arabia, Iran, and Pakistan differ by gender, religion, and nationality.
- In Iran, a woman’s compensation is half that of a man’s, though there have been efforts to equalize it.
- Pakistan incorporates ‘blood money’ and retribution in its legal system.
- Yemen also allows the parties to reach a compensation agreement, with judicial oversight.
India’s Stand on ‘Blood Money’
- India does not have a formal legal provision for ‘blood money’.
- However, India has a similar concept known as ‘plea bargaining’, introduced by the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2005.
- Plea bargaining allows the accused to plead guilty in exchange for a reduced sentence or fewer charges.
- Unlike ‘blood money’, plea bargaining has limitations; it only applies to offenses punishable with less than seven years of imprisonment and cannot be used in heinous crimes like murder or rape.
- In plea bargaining, victims may receive compensation, similar to ‘blood money’, under Section 265E of the Criminal Procedure Code.
| Historical Practices Similar to ‘Blood Money’ |
|
Indian Cases Involving ‘Blood Money’
- Several Indian nationals have been pardoned through ‘blood money’ in the past.
- In 2019, the death sentence of an Indian in Kuwait was commuted to life imprisonment after his family paid ‘blood money’.
- Other Indian nationals in the UAE were pardoned after paying ‘blood money’ for serious crimes.
- In the current case, efforts are underway to see if a death sentence can be commuted through ‘blood money’.
Conclusion
- ‘Blood money’ serves as a tool for reconciliation in certain legal systems, aiming to compensate victims’ families.
- It remains a contentious issue, with debates on its fairness and implementation across different countries.
7. Fast Track Immigration Programme
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Overview of the FTI-TTP Initiative
- The Fast Track Immigration – Trusted Traveller Programme (FTI-TTP), launched by Union Home Minister Amit Shah, is designed to streamline and expedite international travel.
- It aims to provide world-class immigration facilities for travelers, offering a faster and more secure immigration process.
- The initiative will be inaugurated at key airports across India, including Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Cochin, and Ahmedabad, after its initial rollout at New Delhi’s IGI Airport in June 2024.
Objectives and Timeline
- The FTI-TTP is part of the Indian government’s vision for a ‘Viksit Bharat @2047’, aligning with the goal of transforming India into a developed nation by its centenary of independence.
- It was first launched at IGI Airport with a focus on Indian Nationals and Overseas Citizens of India (OCI), providing these groups with free and faster immigration clearance.
- The programme has now expanded to seven airports and will later extend to foreign travelers, aiming to simplify the immigration process.
Functionality and Operation
- The FTI-TTP is based on a digital platform, allowing travelers to register online and submit necessary documents.
- Once approved, travelers become part of a ‘Trusted Traveller’ list and can access e-gates at the airport for seamless immigration clearance.
- At the e-gates, passengers will scan their boarding passes and passports, while biometric authentication will grant them automatic immigration clearance, reducing wait times and enhancing security.
Required Documentation
- Applicants must upload a passport-sized photograph that meets specific standards, along with scanned copies of their passport and, for OCI cardholders, their OCI card.
- The documentation process ensures that only authorized individuals are enrolled in the programme, helping to maintain security while enhancing convenience for legitimate travelers.
Implementation Phases
- The FTI-TTP will be rolled out in two phases. The first phase, which begins on January 16, will cover Indian citizens and OCI cardholders, while the second phase will extend the programme to foreign travelers.
- The programme will eventually be implemented at 21 major airports across India, streamlining the international travel experience for a larger number of passengers.
8. Parliament Should have Annual Calendar: O’Brien
| Context |
|
Issues Associated with Short Notice for Parliament Sessions
Inadequate Preparation Time:
- Short notice leaves lawmakers with little time to prepare for crucial debates and discussions.
- This can lead to superficial scrutiny of bills and motions, affecting the quality of legislative work.
Reduced Accountability and Scrutiny:
- With insufficient time, Parliament members are unable to hold the government accountable effectively.
- Parliamentary debates on national issues are rushed, reducing the chances for detailed examination.
Impact on Members’ Engagement:
- Short session notices disrupt MPs’ schedules, especially those with constituency commitments.
- Lack of preparation time affects both the members and their ability to represent the people they serve effectively.
Public Distrust:
- Unpredictable parliamentary schedules erode public trust in the functioning of the government.
- Citizens expect transparency, and sudden session announcements may raise concerns about the legislative process being manipulated.
Legislative Disorganization:
- When sessions are not planned in advance, there’s a lack of structured business, affecting the prioritization of critical national issues.
- Lack of a predictable calendar results in chaotic and disorganized parliamentary proceedings.
Way Forward: Structured Parliamentary Calendar
Introducing an Annual Parliamentary Calendar:
- The government should publish an annual calendar for Parliament, enabling all stakeholders to plan ahead.
- This can include expected session dates, discussion topics, and important legislative matters.
Mandating Minimum 100 Parliamentary Sessions:
- To ensure proper legislative functioning, at least 100 sittings per year should be conducted.
- This ensures that there’s adequate time for legislation, debates, and holding the government accountable.
Improved Session Planning:
- The planning should allow for a sufficient gap between sessions, giving members enough time for preparation and constituency work.
- A predictable session structure also improves the quality of debates and deliberations.
Conclusion
- By establishing a predictable calendar, Parliament can become more accountable, transparent, and better equipped to serve the public’s interests.
9. SC Ruling On Abetment of suicide charges
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
About Section 306 of IPC
- Section 306 of IPC deals with the Abetment of suicide whereas the same provision has been covered under Section 108 of the Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023(BNS).
- It states that if any person commits suicide, whoever abets the commission of such suicide, shall be punished with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to ten years, and shall also be liable to fine.
Sensitizing Investigation Agencies and Courts in Abetment of Suicide Cases
- The Supreme Court cautioned against the misuse of the provision (Section 306 of the IPC) to satisfy the immediate emotions of a deceased’s family, stressing that only genuine cases meeting the legal threshold should lead to prosecution.
- The Court highlighted the abuse of process in cases lacking adequate evidence of abetment.
Legal Framework for Abetment of Suicide
- Section 306 IPC criminalizes abetment of suicide, which is defined under Section 107 IPC as acts of instigation, conspiracy, or intentional aiding.
- Prosecution under this section requires proof of direct instigation or acts that leave the deceased with no alternative but to die by suicide.
- Punishment includes up to 10 years of imprisonment and a fine. However, conviction rates remain low at 17.5% in 2022, highlighting challenges in proving intent and direct abetment.
The Supreme Court’s Intervention in the Bank Manager Case
- In the case of a bank manager accused of abetting a borrower’s suicide, the Supreme Court discharged the manager, stating that mere allegations of harassment for loan recovery do not meet the threshold for abetment.
- It criticized trial courts for framing charges mechanically and stressed the need for a practical approach in evaluating evidence.
- The Court reiterated that casual exchanges or hyperboles should not be misconstrued as instigation to suicide.
Higher Standard for Proof in Workplace-Related Cases
- The Supreme Court has set a higher bar for proof in abetment of suicide cases stemming from workplace or official relationships.
- In cases like M Mohan v State (2011) and Ude Singh v State of Haryana (2019), the Court emphasized that prosecution requires evidence of direct incitement or a continuous course of conduct that left the deceased with no alternative but suicide.
- It clarified that indirect acts or vague allegations without proof of intent do not suffice for prosecution.
Conclusion
- The Court has repeatedly cautioned against unnecessary prosecutions under Section 306 IPC, highlighting the need for evidence-based investigations and judicial prudence.
- A balance must be struck between protecting genuine victims and preventing misuse of the law, which could otherwise lead to undue harassment of accused individuals.
- Sensitization of investigating agencies and trial courts is critical to ensure fair application of the law.
| What is the Statistics Related to Suicide in India? |
The data compiled by the NCRB is based on police-recorded first information reports (FIRs).
|
10. Life Imprisonment for RG Kar Convict
| Context |
| A sessions court in Kolkata sentenced Sanjoy Roy to life imprisonment for the rape and murder of a doctor at RG Kar Medical College. |
The ‘Rarest of Rare’ Doctrine
- The Supreme Court, in Bachan Singh v. State of Punjab (1980), upheld the constitutionality of the death penalty but limited its application to the “rarest of rare” cases.
- Courts must consider aggravating and mitigating circumstances to determine whether a death sentence is warranted.
Aggravating Circumstances:
- Pre-planned, brutal, and depraved murders.
- Murders of public servants or law enforcement officers on duty.
Mitigating Circumstances:
- Emotional or mental disturbance of the accused.
- Young or advanced age.
- Potential for reformation and rehabilitation.
Evolving Interpretations
The understanding of these circumstances has evolved, with varying emphasis on factors like age and the possibility of reform. For instance:
- Age: In Ramnaresh v. State of Chhattisgarh (2012), the young age of the accused was considered a mitigating factor. However, inconsistency in considering age was noted in Shankar Khade v. State of Maharashtra (2013).
- Nature of Offence: In Machhi Singh v. State of Punjab (1983), the court emphasized societal conscience, often prioritizing crime severity over the possibility of reform.
Focus on Reformation
- In Bachan Singh and subsequent cases like Santosh Bariyar v. State of Maharashtra (2009), the SC stressed that the state must provide evidence that the convict cannot be reformed, with a presumption against the death penalty.
- Clear, objective evidence is crucial to ensure fairness in sentencing.
Sentencing Procedures
- A separate hearing after conviction is essential for determining the penalty. However, the SC has raised concerns over the adequacy of such hearings, particularly when they occur on the same day as the conviction.
- In Dattaraya v. State of Maharashtra (2020), lack of an effective hearing led to commuting a death sentence to life imprisonment.
Conclusion
- The sentencing in the RG Kar case highlights the judiciary’s reliance on the “rarest of rare” doctrine, balancing crime severity and the potential for reformation.
- The decision reflects the evolving discourse on mitigating circumstances, procedural fairness, and the critical need for a consistent, objective approach to death penalty cases.
| Scope of the Rarest of Rare Test |
Dimensions of the Rarest of Rare Test:
|
11. About PMLA Bail Exception Rule
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Bail Provisions Under PMLA
- Section 45 of the PMLA imposes stringent conditions for bail, requiring the accused to prove no prima facie case against them.
- However, an exception exists for women, minors, and the sick or infirm, allowing for bail at the discretion of the Special Court.
- This exception aligns with similar exemptions under the Indian Penal Code (IPC).
Legal Precedents on Women’s Bail Exception
- Delhi High Court (2023): In Preeti Chandra v. Directorate of Enforcement, the court rejected attempts to restrict the exception for women based on socio-economic status or education level, affirming the broad application of the law.
- K Kavitha Case (2024): A trial court denied bail, citing the accused’s education and societal position. However, the Supreme Court later overruled this decision.
These cases highlight judicial inconsistency in interpreting the exception for women under PMLA.
Case Analysis: Shashi Bala
- Shashi Bala, accused of assisting the Shine City Group in laundering ₹36 lakh, was arrested in 2023.
- The Allahabad High Court denied her bail, arguing she was not a “vulnerable” woman under the PMLA exception.
- The Supreme Court rejected the ED’s argument, emphasizing that the law does not differentiate among women based on social or economic factors.
Judicial Observations
- Justice Oka criticized the ED’s argument, stating, “We will not tolerate conduct…contrary to statute.”
- The SC underscored that statutory exceptions must be uniformly applied without arbitrary classifications, ensuring the rule of law prevails.
Conclusion
- The Shashi Bala case underscores the need for consistent judicial interpretation of PMLA provisions.
- The Supreme Court’s stance reinforces the importance of statutory safeguards for women, emphasizing the principle of equal access to justice.
| The Prevention of Money-Laundering Act (PMLA) |
|
PYQ: With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2021)
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither I nor 2 Ans: (b) |
12. Birla urges parties to devise internal code
| Context |
|
Need for Internal Code of Conduct:
- Ensures orderly proceedings and upholds the decorum of the House, maintaining a professional environment for legislative work.
- Prevents disruptive behavior and encourages meaningful debates, thus improving the quality of discussions.
- Strengthens democratic values by ensuring that elected representatives respect constitutional and parliamentary traditions.
Benefits:
- A well-implemented code of conduct promotes constructive dialogue and reduces conflicts during sessions.
- It provides clarity on acceptable behavior, thereby preventing unruly incidents and frequent adjournments.
- The House remains focused on legislative work, improving the efficiency and productivity of sessions.
- Encourages legislators to fulfill their duties responsibly and respect the roles and opinions of other members.
- A code of conduct can lead to enhanced cooperation across party lines, fostering a more collaborative approach to governance.
Challenges:
- Political parties may face difficulty in implementing due to differing political ideologies and agendas.
- Resistance from members who might view the code as limiting their freedom of expression or political strategy.
- Ensuring compliance with the code across a diverse group of legislators from various backgrounds and states.
- Overcoming entrenched partisan behavior and the reluctance to adopt reforms.
Way Forward:
-
- Political parties must engage in constructive dialogue to devise a code of conduct that aligns with democratic principles and respects constitutional values.
- Empowering presiding officers to enforce the code and ensuring accountability.
- Promoting training and awareness programs for legislators about the importance of maintaining decorum.
13. JPC rejects all amendments to Waqf Bill made by Opposition
| Context |
|
Key Features of the Bill

- Main Proposal: The Bill initially sought to remove the concept of “Waqf by user”, which allowed properties to be considered Waqf simply due to their long-term use for religious purposes. This proposal caused concern over the potential threat to several religious structures.
Amendments Accepted:
- Waqf by User: A concession was offered, allowing Waqf properties under “Waqf by user” to remain, except for those in dispute or government facilities. These properties must be registered before the new law comes into effect.
- Dispute Resolution: The Bill removed the requirement for District Collectors to inquire into disputes over government property, instead allowing state governments to designate a higher-ranking officer for the task.
- Non-Muslim Members on Waqf Board: The amendment allows up to four non-Muslim members on the Waqf Board, even though this move was opposed by Muslim bodies.
- Mutawalli Authority: An amendment gives the caretaker (Mutawalli) authority to extend the period for declaring property details, with consent from the Waqf tribunal.
- Waqf Tribunals: An amendment was made to include a member with knowledge of Muslim law in Waqf tribunals.
Opposition’s Concerns
- The Opposition moved amendments to remove provisions they felt were detrimental to minority rights, including the inclusion of non-Muslims in the Waqf Board and the donation rights for non-Muslims.
- They expressed dissatisfaction with being unable to discuss amendments or present their views, citing their concern over minority protection.
14. Whip System
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Party Whips in Practice
- In parliamentary politics, party whips are crucial for ensuring party discipline, especially during important votes.
- MPs are often required to adhere to the party line, with noncompliance leading to consequences such as expulsion.
- This system is seen as essential for maintaining the integrity of party positions on key issues.
Origins and History of Whips
Etymology of “Whip”
- The term originates from England’s hunting tradition, where a “whipper-in” managed hounds.
- Politically, it was popularized by Edmund Burke, who described the effort of “whipping in” followers to align them with party goals.
Introduction in India
- India adopted the whip system during its parliamentary formation. It ensures party cohesion and demonstrates majority strength in crucial divisions.
- Violating a whip, particularly a strict three-line whip, can lead to disqualification under the Anti-Defection Law, a key provision of Indian democracy since 1985.
Types and Enforcement of Whips
Kinds of Whips
- One-line whip: Informs members about a vote, allowing abstention.
- Two-line whip: Requests presence but permits voting discretion.
- Three-line whip: Mandates attendance and voting as per the party line.
Enforcement Mechanism
- The party’s chief whip communicates directives to MPs, ensuring attendance and adherence.
- The Minister of Parliamentary Affairs oversees the system, coordinating compliance among ruling alliance members.
Importance of the Whip System
Democracy and Stability
- The whip system is vital for parliamentary functioning and party discipline.
- It ensures coherent policymaking and strengthens party accountability.
- Former Lok Sabha Speaker Sumitra Mahajan emphasized that MPs elected on a party ticket must align with their party’s ideology or exit.
Whips Conference
- Since 1952, the All-India Whips Conference has provided a platform for whips across parties to share perspectives.
- This forum, organized by the Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs, reinforces the whip system’s role in safeguarding democratic processes.
15. Use Loudspeakers “Not Essential part of Religion”
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

Noise Pollution Laws and Observations
- The Noise Pollution (Regulation and Control) Rules, 2000, mandate noise levels in residential areas to remain within 55 decibels during the day and 45 decibels at night.
- The HC observed that cumulative sound levels of multiple loudspeakers in an area should be considered when evaluating compliance, emphasizing the need for strict enforcement of noise pollution laws.
Directions Issued by the HC
- The court directed the government and police to enforce noise pollution regulations uniformly, ensuring anonymity for complainants to protect them from retaliation.
- It recommended an inbuilt mechanism, such as automatic decibel calibration in loudspeakers, and suggested using mobile applications to measure noise levels.
Graded Penalty System for Violations
The HC prescribed a four-step graded penalty system:
- First Offense: Issuance of a caution.
- Repeat Offense: Imposition of fines on trusts or organizations.
- Further Violations: Seizure of loudspeakers.
- Persistent Violations: License cancellation and legal action.
Reference to Previous Rulings
- The HC referred to its 2016 judgment in Dr. Mahesh Vijay Bedekar v. Maharashtra, which affirmed that loudspeakers are not integral to any religion.
- The 2016 ruling prohibited loudspeakers between 10 PM and 6 AM and upheld noise restrictions in silence zones, allowing limited exemptions for cultural or religious occasions.
Ensuring Compliance and Balanced Implementation
- The court emphasized the state’s role in creating systems to regulate noise levels, balancing individual rights with public welfare.
- By implementing these measures, authorities can ensure adherence to constitutional provisions while safeguarding citizens’ rights to a peaceful environment.
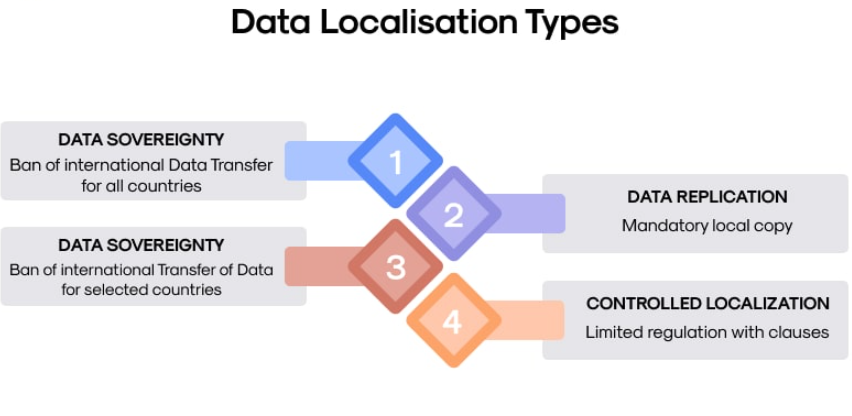
16. Data Localisation Returns
Analysis of the news:
Data Localisation Reintroduced
- The draft Digital Personal Data Protection Rules, 2025, reintroduce data localisation requirements, mandating significant data fiduciaries to store and process specific personal and traffic data within India.
- This marks a shift from the 2023 Act, which allowed cross-border data transfer with notified restrictions.
Significant Data Fiduciaries: Defined and Regulated
- Entities handling vast or sensitive data with implications for sovereignty, security, or public order, like Big Tech companies, are categorized as significant data fiduciaries.
- They will be subject to stringent data localisation norms and compliance requirements.
Safeguards for Government Data Processing
- The draft rules propose “lawful” data processing by government entities but face scrutiny due to exemptions granted under the 2023 Act for national security and public order. Safeguards are expected to address these broad exemptions.
Parental Consent Mechanism for Children’s Data
- Tech companies must devise verifiable mechanisms for parental consent when processing children’s data, though this remains challenging.
- Exceptions are made for health, education, and childcare-related establishments.
Data Breach Notification and Penalties
- Data fiduciaries must notify users promptly about breaches, detailing their nature, impact, and mitigation measures.
- Non-compliance with safeguards can result in penalties of up to ₹250 crore.
Enhanced User Consent Requirements
- The draft mandates clear, specific, and standalone notices for data collection, ensuring transparency about the type of data collected and its intended purpose.
Implications for Big Tech
- While promoting data sovereignty, the reintroduction of localisation may increase operational costs for companies like Meta and Google, potentially impacting their services.
- Industry resistance to localisation persists due to its broad implications for global operations.
Governance
1. Experts on GM crop panels to declare conflict of interest
| Context |
|
Amendment to GEAC Rules
- Under the new rules, expert members are required to disclose any interests that might conflict with their duties.
- Experts must take measures to ensure that conflicts of interest do not influence the committee’s decisions.
| Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) |
|
Conflict of Interest Provisions
- Expert members with direct or indirect associations with matters being discussed in committee meetings must disclose these associations prior to the meetings.
- Unless specifically requested by the committee, such members are expected to recuse themselves from the discussion.
- Selected members must submit a form detailing their professional affiliations over the past decade before joining the committee.
Supreme Court’s Order on GM Crops
- In July 2023, the Supreme Court directed the Centre to form a national policy on GM crops.
- The court delivered a split verdict on the Centre’s 2022 conditional approval for the environmental release of GM mustard.
- The court concurred on the need for a process to address conflict of interest issues.
Allegations of Conflict of Interest
- Allegations of conflict of interest in GM crop regulation arose in 2013.
- Activist group Coalition for GM-Free India alleged that a member of the Technical Expert Committee, appointed by the court, was associated with an organization funded by Monsanto, a major multinational biotech company.
| Conflict of interest and its potential implications: |
|
2. UGC Guidelines on VC Appointments
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

VC Appointment Process: Current and Proposed Framework
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) regulations of 2018 mandated a search-cum-selection committee to shortlist candidates for Vice Chancellor (VC) appointments through public notifications or nominations.
- For central universities, the President (Visitor) appoints VCs, while state laws govern appointments for state universities, with significant involvement of Governors (Chancellors).
- The 2025 draft regulations propose that the Chancellor/Visitor appoint the committee, comprising three experts—nominees of the Chancellor, UGC Chairman, and the university’s apex body.
- This marks a shift, granting greater central influence and introducing the possibility of industry or policy professionals as VCs.
State-Centre Disputes Over VC Appointments
Several states, especially those with non-BJP governments, oppose the enhanced role of Governors (Chancellors) in appointing VCs:
- Kerala: Passed a Bill to replace the Governor with educationists as Chancellors, yet to receive presidential assent.
- West Bengal: Legal disputes arose over Governor’s unilateral appointments; the Assembly passed a Bill to make the Chief Minister the Chancellor.
- Karnataka: Legislation to replace the Governor with the Chief Minister as Chancellor remains pending.
- Maharashtra: A 2021 Bill reducing the Governor’s powers was withdrawn by the succeeding government.
- Tamil Nadu: Passed Bills to vest VC appointment powers with the state government, yet to be approved by the Governor.
Federalism at the Core of the Debate
- Critics, including Chief Ministers of Kerala and Tamil Nadu, argue that the draft regulations undermine federalism by stripping states of their autonomy over state university administration.
- They contend that this shift imposes central authority over state-run institutions and diminishes democratically elected governments’ roles.
- Conversely, UGC Chairman Jagadesh Kumar defends the regulations, emphasizing transparency, alignment with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, and resolving ambiguities in the 2018 guidelines.
Implications for Governance and Education
- The draft regulations aim to standardize VC selection, enhance transparency, and expand eligibility criteria.
- However, they also risk exacerbating state-Centre conflicts and raising questions about the autonomy of state universities.
- Striking a balance between quality education governance and respecting federal principles will be crucial as the debate unfolds.
| About Universal Grant Commission (UGC) |
The UGC`s mandate includes:
|
3. What do draft data protection rules state?
| Context |
|
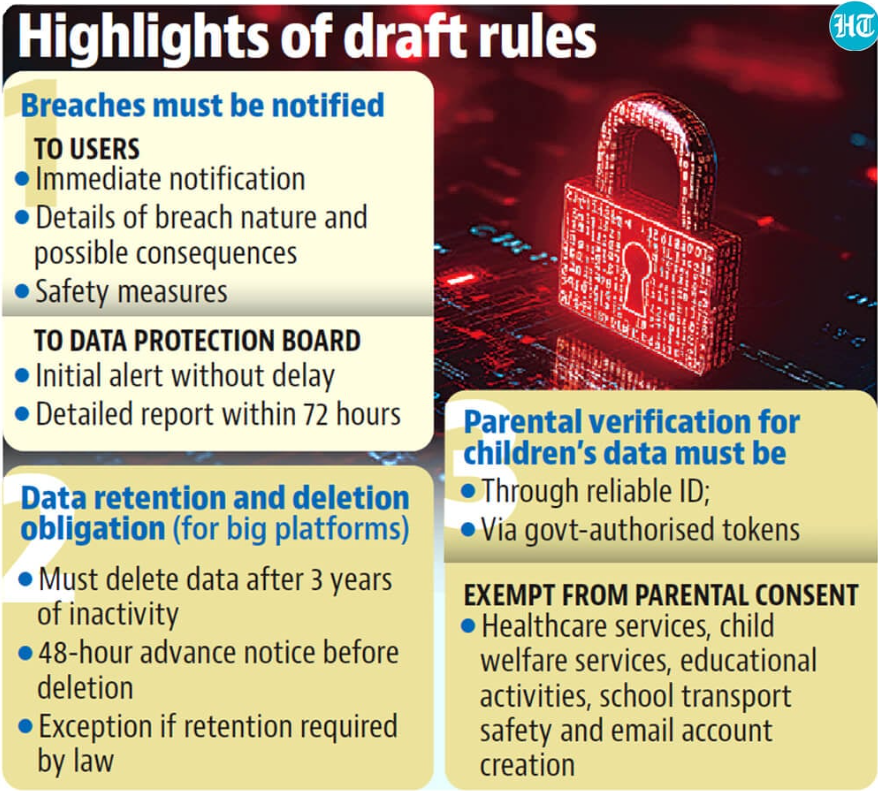
Introduction to Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Draft Rules
- These rules were introduced 16 months after the DPDP Act was notified in August 2023.
- The government is seeking public feedback on these draft rules.
Concerns Over the Data Privacy Framework
- Critics argue that the DPDP Act, along with the draft rules, is insufficient to establish a comprehensive data privacy framework.
- Concerns include the need for further scrutiny and review of these rules by a parliamentary standing committee before final approval.
Data Localisation Mandate
- The draft rules propose a data localisation mandate that goes beyond what was initially intended by the DPDP Act.
- Data localisation refers to restrictions on transferring data outside the country’s borders.
- The rules suggest that a government-appointed committee will define which types of data cannot be exported.
- Significant data fiduciaries (SDFs), such as large tech companies, are likely to be affected by this rule.
- The main motivation for this provision is to help law enforcement access cross-border data for investigations more easily, as seen with the Reserve Bank of India’s 2018 mandate for payment data localisation.
- A two-year timeline is proposed for the industry to set up systems for compliance with data localisation requirements.
Challenges of Data Localisation
- Data localisation could pose operational challenges for both large tech companies and start-ups.
- Companies may face difficulties in segmenting and determining which data to store where, leading to higher operational costs and limitations on business operations.
- The process could be complex and costly for businesses to comply with, especially for international companies with vast data needs.
Executive Overreach and Government Powers
- Section 36 of the DPDP Act grants sweeping powers to the government to demand information from data fiduciaries or intermediaries in the name of national security, sovereignty, or integrity.
- These powers could be misused for surveillance or political control, with concerns about compromising privacy.
- Rule 22 also prevents companies from disclosing government demands for information if it could harm national security, raising fears of government overreach and lack of transparency.
Concerns Over Lack of Safeguards
- Critics argue that these provisions give the government excessive discretion without proper checks and balances.
- There are concerns that the government could access data without notifying individuals involved, undermining transparency and accountability.
- Some suggest that the government should adopt safeguards, similar to those in the Information Technology Act, 2000, to protect citizens’ privacy while ensuring the proper management of data requisition by authorities.
Conclusion
- The draft rules, although aimed at enhancing data protection, raise concerns about operational challenges, government overreach, and the absence of adequate privacy safeguards.
- The industry and legal experts recommend more scrutiny and proper checks before final implementation.
4. Should Governors head State universities?
| Context |
|
Governor as Chancellor of State Universities: A Colonial Legacy
- It originated during British rule and was designed to restrict university autonomy rather than promote it.
- The position was formalized by British authorities in 1857 when they set up the first universities in Calcutta, Bombay, and Madras.
- Governors of the presidencies were made ex-officio Chancellors to maintain control over these universities.
- The role was adopted post-Independence without reassessment and continues in India today. It is not mentioned in the Constitution but is included in State university laws.
Politicisation of the Governor’s Role
-
- From 1947 to 1967, the dominance of the Congress party led to Governors being mostly ceremonial figures, with Chief Ministers holding the real power.
- However, post-1967, as several states were ruled by opposition parties, Governors started to play an active role in university governance. This led to clashes with state governments.
- The office of the Governor began to be politicised, with many Governors appointed for their political loyalty rather than for academic expertise, leading to a decline in the office’s credibility.
- The First Administrative Reforms Commission (1966–77) and the Sarkaria Commission (1983-88) criticized this politicisation.
Dual Role of Governors
- The Governor’s role is divided constitutionally into two categories: acting on the advice of the Council of Ministers (Article 163) and acting independently in certain functions, like being the Chancellor of State universities.
- The Governor’s discretion in university matters, such as appointing Vice-Chancellors and presiding over convocations, has caused issues, particularly in states ruled by opposition parties.
Challenges of the Current System
- Governors have significant power over State universities despite these universities being funded by State governments. This creates confusion and conflicts.
- Delays in appointing Vice-Chancellors and other administrative issues affect the functioning of universities.
- Governors, often lacking academic experience, make decisions based on limited, non-transparent advice.
- Political interference by Governors often prioritises central government agendas over universities’ needs.
- The system undermines the principle of federalism, as it places State universities under control by Governors appointed by the Centre.
Commission Insights and Recommendations
- The Rajamannar Committee (1969-71) and the Sarkaria Commission (1983-88) recommended that Governors consult with Chief Ministers but retain independent judgment.
- The M.M. Punchhi Commission (2007-10) suggested that the Governor focus on constitutional duties, not statutory roles like Chancellor, to preserve dignity.
- Various commissions, including the National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (2000-02), have advocated for greater university autonomy and a clearer role for Chancellors.
Alternative Models for the Role of Chancellor
- Best practices suggest that the Chancellor should be a ceremonial leader, with no executive authority.
- Some States, like Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Karnataka, have implemented reforms where the Governor’s role is reduced to a ceremonial one.
- The State-appointed Chancellor model, in which eminent academics or public figures serve as Chancellor, has been suggested as a solution.
- This model ensures academic independence while preventing political interference.
- This model is being considered in several States, but many Bills are awaiting Presidential assent.
Dismantling Colonial Legacy
- Reforming the governance of State universities is essential for academic excellence, reduced political interference, and enhanced accountability to State governments.
- The central government should facilitate these reforms and encourage States to align their university governance models with global best practices.
Conclusion
- The Governor’s role as Chancellor of State universities, a legacy of colonial rule, needs reform.
- Shifting to a more neutral, academic-focused leadership model would enhance university autonomy and governance.
5. Odisha tops NITI fiscal health index
| Context |
|
Top-Performing States: Achievers
- Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Goa, and Jharkhand were ranked as “achievers” for their robust fiscal health.
- Odisha led the rankings with a Fiscal Health Index (FHI) score of 67.8, showcasing exceptional performance in debt management and fiscal discipline.
- These States exhibited:
- Capital outlay of up to 4% of Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP).
- Effective mobilisation of non-tax revenues.
- Revenue surplus and low interest payments (up to 7% of revenue receipts).
Front-Runners and Performers
- Front-runners: Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Telangana, Madhya Pradesh, and Karnataka.
- These States reported high developmental expenditure (up to 73% of total spending).
- Consistent growth in own tax revenue and balanced fiscal management were noted.
- Improved debt sustainability was observed, with a debt-to-GSDP ratio of 24%.
- Performers: Tamil Nadu, Bihar, Rajasthan, and Haryana, classified for their moderate fiscal performance.
Aspirational States: Struggling with Fiscal Challenges
- Kerala, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, and Punjab were listed as “aspirational” due to significant fiscal challenges.
- Common issues included:
- Low revenue mobilisation.
- Rising debt burdens and poor debt sustainability.
- Struggles to meet fiscal deficit and revenue deficit targets.
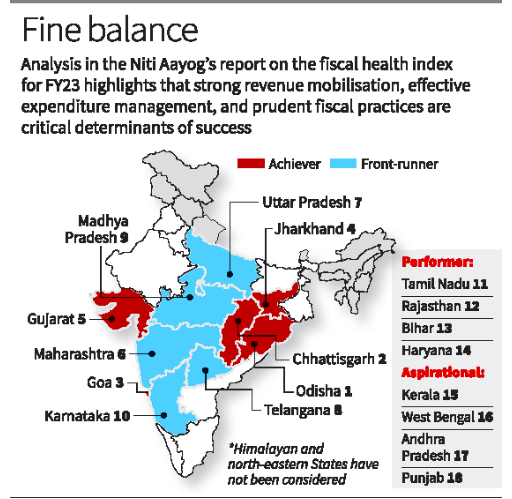
Odisha’s Exceptional Fiscal Strengths
- Odisha ranked highest in debt index (99.0) and debt sustainability (64.0).
- The State maintained low fiscal deficits and demonstrated strong debt management.
- Odisha’s capital outlay to GSDP ratio remained above average.
Long-Term Trends (2014-15 to 2021-22)
- Odisha, Goa, Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Chhattisgarh achieved the highest average FHI scores during this period.
- Data for the FHI was sourced from the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG).
Social Justice
1. UNICEF’s Prospects for Children in 2025 Report
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
About UNICEF:
- The United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF) was established in 1946, in the aftermath of World War II.
- Mandate: To help children and young people whose lives and futures were at risk – no matter what role their country had played in the war.
- It works in over 190 countries and territories to protect the rights of every child.
- Funding: UNICEF’s work is funded entirely through the voluntary support of millions of people around the world and our partners in government, civil society and the private sector.
- Awards: It has received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1965, the Indira Gandhi Prize in 1989, and the Princess of Asturias Award in 2006.
- It publishes important Reports: The State of the World’s Children, The State of the World’s Children reports.
- Global Initiatives:
- In 2012, UNICEF worked with Save the Children and The United Nations Global Compact to develop the Children’s Rights and Business Principles, and now these guidelines form the basis of UNICEF’s advice to companies.
- UNICEF’s Data Must Speak Initiative (DMS) helps countries unlock existing data to expand access to education and improve learning for all.
- Headquarters: It is headquartered in New York City.
Key Highlights of the UNICEF Report on Children’s Challenges
Impact of Conflict on Children
- In 2023, over 473 million children—one in six globally—lived in conflict zones, marking a rise from 10% in the 1990s to 19% today.
- These children face severe risks, including displacement, starvation, disease, and psychological trauma, highlighting the urgent need for protective interventions.
Debt Crisis and Its Impact on Children
- Nearly 400 million children live in countries struggling with heavy debt burdens, which restrict investments in essential sectors like education, healthcare, and social services.
- A 5% increase in external debt for low- and middle-income countries could slash education budgets by $12.8 billion.
- In several low-income nations, debt servicing far exceeds spending on health and education, leaving 1.8 billion children vulnerable to poverty and economic shocks.
Climate Change Impact
- Only 2.4% of global climate finance is allocated to child-responsive initiatives, weakening crucial social services such as healthcare and education.
- This underinvestment in children during climate crises underscores the need for targeted financing to protect their future.
Digital Inequality
- While Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) is transforming service delivery, a digital divide persists.
- In high-income countries, most youth (15-24 years) have internet access, but in Africa, only 53% of youth are connected, with adolescent girls and children with disabilities particularly disadvantaged.
- Nine out of ten adolescent girls in low-income countries remain offline, limiting their opportunities.
Way Forward
- The report calls for increased financing for climate recovery, focusing on child-responsive healthcare, education, and psychological well-being during crises.
- It urges the creation of inclusive systems that prioritize children’s rights and the integration of child rights into digital initiatives to bridge inequality gaps.
| Constitutional Provisions for Child Protection in India |
|
PYQ: With reference to the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child, consider the following: (2010)
Which of the above is/are the Rights of the child? (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 3 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (d) |
2. Obesity
| Context |
|
Obesity and Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs)
- Obesity is a chronic disease characterized by excessive fat deposits that can harm an individual’s health.
- It significantly increases the risk of several NCDs, including diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, and certain cancers.
- Additionally, obesity impacts quality of life factors such as sleep, mobility, and mental well-being.
- Obesity has been identified as a soft core for the epidemic of NCDs, exacerbating other health problems, and leading to early mortality.
Global and Childhood Obesity
- The World Health Organization (WHO) states that one in eight people worldwide are obese, and one in three are overweight.
- Worldwide, obesity in adults has doubled since 1990, and adolescent obesity has quadrupled.
- As of now, 37 million children under five years are overweight, while 390 million children and adolescents aged 5-19 years are overweight, and 160 million are obese.
- Childhood obesity in India is a growing concern, with the country ranking second globally for the highest number of obese children.
- Factors contributing to childhood obesity include a lack of physical activity, high-calorie foods, sugary drinks, and genetic influences.
| The Indian Scenario |
|
Obesity and Its Impact
- Obesity causes 3.4 million deaths annually worldwide, and India ranks third after China and the USA in terms of obesity-related deaths.
- Beyond the medical costs, obesity has economic repercussions, including loss of productivity, absenteeism from work, and premature mortality.
- The psychological effects of obesity are severe, leading to low self-esteem, mood disorders, and poor body image.
Addressing Obesity
- Weight loss is critical in preventing and treating obesity-related NCDs. Even modest weight reduction can lead to reduced blood pressure, improved cholesterol levels, and reduced diabetes risk.
- Treatments for obesity include newer medications and bariatric surgery, though they come with high costs and side effects.
- Prevention and treatment also focus on lifestyle changes like regular physical activity and avoiding unhealthy food.
- Recommendations include 6,000-8,000 steps daily, avoiding lifts, walking instead of driving, and limiting screen time.
- Employers can support by setting walking targets for their employees, and individuals should monitor their weight and waist circumference regularly.
Conclusion
- Addressing obesity requires a multifaceted approach, including awareness, advocacy, medical treatments, and changes in lifestyle.
- Simple interventions like regular exercise, balanced diets, and reducing sedentary behavior can significantly help in managing obesity and its related NCDs.
3. In Madurai, mining for tungsten and trouble
| Context |
|
Background of the Protest
- Women in Kesampatti village, Madurai, Tamil Nadu, protest through kummi, a traditional folk dance, against proposed tungsten mining.
- Tungsten mining rights have been granted to Hindustan Zinc Limited by the Union Government.
- Protesters highlight that the land is tied to their art, culture, and religion.
Opposition to Mining
- Mining regions, including Arittapatti, are biodiversity heritage sites with historical and environmental significance.
- Key heritage includes Tamil Brahmi inscriptions, megalithic structures, and diverse wildlife (e.g., Indian pangolin, slender loris).
- Environmental concerns include potential contamination and ecological damage.
Government Stance and Legal Context
- The Tamil Nadu government opposes the project but has limited authority due to centralization under the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957.
- The Union Government cites national interest and geopolitical importance of tungsten, a critical mineral for renewable energy and defense industries.
Community and Expert Concerns
- Activists and villagers demand the exclusion of heritage sites and farmland from mining zones.
- Concerns about health risks, citing Chinese studies linking tungsten mining to elevated soil and water contamination levels.
- Historical instances like the Bhopal Gas Tragedy are cited as warnings of potential neglect.
Political Dynamics
- Local and national political parties express varied opposition or blame shifting.
- Efforts include petitions, Gram Sabha resolutions, and public protests
Conclusion
- This conflict encapsulates the clash between environmental conservation, community rights, and the growing demand for critical minerals in global markets.
4. Rising maternal mortality rates Kerala
| Context |
|
Kerala’s Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR)
- Kerala’s MMR has increased, moving from 19 to 29 per one lakh live births.
- This rise is not due to more maternal deaths but fewer childbirths.
- The drop in the number of live births has pushed the MMR higher.
- Kerala’s MMR spike follows a dip in births from 5-5.5 lakh annually to 3.93 lakh.
- In 2020-21, many deaths were linked to COVID-19 among pregnant women.
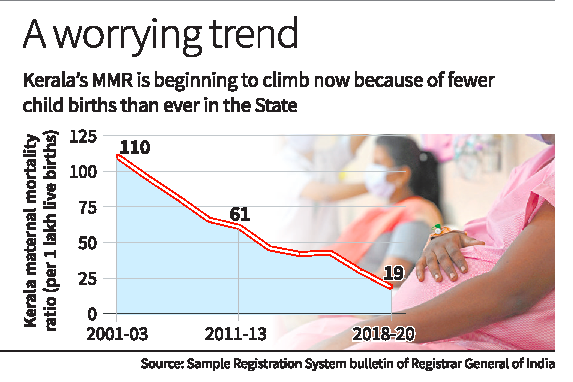
Decline in Fertility Rate
-
- Kerala’s fertility rate has been decreasing for over three decades.
- In 1991, the fertility rate went below replacement level (2.1 children per woman) and stayed at 1.7-1.8.
- In 2020, the total fertility rate (TFR) dropped to 1.5 and is currently at 1.46.
- The TFR means couples in Kerala mostly have one or no children.
- The state’s declining birth rates have significant social consequences.
Impact of Migration and Social Changes
- Many young people in Kerala migrate for jobs or education, affecting fertility rates.
- Delayed marriage and childbearing also contribute to the decline in births.
- Over the next decade, the elderly population in Kerala will surpass the number of children, causing concerns for care and welfare.
Challenges in Data Collection
- Kerala’s birth registration has issues, and official data on live births is not available publicly after 2021.
5. Pink Fire Retardent
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

What is Pink Fire Retardant?
- Pink fire retardant, primarily Phos-Chek, is a chemical solution used to slow or prevent the spread of wildfires.
- Its main component is ammonium phosphate-based slurry, mixed with salts like ammonium polyphosphate.
- The solution is sprayed ahead of fires to coat vegetation and inhibit oxygen supply, thus reducing flammability.
- The bright pink color ensures visibility for firefighters, aiding in creating fire lines for containment.
Effectiveness and Limitations
- While pink fire retardants are a long-standing firefighting tool, their effectiveness remains debatable.
- Studies suggest their success depends on variables such as terrain, fuel type, and weather conditions.
- Their role is often hard to isolate, as they are used alongside other suppression tactics.
- Critics argue that the narrow conditions under which they are effective are shrinking due to climate change.
Environmental Concerns
The use of aerial fire retardants raises significant environmental issues:
- Toxic Metals: Research shows Phos-Chek contains harmful metals like chromium and cadmium, which pose risks of cancer, kidney, and liver diseases.
- Impact on Waterways: Retardants entering rivers and streams harm aquatic life, with heavy metals causing long-term ecological damage.
- Pollution: Between 2009 and 2021, over 440 million gallons of retardant were used, releasing an estimated 400 tons of heavy metals into the environment.
6. India’s first robotic system performs telesurgeries
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- India achieved a historic milestone in medical innovation with the successful completion of two robotic cardiac surgeries via telesurgery, facilitated by the indigenous SSI Mantra 3 Surgical Robotic System.
- This achievement signifies a transformative leap in healthcare accessibility and precision surgery.
Details of the Surgeries
- Telerobotic Internal Mammary Artery Harvesting
- Procedure: Performed remotely at Manipal Hospital, Jaipur, from Gurugram.
- Duration: Completed in just 58 minutes.
- Latency: Ultra-low latency of 35-40 milliseconds ensured remarkable precision.
- Robotic Beating Heart TECAB
- Procedure: A highly complex Totally Endoscopic Coronary Artery Bypass (TECAB) on a beating heart.
- Significance: A world-first surgery, showcasing technological advancement in cardiac procedures.
- Latency: Similarly low latency of 40 milliseconds enabled seamless execution.
Technological Advancements
- SSI Mantra 3: The first and only robotic system worldwide with regulatory approval for telesurgery and tele-proctoring.
- Regulatory Approval: Certified by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO), enabling remote surgeries and medical training.
Impact on Healthcare
- Bridging Geographical Gaps: Provides expert care to underserved regions, addressing healthcare disparities in rural India.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: Facilitates accurate, timely interventions regardless of location.
- Medical Collaboration: Enables remote mentoring and training, fostering skill development in distant areas.
7. Anaemia in India
| Context |
|
Anaemia in Women and Adolescents
- Anaemia prevalence in women aged 15-49 was 41.1%, lower than the 60.8% recorded in the National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5).
- Among adolescent girls aged 15-19, 44.3% were anaemic, compared to 62.6% in NFHS-5.
Study Overview
- Researchers from institutions like St. John’s Medical College and the National Institute of Nutrition conducted the study.
- Published in the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, the study tested 4,500 individuals across eight states.
Possible Causes of Anaemia
- In addition to iron deficiency, the study suggests other potential causes of anaemia, including:
- Vitamin B12 or folate deficiencies.
- Blood loss.
- Environmental factors such as air pollution.
Difference in Testing Methods
- The study used venous blood draws for testing, which may have led to lower estimates of anaemia compared to the NFHS, which used capillary blood (from a pinprick).
- This study provides valuable insights into anaemia prevalence and its potential causes, particularly among women and adolescents.
| Anaemia in India |
Reasons for High Prevalence:
Challenges in Combatting Anaemia:
Way Forward:
|
8. Snakebite in India
| Context |
|
What Are Antivenoms?
- Antivenoms are life-saving medicines used to treat snakebites.
- They are made by injecting small amounts of venom into animals, usually horses, which produce antibodies that neutralize venom toxins.
How Snake Venom Affects the Body
- Snake venom contains haemotoxins, neurotoxins, and cytotoxins that damage blood cells, paralyze nerves, and dissolve tissue.
- Without medical intervention, venom can lead to death.
How Antivenoms Work
- Antivenoms work by binding to venom toxins and rendering them inactive.
- They are produced by injecting venom into horses, and the antibodies are extracted and purified.

Challenges in Accessing Antivenoms
- Despite India being the largest producer of antivenoms, many people in rural areas struggle to access timely treatment.
- Issues like poor storage conditions, high costs, and logistical problems worsen the situation.
Future of Antivenoms
- Future antivenoms may be synthetic, using AI and recombinant DNA technology for improved safety and effectiveness.
- Region-specific antivenoms could provide more precise treatments.
Conclusion
- India’s snakebite crisis requires improved access to timely medical care, better antivenom storage, and advanced research for more effective treatments.
- Continued innovation and infrastructure are essential for saving lives.
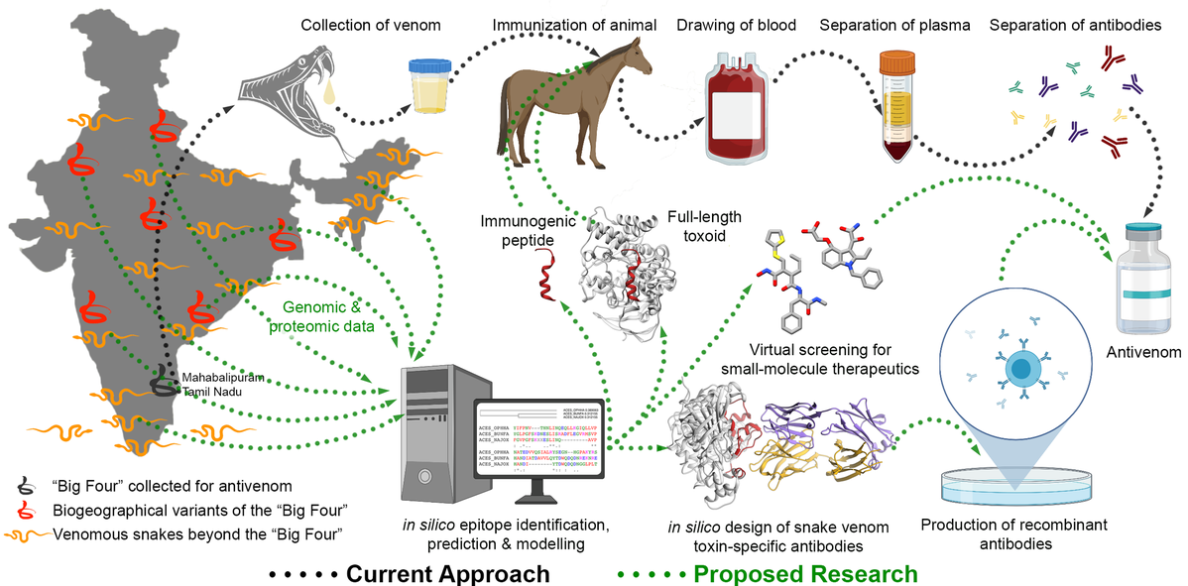
9. Is the government encouraging ‘crosspathy’?
| Context |
|
Previous Notification and Legal Challenge
- In 2017, the Maharashtra Medical Education and Drug Department had issued a notification allowing homeopathic practitioners with the Licentiate of the Court of Examiners of Homeopathy degree (issued from 1951-1982) to practice modern medicine.
- This was later challenged in the Bombay High Court by the Indian Medical Association (IMA), questioning the safety and risk of allowing these homeopathic practitioners to prescribe modern medicines.
- The court issued a stay on the notification, raising concerns about potential harm to patients if homeopathic practitioners were allowed to practice allopathy.
Confusion Over Recent FDA Directive
- The IMA expressed confusion over the Maharashtra FDA’s recent directive, as the central homeopathy body does not permit its practitioners to prescribe allopathic medicines.
- The IMA also clarified that the directive issued by the FDA does not allow homeopathic practitioners to practice modern medicine, as the High Court’s stay is still in place.
| What is ‘crosspathy’? |
|
Supreme Court’s Stance on ‘Crosspathy’
- In the 1996 case Poonam Verma versus Ashwin Patel, the Supreme Court found that a homeopath who prescribed allopathic medications was guilty of negligence, as they lacked the required qualifications.
- The Court has consistently ruled that cross-system practice, or prescribing treatments outside one’s medical expertise, is considered negligent, unless authorized by the government through specific orders.
| Concerns Regarding ‘Crosspathy’: |
|
Shortage of Doctors in India
- India faces a severe shortage of doctors, especially in rural areas. As of June 2022, there are over 13 lakh allopathic doctors and 5.65 lakh AYUSH doctors in India.
- The shortage of specialist doctors is critical, with reports revealing an 80% shortage in community health centers in rural areas.
- Experts argue that while mid-level health providers can offer quality care, it is important to integrate them properly into the system.
- Allowing alternative medical practitioners to take on roles meant for trained doctors could lead to confusion and mismanagement.
Conclusion
- The Maharashtra FDA’s directive has raised legal concerns and confusion regarding the role of homeopathic practitioners.
- Patient safety is at risk if proper guidelines are not followed.
- A more structured integration of healthcare professionals is essential.
10. National Health Mission
| Context |
|

Achievements in Human Resources
- NHM has expanded human resources in the healthcare sector.
- In FY 2021-22, NHM added 2.69 lakh healthcare workers, including doctors, nurses, allied health professionals, and public health managers.
- In FY 2022-23, 4.21 lakh workers were engaged, including 1.29 lakh community health officers (CHOs).
- In FY 2023-24, 5.23 lakh healthcare professionals were added, including 1.38 lakh CHOs.
Decline in Maternal and Infant Mortality
- The Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) has dropped by 83% since 1990, a much higher reduction than the global average of 45%.
- The Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) fell from 39 per 1,000 live births in 2014 to 28 in 2020.
- The Total Fertility Rate (TFR) decreased from 2.3 in 2015 to 2.0 in 2020.
India’s Progress Toward SDG Targets
- These improvements are indicators that India is on track to meet its United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) targets for maternal, child, and infant mortality ahead of the 2030 deadline.
- NHM has also contributed to the elimination and control of various diseases, including reducing the incidence of tuberculosis (TB).
| National Health Mission (NHM) |
|
11. Retinal diseases
| Context |
|
Gene Therapy Breakthroughs
- In 2017, the U.S. FDA approved the first gene therapy for blindness caused by RPE65 gene mutations.
- Over 50 clinical trials are exploring gene therapies for IRDs, but awareness in India remains low.
| Inherited Retinal Diseases (IRDs) and Their Impact |
|
RNA-Based Therapies: A Safer Alternative
- RNA-based therapies, like antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), offer temporary, precise treatments without altering DNA.
- ASOs have successfully treated diseases like spinal muscular atrophy and are now being tested for retinal conditions.
- Advanced RNA-editing techniques, such as ADAR enzymes and suppressor tRNAs, can correct genetic mutations and restore retinal function.
Precision Medicine in India
-
- Precision medicine tailors treatments to genetic makeup, lifestyle, and other factors.
- India lacks large-scale studies to map IRD mutations, essential for developing targeted therapies.
- Genetic mutations vary across India’s diverse population, requiring extensive research.
Barriers and Solutions
- Challenges include low awareness, limited genetic counselling, insufficient funding, and poor diagnostic access in rural areas.
- Collaboration between research institutions, like CSIR-IGIB and L.V. Prasad Eye Institute, has led to precision therapy development.
- Partnerships between global and local pharmaceutical companies can improve treatment accessibility.
Conclusion
- RNA-based therapies offer hope for treating IRDs in India.
- Prioritizing genetic research, raising awareness, and fostering collaborations are crucial to making these treatments accessible and effective for patients.
12. ASER 2024
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
What is the Annual Status of Education Report (ASER)?
- The ASER, is an annual, citizen-led household survey that aims to understand whether children in rural India are enrolled in school and whether they are learning.
- ASER has been conducted every year since 2005 in all rural districts of India. It is the largest citizen-led survey in India.
- ASER surveys provided representative estimates of the enrolment status of children aged 3-16 and the basic reading and arithmetic levels of children aged 5-16 at the national, state and district level.
Improvement in Learning Levels
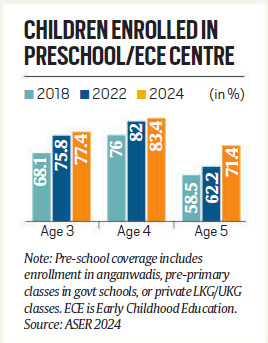
- Children aged 6 to 14 years showed a marked improvement in reading and arithmetic across grades, especially in Classes 1 to 3.
- Among younger children (3–6 years), preschool enrollment rose to 77.4%, a major achievement in ensuring early childhood education.
Impact of NEP 2020 and FLN Initiatives
- The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 prioritized Foundational Literacy and Numeracy (FLN) through programs like NIPUN Bharat (2021).
- The ASER survey found 83% of schools received government directives for FLN implementation, with significant improvements in teacher training (78%) and learning materials (75%), leading to enhanced early-grade learning outcomes.
Focus on Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE)
- The NEP recommends Class 1 enrollment at age six, ensuring children are cognitively and socially ready for formal schooling.
- Anganwadis play a crucial role in bridging this gap, with more than one-third of children aged 3-5 enrolled.
- Some states, like Himachal Pradesh and Punjab, have shifted towards pre-primary classes in schools, while others, like Rajasthan, have seen a rise in both Anganwadi and private LKG/UKG enrollments.
Trends in Digital Literacy Among Adolescents (15-16 years)
- The school dropout rate in this age group has declined to 7%, and over 90% of rural adolescents now have smartphone access.
- However, gender gaps persist in digital skills—80.1% of boys could browse online, compared to 78.6% of girls, though in southern states, girls performed equally or better.
Conclusion:
- Achieving quality ECCE requires continuous data collection beyond ASER and UDISE to understand evolving education trends.
- Strengthening Anganwadi training, parental engagement, and digital literacy can further accelerate learning improvements in rural India.
| What are the Issues Faced by Elementary Education in India? |
School Infrastructure and Amenities:
Teacher Shortage and Quality:
Social Divides:
|
13. WHO recommends lower sodium Intake
| Context |
|
Historical Role of Salt in Public Health
- Salt was introduced in India in the 1950s with iodine fortification, successfully combating iodine deficiency.
- This helped prevent hypothyroidism and other health issues, improving public health over generations.
| WHO’s New Guidelines on Low-Sodium Salt Substitutes (LSSS) |
|
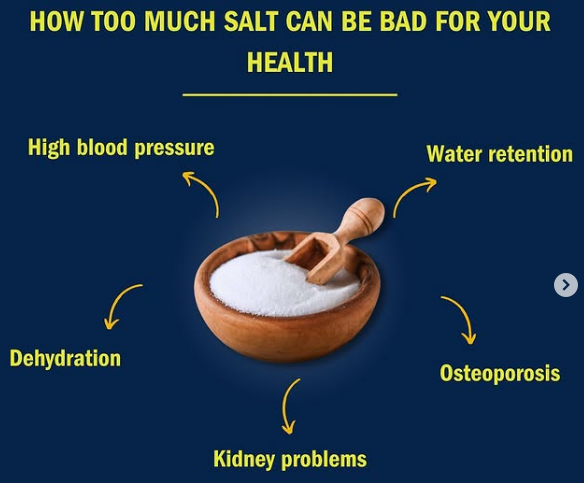
Impact of Salt on the Human Body
- Sodium retains water in the body, increasing blood volume and pressure.
- Reducing salt lowers blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart disease and strokes.
- Hypertension contributes to atherosclerosis, vascular stiffness, and cardiovascular diseases.
- Potassium helps improve vascular function, reducing arterial stiffness.
Global and Indian Health Concerns
- High sodium intake is responsible for 1.9 million deaths globally each year.
- Studies show that reducing salt intake by 4.4g/day lowers systolic blood pressure by 4mmHg and diastolic pressure by 2mmHg.
Initiatives to Reduce Salt Intake
- Sapiens Health Foundation has launched the ‘Losalter Group’ to raise awareness and train physicians.
- Experts suggest that reducing salt intake requires action from individuals, the government, and the food industry.
Challenges in Implementing Low-Sodium Salt Alternatives
- Low-sodium salt options are costlier than regular salt, making them less accessible.
- Experts suggest government intervention to regulate pricing and ensure proper display of these alternatives in stores.
Concerns About Potassium-Based Substitutes
- Potassium-enriched salts are beneficial but may be harmful to people with kidney diseases.
- Experts warn about the risk of hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) due to undiagnosed kidney issues in India.
Conclusion
- Reducing sodium intake is essential for combating hypertension, heart disease, and stroke in India.
- Government policies, industry cooperation, and public awareness are key to promoting low-sodium salt alternatives while ensuring safety for all.
14. Does cow urine have anti-infective properties?
| Context |
|
Details of the Papers Cited
Peptide Profiling in Cow Urine
- Published in Nature Scientific Reports in 2021, this study analyzed peptides in bovine urine.
- Experts, however, stated that the study was a basic analysis of urine and did not support medicinal claims.
- There are similar studies on other mammal urine, and the study did not suggest human consumption of cow urine.
Benefits of Cow Urine
- This paper, published in 2017, listed several claimed health benefits of cow urine, such as treating diseases like diabetes, kidney issues, and cancer.
- Experts, however, warned that consuming urine could be harmful due to the presence of bacteria.
Other Studies on Cow Urine
- A 2022 study by Dr. Bhoj Roj Singh found that cow urine contains harmful bacteria, including E. coli, and does not inhibit bacterial growth.
- Even urine distillates, sold commercially, were found to contain microbes, making their consumption risky and not therapeutically beneficial.
International Relations
1. Four UN environmental summits fell short in 2024.
| Context |
|
Failures at Key Environmental Summits
- These meetings aimed to align global goals, ensure equitable accountability, and mobilize adequate financing but yielded no or limited progress.
- The lack of consensus has delayed critical actions on biodiversity loss, climate finance, drought mitigation, and plastic pollution, impacting vulnerable countries the most.
Diverging National Priorities
- A significant reason for the setbacks is the growing divide in national interests between developed and developing countries.
- Developing nations demand increased financial and technological support to address their economic and climate challenges.
- Developed countries, citing domestic constraints, are reluctant to commit additional resources.
Examples of Stalemates
- At the Colombia summit, disagreement over a $700 billion annual requirement for financing biodiversity conservation led to a gridlock.
- In Azerbaijan, developing nations demanded $1.3 trillion in annual climate finance, but only vague commitments to raise funds from diverse sources were made.
- Discussions on transitioning from fossil fuels and implementing the Paris Agreement’s global stocktake faltered over accountability mechanisms.
- Talks in South Korea on plastic pollution failed due to opposition from economies dependent on plastics to a legally binding treaty, favoring recycling initiatives instead.
Challenges from Global Crises
- The COVID-19 pandemic, geopolitical conflicts, and economic instability diverted resources and attention from environmental priorities.
- Many developing nations face the dual burden of inflation, debt, and climate vulnerabilities, weakening their negotiating positions.
Implications of Failed Negotiations
- Delayed Action: Critical measures to combat biodiversity loss, climate change, and pollution are postponed, increasing the risk of irreversible tipping points.
- Fragmented Efforts: The failure of multilateral processes may lead to incoherent regional actions that lack global coordination.
- Erosion of Trust: Repeated failures undermine confidence among nations, complicating future negotiations.
- Increased Pressure on Future Summits: Upcoming meetings face heightened expectations to deliver meaningful results.
Strategies to Rebuild Momentum
- Climate Finance: Developed countries must fulfill financial and technological commitments to build equitable negotiations.
- Transparency and Accountability: Robust mechanisms to monitor progress and commitments are critical for restoring trust.
- Inclusive Diplomacy: Geopolitical tensions must be addressed to ensure equitable participation, especially for vulnerable nations.
- Implementation Focus: Emphasis should shift from pledges to measurable actions and tangible outcomes.
- Integrated Solutions: Recognizing connections between climate change, biodiversity loss, land degradation, and plastic pollution is essential for comprehensive strategies.
Conclusion
- The stakes in addressing environmental crises are immense. Nations must prioritize collective action, moving beyond short-term interests to adopt a shared vision for a sustainable future.
2. ‘Grand strategy’ for India’s foreign policy
| Context |
|
India’s Core Strategic Partnerships
- India’s most significant strategic relationships include Japan, Australia, the U.S., Russia, France, Israel, and the UAE.
- These partnerships, though not formal alliances, are essential for advancing India’s ambition to become a leading global power.
- These nations support India’s strategic autonomy and share common interests in countering China’s growing regional and global influence.
| Key Pillars of India’s Grand Strategy |
|
Challenges in India’s Strategic Landscape
- U.S. Approach: The U.S. sometimes poses challenges to India’s autonomy, urging partners to take sides in conflicts, which complicates India’s independent stance in global issues.
- Russia’s Role: Russia’s push for closer ties between India and China poses a challenge to India’s desire to maintain independent and balanced relations with both nations.
- Neighbourhood Dynamics: India’s relationships with its neighbouring countries, particularly in South Asia, remain complex and are not seen as key to its global rise, sparking debate on the regional approach.
India’s Global Power Ambitions
- India’s rise as a global power is underpinned by its growing economic and military strength.
- However, achieving this status may not necessarily require dominance in South Asia.
- India’s cultural, religious, and diplomatic attributes contribute significantly to its soft power, reinforcing its position as a peaceable and liberal global player.
The Influence of China
- China’s rise is a central element in shaping India’s foreign policy, with its growing influence in Asia and the Indo-Pacific presenting both a challenge and a driver for India’s strategic direction.
- To counter China’s dominance, India is focusing on strengthening its partnerships, particularly with the Quad and other regional allies.
Distinguishing Between Grand Strategy and Tactics
- A key insight in India’s foreign policy is the distinction between grand strategy and tactics.
- While symbolic gestures like diaspora engagement and personalized diplomacy have a place, they are not substitutes for long-term strategic objectives.
- India’s evolving foreign policy reflects a more thoughtful and deliberate approach to securing its place as a leading global power.
Conclusion
- India’s foreign policy and global ambitions are shaped by its strategic relationships, its quest for autonomy, and the need to manage China’s rise.
- These elements are balanced with India’s soft power and its evolving role in global geopolitics.
3. Russia Halts Gas Transit Through Ukraine
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
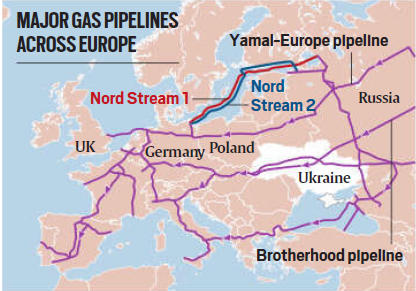
End of Russian Gas Transit via Ukraine
- On New Year’s Day, Russian natural gas exports through Soviet-era pipelines via Ukraine ceased as a transit agreement expired, marking the end of a historic energy route to Europe amidst ongoing conflict.
- This shutdown follows years of deteriorating relations between Moscow and Kyiv since Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014 and Ukraine’s subsequent decision to halt direct gas imports in 2015.
Strategic and Financial Impacts
- The stoppage signifies substantial financial losses for both nations. Ukraine faces an estimated $800 million annual loss in transit fees, while Gazprom, Russia’s state-owned energy company, could lose approximately $5 billion in gas sales.
- Russia’s share of Europe’s gas market, once 35%, has drastically diminished due to geopolitical tensions and Europe’s active diversification of energy sources since the onset of the war in 2022.
Shifting European Energy Dynamics
- The European Union, determined to reduce dependency on Russian energy, has secured alternative supplies for countries like Slovakia and Austria.
- However, nations like Moldova, heavily reliant on Russian gas, are introducing austerity measures to manage reduced energy availability.
- Other major Russian export routes, such as the Yamal-Europe pipeline and Nord Stream, are also defunct, leaving TurkStream as the primary conduit to Turkey and parts of Central Europe.
Historic Decline in Gas Transit
- Russia’s gas exports via Ukraine, which peaked at 65 billion cubic meters (bcm) annually in 2020, dwindled to 15 bcm by 2023.
- The cessation of this route underscores the collapse of a half-century-long energy partnership, highlighting the economic and strategic consequences of prolonged geopolitical conflict.
| Significance of the Pipelines |
(A) For Europe:
(B) For Russia:
|
4. China’s Mega Dam on Yarlung Tsangpo
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Overview of the Project
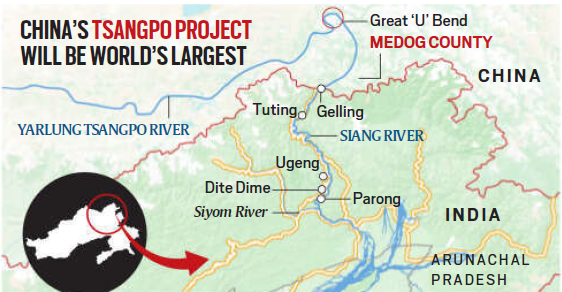
- China’s approval of a massive hydropower project on the Yarlung Tsangpo, the world’s largest of its kind, raises significant geopolitical and environmental concerns.
- With a capacity of 60,000 MW, three times that of the Three Gorges Dam, the project leverages the river’s steep gradient in Tibet.
- However, its implications extend downstream to India and Bangladesh, affecting millions dependent on the Brahmaputra system for water, agriculture, and livelihoods.
Impact of the Dam
- Mega-dams are seen as tools for asserting sovereignty, with upstream countries like China using them to control natural resources.
- The proposed Medog dam could disrupt the natural flow of the Brahmaputra, which is crucial for agriculture and ecosystems downstream.
- The blocking of water for hydropower generation may impact surface water levels, monsoon patterns, groundwater systems, and agriculture in India, Bhutan, and Bangladesh.
| Brahmaputra River |
|
Hydropower Competition
- China and India are competing with major hydropower projects, such as the Great Bend Dam in China and the Upper Siang Dam in India.
- Bhutan also has smaller dams, raising concerns about downstream impacts.
- The lack of a comprehensive treaty on shared rivers, coupled with unresolved territorial disputes, heightens the geopolitical tensions in the region.
Community Risks
- Local communities along the Brahmaputra river, both upstream and downstream, rely on traditional knowledge of the river’s cycles.
- Mega-dams threaten this knowledge and exacerbate disaster risks, impacting agriculture, biodiversity, and the sensitive Himalayan ecology.
Climate Change and Natural Disasters
- The Himalayas play a key role in global climate systems, regulating monsoons and glacier dynamics.
- Climate change is increasing Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs), as seen with the 2023 Chungthang Dam collapse in Sikkim.
- Dams disrupt natural cycles, affecting ecosystems, communities, and the water system.
India’s Concerns
- India, as a lower riparian state, depends on the Brahmaputra system for agriculture and livelihoods.
- Any disruption in water flow or silt deposition from China’s upstream activities could severely impact Assam and Arunachal Pradesh.
- The project’s location near the “Great Bend,” just before the river enters India, heightens these concerns.
- Historical incidents, like the 2004 Parechu Lake landslide, underline the risks of unilateral actions in such fragile regions.
Bilateral Mechanisms and Their Limitations
- Existing cooperation frameworks, including MoUs on the Brahmaputra and Sutlej rivers, have proven inadequate.
- While mechanisms like the 2013 umbrella MoU and the 1997 UN Watercourses Convention offer guidelines, their scope and enforcement remain limited.
- Data sharing, crucial during crises, has often been interrupted due to political tensions, such as during the Doklam and Ladakh standoffs.
India’s Options
India must adopt a multi-pronged approach:
- Diplomatic Engagement: Strengthen dialogue with China, emphasizing transparency and consultation under international norms.
- Public Advocacy: Actively challenge China’s claims about the project’s downstream impacts to avoid tacit acceptance.
- Regional Alliances: Collaborate with other affected nations like Bangladesh to present a united front.
- Domestic Preparedness: Enhance disaster management infrastructure and explore alternative water management strategies.
Water security should become a core issue in India-China relations, with clear signaling that neglecting India’s concerns could adversely affect bilateral ties.
Conclusion
- China’s Yarlung Tsangpo project exemplifies the complexities of transboundary river management.
- For India, safeguarding its interests requires a blend of assertive diplomacy, regional cooperation, and robust domestic measures to mitigate potential risks.
- The project’s scale and potential consequences demand sustained attention and proactive action.
| India’s Initiatives to Counter such Projects |
|
5. India Deepens Engagement with Taliban
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Key Issues Discussed
- Security Concerns:
India reiterated its primary concern that Afghan soil should not harbor anti-India terror groups. The Taliban acknowledged India’s sensitivities and assured cooperation. - Humanitarian and Development Aid:
India has extended substantial humanitarian support, including food, medical supplies, and earthquake relief. The meeting also explored India’s potential involvement in development projects in Afghanistan, addressing urgent needs like healthcare and refugee rehabilitation. - Trade and Connectivity:
Both sides discussed leveraging Iran’s Chabahar Port to facilitate trade and humanitarian assistance. This is part of India’s broader strategy to maintain its presence in Afghanistan despite regional challenges. - Sports Diplomacy:
Strengthening cricket ties emerged as a soft power tool to enhance relations, with India providing facilities for Afghan players to train.
Geopolitical Context
India’s engagement occurs against a backdrop of regional flux:
- China’s Growing Influence: Beijing’s active engagement with the Taliban, including urban development projects and diplomatic exchanges, has prompted India to assert its presence.
- Tensions Between Taliban and Pakistan: Strained relations between Pakistan and the Taliban have reduced Islamabad’s leverage, opening opportunities for India.
- Weakened Regional Players: With Iran preoccupied and Russia focused on Ukraine, India seeks to fill the vacuum and protect its investments in Afghanistan.
Strategic Implications
- India’s calibrated approach balances engagement with the Taliban while withholding official recognition.
- This strategy aims to protect India’s $3 billion investments in Afghanistan, counter Chinese influence, and ensure regional stability.
- By addressing humanitarian needs and emphasizing development, India positions itself as a key partner for Afghanistan’s future.
- India’s primary objective remains clear: preventing the resurgence of terrorism while fostering stability and development in Afghanistan.
| What are the roadblocks in India-Afghanistan relations? |
There are several roadblocks in India-Afghanistan relations, including:
|
6. NATO members reluctant to endorse Trump’s defence spending proposal
| Context |
|

Proposal for NATO Defence Spending Increase:
Trump’s Proposal:
- U.S. President-elect Donald Trump proposed that NATO countries should raise their defense spending to 5% of their GDP.
- This would be a significant increase from the current target of 2%, which no NATO member, including the United States, currently meets.
Political and Economic Challenges:
- NATO officials acknowledged the need for increased defense spending, but expressed that the 5% target would be politically and economically unfeasible for most members.
- Reaching such a target would require hundreds of billions of dollars in additional funding, which is deemed unrealistic for many nations.
Expected Outcome:
- A new defense spending target is expected to be set at the NATO summit in The Hague in June.
- The new target is likely to be around 3% of GDP.
- Even this figure presents challenges for several NATO members, with some struggling to meet the existing 2% target.
Rationale for Increased Spending:
- The push for higher defense spending is in response to Russia’s aggression in Ukraine and broader security concerns.
- There is also an increasing push to reduce reliance on the United States for NATO’s defense capabilities.
European Concerns:
- While European countries agree on the need for increased defense spending, they are also advocating for more self-reliance in defense matters.
- Proposals include joint EU borrowing to fund military capabilities, aiming to strengthen Europe’s defense capacity independently.
7. Trump sentenced in hush money case
| Context |
|

Hush Money Case:
- Donald Trump was convicted in May 2024 for hiding hush money payments to an adult film actress.
- The payments were made to stop the actress from talking about their alleged affair before the 2016 election.
- He was sentenced to an unconditional discharge, meaning he was guilty but received no jail time or fine.
- This made Trump the first US President-elect to be convicted of a felony.
- The judge explained that this punishment avoided interfering with Trump’s presidential duties.
- Trump attended the sentencing virtually and called the case a “witch hunt” aimed at harming his reputation.
- Prosecutors argued that Trump’s actions were a deliberate attempt to deceive and damage trust in the justice system.
8. India-Bangladesh Border Fencing Dispute
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
The Recent Dispute in Malda and Cooch Behar
- Recent incidents in West Bengal’s Malda and Cooch Behar highlighted tensions between the Border Security Force (BSF) and Border Guard Bangladesh (BGB).
- In Malda, BGB intervened in BSF’s fencing efforts, claiming a violation of the 1975 agreement prohibiting construction within 150 yards of the international boundary.
- Similarly, in Cooch Behar, BGB objected to fencing efforts by villagers with BSF support to prevent cross-border cattle movement.
The 1975 Border Guidelines
- The 1975 Joint India-Bangladesh Guidelines prohibit defense structures within 150 yards of the zero line.
- India, however, considers barbed-wire fences as non-defensive, unlike Bangladesh, which views them as potential security concerns.
- Complex border terrain, including villages and rivers along the 4,096.7 km border, often necessitates exceptions to these guidelines, requiring bilateral negotiations.
Bangladesh’s Objections
Bangladesh objects to fencing for two primary reasons:
- Violation of the 1975 Agreement: Fences closer than 150 yards to the border are perceived as breaches.
- Inconvenience to Residents: Fencing disrupts the daily lives of border residents, especially where villages lie close to or across the boundary.
Additionally, smart fencing with surveillance capabilities has been criticized for allowing India visibility into Bangladeshi territory.
India’s Perspective on Fencing
- India asserts that single-row fences (SRF) are essential to curb cross-border crimes like smuggling and illegal migration.
- Unlike defensive structures, SRF is seen as a non-military tool to manage border security.
- With over 81.5% of the West Bengal-Bangladesh border already fenced, the process continues to face challenges due to land acquisition issues and local resistance.
Challenges and Implications
- Geopolitical Sensitivities: Fencing disagreements strain diplomatic relations, especially amid political transitions in Bangladesh.
- Cross-Border Crime: Unfenced areas see high crime rates, necessitating stricter measures.
- Local Disruptions: Border residents face restrictions on movement and livelihood activities, complicating bilateral agreements.
Conclusion:
- Balancing security needs with diplomatic agreements and local interests remains crucial.
- India and Bangladesh must engage in consistent dialogue to address disputes and ensure smoother border management while respecting bilateral commitments.
| What is the significance of Bangladesh to India? |
Bangladesh is important to India for several reasons, including
|
| PYQ: Analyze internal security threats and transborder crimes along Myanmar, Bangladesh and Pakistan borders including Line of Control (LoC). Also discuss the role played by various security forces in this regard. (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2020) |
9. Phased Ceasefire in Gaza
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Phased Ceasefire and Exchange of Detainees
- In the first 42-day phase, Hamas will release 33 hostages, while Israel will free 900-1,650 Palestinian detainees, including those detained post-October 7, 2023.
- This phase sets the groundwork for eventual Israeli withdrawal from Gaza, including critical areas like the Netzarim and Philadelphi Corridors, contingent on subsequent negotiations.
- The phased structure aims to build trust while addressing humanitarian concerns.
Geopolitical and Domestic Shifts Enabling the Deal
- Key changes in Israel’s political landscape, such as Gideon Sa’ar joining Netanyahu’s coalition, diluted the influence of far-right figures.
- International pressure, particularly from the U.S. under Biden and President-elect Trump, further propelled the ceasefire.
- Netanyahu’s strategic considerations for leveraging U.S. relations during Trump’s second term also influenced his decision to accept the agreement.
Key Terms and Implications
- Withdrawal from the Philadelphi Corridor:
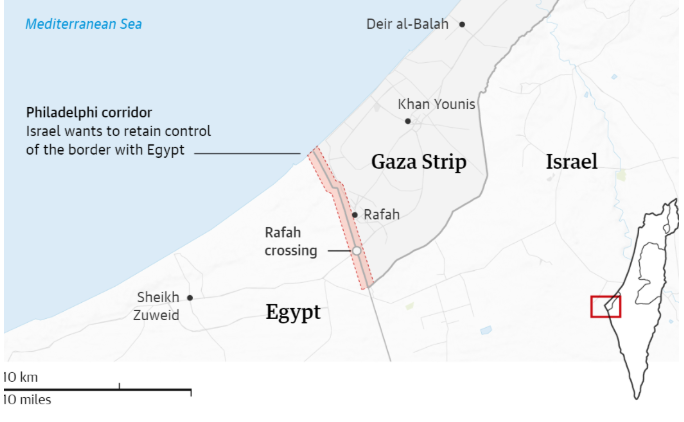 Israel’s commitment to vacate this critical buffer zone by the end of phase one addresses long-standing Egyptian and Hamas demands.
Israel’s commitment to vacate this critical buffer zone by the end of phase one addresses long-standing Egyptian and Hamas demands.
- However, Israeli officials remain cautious, leaving room for renegotiation based on security concerns.
- Prisoner Exchange Dynamics:
Israel’s history of high-stakes prisoner swaps resurfaces, with at least 250 life-sentenced detainees set for release. This concession risks political backlash, challenging Israel’s 2014 law limiting such exchanges.
Implications for Hamas and Israel
- Hamas
The ceasefire offers Hamas breathing space to regroup, rebuild its resources, and maintain its influence in Gaza. Its evolving tactics and local command strength highlight resilience, despite leadership losses.- Hamas appears to be positioning itself for a permanent role in Gaza’s governance, emulating Hezbollah’s integration into Lebanon’s post-war framework.
- Israel
Despite military successes against Hamas and Hezbollah, Israel’s core objective of eradicating Hamas from Gaza remains unmet. While the deal secures the release of hostages, Netanyahu risks domestic criticism for perceived concessions, potentially weakening his far-right support.
Conclusion: A Complex Road Ahead
- The ceasefire reflects a temporary pause in violence and opens pathways for broader negotiations, including reconstruction and governance in Gaza.
- However, unresolved security and political challenges highlight the fragility of this agreement, leaving the region’s long-term stability uncertain.
| About Gaza Strip |
|
10. Trump’s Withdraw from the Paris Agreement
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Trump’s Withdrawal from the Paris Agreement: Key Actions and Implications
- Trump revoked all US climate finance commitments, signaling a reversal of climate-friendly policies.
- His administration aims to boost domestic energy production, particularly in oil, gas, and coal, while reducing dependence on international energy supply chains, especially those tied to China.
Greater Impact of the Second Withdrawal
- Unlike the first withdrawal in 2017, which was delayed by procedural timelines, Trump’s second exit will be swift, becoming effective within a year.
- This decision, accompanied by rollbacks in energy and environmental regulations, threatens to dismantle US climate policy entirely.
- The US, being the world’s second-largest emitter, plays a critical role in global efforts to meet the Paris Agreement’s objectives.
- Its absence will significantly hinder progress, potentially adding billions of tonnes of emissions over the next four years.
Impact on Climate Finance
- Trump’s revocation of the US International Climate Finance Plan will reduce financial resources for global climate action.
- The US’s influence on private and international finance could lead to a broader funding shortfall for developing countries.
- This move is likely to weaken the financial mechanisms critical for supporting global mitigation and adaptation efforts, disproportionately affecting vulnerable nations.
Conventional Energy Push and Domestic Policies
- Trump’s administration has prioritized boosting oil, gas, and coal production, arguing that this will enhance energy security, reduce reliance on China, and create domestic jobs.
- While renewable energy remains part of the agenda, Trump has focused on imposing tariffs on Chinese equipment to encourage domestic manufacturing.
- This policy shift underscores his broader goal of prioritizing American interests over international commitments.
The Fallout for International Climate Action
- The US’s withdrawal from the Paris Agreement highlights Trump’s long-standing complaint that climate regulations unfairly burden the US while exempting countries like China.
- However, as the largest historical emitter, the US bears significant responsibility for climate mitigation.
- The failure to meet its 2030 emission reduction targets now seems inevitable, further weakening global climate goals.
Conclusion
- Trump’s second withdrawal from the Paris Agreement reflects a fundamental shift in US climate policy, with far-reaching consequences for global efforts to combat climate change.
- The rollback of domestic and international commitments risks derailing the progress made under previous administrations, underscoring the challenges of maintaining global unity in addressing climate change.
11. Indus Waters Treaty
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
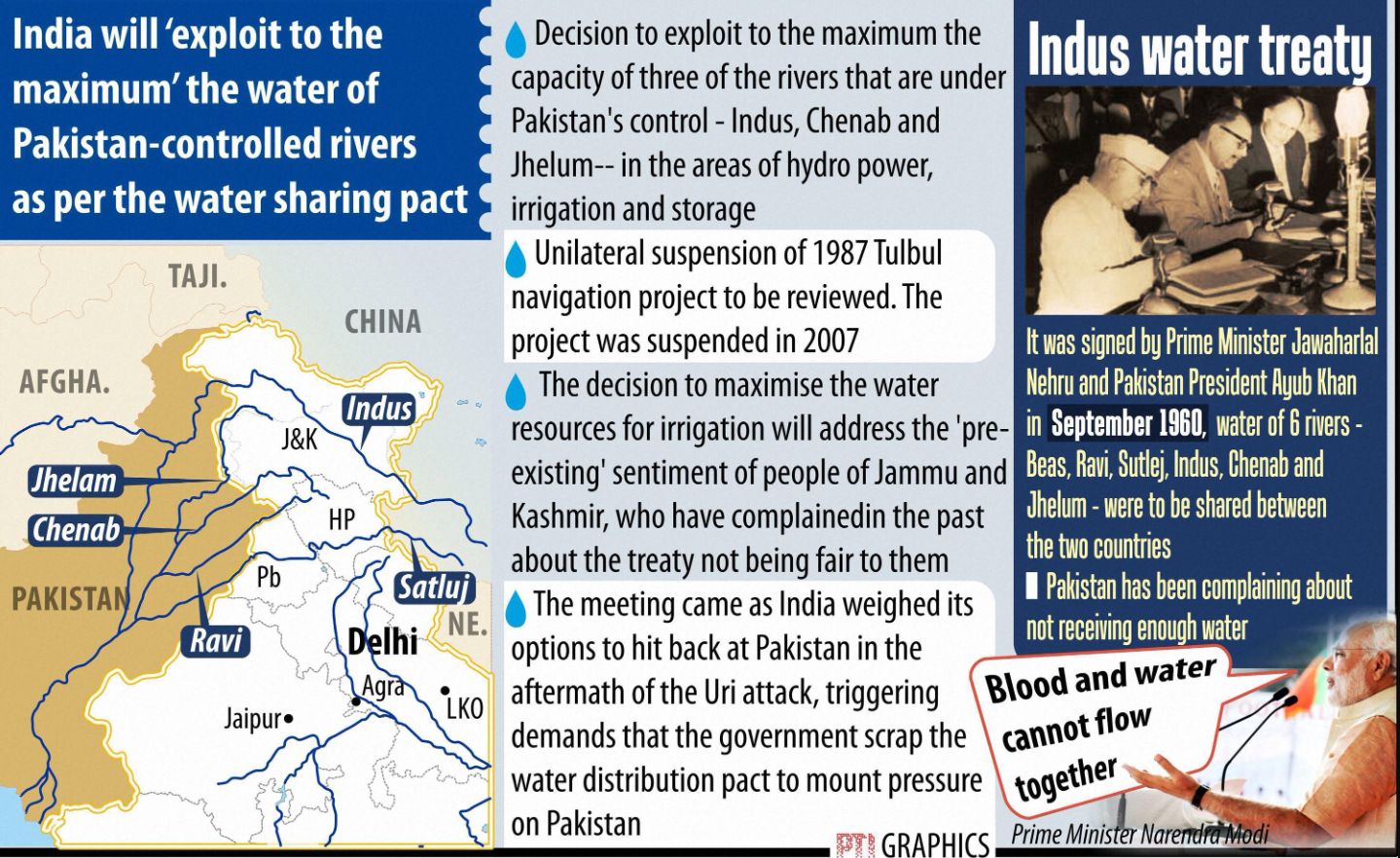
What is Indus Water Treaty (IWT)?
- Indus Waters Treaty was signed on September 19, 1960, between India and Pakistan and was brokered by the World Bank.
- The treaty sets out a mechanism for cooperation and information exchange between the two sides on the use of the water of the Indus River and its five tributaries Sutlej, Beas, Ravi, Jhelum, and Chenab.
Neutral Expert’s Decision
- The Neutral Expert validated India’s position that the seven questions referred to him fall under his jurisdiction per Paragraph 7 of Annexure F of the treaty.
- This aligns with India’s consistent claim that only the Neutral Expert has the competence to decide these issues.
- The decision marks the beginning of the merits phase, which will evaluate the specific technical differences and lead to a final decision.
India’s Stand
- India welcomed the Neutral Expert’s decision, emphasizing its commitment to the sanctity of the IWT and rejecting the parallel proceedings initiated by Pakistan in the PCA, which India deems “illegally constituted.”
- The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) reiterated India’s readiness to cooperate within the Neutral Expert process to resolve differences consistent with treaty provisions.
Pakistan’s Position and Actions
- Pakistan had initially sought the appointment of a Neutral Expert in 2015 but later unilaterally withdrew the request in 2016, opting instead for arbitration through the PCA.
- This shift, according to India, violated the graded dispute resolution mechanism stipulated in Article IX of the IWT.
Broader Context of Disputes
- India is constructing the Kishenganga hydroelectric project on the Kishenganga River (a tributary of Jhelum) and the Ratle hydroelectric project on the Chenab River.
- Pakistan has raised technical objections, citing potential violations of the IWT. In response, India has invoked Article XII (3) to initiate reviews and potential modifications to the treaty, reflecting its evolving water management priorities and the need to address procedural ambiguities.
Conclusion and Implications
- The Neutral Expert’s decision reinforces the treaty’s dispute resolution mechanism and validates India’s adherence to its provisions.
- Moving forward, the merits phase will be critical in resolving technical differences.
- The case highlights the enduring challenges in Indo-Pak relations concerning shared water resources under the IWT framework.
| PYQ: With reference to the Indus river system, of the following four rivers, three of them pour into one of them which joins the Indus directly. Among the following, which one is such a river that joins the Indus direct? (2021)(a) Chenab
(b) Jhelum (c) Ravi (d) Sutlej Ans: (d) |
12. India-China Resume Bilateral Engagements
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Resumption of Bilateral Engagements
- Measures include resuming the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra in summer 2025, restarting direct flights, issuing visas for journalists and think tanks, and discussing trans-border river data sharing.
- These steps aim to enhance people-to-people exchanges and stabilize relations after years of strained diplomacy.
High-Level Diplomatic Engagements
- The breakthrough came after Foreign Secretary Vikram Misri’s meetings with Chinese officials, including Vice Foreign Minister Sun Weidong and Foreign Minister Wang Yi.
- These talks followed discussions between Prime Minister Narendra Modi and President Xi Jinping in October 2023 during the BRICS Summit, signaling efforts to address lingering tensions while prioritizing areas of mutual interest.
Border Issue: An Underlying Concern
- Although the Indian statement made no explicit mention of the border standoff, it hinted at addressing “priority areas of interest and concern” step by step.
- The absence of specific timelines or pathways for de-escalation along the LAC indicates a cautious approach to the unresolved border situation, underscoring its centrality in bilateral relations.
Building Mutual Trust and Confidence
- Both sides acknowledged the importance of the 75th anniversary of diplomatic relations in 2025 as an opportunity to strengthen public diplomacy.
- Commemorative activities and initiatives to rebuild trust are expected to address the erosion of mutual confidence since the 2020 incursions.
Contrasting Diplomatic Narratives
- China’s Foreign Ministry emphasized avoiding “mutual suspicion, estrangement, and exhaustion,” contrasting with India’s stance of “mutual respect, sensitivity, and interests,” as reiterated by External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar.
- This divergence in diplomatic framing reflects differing priorities and approaches to repairing ties.
Geopolitical Implications
- China highlighted the broader significance of improved India-China relations, linking them to the interests of the Global South and regional stability.
- Both nations recognize the potential impact of their relationship on global peace and prosperity, underscoring the need for pragmatic collaboration despite existing challenges.
Conclusion
- The resumption of bilateral engagements between India and China marks a cautious step toward repairing strained ties.
- While people-centric initiatives and public diplomacy efforts offer hope, unresolved border tensions and divergent narratives underscore the complexities in rebuilding trust and fostering long-term stability.
| What Measures can India Adopt to Balance its Relations with China? |
|
| PYQ: “Belt and Road Initiative” is sometimes mentioned in the news in the context of the affairs of : (2016)(a) African Union
(b) Brazil (c) European Union (d) China Ans: D |
13. US birthright citizenship
| Context |
|
What is Birthright Citizenship?
- Birthright citizenship grants automatic citizenship to individuals born within a country’s territory, regardless of their parents’ citizenship status.
- In the U.S., it is based on the 14th Amendment of the Constitution (1868), which states that anyone born in the U.S. is a citizen.
| Provisions in US Constitution about Birthright Citizenship: |
|
Trump’s Executive Order
- Trump’s executive order sought to limit birthright citizenship, excluding children of undocumented immigrants or those with temporary legal status.
- It argued that children born in the U.S. to non-citizen parents should not automatically get citizenship.
Why the Judge Blocked the Order
- U.S. District Judge John Coughenour blocked Trump’s executive order, calling it “blatantly unconstitutional.”
- He expressed disbelief that the order could be deemed constitutional, questioning its legality.
Next Steps
- Trump could propose a constitutional amendment to change the law.
- Legal challenges are still ongoing, with the final decision possibly resting with the U.S. Supreme Court.
| Impact on India: |
|
14. India and Indonesia Forge Deeper Ties
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Historical Ties Rooted in Anti-Colonial Solidarity
- India and Indonesia’s relationship dates back to their shared struggle against colonialism.
- In the late 1940s, India, under Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru, extended unwavering support to Indonesia’s independence movement.
- Efforts ranged from diplomatic backing to practical actions such as banning Dutch flights over Indian airspace and supporting Indonesian rebels with aid.
- This era of solidarity culminated in a decade of mutual respect and collaboration, symbolized by Sukarno’s participation as the chief guest at India’s first Republic Day in 1950.
Divergence in the 1960s: A Strain in Relations
- The 1960s marked a significant downturn in bilateral ties. Diverging policies towards China, with India’s relations souring after the 1959 Tibetan uprising and Indonesia’s growing closeness to Beijing, created rifts.
- Sukarno’s support for Pakistan during the 1965 India-Pakistan war further strained relations, compounded by the domestic political upheaval in Indonesia that led to Suharto’s rise to power.
The Cold War Drift and Limited Engagement
- During the Cold War, India aligned with the USSR, while Indonesia leaned towards the US.
- Although the two countries signed key agreements like the 1977 maritime boundary pact, relations stagnated.
- Mutual visits by leaders in the 1980s maintained minimal engagement, but ties remained far from the highs of the early 1950s.
Revitalization: Look East and Act East Policies
- A turning point came in the 1990s with India’s ‘Look East’ policy under P.V. Narasimha Rao, aimed at strengthening ties with Southeast Asia.
- Economic liberalization and the shared goal of regional cooperation in the post-Cold War era provided fertile ground for growth.
- In 2014, the Modi government upgraded the approach to an ‘Act East’ policy, emphasizing tangible outcomes in areas like trade, security, and cultural exchange.
Contemporary Ties: Economic and Strategic Cooperation
- India and Indonesia have developed robust trade relations, with Indonesia being India’s second-largest trading partner in ASEAN.
- Bilateral trade surged from $4.3 billion in 2005-06 to $38.84 billion in 2022-23, fueled by commodities like coal, palm oil, and refined petroleum.
- Strategic cooperation in maritime security and defense has also grown, reflecting shared interests in the Indo-Pacific.
Challenges and Future Prospects
- Despite significant progress, India-Indonesia ties remain below potential.
- Key challenges include limited diversification of trade, underutilization of cultural linkages, and insufficient alignment in Indo-Pacific strategies.
- Strengthening people-to-people ties, expanding trade portfolios, and enhancing maritime collaboration could unlock the full potential of this partnership.
Conclusion
- India and Indonesia, as major powers in the Indo-Pacific, hold immense potential to shape regional stability and economic growth.
- Enhanced cooperation in this strategically vital region will benefit not only the two nations but also the broader international community.
15. Trump’s Withdrawal from WHO
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
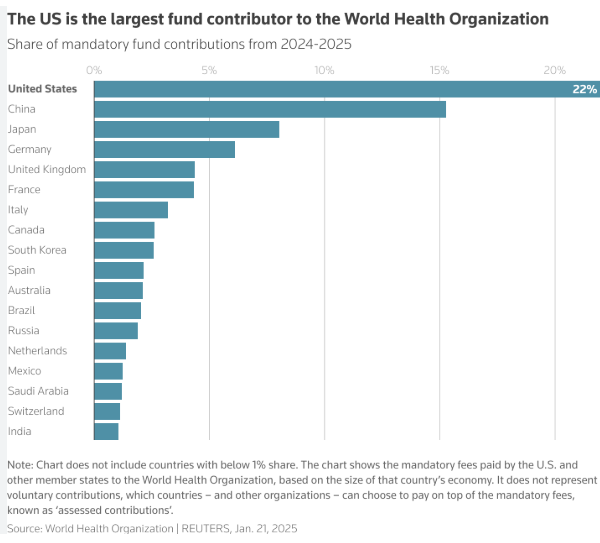
Trump’s Withdrawal from the WHO: Reasons and Immediate Actions
- The reasons cited included the WHO’s mishandling of the COVID-19 pandemic, its failure to adopt necessary reforms, and concerns over its independence from political influences.
- The order also halted US funding to the organization, recalled American personnel, and ended negotiations on the WHO’s pandemic treaty.
- This decision, although not unexpected, has raised concerns among health experts about the resulting loss of funding and expertise for the global health body.
Financial Implications for the WHO
- The US is a major contributor to the WHO, providing around 20% of its total funding.
- Trump’s withdrawal directly impacts the organization’s finances, particularly in terms of voluntary contributions, where the US remains the largest donor.
- In contrast, China’s contributions, both mandatory and voluntary, are considerably lower.
- Experts have warned that the loss of US funding could hinder the WHO’s ability to support global health initiatives, especially in developing countries.
- Other nations, such as Australia and Indonesia, have stepped in to fill some of the financial gap, but the overall impact on global health efforts remains significant.
WHO’s Reaction and Global Health Concerns
- The WHO expressed regret over the US’s decision, emphasizing its crucial role in global health, including addressing health security and protecting the population’s well-being worldwide.
- The organization pointed to the reforms it has undertaken in recent years, highlighting its commitment to transparency and cost-effectiveness.
- However, the withdrawal threatens the collaborative framework between the US and the WHO, particularly the partnership with the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), which is vital for international health surveillance and response.
Impact on India and Global Health Programs
- India, which benefits from various health programs supported by the WHO, will also feel the effects of the US’s withdrawal.
- The WHO plays a significant role in India’s immunization programs, as well as efforts to combat diseases like malaria, tuberculosis, and HIV.
- A reduction in funding and the loss of US expertise may affect the WHO’s ability to provide vital health guidelines and support local health initiatives.
- Moreover, the absence of US contributions will likely strain the WHO’s capacity to assist India and other countries in tackling pressing health challenges.
Global South’s Role and the Path Forward
- The vacuum left by the US could be filled by China and countries from the global south, including India.
- Experts suggest that nations like India, South Africa, and others must step up to provide leadership and financial support for global health initiatives.
- India’s increasing role in global health, alongside its position as a voice of the global south, makes it crucial in guiding collective efforts to ensure continued progress in addressing global health challenges.
- Philanthropic organizations, such as the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, may also play a larger role in bridging the funding gap left by the US.
Conclusion
- The US’s withdrawal from the WHO is a significant blow to global health initiatives, particularly in terms of funding and expertise.
- The decision will affect the WHO’s ability to operate effectively, especially in countries like India that rely on its programs.
- While the global south, led by nations like India, may need to step in to fill the void, the long-term impact on global health security remains a pressing concern.
- The WHO’s response and the international community’s efforts will determine how effectively the world can address future health crises.
| What is World Health Organisation, and its objectives? |
The World Health Organization (WHO), established in 1948, is a specialized agency of the United Nations that connects nations, partners and people to promote health, keep the world safe and serve the vulnerable – so everyone, everywhere can attain the highest level of health. Some of the important objectives of WHO are:
|
16. Trump’s Greenland Gambit
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Trump’s Renewed Interest in Greenland
- US President Donald Trump’s remarks on Greenland highlight his intent to bring the autonomous Danish territory under American control, citing its strategic importance for the “protection of the free world.”
- While this ambition appears unconventional in the 21st century, it is rooted in historical and geopolitical factors, including concerns over China’s growing influence in the Arctic.
Historical Context of US Interest in Greenland
- The US has shown interest in Greenland since the 1940s, initially driven by World War II security concerns.
- In 1946, America proposed to buy Greenland, aiming to counter Soviet influence in the Arctic.
- Although Denmark rejected the offer, subsequent agreements allowed the US to establish military bases on the island, underscoring its strategic importance.
Greenland’s Geopolitical and Economic Significance

- Greenland’s location near emerging Arctic shipping routes and its abundance of critical natural resources, including rare earth minerals, makes it highly valuable.
- These minerals, essential for renewable energy, military technologies, and electronics, are largely controlled by China.
- Greenland’s untapped reserves offer an opportunity to reduce reliance on Chinese supply chains, adding urgency to US efforts to secure the island.
China’s Growing Influence in Greenland
- China has established a significant presence in Greenland, with investments in mining, infrastructure, and its Arctic “Polar Silk Road” initiative.
- This has raised alarms in the US, which views Chinese activities as a threat to its Arctic strategy and global mineral supply security.
- Trump’s push for Greenland reflects a strategic counter to China’s expanding footprint.
Confrontation with Denmark
- Denmark, which oversees Greenland’s foreign policy, has firmly rejected Trump’s proposals, asserting that Greenland is not for sale and that its future lies with its residents.
- Reports of Trump’s confrontational tone and threats of tariffs during discussions with Danish officials have strained relations between the two nations, further complicating America’s ambitions.
Conclusion:
- Trump’s renewed push for Greenland is emblematic of the shifting global power dynamics, where strategic territories like Greenland play a pivotal role.
- While the bid reflects America’s desire to counter China’s Arctic ambitions, the confrontational approach risks diplomatic fallout.
- Greenland remains a crucial piece in the global geopolitical chessboard, with its future hinging on both local autonomy and international negotiations.
| Key Facts About Greenland |
|
17. Singapore to help India’s semiconductor industry
| Context |
|
Strategic Relationship
- Singapore’s President, Tharman Shanmugaratnam, emphasized the strong and long-standing partnership between India and Singapore, established since India’s recognition of Singapore’s independence in 1965.
- Singapore has been the largest investor in India for several years.
Digital Initiatives
- Both nations are exploring the possibility of a secure data corridor between Gift City (India) and Singapore to facilitate safe financial data exchange.
- Renewable Energy and Regional Development
- Collaboration is being pursued in renewable energy.
- India’s eastern states, such as Odisha and Assam, were highlighted for their natural resources and potential in logistics, connectivity, and petrochemicals.
Upgraded Relations
- Relations between India and Singapore were upgraded to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership during Prime Minister Modi’s visit to Singapore in September 2024.
Commemoration of Diplomatic Ties
- President Shanmugaratnam, along with President Droupadi Murmu, launched a joint logo to mark the 60th anniversary of diplomatic relations between the two nations.
- The year 2025 will witness a series of events and exchanges to celebrate this milestone.
18. Russia, Iran Ink Broad Strategic Partnership
| Context |
|
Key Objectives:
- Strengthen economic and trade relations, addressing technical obstacles for gas shipments and transport corridors.
- Enhance military and technological collaboration, particularly in response to Western sanctions.
- Foster regional stability through mutual cooperation, countering external interference (especially the U.S.).
Context and Necessity:
- Sanctions: Both Russia and Iran are facing severe Western sanctions, prompting the need for closer ties.
- Geopolitical Alignment: Russia and Iran share common interests in countering U.S. influence in the region, particularly in West Asia.
- Past Cooperation: Historical ties include nuclear energy projects and mutual support in Syria and Ukraine.
Significance:
- The treaty is seen as a strategic move to secure economic and military support amid growing external pressures, especially from the U.S.
19. Rights situation is ‘worsening’ in Central Asia: HRW
| Context |
|
Human Rights Watch:
-
- Human Rights Watch is an independent, international organization that works to defend human rights around the world.
- It was founded in 1978 and is headquartered in New York City.
- The organization conducts research and advocacy on human rights issues, exposing abuses and pressuring those in power to respect human rights.
- Human Rights Watch works on behalf of a wide range of people whose rights are violated, including refugees, children, migrants, and political prisoners.
- It publishes reports and briefings on human rights conditions in some 70 countries each year.
- Human Rights Watch advocates for policies to prevent human rights abuses and regularly meets with government officials and international organizations to press for change.
- The organization is a founding member of the International Freedom of Expression Exchange and co-chair of the International Campaign to Ban Landmines.
20. South African court upholds ‘Cancel Coal’ case
| Context |
|
The ‘Cancel Coal’ Case
- Civil organizations, including the African Climate Alliance and Vukani Environmental Justice Movement, challenged the government’s 2019 Integrated Resource Plan.
- The government planned to add 1,500 MW of coal power by 2027, but the organizations argued it would harm the environment and public health, especially children.
South Africa’s Energy Mix and Climate Commitments
- Coal accounted for 71% of South Africa’s energy supply in 2022.
- The country is the 16th largest emitter of greenhouse gases and has committed to cutting emissions and achieving net-zero by 2050, in line with the Paris Agreement.
Details of the Judgement
- The court found that the government did not adequately consider the harmful effects of coal power on health and the environment, particularly for children.
- The ruling emphasized the government’s failure to fulfill its constitutional obligation to protect the environment for future generations.
Environmental Justice and Global Transition
- The case underscores the growing need to transition from coal to cleaner energy sources globally, a vital step in combating climate change and protecting public health.
21. U.S. to remove Indian entities from restricted lists – Jake Sullivan
| Context |
|
What is a restricted list?
- The restricted list refers to a list of entities and individuals in certain countries, including India, that face trade or cooperation restrictions, particularly in sensitive areas like nuclear technology and scientific advancements.
- These restrictions prevent U.S. companies and government entities from engaging in civil nuclear cooperation or providing certain technologies to the listed entities.
- The list was a result of concerns over the proliferation of nuclear weapons and the potential for sensitive technologies being misused.
- For India, many of its leading nuclear and scientific entities have been on this list, hindering full cooperation with the U.S. in civil nuclear and space sectors.
- Recent policy shifts aim to remove these entities from the list to foster greater collaboration in these areas.
| Benefits for India: |
|
22. Hundreds of migrants arrested as Trump’s deportation drive begins
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
-
- Hundreds of migrants were arrested in the United States as President Donald Trump’s deportation operation began.
- The operation is being described as the largest mass deportation in U.S. history.
- The White House confirmed the start of this operation, with migrants flown out on military aircraft.
- The UN rights office emphasized that the right to seek asylum is a universally recognized human right.
- On his first day in office, Trump declared a “national emergency” at the southern border and deployed more troops.
- An estimated 11 million undocumented migrants live in the U.S.
23. ECB cuts rate again as eurozone falters
| Context |
|
Economic Challenges in the Eurozone
- The eurozone economy has been facing stagnation, with little to no growth in recent months.
- Major economies like Germany and France have experienced economic contractions, adding to concerns.
- High energy costs and a slowdown in manufacturing have significantly weakened overall economic performance.
| What is Eurozone? |

|
Inflation and Future Outlook
- Inflation remains slightly above the central bank’s target, causing concerns among policymakers.
- Despite the rise, experts anticipate inflation to decline in the coming months.
- The central bank is expected to continue reducing interest rates to support economic recovery.
Uncertainty Due to U.S. Policies
- The possibility of new trade tariffs from the United States has created economic uncertainty.
- Potential tariffs on European imports could negatively impact trade and economic stability in the eurozone.
- Policymakers are closely monitoring global trade developments to assess future risks.
Indian Economy
1. US Sanctions on Russia’s Oil Pose Challenges for India
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Implications for India
- Russia, India’s largest crude oil supplier, accounted for nearly 38% of India’s imports in 2024.
- While Indian refiners can fulfill existing contracts until March 12, the sanctions are likely to disrupt the India-Russia oil trade beyond this wind-down period.
- However, India’s overall oil imports will remain stable as alternative supplies from West Asia are readily available.
Rising Freight Costs and Shifting Suppliers
- Sanctions will limit the availability of tankers to transport Russian oil, causing freight costs to rise.
- This, in turn, will erode the discounts on Russian crude, making oil from traditional suppliers like Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE more competitive.
- Indian refiners have already begun increasing imports from these countries to offset potential disruptions.
Russia’s Dilemma and the Price Cap
- The sanctions further pressure Russia’s shadow fleet, which operates outside Western restrictions.
- To maintain exports, Russia may be forced to sell oil below $60 per barrel to comply with Western price caps, allowing access to Western shipping and insurance.
- This would reduce revenues for Russia but ensure continued exports to India and China.
Impact of the Incoming US Administration
- Donald Trump’s upcoming presidency could reshape US policy on Russia and Ukraine.
- While Trump has expressed intentions to broker peace, his administration’s stance on sanctions remains uncertain.
- The new sanctions may serve as leverage for Trump in negotiations with Moscow, potentially influencing the trajectory of the Russia-Ukraine conflict and global oil trade.
Conclusion
- India’s oil trade with Russia faces near-term disruptions due to US sanctions, but ample alternative supplies from West Asia ensure stability in imports.
- The evolving US policy under Donald Trump will play a key role in shaping the global oil trade and geopolitical dynamics around the Russia-Ukraine war.
| How has India Benefitted from Discounted Russian Oil? |
Significant Savings by Indian Refiners
Emergence of India as a Major Supplier of Refined Petroleum Products
|
2.Centre approves Eight pay panel
| Context |
|
Approval of Eighth Pay Commission
- The Union government has approved the establishment of the Eighth Pay Commission, fulfilling the long-standing demand of Central trade unions and employees’ organizations.
Beneficiaries
- The recommendations of the Pay Commission will benefit approximately 50 lakh employees and 65 lakh pensioners, including serving and retired defense personnel.
- Delhi alone houses around 4 lakh Union government employees.
Composition and Appointment
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi has approved the formation of the commission ahead of the Seventh Pay Commission’s term ending in 2026.
- The Chairperson and two members will be appointed soon, with the chair traditionally being a retired Supreme Court judge (e.g., Justice A.K. Mathur headed the Seventh Pay Commission).
Impact of Recommendations
- The recommendations will serve as the basis for wage settlements in public sector undertakings and similar pay revisions in States.
- The Seventh Pay Commission’s implementation in 2016 cost the exchequer ₹1 lakh crore in the fiscal year 2016-17.
Economic and Social Benefits
- The decision is expected to boost consumption and economic growth while improving the quality of life for government employees.
- It reflects the government’s commitment to enhancing employee welfare.
Trade Union Reactions
- Trade unions welcomed the move and emphasized the need for clear terms of reference, particularly on “living wage” and “living pension” concepts.
- The Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh-backed Bharatiya Mazdoor Sangh (BMS) appreciated the decision and urged for the early constitution of the panel.
Timeline for Recommendations
- As per precedence, a Pay Commission usually takes about two years to submit its report, making this early approval significant for timely implementation.
Significance
- The establishment of the Eighth Pay Commission underscores the government’s proactive approach to addressing employee demands and ensuring their financial well-being, further contributing to economic growth.
Conclusion
The approval of the Eighth Pay Commission highlights the government’s commitment to employee welfare and economic growth. Its timely formation will address wage and pension demands, benefiting millions of employees and pensioners while boosting consumption and overall economic activity.
3. DAP Beyond NBS Subsidy
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

About Fertilizer subsidy in India
- It is financial support provided by the government to make fertilizers affordable for farmers, especially small and marginal ones.
- Fertilizers are essential for enhancing agricultural productivity, but they are costly, so the subsidy helps to reduce the financial burden on farmers.
- The Union Budget for 2024 allocated Rs 164,000 crore for fertilizer subsidy.
Extension of Subsidy on Di-Ammonium Phosphate (DAP)
- The Centre has extended the special subsidy of ₹3,500 per tonne on DAP for one more year starting January 1, 2025.
- Initially set to expire on December 31, 2024, this decision aims to curb farmgate price hikes for India’s second most-used fertiliser.
- This move is particularly significant given the rupee’s depreciation against the US dollar, which adds to cost pressures.
Impact of Fixed Maximum Retail Prices (MRPs)
- Despite DAP and other non-urea fertilisers being decontrolled on paper, the government has informally capped MRPs to shield farmers from price shocks.
- The MRP for DAP remains at ₹1,350 per 50-kg bag, while similar price caps exist for other fertilisers like 20:20:0:13 and muriate of potash.
- However, the steep fall in the rupee, coupled with rising import costs, has made it challenging for fertiliser companies to sustain these price caps.
Economic Pressures on Fertiliser Companies
- The current landed cost of imported DAP stands at ₹54,160 per tonne, significantly higher than the ₹52,960 per tonne recorded three months ago.
- Factoring in additional costs like customs duties, port handling, and dealer margins, the total cost exceeds ₹65,000 per tonne.
- In contrast, the combined government subsidy and MRP yield ₹52,411 per tonne, leaving a considerable gap that makes imports financially unviable without further government intervention.
Government Compensation and Fiscal Cost
- To mitigate industry losses, the government approved full compensation for DAP imports priced above $559.71 per tonne from September 1, 2024, to March 31, 2025.
- However, the subsidy scheme’s effectiveness has been undermined by the rupee’s plunge to ₹85.7-to-the-dollar.
- Extending the ₹3,500 per tonne subsidy reduces the potential fiscal cost, estimated at ₹6,475 crore, and limits the required MRP hike for companies.
Challenges in Fertiliser Availability
- Stock levels of DAP and complex fertilisers, as of mid-December, are lower than last year’s levels.
- The government must ensure sufficient imports of both finished products and raw materials to avoid shortages in the next kharif season.
- Failure to secure adequate supplies could disrupt agricultural productivity.
In conclusion, while the subsidy extension alleviates some immediate pressures, long-term challenges like exchange rate volatility, import viability, and stock replenishment remain critical for stabilising the fertiliser sector.
| About Di-Ammonium Phosphate (DAP) |
|
| About Di-Ammonium Phosphate (DAP) |
|
4. Income Inequality In India
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Income Inequality Trends: Improvement with Persistent Concerns
- After worsening during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020-21, income inequality in India improved in 2022-23, reflecting effective recovery measures, according to a working paper by the People Research on India’s Consumer Economy (PRICE).
- Despite this progress, wealth remains highly concentrated among top income earners, while the bottom 10% continue to struggle, highlighting the need for sustained, inclusive economic strategies.
The Gini Index: A Mixed Journey
- The Gini index, a measure of income inequality (0 indicating perfect equality, 100 indicating perfect inequality), shows India’s fluctuating inequality patterns.
- Post-independence, the index improved to 0.367 by 2015-16 but worsened to 0.506 in 2020-21 due to the pandemic.
- It has since improved to 0.410 in 2022-23, signaling recovery but underscoring persistent disparities.
Income Share Distribution: Rising Inequality Amid Recovery
- The bottom 50% of earners experienced a modest rise in income share from 15.84% in 2020-21 to 22.82% in 2022-23, though it remains below the 2015-16 level of 24.07%.
- Similarly, the middle 40% saw their share grow to 46.6%. In contrast, the top 10% peaked at 38.6% during the pandemic, dropping slightly to 30.6% by 2022-23.
- The top 1% retained a disproportionate share of wealth, highlighting entrenched disparities.
Key Drivers of Inequality: Structural and Sectoral Imbalances
- COVID-19 exacerbated structural inequalities, as job losses and economic instability disproportionately affected the bottom 50%, while sectors like technology and e-commerce boosted incomes for the top 10%.
- Even with a post-pandemic recovery, the wealth gap remains significant.
Policy Recommendations: Building an Inclusive Framework
- The paper emphasizes investments in education, healthcare, and rural infrastructure as pivotal to addressing inequality.
- Social safety nets like MGNREGA and financial inclusion initiatives have contributed to slight improvements but require scaling and refinement.
- Progressive taxation and portability of benefits can further ensure equitable growth distribution.
5. Indian coffee exports surpass $1bn
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
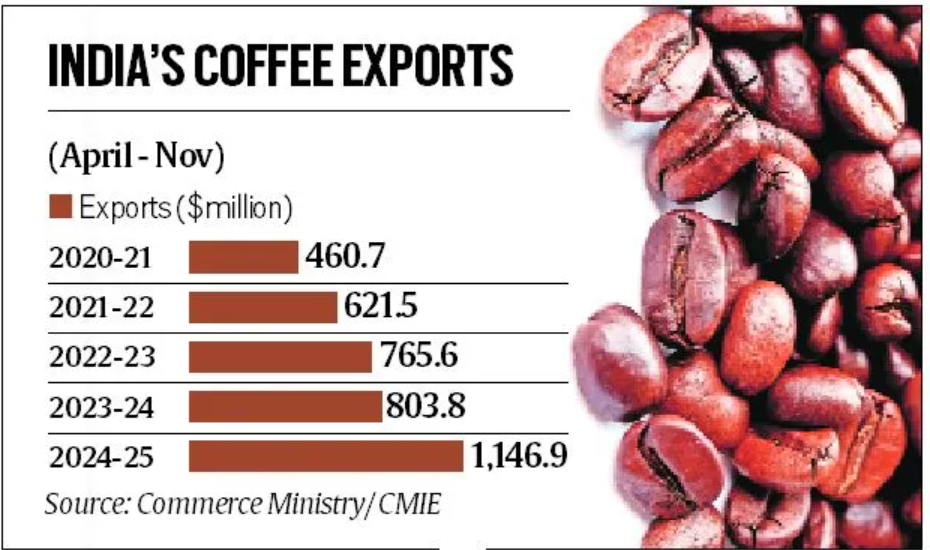
India’s Rise in Coffee Exports
- India, traditionally known for tea exports, is emerging as a significant player in the global coffee export market.
- In FY24, exports reached a record $1.146 billion between April and November, a 29% increase compared to $803.8 million in the same period last year.
- This marks a nearly twofold increase since FY21. The growth is fueled by rising global Robusta coffee prices, supply constraints in leading producers like Brazil and Vietnam, and pre-emptive stocking by European buyers ahead of new EU regulations.
Drivers of Growth in Coffee Exports
- Surge in Robusta Prices:
Robusta prices hit multi-decade highs due to supply disruptions in Brazil and Vietnam. Prices peaked at $4,667/metric ton in June, marking a 63% increase in 2023. - European Stockpiling:
Anticipation of the European Union’s Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) led to pre-implementation stockpiling, boosting Indian exports. - Premium Positioning:
Unlike tea exports, Indian coffee has captured the premium export market segment, enhancing profitability.
Global Coffee Market Dynamics
- Brazil and Vietnam’s Production Challenges:
Brazil’s production, affected by droughts and high temperatures, dropped by 2.6 million bags to 40.5 million. Vietnam’s output, though recovering, remains below its 2021/22 record. - Impact on Global Supply:
These constraints, combined with robust demand, have elevated global coffee prices.
Regional Contributions in India
- Top Coffee Producers:
Karnataka dominates with 248,020 MTs (Arabica and Robusta), followed by Kerala (72,425 MTs) and Tamil Nadu (18,700 MTs).
Export Destinations and Regulatory Challenges
- Key Markets:
The EU remains the largest destination, with Italy, Belgium, and Germany accounting for nearly half of exports. Other major importers include the US, Russia, and UAE. - EU’s Deforestation Regulation (EUDR):
The regulation aims to curb imports of products linked to deforestation, affecting $1.3 billion worth of Indian agricultural exports, including coffee. Compliance is expected to increase costs due to complex verification mechanisms.
6. Decoding India’s growth slowdown
| Context |
|
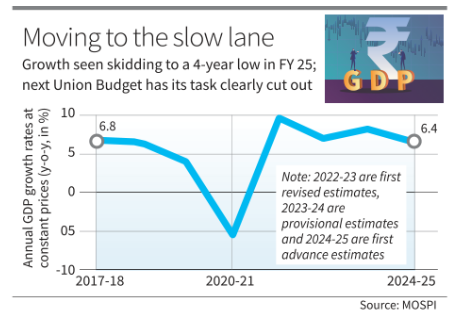
Decline in GDP Growth
- This estimate is below the 6.5% to 7% range projected in the Economic Survey of July 2024.
- The nominal GDP growth rate, which accounts for inflation, is expected to be 9.7%, lower than the 10.5% projected in the Union Budget.
Discrepancies in Data Estimation
-
- Experts, including the IMF, have criticized the official GDP estimates, particularly the use of the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) as a deflator.
- The IMF has suggested using the Producer Price Index (PPI) instead of WPI for more accurate GDP deflation.
- Data issues such as revisions to historical series and discrepancies between GDP by activity and expenditure complicate monitoring of India’s economy.
| What is GDP Deflation? |
|
| What is GDP Deflation? |
|
Impact of Volatility in WPI
- WPI has shown significant volatility over the years, which has caused discrepancies between the WPI and the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- For example, in 2023-24, the nominal GDP showed a deceleration, while real GDP growth indicated acceleration due to discrepancies in the GDP deflator, which misrepresents economic conditions.
| Wholesale Price Index (WPI) |
|
Private Investment Challenges
- Despite the Economic Survey highlighting the private sector’s slow response to tax cuts, the Union Budget projected a revival in private corporate investment to fund the ‘Prime Minister’s Package for Employment and Skilling.’
- However, the latest GDP estimates show a decline in real gross fixed capital formation from 9% in 2023-24 to 6.4% in 2024-25, signaling weak investment performance.
Investment and Consumption Trends
- During the UPA era, real private investment growth was over 10%, significantly higher than under the NDA regime, where private investment growth stagnated.
- Despite tax cuts in 2019, corporate investment has failed to drive substantial economic activity, highlighting the lack of a private investment-led recovery in the post-pandemic period.
Fiscal Strain and Budgetary Challenges
- Tax revenue growth is below target, with only 56% of the net tax revenue goal met by November 2024.
- Capital expenditure has been underutilized, with less than half of the projected ₹11.11 trillion capex spent by November.
- The government faces the dilemma of maintaining fiscal discipline while addressing the economic slowdown, requiring adjustments to revenue mobilization strategies, such as increasing taxation on wealth and profits.
Conclusion
- The ongoing economic slowdown is evident, affecting key sectors like agriculture, manufacturing, and services.
- To avoid worsening the fiscal situation, the government must reassess its revenue mobilization strategy and prioritize spending on capital and welfare.
7. PM to open Z-Morh tunnel
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Location and Purpose: The Z-Morh tunnel is located in Ganderbal district, Jammu & Kashmir, and is part of a strategic corridor linking Kashmir and Ladakh.
- Tourism Benefits: The tunnel will keep Sonamarg open for year-round tourism, preventing closures due to snowfall and avalanches.
- Strategic Importance: It provides continuous access to Ladakh and enhances connectivity, crucial for both civilian and military purposes.
- Construction: Built at a cost of ₹2,680 crore, the tunnel is 6.5 km long with advanced features, including a modified escape tunnel and ventilation systems.
- Economic Impact: It is expected to boost winter tourism and adventure tourism in the region.
8. Govt. lifts ban, gives nod for sugar Export
| Context |
|
Potential Benefits:
- Price Stability: The decision aims to stabilize domestic sugar prices by allowing controlled exports, preventing prices from plummeting due to surplus stocks.
- Support for Farmers: By enabling exports, sugar mills will have better liquidity, ensuring timely payments to the five crore farmer families involved in sugarcane production.
- Boost to Sugar Mills: The export allowance helps sugar mills by clearing surplus stock, improving cash flow, and enhancing their financial position.
- Employment Boost: The move is expected to benefit approximately five lakh workers in the sugar industry, contributing to job security.
- Enhances India’s Sugar Sector: This decision strengthens the sugar sector by improving overall market stability and ensuring its growth potential.
Challenges:
- Risk of Domestic Shortages: Exporting sugar could potentially create a shortage in the domestic market if not monitored carefully, which may lead to price hikes.
- International Market Dynamics: The global sugar market’s volatility could affect the benefits of export, especially if demand fluctuates or international prices fall.
- Logistical and Regulatory Hurdles: Coordinating exports through traders and ensuring compliance with export quotas can create operational challenges.
Conclusion:
- The move to allow sugar exports is a balanced approach to support the sugar industry, farmers, and workers – but requires careful monitoring to avoid negative consequences on domestic availability and prices.
9. World Economic Forum 2025
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Purpose and Initiation of the WEF
- The World Economic Forum was founded by German professor Klaus Schwab in 1971, originally as the European Management Forum.
- Schwab, a professor of business policy, introduced the concept of “stakeholder capitalism,” advocating for businesses to create long-term value by considering the interests of all stakeholders, not just shareholders.
- This vision evolved the WEF into a platform for global leaders to come together and address economic and social challenges.
WEF’s Evolution and Activities
- Initially focused on improving European management practices, the WEF shifted its scope after significant global events in 1973, such as the collapse of the Bretton Woods system and the Arab-Israeli War.
- By 1975, the Forum expanded its membership to include the world’s leading 1,000 companies.
- Over the years, it has become a prominent venue for tackling critical global issues, including AI, geopolitical risks, and climate change, and features over 500 sessions where thousands of participants, including business leaders, politicians, and experts, collaborate on solutions.
Funding and Location of the WEF
- The WEF is largely financed by global corporations with annual revenues exceeding $5 billion.
- The choice of Davos, a serene Swiss town, as the meeting location is inspired by its calm and focused atmosphere, which helps foster effective discussions.
- This setting has also witnessed landmark moments in international diplomacy, such as the first meetings between North and South Korea and key interactions during the South African political transition.
Historical Significance and Diplomatic Impact
- Throughout its history, the WEF has been a venue for groundbreaking diplomatic engagements.
- It played a key role in South African reconciliation, including the first joint appearance of Nelson Mandela, F.W. de Klerk, and Mangosuthu Buthelezi in 1992.
- Additionally, the WEF has been instrumental in the establishment of the G20, which was first discussed at the 1998 meeting, and continues to influence global policy decisions through initiatives like the Global Competitiveness Report and the Global Gender Gap Report.
10. ‘Need policy for affordable bioethanol’
| Context |
|
Introduction to Bioethanol and Challenges
-
- Bioethanol and renewable energy-based electrification can help India achieve carbon neutrality.
- However, the high running costs of bioethanol fuel due to lower fuel efficiency remain a significant barrier.
- The government must create mechanisms to make bioethanol more affordable for consumers.
Making Bioethanol Pricing Affordable
- Although bioethanol reduces carbon emissions, its higher cost of operation compared to conventional fuels is an issue.
- A key strategy to make bioethanol viable is through policy changes that ensure affordable pricing for users.
- The government should focus on reducing fuel costs to make it economically competitive with gasoline.
Improving Fuel Efficiency
- Vehicle manufacturers must work on improving fuel efficiency to lower the cost per kilometer of ethanol-powered vehicles.
- Maintaining or reducing the fuel cost per kilometer is essential for ethanol to remain competitive with gasoline.
Proposed Price Reductions
- A potential solution is to reduce the price of ethanol (E100) from ₹95 per liter to ₹65 per liter to lower vehicle running costs.
- Improving vehicle mileage is another way to reduce the overall cost of ethanol-based transportation.
Economic Benefits for Farmers
- Promoting ethanol fuel will have positive socio-economic impacts, particularly in rural India, where agriculture is a major livelihood.
- The use of bioethanol can support farmers and contribute to rural development.
Availability of Bioethanol
- Ethanol can be distributed through existing gasoline stations, ensuring its widespread availability.
- In comparison, infrastructure for other alternative fuels like CNG is still developing, which makes ethanol more accessible in the short term.
Environmental Benefits of Ethanol
- Bioethanol has an environmental advantage over other fuels by significantly reducing carbon emissions.
- Both flex-fuel vehicles and electric vehicles are necessary for achieving long-term carbon neutrality goals.
Conclusion
- To make bioethanol a sustainable and viable fuel option, India needs support from the government, manufacturers, and farmers.
- Affordable pricing and infrastructure improvements are critical for the success of ethanol in the Indian market.
11. India’s oil demand likely to hit yet another record in 2025-26
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Record Petroleum Consumption in FY26
- The Petroleum Planning & Analysis Cell (PPAC) projects a 4.7% growth over FY25 estimates, with total consumption expected to reach 252.93 million tonnes, up from the revised FY25 estimate of 241.68 million tonnes.
Key Drivers of Consumption Growth
- Major Fuels: Petrol, diesel, aviation turbine fuel (ATF), liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), and petroleum coke are anticipated to lead the growth.
- Sectoral Demand: Transportation, industrial activity, aviation, and energy-intensive industries are key contributors.
- Aviation Growth: ATF demand is projected to grow nearly 10% year-on-year, mirroring the rapid expansion of India’s civil aviation sector.
- Petroleum Coke Usage: Petcoke demand is expected to rise 10% to 24.85 million tonnes, fueled by its applications in industries such as power, cement, and steel.
Historical Trends and Recovery Post-Pandemic
- India’s petroleum consumption has been on a consistent upward trajectory, barring FY21 when the COVID-19 pandemic caused a temporary decline.
- The pre-pandemic high of 214.13 million tonnes in FY20 was surpassed in FY23, with current fiscal projections reaching 241.68 million tonnes, setting the stage for FY26 to exceed all previous records.
India’s Strategic Role in Global Oil Demand
India is emerging as a major growth hub for global oil demand due to:
- Energy-intensive industries and growing vehicle sales.
- Rapidly expanding aviation and petrochemical sectors.
- Low per-capita energy consumption compared to developed nations.
India’s refining capacity, currently at 257 million tonnes per annum, is poised for further expansion, highlighting its strategic role in meeting future demand.
Challenges of Rising Import Dependency
- Despite robust growth, India’s stagnant domestic oil production necessitates increasing reliance on imports, with over 85% of crude oil sourced from abroad.
- As the world’s third-largest consumer of crude oil, this dependency presents significant economic and strategic challenges.
Global Context and India’s Edge Over China
- India is expected to lead global oil demand growth, surpassing China in growth rates by FY24, according to S&P Global Commodity Insights.
- While China, the world’s second-largest oil consumer, faces subdued demand due to structural and demographic shifts, India’s strong economic and population growth underpins its rising demand.
- The International Energy Agency predicts India will overtake China as the largest driver of global oil demand growth by 2027.
Consumption Growth by Fuel Type (FY26 Projections)
- Diesel: 94.12 million tonnes (+2.8% YoY), reflecting robust industrial and transportation activity.
- Petrol: 42.64 million tonnes (+6.6% YoY), driven by rising vehicle sales.
- LPG: 33 million tonnes (+4.7% YoY), indicating higher household and industrial consumption.
- ATF: 9.95 million tonnes (+10% YoY), reflecting booming aviation activity.
- Petcoke: 24.85 million tonnes (+10% YoY), driven by industrial applications.
Conclusion
- India’s rising petroleum consumption underscores its growing energy needs and economic expansion.
- However, balancing this growth with the challenges of import dependency, energy transition efforts, and environmental sustainability will be critical for the country’s long-term energy security and economic resilience.
12. How can the Budget arrest growth decline?
| Context |
|
Current Economic Situation
- India’s GDP growth rate is lower than expected, despite increased government capital expenditure.
- The Economic Survey highlighted concerns about sluggish private consumption and investment.
- Major economic shocks, such as demonetization, GST implementation, and COVID-19 lockdowns, have contributed to the slowdown.
Three Phases of Post-Reform Growth
- 1991-2004: Initial phase of economic reforms with moderate growth.
- 2004-2011: High growth with poverty reduction, increased state intervention, and welfare schemes.
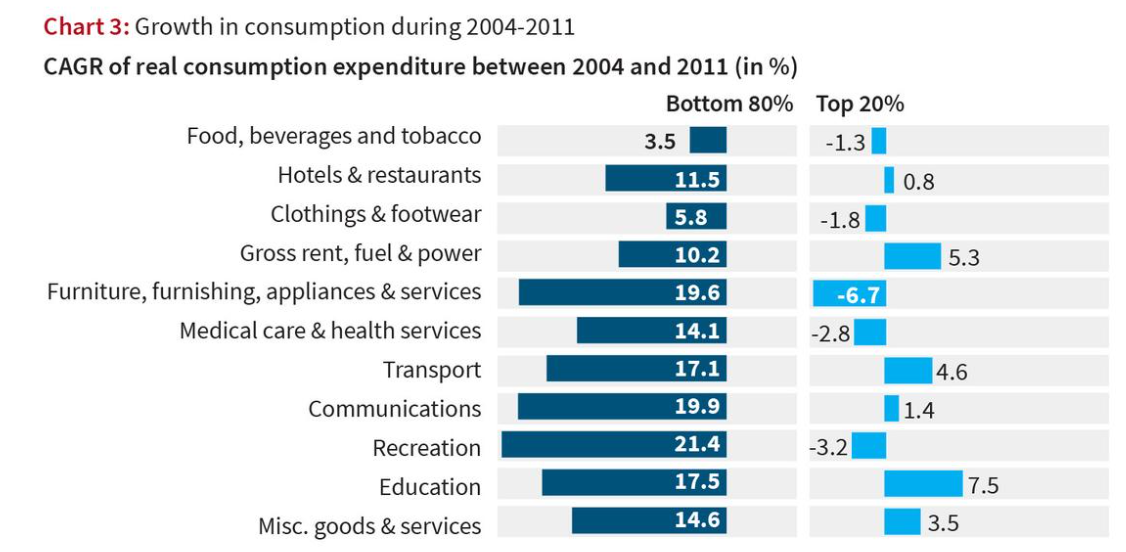
- 2011-2023: Economic slowdown, particularly after 2019, with weak private consumption and investment.
Reasons for High Growth (2004-2011)
- During this phase, the share of consumption of the richest 20% declined, while the bottom 80% saw an increase in consumption.
- Government policies played a key role in boosting demand among lower-income groups.
- Increased spending on social welfare programs had a strong income and employment multiplier effect.
- Schemes like NREGA ensured job creation and wage growth, particularly in rural areas.
- Investment in agriculture and rural development further strengthened the economy.
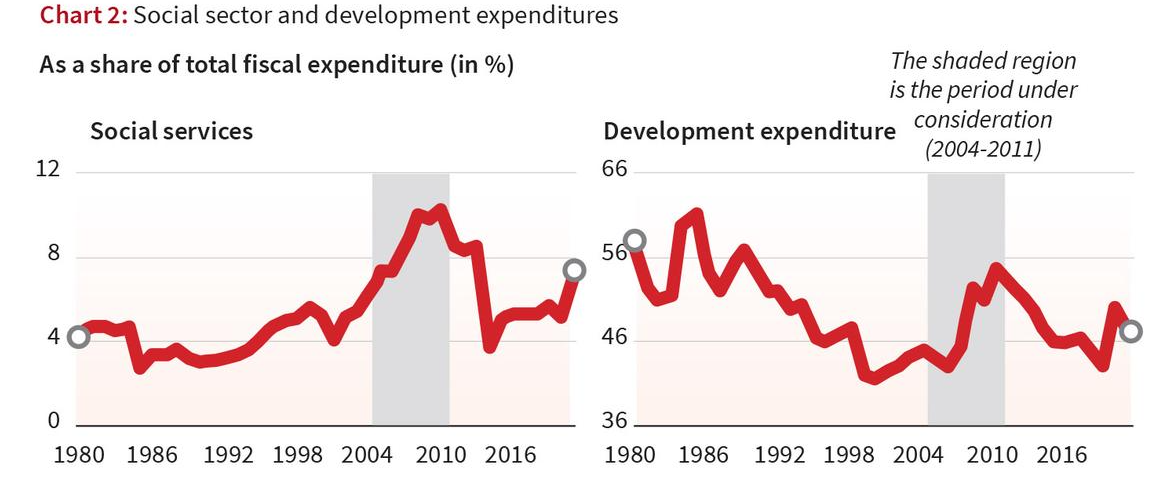
| Capital vs. Revenue Expenditure |
|
Government’s Response to Slowdown
- The government has primarily focused on capital expenditure to revive growth.
- Despite corporate tax cuts from 30% to 22% in 2019, private investment has not increased.
- Weak demand and low capacity utilization prevent companies from investing further.
- The expectation that capex would attract private investment has not materialized.
Proposed Solutions
- The government should increase revenue expenditure to boost demand and employment.
- Focus should shift to labour-intensive capital projects rather than capital-intensive ones.
- Fiscal expenditure as a share of GDP needs to rise to sustain economic recovery.
- A balance between capital and revenue expenditure is essential for long-term growth.
Conclusion
- The upcoming budget will indicate whether the government prioritizes market-friendly policies or social welfare.
- A policy shift toward increasing revenue spending could help reverse the economic slowdown and improve living conditions.
| PYQ: Distinguish between capital budget and revenue budget. Explain the components of both these Budgets. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2021) |
13. Argentine inflation drops
| Context |
|

Status of Argentine Economy:
- In 2024, Argentina’s inflation rate dropped to 117.8%, a sharp decline from previous years, signaling a reduction in price increases.
- The government, under President Javier Milei, claims this drop in inflation reflects the success of its stabilization plan, which began with his tenure.
- Milei’s austerity measures, which included a 52% devaluation of the peso and the firing of over 33,000 public sector employees, played a key role in reducing inflation.
- Despite these efforts, poverty is high, with 57.4% of people living below the poverty line.
- Instead these reforms plunged Argentina into a deep recession, pushing an additional five million people into poverty in 2024.
- Despite facing protests, Milei asserts that the economic pain will result in long-term economic stability and growth.
14. Union Budget
| Context |
|
Overview of the Union Budget
- The Union Budget is a financial plan presented by the Finance Minister.
- It includes details about the government’s spending, taxes, and economic activities.
- The main components are expenditure, receipts, and deficit indicators.
Expenditure in the Budget
- Expenditure is divided into two types:
- Capital Expenditure: Spending on creating long-lasting assets like new schools and hospitals.
- Revenue Expenditure: Spending that doesn’t create assets, like salaries, subsidies, and interest payments.
- Expenditure is further classified into:
- General Services: Basic services like administration.
- Economic Services: Spending on infrastructure, rural development, and agriculture.
- Social Services: Expenditure on education, healthcare, and welfare programs.
- Grants-in-aid: Money given to other bodies or sectors.
- Development expenditure includes spending on economic and social services and is classified as capital or revenue.
Government Receipts
- Receipts are the government’s earnings, classified into:
- Revenue Receipts: Earnings from taxes and non-tax sources that don’t add to liabilities.
- Non-debt Capital Receipts: Earnings like loan recoveries or proceeds from selling assets, which don’t create debt.
- Debt-creating Capital Receipts: Earnings from loans or borrowings that increase government liabilities.
Deficits in the Budget
- Fiscal Deficit: Difference between total expenditure and receipts. It shows how much the government borrows.
- Primary Deficit: Fiscal deficit minus interest payments.
- Revenue Deficit: Fiscal deficit minus capital expenditure.
Impacts of the Budget on the Economy
- Government expenditure creates demand in the economy.
- Taxes and other revenues reduce income in the private sector, leading to reduced demand.
- To analyze the budget, we look at trends in expenditure and revenue in relation to GDP.
Income Distribution
- The Budget affects different income groups in different ways.
- Welfare schemes like subsidies help the poor, while tax reductions benefit businesses.
- Although these decisions increase the fiscal deficit, they have distinct effects on income distribution.
Fiscal Rules
- Fiscal rules set targets for managing government debt and deficits.
- In India, these rules are based on the N.K. Singh Committee recommendations.
- Fiscal rules help guide government expenditure and tax policies.
15. ‘India’s maritime sector needs $1 trillion by 2047’
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
-
- Steps have been taken to establish green hydrogen production hubs at Paradip, Tuticorin, and Kandla ports to decarbonize the shipping sector.
- India’s port capacity is set to increase sixfold by 2047, making the country one of the top 10 maritime nations.
- India’s major ports have shown significant growth, with a 47% increase in cargo handling since 2014.
- Modernization efforts have reduced container dwell time to three days and vessel turnaround time to 0.9 days.
- Nine Indian ports are listed in the World Bank’s Container Port Performance Index 2023, with Visakhapatnam among the top 20.
Environment
1. Cryodrakon Boreas
| Context |
|
Species in News: Cryodrakon Boreas

- About 76 million years ago, a young Cryodrakon boreas, one of the largest flying creatures in history, was likely ambushed by a crocodilian while drinking water.
- Cryodrakon boreas was a species of pterosaur, a flying reptile that lived during the Cretaceous Period, about 76 million years ago.
- It was discovered in Dinosaur Provincial Park, Alberta, Canada.
- The name Cryodrakon boreas means “Cold Dragon of the North” in Greek.
- It was one of the largest flying creatures in history, with adult wingspans reaching 10 metres and standing as tall as a giraffe.
- Juveniles had a smaller wingspan of about 2 metres.
- It had a long neck, a large toothless beak, and a short tail.
- Scientists believe it was carnivorous, but its exact feeding strategy is debated.
2. Greenland’s Lakes Transform Due to Extreme Weather
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

Rapid Transformation of Greenland’s Lakes
- These lakes, once pristine, play a crucial role in providing drinking water, supporting biodiversity, and acting as carbon sinks.
- The transformation, which typically takes centuries, occurred within months—an unprecedented rate of change.
What Triggered the Change?
- In 2022, warmer temperatures caused rainfall instead of snowfall, leading to permafrost thawing.
- As a result, organic carbon, iron, and minerals were released into the lakes.
- This process was driven by atmospheric rivers—long, narrow air currents carrying moisture—that intensified due to climate change.
- Scientific models predict a 50–290% increase in atmospheric rivers by the end of the 21st century, particularly affecting Greenland, North America, East Asia, Western Europe, and Antarctica.
Consequences of the Extreme Weather Events
The lakes underwent drastic physical, chemical, and biological changes:
- Water quality deterioration – The release of organic matter altered taste, odour, and clarity, making drinking water unsafe.
- Increased carbon emissions – The lakes, once carbon sinks, saw emissions rise by 350% due to reduced phytoplankton activity and increased organic matter breakdown.
- Disrupted ecosystems – Reduced sunlight penetration affected phytoplankton, limiting photosynthesis-based carbon absorption.
Why This Matters for Climate Change
- The study follows another alarming finding that land-based carbon absorption in 2023 hit its lowest level since 2003.
- Natural carbon sinks—forests, soil, and oceans—absorb half of human emissions, but as they weaken or turn into carbon sources, atmospheric carbon levels will surge, worsening global warming.
- The Greenland lake crisis serves as a stark warning of accelerating climate shifts and the urgent need for mitigation strategies.
| About Greenland |
|
3. Yamuna Water Dispute
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
What is Ammonia?
- Ammonia is a colourless, gaseous chemical with a sharp odour, highly soluble in water. It is widely used in industries, agriculture, and manufacturing.
- Major sources of ammonia pollution include industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and untreated sewage.
- It can also form naturally due to organic matter degradation. Prolonged exposure can cause severe internal organ damage due to its corrosive properties.
Impact of Ammonia on Delhi’s Water Supply
- Industrial units and sewage discharges in Haryana’s Panipat and Sonipat districts pollute the Yamuna before it reaches Delhi at Wazirabad.
- This reduces dissolved oxygen levels to zero, especially in winter when freshwater flow is minimal.
- High ammonia levels hinder the efficiency of water treatment plants, leading to water shortages in the capital.
Government Responses and Challenges
- Delhi’s water treatment plants use chlorine to neutralize ammonia, requiring 11.5 kg per litre per hour for one ppm of ammonical nitrogen.
- However, treatment plants cannot handle ammonia levels beyond one ppm, leading to water disruptions.
- Despite multiple discussions, Delhi and Haryana have not found a permanent solution.
- Delhi proposed an in-situ ammonia treatment plant in Wazirabad in March 2023, but it remains incomplete.
- Haryana is also yet to finalize a pipeline to prevent pollutant mixing.
Conclusion
- The recurring issue of ammonia pollution in the Yamuna highlights both environmental and political challenges in Delhi’s water management.
- While short-term measures like chlorine treatment help mitigate the crisis, the lack of a long-term solution continues to disrupt the capital’s water supply.
- Effective coordination between the Delhi and Haryana governments, along with infrastructure upgrades, is crucial to ensuring safe and sustainable water for Delhi’s residents.
4. In Odisha, coal dust is clogging leaves
| Context |
|
Discovery of Coal in Jharsuguda
- Jharsuguda, Odisha, became a coal-rich area after coal deposits were discovered in 1900 during railway construction.
- The first coal mine in the area was established in 1909, and the region now produces over 15 million tonnes of coal annually.
Importance of Coal
- Coal is formed by the decomposition of plants and is vital for electricity generation, iron, steel, cement, and fertilizer industries.
- Around three-fourths of India’s electricity comes from coal-fired power plants, making India the second-largest global coal producer and consumer after China.
Impact of Open-Cast Mining
- Open-cast mining, the dominant method in Jharsuguda, creates more air pollution than underground mining due to dust generation.
- Dust from mining operations spreads up to 30 km, affecting nearby vegetation and air quality.
- Dust clogs the stomata of plants, hampering photosynthesis and temperature regulation.
Use of Satellite Data for Monitoring
- Researchers used data from satellites like Landsat and Sentinel to study dust effects on vegetation.
- Satellite data showed significant impacts of dust on plants’ ability to absorb carbon dioxide.
- Field samples validated the accuracy of satellite estimates.
Environmental Consequences
- Clogged stomata, caused by the settling of dust on plant leaves, hinder the plant’s ability to absorb carbon and release oxygen.
- Increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere contributes to global warming over time.
- The reduced ability for transpiration causes plants to retain excess heat, leading to overheating.
- Overheated plants struggle to photosynthesize efficiently, causing stunted growth.
- In severe cases, plants may die due to the inability to regulate temperature and carry out essential functions.
- These changes ultimately harm local ecosystems, reducing biodiversity and disrupting the ecological balance.
Recommendations And Conclusion
- Governments can use satellite data to monitor dust pollution and address hotspots.
- Measures like water sprays and dust barriers can reduce mining dust and protect vegetation.
| PYQ: In spite of adverse environmental impact, coal mining is still inevitable for development.” Discuss. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2017) |
Science and Technology
1. Sriharikota to get third launch pad
| Context |
|

Approval of Third Launch Pad
- The Union Cabinet has approved the construction of a third launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), Sriharikota.
- The project aims to strengthen India’s space infrastructure, with an allocated outlay of ₹3,984.86 crore.
Planned Timeline
- The construction of the launch pad is expected to be completed by early 2029, ensuring readiness for future space missions and advancements in space technology.
Facilitating Next-Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLVs)
- The third launch pad will support the launch of Next-Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLVs), which ISRO plans to operationalize by 2031.
- This development aligns with ISRO’s vision to cater to the growing demands of advanced and heavier-class launch vehicles.
Support for Human Spaceflight Missions
- The new launch pad will also play a key role in India’s manned spaceflight program, with the first mission targeted for 2026, as stated by ISRO Chairman V. Narayanan.
Universal and Adaptable Design:
The third launch pad is being designed with universal and adaptable configurations to support:
- NGLVs equipped with semi-cryogenic stages.
- Launch Vehicle Mark 3 (LVM3) and its enhanced configurations.
- Future advancements in launch vehicle technology.
Enhancing ISRO’s Launch Capabilities
- With the second launch pad in operation for nearly two decades, the addition of the third launch pad will act as a standby and expand India’s launch capacity, meeting the needs of evolving space transportation requirements.
Catering to Future Needs
- This facility is designed to address India’s space transportation demands for the next 25-30 years, supporting both heavier-class vehicles and advanced mission profiles.
Strategic Importance
- The establishment of the third launch pad underscores India’s commitment to enhancing its space exploration capabilities, enabling greater frequency and diversity in launch missions while strengthening its position in the global space sector.
Conclusion
The approval for the third launch pad at SDSC Sriharikota marks a crucial step in enhancing ISRO’s space infrastructure. This new facility will support Next-Generation Launch Vehicles, manned space missions, and future technological advancements, strengthening India’s position in global space exploration. The project ensures ISRO’s readiness to meet evolving space transportation needs for the next 25-30 years.
2. ISRO Successfully Grows Cowpea Seedlings in Space
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Success of the Experiment
- The experiment involved growing cowpea seedlings (Vigna unguiculata) aboard the POEM-4 module in the microgravity environment of space.
- Out of eight cowpea seeds cultivated within a controlled environment featuring active thermal management, three successfully sprouted leaves.
- This accomplishment demonstrates ISRO’s ability to grow plants in space and offers insights into sustainable human presence during long-duration space missions.
Significance for Future Missions
- The success of the CROPS experiment is a step forward in developing technologies for space-based agriculture, which will be essential for sustaining life during future deep-space missions.
- The insights gained from this experiment will contribute to ensuring food security and long-term habitability in extraterrestrial environments.
Broader Implications
- This experiment highlights ISRO’s advancements in integrating biological research with space exploration, paving the way for innovative approaches to support human life in space.
- The mission also serves as a foundation for further studies in astrobiology and the development of self-sustaining ecosystems beyond Earth.
3. India Achieves Historic Space Docking Milestone
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

What is Space Docking?
- Space docking is the process of bringing two fast-moving spacecraft into the same orbit, maneuvering them close to each other, and finally joining them together.
- This capability is essential for missions requiring the assembly of large structures like space stations, refueling in orbit, or carrying crew and supplies to orbiting platforms.
- India’s successful docking demonstration makes it the fourth country globally, after the US, Russia, and China, to achieve this feat, marking a significant step in ISRO’s technological evolution.
Significance of the Achievement
This accomplishment is critical for future space missions:
- Space Station Development: India’s Bharatiya Antariksh Station, planned by 2035, will rely on docking to assemble its modular components in orbit.
- Lunar Missions: Chandrayaan-4, India’s planned lunar sample-return mission, will require docking capabilities to transfer collected samples back to Earth.
- Human Spaceflight: Future manned missions, including those to the Moon by 2040, will depend on docking technology for crew and equipment transfers.
Details of the Docking Experiment
ISRO used two 220-kg satellites, SDX01 (“Chaser”) and SDX02 (“Target”), for the experiment. The process involved:
- Sequentially bringing the satellites closer, holding positions at key distances (5 km, 500 m, 3 m, etc.).
- Successfully joining and locking the satellites in orbit.
- Demonstrating combined control and functionality of the satellites as a composite unit.
Future steps include sharing electrical power between the satellites and demonstrating “undocking,” where the satellites separate and drift apart.
Challenges Overcome During the Mission
- The docking faced delays due to unexpected drifts and inaccuracies during initial attempts.
- ISRO refined simulations and conducted additional maneuvers to achieve the precise alignment needed for successful docking.
- This iterative process highlights ISRO’s growing expertise in handling complex space operations.
Key Technologies and Innovations
- Sensors: Advanced sensors like Laser Range Finder and Proximity and Docking Sensor were used for precise measurements.
- Navigation: A new processor based on satellite navigation determined the relative positions and velocities of the spacecraft.
- Simplified Mechanism: The androgynous docking system used only two motors, compared to the 24 used in international standards, demonstrating innovation and efficiency.
Future Implications
This mission is a precursor to India’s broader space ambitions:
- Space Station: The Bharatiya Antariksh Station will use this technology for modular assembly.
- Lunar Exploration: Docking will be central to sample-return missions and potential human expeditions to the Moon.
- Autonomy: Developing autonomous docking systems will reduce dependency on navigation data, enhancing efficiency for future missions.
Conclusion
- The SpaDeX docking mission underscores India’s growing technological prowess in space exploration.
- It is a critical step toward ISRO’s ambitious goals of establishing a space station, conducting lunar sample-return missions, and enabling human exploration of the Moon, marking India’s ascent as a significant player in global space endeavors.
| PYQ: Consider the following statements: (2016)The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after USA made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit the Mars in its very first attempt
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only Ans: (c) |
4. Alcohol
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

Alcohol as a Leading Cause of Cancer
- According to the US Surgeon General’s latest report, alcohol is the third leading preventable cause of cancer in the United States, following tobacco and obesity.
- Alcohol use is linked to approximately 100,000 cancer cases and 20,000 related deaths annually.
- The report emphasizes the necessity of labeling alcoholic beverages with cancer risk warnings, akin to cigarette packaging.
Dispelling Myths about Moderate Drinking
- The advisory challenges the belief that moderate alcohol consumption may have health benefits, such as preventing heart attacks or strokes.
- Emerging research indicates that even light drinking—one drink per day or less—raises the risk of cancers such as breast, mouth, and throat cancers.
Mechanisms Linking Alcohol to Cancer
- DNA Damage
Alcohol metabolism produces acetaldehyde, a compound that damages DNA and impairs cellular repair mechanisms, increasing the likelihood of mutations and tumor formation. - Oxidation and Inflammation
During alcohol metabolism, oxidation generates unstable molecules, leading to cellular damage and inflammation, which are known contributors to cancer. - Synergy with Tobacco
Alcohol dissolves tobacco carcinogens, facilitating their absorption and amplifying cancer risks in alcohol-tobacco users. - Hormonal Effects
Alcohol raises levels of hormones like estrogen, heightening the risk of hormone-sensitive cancers such as breast and ovarian cancers.
Types of Cancers Linked to Alcohol Use
The report identifies several cancers linked to alcohol consumption:
- High-Risk Cancers: Breast, mouth, throat, esophagus, and liver cancers.
- Moderate Risk Cancers: Colon, rectum, and larynx cancers.
Even minimal alcohol intake (one drink daily) significantly increases the risk of these cancers.
Alcohol’s Impact on Protective Mechanisms
- Alcohol irritates and damages the mucosal lining, a crucial protective barrier in the mouth, nose, lungs, and stomach.
- This damage allows carcinogens to interact more directly with vulnerable cells, escalating cancer risk.
5. Air India Introduces In-Flight Wi-Fi
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
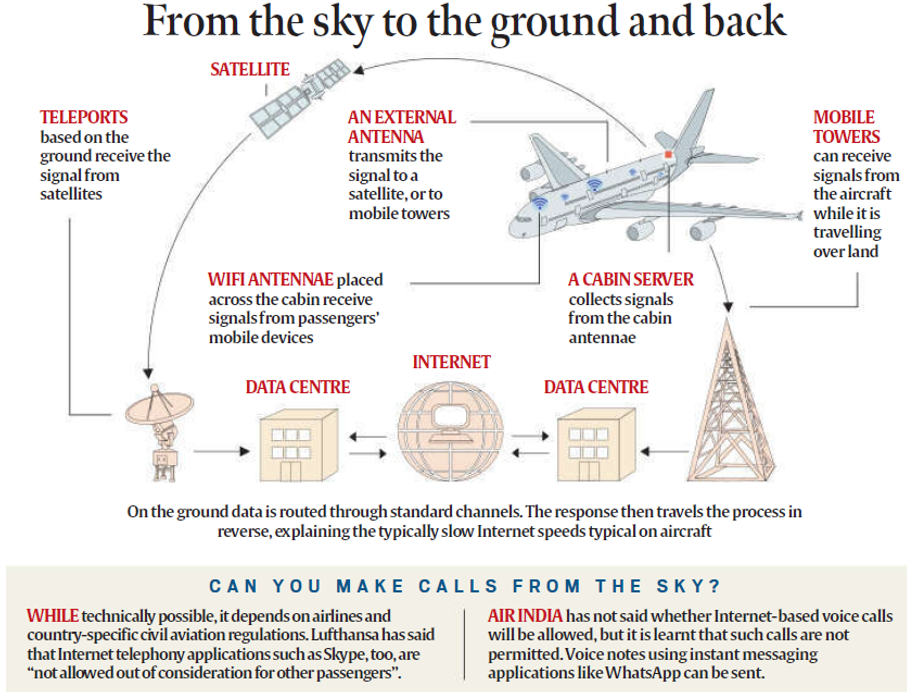
Technologies Behind In-Flight Connectivity
In-flight Internet relies on two main technologies:
- Air-to-Ground (ATG): Uses cellular towers on the ground to transmit signals, effective over land but limited over large water bodies or remote areas.
- Satellite-Based: Transmits signals via satellites, offering broader coverage and reliability, especially over remote regions or oceans.
Both systems require specialized antennae and equipment, with satellite-based connectivity being the preferred choice for global coverage.
Cost Implications
- Installing Wi-Fi equipment is a significant expense for airlines, especially when retrofitting older planes.
- While Air India is currently offering free Wi-Fi, this may change as airlines globally often charge for such services or provide them as perks for premium passengers.
- For Air India, the service could eventually become a source of ancillary revenue.
Future Prospects
- As demand for in-flight connectivity grows, Air India’s initiative marks a step toward modernizing its fleet and improving passenger satisfaction.
- However, challenges such as high costs, slower speeds compared to ground networks, and potential pricing strategies remain critical considerations for long-term implementation.
6. Mystery of Gene Creation
| Context |
|
How Genes Are Made: New Research Insights
Gene Duplication
- Gene duplication is a key process in creating new genes.
- When a gene is duplicated, one copy keeps its original function, while the other is free to mutate and develop new functions.
- Researchers discovered that duplicated genes have more methylated DNA, which helps prevent the overproduction of proteins.
Methylation and Mutation
- Methylation refers to the addition of a methyl group to a DNA molecule, affecting its function.
- Methylated genes tend to mutate more, which helps generate diversity in genetic functions.
Exogenous DNA and Random Sequences
- Researchers inserted random DNA sequences into human cells to observe their effects.
- Some of these random sequences helped cells grow, acting like early-stage genes that could evolve.
Retaining Useful Genes
- For a gene to stay in the genome, it must be useful or allow the organism to survive.
- Non-essential genes, like those for blood types, may not have a clear function but are retained due to evolution.
Conclusion
- These findings show how new genes emerge through duplication, mutations, and the survival of useful genetic changes over time.
7. Discovery of semi-Dirac fermions
| Context |
|
| Understanding Subatomic Particles |
|
Types of Fermions
- Fermions are classified into Dirac fermions and Majorana fermions.
- Dirac fermions may or may not have mass and are different from their antiparticles.
- Majorana fermions are their own antiparticles, with neutrinos suspected to belong to this category.
Challenges in Particle Physics
- Physicists face challenges in identifying missing particles, such as those responsible for gravity.
- Some particles, like Higgs bosons and neutrinos, are heavier than expected.
- Dark matter remains a mystery, as its presence has not been directly detected.
- The Standard Model (SM) organizes known particles but has gaps that need filling.
Discovery of Semi-Dirac Fermions
- Semi-Dirac fermions are unique particles with mass in one direction but not in another.
- They were discovered in zirconium silicon sulphide (ZrSiS), a crystalline material.
- These particles behave as fermions under specific electric and magnetic forces.
Role of Condensed Matter Physics
-
- Condensed matter physics allows the discovery of exotic particles in smaller, controlled experiments.
- Materials like graphene and ZrSiS act as hosts for particles like semi-Dirac fermions.
- This field provides valuable insights without requiring massive particle colliders.
Future Research and Implications
- Researchers aim to explore ZrSiS further to understand its unusual properties.
- Each discovery helps expand the “particle zoo” and reveals new aspects of the universe.
- Understanding these particles brings physicists closer to uncovering the fundamental laws of nature.
8. DRDO conducts scramjet engine ground test
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

Hypersonic Missiles: Capabilities and Global Context
- Hypersonic missiles, traveling at speeds greater than Mach 5, offer unparalleled advantages in speed, precision, and ability to evade existing air defense systems.
- Nations like the US, Russia, China, and India are actively pursuing hypersonic technology, recognizing its strategic and tactical importance for modern warfare.
- These advanced weapons promise rapid, high-impact strikes that can redefine future combat scenarios.
Scramjet Engine: The Core of Hypersonic Systems
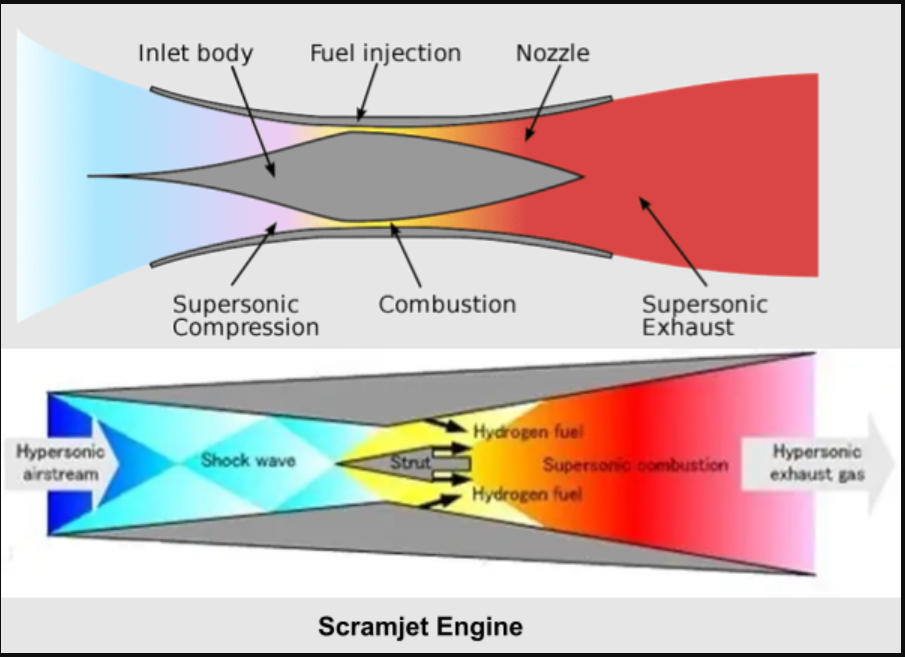
A scramjet engine is an upgraded variant of a ramjet where combustion occurs due to supersonic airflow.
- This supersonic flow allows the jets to achieve even faster speeds than the standard ramjets.
- This engine does not need to slow the incoming air for combustion like a typical turbojet or even ramjet.
- It carries liquid Hydrogen as fuel and liquid Oxygen for combustion (oxidiser) to generate thrust.
- The fuel efficiency of the scramjets tends to be significantly better than that of traditional turbojets and ramjets.
- It makes them ideal for various high-speed applications.
- Due to the complexities of maintaining the supersonic airflow, scramjets are often more expensive and difficult to manage than other engines.
- They operate more efficiently at very high speeds (Mach 12 to 24).
- Just like the Ramjet engines, they also have no moving parts.
- DRDO’s scramjet combustor test showcased critical achievements such as successful ignition, stable combustion, and innovative flame stabilization, described as akin to “keeping a candle lit in a hurricane.”
Key Technological Breakthroughs
- Indigenous Scramjet Fuel: DRDO, in collaboration with industry partners, developed India’s first endothermic scramjet fuel, ensuring efficient cooling and ignition at hypersonic speeds.
- Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC): A novel ceramic TBC capable of withstanding extreme temperatures beyond the melting point of steel was developed, enhancing engine durability and performance.
- Advanced Computational Tools: Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations were instrumental in optimizing engine design and predicting performance.
Previous Milestones in Hypersonic Technology
- India has consistently advanced hypersonic technology, exemplified by the successful flight test of the Hypersonic Technology Demonstrator Vehicle (HSTDV) in September 2020.
- This test validated key technologies like aerodynamic heat shielding, hypersonic combustion, and sustained flight at Mach speeds for over 20 seconds.
Strategic Implications
- With demonstrated capabilities in scramjet engines, advanced thermal management, and indigenous fuel development, India is poised to operationalize hypersonic missiles.
- These weapons enhance the nation’s defense capabilities, ensuring strategic parity with global powers.
9. Indian cryptography research gears up to face the quantum challenge
| Context |
|
Introduction to Cryptography
- Cryptography is a technique used to secure information by converting plain text into unreadable ciphertext.
- Its main goal is to ensure system security and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- The practice of sending secret messages has existed since ancient times, with notable historical examples such as Julius Caesar’s cipher and the Enigma system used during World War II.
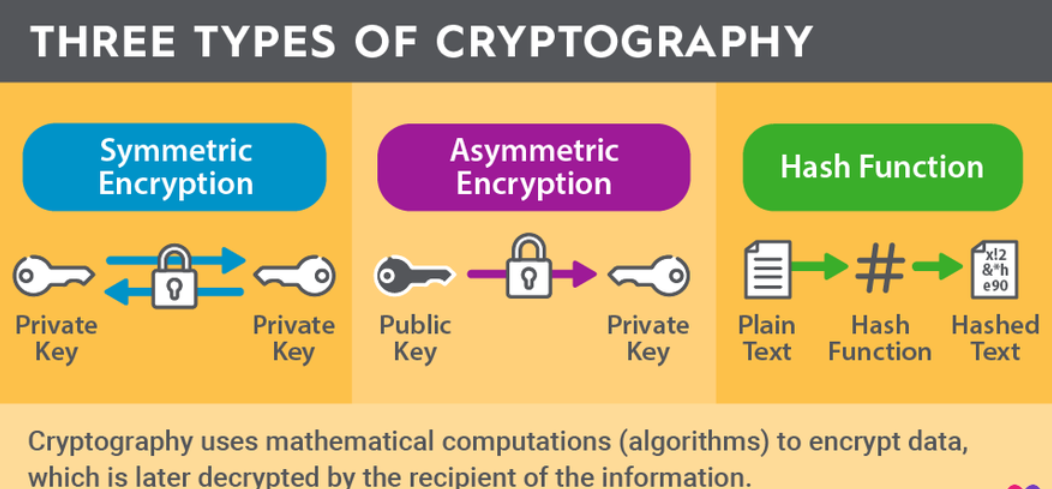
The Importance of Cryptography
|
Challenges and Slow Progress
- Cryptography is a slow-moving field due to its complexity and the close connection between complexity theory and cryptography.
- Research in India focuses on areas like communication complexity, proof complexity, and algebraic coding theory, aiming to enhance security.
Cryptography Keys and Their Function
- The core of cryptosystems is the key, which is a secret value used for encrypting or decrypting data.
- Modern systems, like public-key cryptography, use two keys: a public one shared with the sender and a private one kept by the receiver.
- One-way functions are used to make encryption easy but decryption very difficult without the key.
Emerging Research and Challenges
- Two disruptive research areas in cryptography are homomorphic encryption, which allows computations on encrypted data, and quantum-resistant cryptography, which ensures systems can withstand quantum computing threats.
- Indian researchers are making progress in these areas, and the government is funding cryptography research, including the National Quantum Mission and quantum communication developments.
Future of Cryptography in India
- India is advancing in cryptography research, particularly in quantum communication and data security, with government support and collaboration from various institutions.
- The importance of encryption will grow as sensitive data continues to increase, especially in cloud storage.
10. China’s Fusion Breakthrough
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
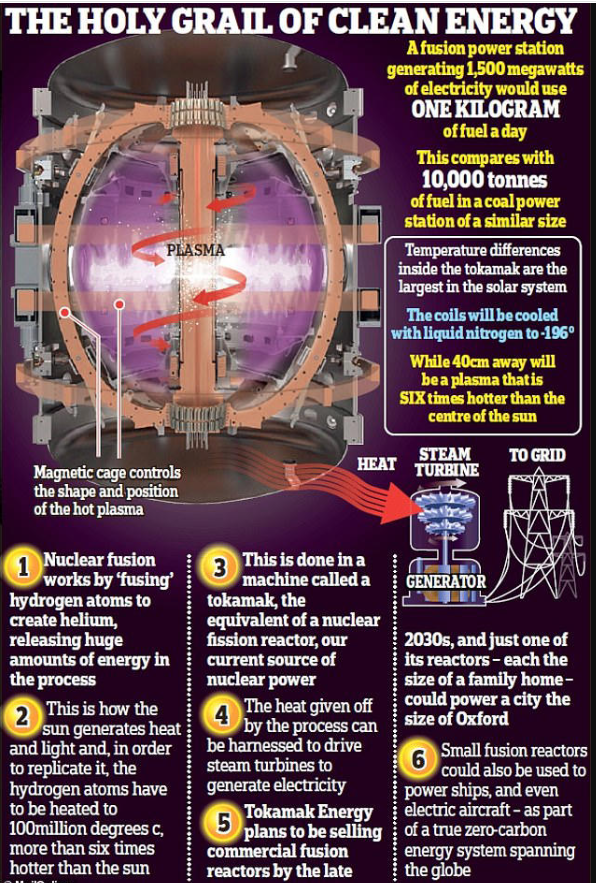
Tokamak
- The tokamak is an experimental machine designed to harness the energy of fusion.
- Inside a tokamak, the energy produced through the fusion of atoms is absorbed as heat in the walls of the vessel.
- Like a conventional power plant, a fusion power plant uses this heat to produce steam and then electricity by way of turbines and generators.
Breakthrough in Fusion Technology
- China’s Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) reactor achieved a significant milestone by maintaining plasma confinement for over 1,000 seconds, surpassing its previous record of 400 seconds.
- While the reactor did not produce electricity or achieve fusion, this steady-state plasma confinement is a critical step toward realizing fusion energy.
- Fusion, the process powering stars, requires extreme temperatures (millions of degrees Celsius) to create plasma, which must be contained using strong magnetic fields.
- The EAST reactor’s success demonstrates progress in managing this delicate process, though commercial reactors will need to sustain these conditions for hours or days.
Fusion Energy: Potential and Challenges
- Fusion energy promises a revolutionary solution to global energy and climate crises.
- It produces vast amounts of energy with minimal environmental impact—no greenhouse gas emissions or long-lived nuclear waste.
- Fusion uses abundant fuels like deuterium and tritium, making it a sustainable option.
- However, despite over 70 years of research, practical fusion reactors remain elusive.
- Optimistic projections suggest commercial viability by 2050, but current energy transition plans do not yet account for fusion due to its developmental uncertainties.
Recent Global Advancements
- Recent breakthroughs have reignited optimism. In 2021, the UK’s JET laboratory produced 12 MW of fusion energy for five seconds.
- In 2022, a US reactor achieved a net energy gain, a critical milestone. Innovations like MIT’s new materials for reactor durability and China’s laser-ignited fusion research further highlight progress.
- Private investment in fusion has surged, with $6.2 billion raised in 2023 alone.
- Companies like Helion and Commonwealth Fusion Systems aim to deliver commercial fusion power by the late 2020s and early 2030s.
ITER: A Global Collaboration
- The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), under construction in France, represents the largest fusion project, involving over 30 countries, including India.
- Slated to begin deuterium-tritium reactions by 2039, ITER aims to produce 500 MW of fusion power.
- While it won’t generate electricity, its success could catalyze the development of commercial fusion reactors.
- Experts believe a 15-year timeline for commercial fusion energy, though ambitious, is achievable.
Conclusion
- China’s EAST reactor breakthrough underscores the growing momentum in fusion research.
- While challenges remain, advancements in plasma confinement, energy output, and international collaboration are bringing the dream of clean, limitless fusion energy closer to reality.
- Fusion’s potential to transform global energy systems and combat climate change makes it a critical area of scientific and technological investment.
11. Willow
| Context |
|
What is Willow?

- Willow is a quantum processor developed by Google.
- It has 105 physical qubits, which are used to store and process information.
- Willow operates at extremely low temperatures, close to absolute zero (-273°C).
- The processor uses both data qubits and measurement qubits to handle errors.
- Quantum computers like Willow work differently from classical computers by using qubits, which can represent both 0 and 1 at the same time (superposition).
- Willow uses error-correction methods, making it faster and more reliable than other quantum computers.
- It completed a difficult task, random circuit sampling, in minutes, which would take classical computers millions of years.
- Willow shows promise for solving complex problems in areas like drug design, climate science, and optimization.
12. U.S., Japan moon landers launch on single rocket
| Context |
|
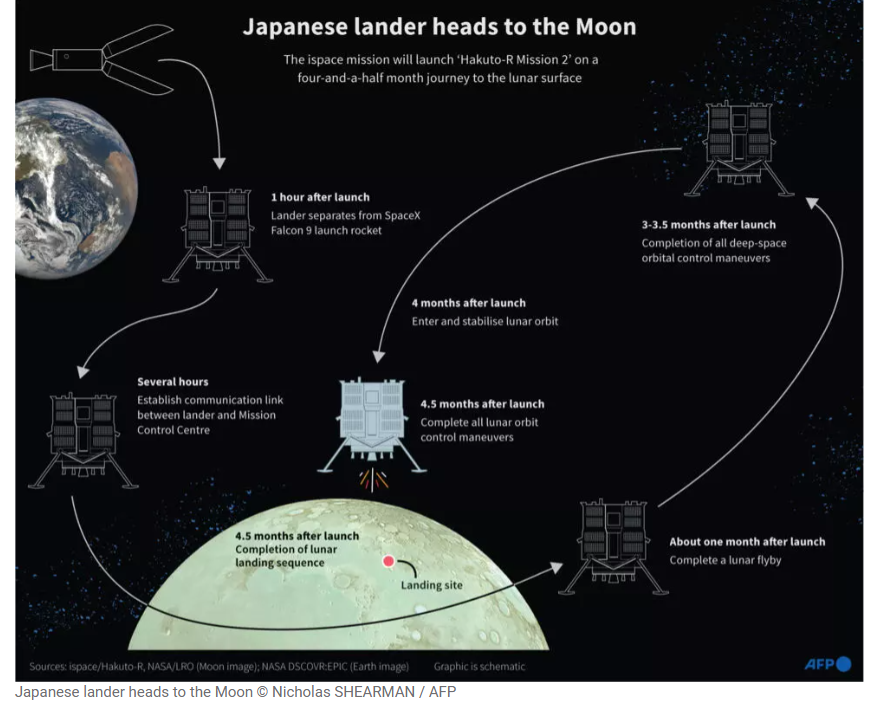
Mission Objectives
- The goal is to achieve soft landings on the moon, building on the success of Intuitive Machines, the first company to land successfully on the moon in 2022.
- The mission is part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program, which aims to reduce costs and promote a lunar economy by partnering with private companies.
Details of the Landers
Blue Ghost:
- Launched first, will take 45 days to reach the moon.
- It will land near Mons Latreille, a volcanic feature on the moon’s northeast side.
- Carries 10 NASA instruments for scientific research, including studying lunar dust, magnetosphere, and the moon’s interior.
Resilience:
- Will take 4-5 months to reach the moon’s Mare Frigoris, located on the far north side.
- It carries a micro rover, ‘Tenacious’, designed to scoop moon dust and send back images.
Challenges
- Both landers must navigate difficult terrain with craters and boulders, relying on thrusters for a soft landing due to the lack of an atmosphere.
13. 10 payloads of ISRO’s POEM-4 module deployed successfully
- IN-SPACe facilitated the operationalisation of 10 payloads on the POEM-4 module of the PSLV-C60/SpaDeX mission for non-government entities.
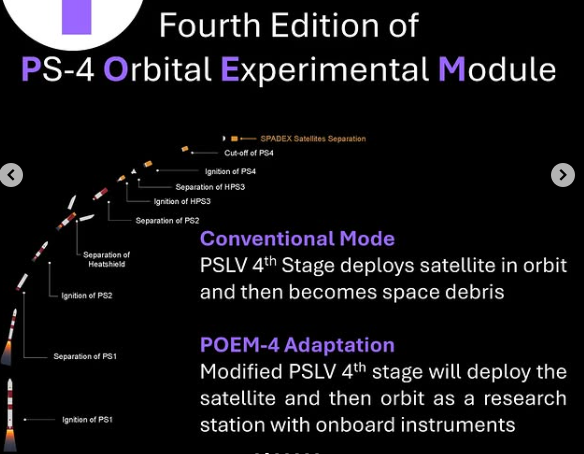
POEM-4 module:
-
- POEM-4 stands for PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-4.
- It is a module used to carry out scientific experiments in space.
- POEM-4 is part of the PSLV-C60/SpaDeX mission, launched by ISRO.
- The module is a repurposed PS4 stage (a part of the PSLV rocket), which is used to deploy payloads in space.
- It operates at an altitude of 350 km with a 55-degree inclination.
- POEM-4 allows non-government entities (NGEs) like start-ups, academic institutions, and research organizations to test space technologies without needing to launch entire satellites.
- It helps reduce entry barriers for these entities to engage in space activities.
- A total of 10 hosted payloads were successfully established and operationalised by IN-SPACe on the POEM-4 module.
| IN-SPACe |
|
14. India’s weatherman to turn 150 on Jan. 15
| Context |
|
India Meteorological Department (IMD)
-
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) was established in 1875 and is one of the earliest government departments in India for systematic weather observation and forecasting.
- Headquarters: New Delhi.
- The IMD has contributed significantly to weather prediction and climate services for over 150 years, with its foundation laid through early meteorological observatories in the country.
- The first Meteorological and Astronomical Observatory was set up in Madras in 1793, marking the beginning of instrumental meteorology in India.
- IMD’s major breakthroughs include:
-
- Preparation of the first weather chart (1877) and Daily Weather Report (1878).
- Establishment of climatology based on long-term data and the commencement of radar services (1947-1959).
- The global satellite era (1960-1970) and modernisation (2006-2013), improving forecasting accuracy by 40-50%.
- IMD is equipped with over 4,000 scientific personnel, advanced meteorological instruments, and modern forecasting and warning systems.
- It provides services across sectors like aviation, shipping, agriculture, flood management, and fisheries.
15. What is the human meta- pneumovirus?
| Context |
|
What is Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)?
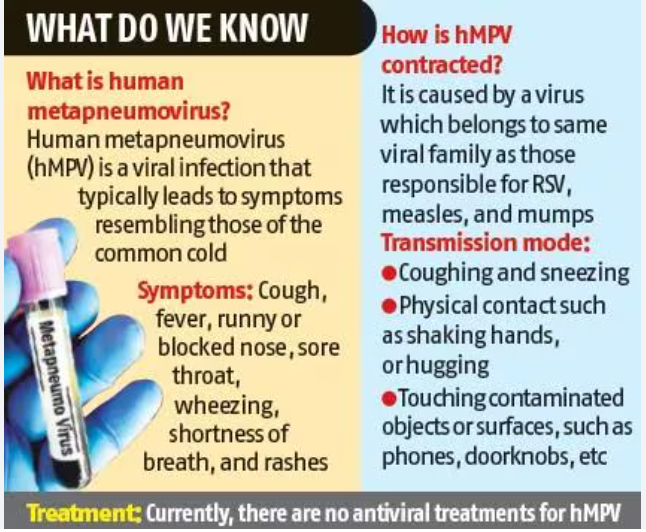
- Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a respiratory virus that causes mild cold-like symptoms, such as cough, fever, sore throat, and runny nose.
- It was identified in 2001 and belongs to the Pneumoviridae family, which includes respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
- The virus can lead to upper and lower respiratory tract infections, particularly in children, the elderly, and those with weak immune systems.
- While most cases resolve with rest, complications like bronchitis or pneumonia may require medical care.
Spread and Treatment of HMPV
- HMPV spreads through respiratory droplets and contact with contaminated surfaces.
- There is no vaccine or specific antiviral treatment; supportive care is used for symptom relief.
- Preventive measures include handwashing, avoiding close contact, and wearing masks.
India’s Response
- The National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) is monitoring respiratory infections, including HMPV cases in Karnataka, Gujarat, and Chennai.
- Union Health Minister J.P. Nadda reassured that HMPV is not a new virus and there is no cause for concern.
16. Injectable hydrogel for cancer treatment
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The hydrogel is designed to deliver anti-cancer drugs directly to the tumor site, reducing the systemic side effects commonly associated with chemotherapy.
- It is composed of ultra-short peptides that remain insoluble in biological fluids, ensuring the hydrogel stays localized at the injection site.
- The hydrogel responds to elevated levels of glutathione (GSH), a molecule found in high concentrations in tumors.
- It releases the drugs in a controlled manner, targeting the tumor while sparing healthy cells from damage.
- This innovation is expected to revolutionize breast cancer therapy by offering more precise treatment.
- The findings were published in the journal Materials Horizons by the Royal Society of Chemistry.

17. Panama Canal Treaty
| Context |
|
Panama Canal Treaty (Torrijos-Carter Treaties, 1977):
- Signed: September 7, 1977, between the U.S. and Panama.
- Main Provisions:
- Transfer of Control: The U.S. agreed to transfer full control of the Panama Canal to Panama by December 31, 1999.
- Canal Zone: The U.S. relinquished control of the Panama Canal Zone, which had been under U.S. sovereignty since 1903.
- U.S. Rights: The U.S. retained the right to intervene militarily to defend the neutrality of the canal under the Permanent Neutrality Treaty.
- Operation and Management: Panama took full responsibility for operating, managing, and maintaining the canal after the transition.
- Neutrality Clause: The Panama Canal was declared neutral, ensuring access for ships of all nations without discrimination.
- Completion: The transition occurred on December 31, 1999.
18. Role of sun in Spadex success
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
India’s Space Docking Milestone
- India successfully achieved satellite docking for the first time through its Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX), becoming the fourth nation to accomplish this challenging feat after the US, Russia, and China.
- On December 30, ISRO launched two satellites, SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target), into low-Earth orbit.
- The Chaser gradually approached the Target over a series of precision maneuvers before the final docking.
Significance of Docking for Future Missions
- Docking is a critical capability for ambitious space projects like Chandrayaan-4 and the development of the Bharatiya Antariksha Station, where multiple components will need to be docked in space.
- It requires exceptional precision to align and connect docking ports at negligible relative velocity, ensuring no collisions or damage.
Role of Solar Activity
- Favorable solar activity played a pivotal role in SpaDeX’s success. Strong solar flares, coronal mass ejections, or high-speed solar wind streams can disrupt sensors, electronic systems, and communication, making docking extremely challenging.
- However, leading up to the SpaDeX docking, solar conditions were unusually calm despite the ongoing peak phase of Solar Cycle 25, which has generally been characterized by intense solar activity.
Challenges Posed by Space Weather
- Adverse space weather conditions, such as high-energy radiation and magnetic storms, can interfere with mission-critical systems, causing positional errors and communication loss.
- Such disruptions are particularly hazardous during docking maneuvers, which demand high precision.
Need for Space Weather Forecasting
- The SpaDeX success highlights the importance of reliable space weather forecasting. Improved real-time assessments of solar activity can help mitigate risks during critical space operations.
- Investments in space weather monitoring and forecasting are as vital as terrestrial weather forecasts to ensure the safety of infrastructure and mission success during periods of heightened solar activity.
The Sun’s Role in SpaDeX
- Despite the ongoing solar maximum phase, the Sun displayed fewer sunspots and calmer conditions in the days leading to SpaDeX docking, contributing significantly to the mission’s success.
- This underscores the collaborative necessity between precise engineering and favorable space weather for future advancements in space exploration.
19. Twigstats
| Context |
|
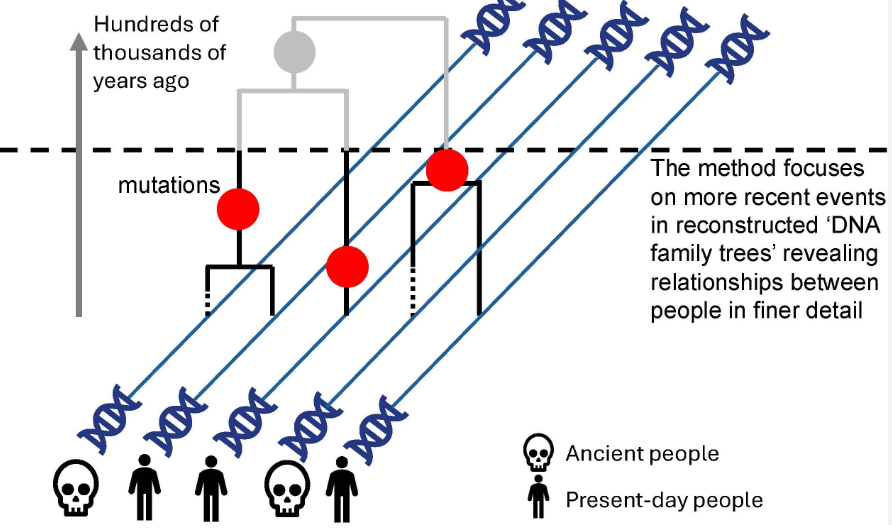
Diagram showing how Twigstats works.
What is Twigstats?
- Twigstats is a new method developed by researchers to study the genetic history of populations.
- It helps scientists trace the ancestry of ancient people and understand how they moved and mixed with other groups.
- This method looks at both shared DNA segments and rare DNA variations to get a clearer picture of population history.
- Twigstats improves the accuracy of genetic studies by reducing errors and increasing the statistical power of existing methods.
- The method can analyze large sets of ancient DNA samples and create detailed maps of population movement and ancestry.
- It has been tested on ancient DNA samples from Europe, especially from the Viking Age, to study migration patterns.
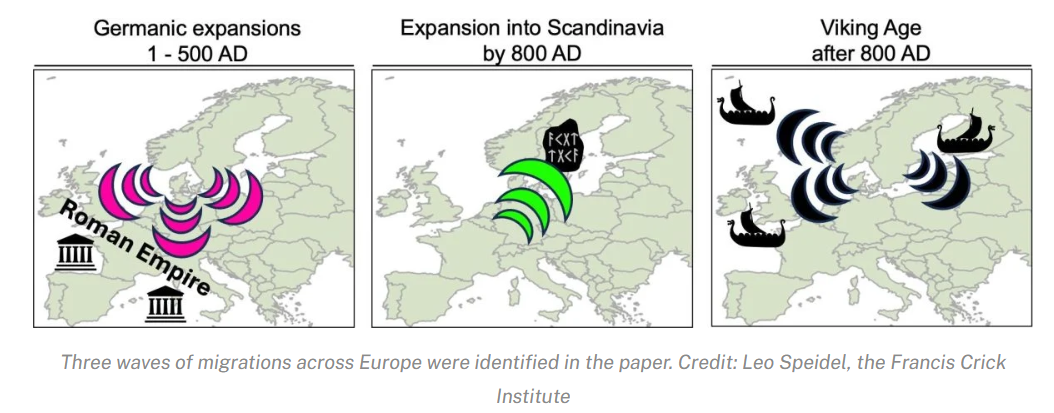
- By using Twigstats, researchers can better understand how cultural and genetic changes happened over time.
- It offers a more precise way to reconstruct the past and track the movement of ancient populations.
20. Dengue Early Warning System
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Key Features of the System
- Climate-Based Predictors:
The system integrates observed climatic variables—temperature, rainfall, and humidity—and analyzes their interactions with dengue transmission at a regional level. - Advance Warning Capability:
The model can predict potential outbreaks with a lead time of over two months, providing a crucial window for health authorities to implement preventive actions.
Research Highlights
- The study, published in Scientific Reports, emphasizes the intricate connections between climate factors and dengue transmission in India.
- Pune, identified as a dengue hotspot, served as a focal region for the research.
The collaborative effort included institutions such as the University of Maryland, University of Pune, and University of Nottingham, along with the Maharashtra and Pune health departments.
Significance of the Study
- Proactive Outbreak Management:
The system offers actionable insights to health authorities, enabling targeted interventions such as vector control and public awareness campaigns. - Understanding Climate-Dengue Links:
By exploring the relationship between monsoon dynamics and dengue, the study highlights the role of changing climatic patterns in influencing disease prevalence.
21. Space telescopes stumble on rule-breaking black hole
| Context |
|
Exceptional Accretion Rate
- LID-568 is a low-mass supermassive black hole that existed 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang, a time when the universe was just 8 years old.
- LID-568’s accretion rate exceeds the Eddington limit by a factor of 40, making it an extreme example of super-Eddington behavior.
| Eddington Limit: |
|
Implications for Black Hole Growth
- This discovery challenges current models of black hole formation.
- It suggests that supermassive black holes could have gained significant mass in shorter periods through rapid feeding, offering an explanation for how they can form quickly in the early universe.
- The findings also indicate that black hole jets and powerful accretion discs might explain this rapid feeding.
Future Research
- Further observations are needed to understand how black holes like LID-568 can exceed the Eddington limit.
- The team plans to study other galaxies with similar black holes to confirm these findings and explore their long-term implications.
22. Use of fingerprints in crimes
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Fingerprint Analysis in Criminal Investigations
- Fingerprints are used either to check an accused’s criminal record or to match prints found at a crime scene.
- Under The Criminal Procedure (Identification) Act, 2022, fingerprints of individuals arrested for crimes with over a one-year sentence can be stored.
- In this case, “chance prints” from the crime scene are being used to confirm the suspect’s presence.
Process of Lifting and Matching Prints
- Fingerprint experts collect prints from surfaces like glass, metal, or plastic.
- The Henry Classification System is used to match fingerprints, requiring a 10-point similarity for a positive identification.
- However, smudged prints lead to inconclusive results.
Importance of a Single Print Match
- Multiple people may leave prints at a crime scene, and not all fingers may leave clear impressions.
- Investigators need just one proper match from any finger of the accused to establish presence at the scene.
23. Paraquat Poisoning
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
What is Paraquat?
- Description: Paraquat, also known as paraquat dichloride or methyl viologen, is a widely used herbicide for weed control and crop desiccation.
- Hazards: The WHO classifies it as a Category 2 (moderately hazardous) chemical. It is banned in over 70 countries, including the EU and China, but remains widely used in India and the US.
- Toxicity: According to the US EPA, even a small accidental sip can be fatal. Some studies suggest a link between paraquat exposure and Parkinson’s Disease.
Modes of Poisoning and Symptoms
Exposure:
- Ingestion: Most common and highly fatal.
- Skin Contact: Prolonged exposure can lead to absorption.
- Inhalation: Can cause respiratory issues.
Symptoms:
- Immediate signs include abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, mouth and throat swelling, and nausea.
- Prolonged exposure can cause kidney, liver, lung, and heart damage, seizures, and respiratory failure.
Treatment for Paraquat Poisoning
Immediate Response:
- Swallowing activated charcoal or Fuller’s earth to bind the chemical.
- Thorough washing of exposed areas with soap and water.
- Cutting and safely disposing of contaminated clothing.
Medical Interventions:
- No specific antidote exists.
- Immunosuppression or charcoal hemoperfusion has been studied as potential treatments.
Regulation and Restrictions
- United States: Paraquat sales are limited to licensed commercial users, with safety measures like blue dye, strong odor, and a vomiting agent added to the chemical.
- India: Governed by the Central Insecticides Board under the Insecticides Act of 1968. A 2021 notification restricts its use to crops like wheat, rice, tea, coffee, and apples, among others. However, enforcement is weak, and untrained applicators often store it unsafely.
24. Indian space programme breaks into 2025 in ‘mission mode’
| Context |
|
PSLV-C60 Mission and SpaDeX Experiment

- On December 30, 2024, the PSLV-C60 mission launched from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), carrying the Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) satellites.
- Two satellites were deployed into a 475-km orbit and began preparations for docking, set for January 7, 2025.
- Initial attempts faced challenges, including unexpected drift between the satellites. ISRO adjusted inter-satellite distances multiple times.
- On January 16, 2025, the two satellites successfully docked, marking India’s first in-orbit rendezvous and docking achievement.
- This milestone is crucial for future lunar and space-station docking operations.
POEM4 Mission
-
- After deploying SpaDeX, PSLV-C60’s fourth stage began the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module (POEM4) phase.
- POEM4 carried 24 payloads, including experiments by ISRO, academia, and private companies.
- The POEM4 mission uses the PSLV’s fourth stage as an experimental platform for scientific payloads.
- It supports research in robotics, propulsion, and plant studies.
| Leadership Transition at ISRO |
|
Leadership Transition at ISRO
- On January 14, 2025, V. Narayanan became ISRO’s new chairman, succeeding S. Somanath.
- Narayanan has expertise in cryogenic and semi-cryogenic engines and led investigations into Chandrayaan-2’s landing failure.
Indian Contributions on SpaceX’s Transporter 12 Mission
- On January 15, 2025, three Indian companies launched payloads aboard SpaceX’s Transporter 12 mission:
- Pixxel Space: Launched three hyperspectral satellites as part of a private constellation.
- Digantara: Deployed a satellite for space situational awareness.
- XDLINX Labs: Deployed a miniaturised communications satellite for Almagest Space Corporation.
Infrastructure and Technological Advances
- The government approved ₹3,984.86 crore for a third launch pad at SDSC, expected by 2029.
- ISRO successfully tested the Vikas engine’s restart capability, essential for atmospheric operations.
- Data from the Aditya-L1 solar mission was released, showcasing India’s advancements in studying the sun.
Conclusion
- These missions advance India’s goals in scientific research, technology development, and future space exploration initiatives.
- Collaborative efforts with private companies highlight the expanding role of India’s private space sector in achieving national objectives.
25. Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

About ADHD
- It is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders of childhood.
- It is usually first diagnosed in childhood and often lasts into adulthood.
- Children with ADHD may have trouble paying attention, controlling impulsive behaviors (may act without thinking about what the result will be), or be overly active.
- Many adults remain undiagnosed, and symptoms can cause difficulty at work, home or relationships.
- Treatments : In most cases, ADHD is best treated with a combination of behavior therapy and medication
- Adderall is the brand name for the formulation that consists of a combination of dextroamphetamine and amphetamine. It is an FDA-approved drug for the treatment of ADHD and narcolepsy, a sleep condition that causes daytime sleepiness.
Study Methodology
- Researchers analyzed primary care data from over 30,000 UK adults diagnosed with ADHD and compared it with more than 300,000 non-ADHD participants matched by age, sex, and healthcare practice.
- Mortality data was used to estimate the death rates across the population lifespan.
Key Findings
The study linked ADHD to reduced life expectancy, though not directly caused by the condition itself. Contributing factors include:
- Health Challenges: Higher prevalence of physical and mental health issues.
- Risky Behaviors: Increased rates of smoking, drinking, binge eating, and risky actions like unsafe driving.
- Suicide Risk: Elevated rates of suicide among people with ADHD.
These findings align with a 2019 study showing children with ADHD had a shorter life expectancy (8.4 years less) when followed into adulthood, due to factors like lower income, poor nutrition, and impulsivity-related risks.
26. Astronomers spot ferocious winds on alien planet
Context
|
Analysis of the news:
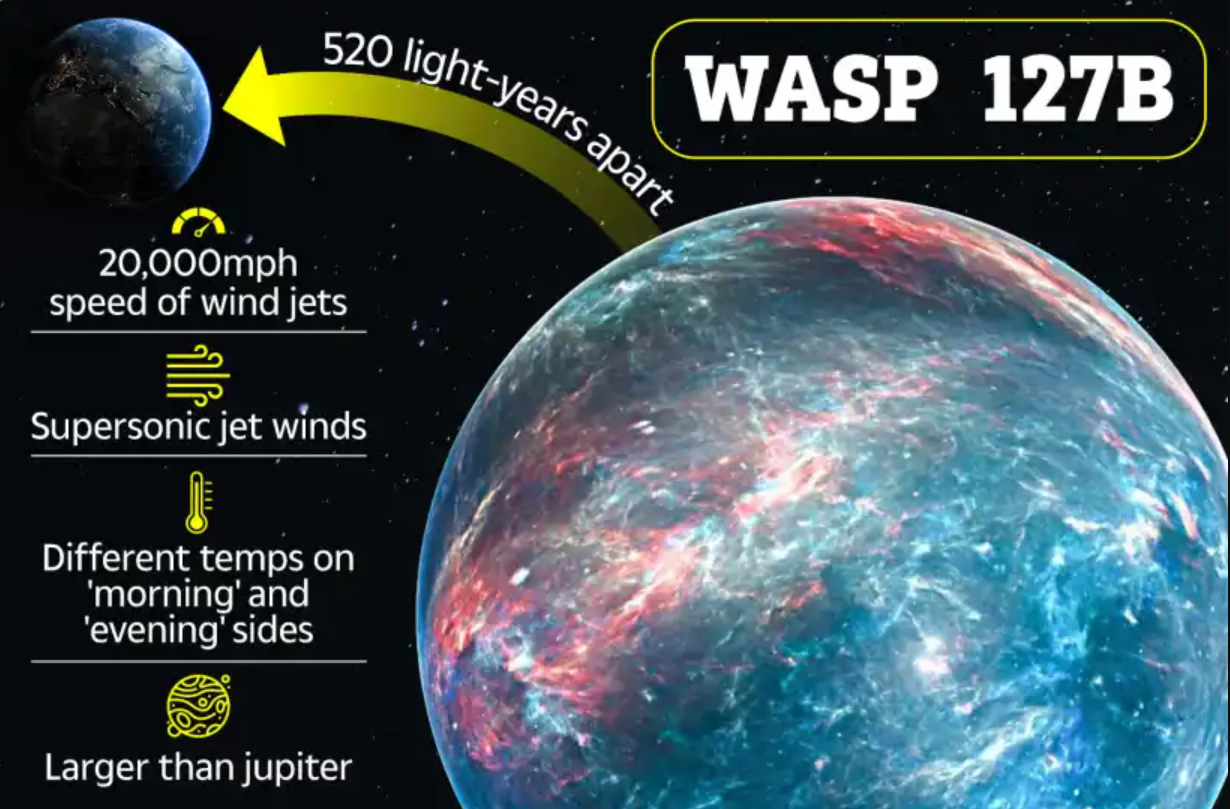
-
- WASP-127b, a gas giant exoplanet, has the fastest jet-stream winds, blowing at 33,000 km per hour.
- It orbits a star similar to our Sun, located 520 light-years from Earth.
- The planet’s diameter is 30% larger than Jupiter, but its mass is only 16% of Jupiter’s.
- WASP-127b is a “hot Jupiter,” with no solid surface, composed mostly of hydrogen and helium.
- Its atmosphere is about 2,060°F (1,400 K), with the day side facing the star constantly, and the night side facing away.
- The intense irradiation from its host star drives the planet’s extreme winds.
- The planet has been studied to understand atmospheric dynamics and wind patterns in exoplanets.
27. Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
What is Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
- GBS is a serious autoimmune disorder that affects the peripheral nervous system. It initially presents weakness, tingling, and numbness in the limbs, which can progress to paralysis lasting 6-12 months or longer.
- The syndrome affects the nerves responsible for muscle movement, pain, temperature, and touch sensations.
- While more common in adults and males, GBS can occur in individuals of all ages.
- Cause: The exact cause of GBS is unknown, but as per the World Health Organisation (WHO), GBS is often preceded by an infection. This could be a bacterial or viral infection. This leads the immune system to attack the body itself.
- In rare cases, vaccinations and surgery may slightly increase the risk of developing GBS, but the likelihood of this happening is very low.
- Studies have shown that the risk of getting GBS from infections like the flu is much higher than the risk from vaccines, such as the flu vaccine.
- Treatment: GBS treatment involves procedures like plasmapheresis, which removes plasma and replaces it with other fluids.
28. Shubhanshu Shukla to pilot Axiom-4 mission
| Context |
|
Axiom-4 Mission:

- Mission Overview: Axiom-4 is a private mission to the International Space Station (ISS) organized by Axiom Space.
- Crew: The mission will include four astronauts, with Indian astronaut Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla serving as the pilot.
- Launch Site: The mission will be launched from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
- Duration: The mission will involve a stay on the ISS for a specified period, allowing crew members to engage in various scientific and research activities.
- Significance: This mission is notable for being the first time an Indian astronaut will travel to the ISS, marking a milestone for India’s space exploration.
- Gaganyaan Connection: Shubhanshu Shukla is also one of the astronaut-designates for India’s Gaganyaan mission.
29. Avian Influenza
| Context |
|

Tracking Bird Flu Variants
- European health agencies are monitoring bird flu virus mutations that may increase the risk of spreading among humans.
- Experts have identified 34 genetic mutations that could raise the possibility of human infections.
- Authorities are using genetic analysis and case studies to assess current risks and provide recommendations.
Menstrual Health Challenges in South Asia
- About 20% of women and girls in South Asia refrain from daily activities during menstruation.
- Teenagers aged 15-19 are the most affected by menstrual restrictions.
- Researchers suggest that menstrual discomfort may contribute to gender inequalities.
- Using hormonal contraceptives has been linked to fewer activity restrictions during menstruation.
Climate Change and Salmonella Outbreaks
- Warmer temperatures, humidity, and longer daylight hours increase the spread of Salmonella bacteria.
- The bacteria cause food poisoning, leading to fever, diarrhoea, and stomach pain.
- The findings emphasize the role of climate in foodborne disease outbreaks and highlight the need for preventive measures.
30. Pralay, India’s first quasi-ballistic missile
| Context |
|
Key Features of the Pralay Missile
- Type: Pralay is a short-range, quasi-ballistic missile developed indigenously by DRDO.
- Purpose: It is the first ballistic missile in India’s arsenal designed for conventional strikes.
- Range: The missile has a strike range of 400 kilometers.
- Deployment: It is intended for use along the Line of Control (LoC) and the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- Development: Trials have been completed, and it has received the Defence Ministry’s Acceptance of Necessity.
- Pralay enhances the arsenal alongside BrahMos and Prahar missiles for stand-off strikes.

31. China’s DeepSeek AI model
| Context |
|
What is DeepSeek?
-
- DeepSeek is a Chinese AI start-up founded in 2023 by Liang Wenfeng, co-founder of the quantitative hedge fund High-Flyer.
- The company has developed cutting-edge AI models, including DeepSeek-R1 and DeepSeek-v3.
- These models are claimed to rival top U.S. AI technologies while being far more affordable.
- DeepSeek’s AI Assistant, powered by DeepSeek-v3, dethroned OpenAI’s ChatGPT as the highest-rated free app on Apple’s App Store.
- The company’s DeepSeek-v3 model was trained with Nvidia’s H800 chips, costing under $6 million, much cheaper than U.S. counterparts.
- DeepSeek’s AI models are reportedly 50 times cheaper to operate than OpenAI’s GPT-4 for specific tasks.
- Despite success, DeepSeek faces scepticism regarding the true cost of development and access to Nvidia chips.
32. ISRO’s 100th launch
| Context |
|

More o the news:
-
- The rocket lifted off from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota at 6.23 a.m.
- The mission placed the NVS-02 satellite into the intended orbit.
- The NVS-02 is part of India’s NavIC system, which provides navigation services to India and surrounding areas.
- NavIC offers two services: Standard Positioning Service (SPS) with 20-meter accuracy and Restricted Service (RS) for secure communications.
- This mission marks a milestone, with ISRO having launched 548 satellites and lifted 120 tonnes of payload.
- The NVS series strengthens India’s satellite navigation capabilities and supports applications like train tracking and vessel navigation.
Environment
1. Tigers on the Move
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Why Tigers Disperse: Natural Behavior and Survival Needs
- Territory and Mating: Male tigers require exclusive territories overlapping with female ranges, leading to dispersal when forests reach carrying capacity or during duels with dominant males.
- Female Behavior: While typically less inclined to wander, tigresses may disperse to protect cubs from threats or establish new territories.
- Relocation Restlessness: Tigers relocated for population management often attempt to return to their original habitats, as seen in Madhya Pradesh and Odisha cases.
Documented Long-Distance Movements
Tiger dispersals have been recorded across the country:
- Examples: A male tiger from Maharashtra traveled 2,000 km across four states, while a tigress walked 340 km to Uttar Pradesh.
- Patterns: Males are more likely to disperse, covering greater distances (up to 650 km), while females tend to explore shorter ranges.
Challenges During Dispersal
- Navigating Non-Forest Landscapes: Tigers traverse fragmented habitats, navigating highways, railways, and human settlements while staying out of sight.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: Movement through populated areas increases risks of conflict, endangering both tigers and local communities.
- Mortality Risks: Dispersals often result in death due to exhaustion, starvation, or accidents.
Ecological Importance of Dispersal
- Gene Flow: Successful dispersals bring genetic diversity, strengthening isolated populations.
- Habitat Identification: Dispersal routes highlight potential for creating protected corridors and revitalizing degraded landscapes.
2. Surpassing 1.5°C
| Context |
|
Humanity’s Shift Towards Climate Crisis
- 2024 marked the first year when the global mean temperature exceeded 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, as reported by the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S).
- This is a significant milestone in global warming, aligning with concerns raised at global climate conferences where leaders aim to limit warming to below 2°C, ideally staying under 1.5°C.
Annual Climate Conference Goals
- The primary objective of annual climate conferences is to establish global agreements to reduce carbon emissions and slow temperature increases.
- The ultimate goal is to prevent global temperatures from exceeding 2°C above pre-industrial levels, with the ideal target of limiting the rise to below 1.5°C to mitigate the most severe climate impacts.
Temperature Thresholds and Significance of 2024
- While surpassing the 1.5°C threshold in a single year does not signal an immediate climate catastrophe, experts warn that continued warming over a decade or more could result in permanent changes.
- The year 2024 is seen as a critical turning point. With rising carbon emissions, experts predict that global temperatures may surpass the 2°C mark by 2050, leading to devastating consequences.
| Record-Breaking Global Temperatures in 2024 |
Sea Surface Temperature and El Niño
|
Implications of Record Temperatures
- Exceeding 1.5°C in 2024 signifies the world is perilously close to irreversible climate impacts.
- While a single year above this threshold is not conclusive, it underscores the urgency for swift and meaningful emissions reductions to avoid exacerbating the harm to ecosystems and human populations.
Concerns Over Financial Support and Climate Disasters
- The rising temperatures have serious consequences for developing economies, which are already grappling with frequent climate disasters.
- The failure of climate talks in Baku, Azerbaijan, to agree on a financial package for carbon emission mitigation worsens concerns, as developing countries now face more financial strain in addressing climate impacts.
- This failure delays action on carbon markets, threatening to undermine efforts for sustainable development in these vulnerable regions.
| PYQ: Discuss global warming and mention its effects on the global climate. Explain the control measures to bring down the level of greenhouse gases which cause global warming, in the light of the Kyoto Protocol, 1997. (250 Words /15 marks)(UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2022) |
3. Uttarakhand Launches Winter Char Dham Circuit
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Introduction to Winter Char Dham
- The Uttarakhand government has launched the winter Char Dham circuit to attract pilgrims and tourists during the off-season.
- This initiative focuses on the winter seats of the four sacred Hindu shrines—Gangotri, Yamunotri, Kedarnath, and Badrinath—which shift to lower-altitude temples during the snow-laden months.
- Early figures show moderate success, with 15,314 pilgrims visiting the winter sites by late December.
Economic Significance of Winter Tourism
- Char Dham pilgrimage significantly drives Uttarakhand’s economy, generating over ₹200 crore daily during the peak season.
- The government aims to extend this economic benefit into winter by promoting lesser-known destinations around the winter shrines and capitalizing on the appeal of “sun tourism” during North India’s smoggy winters.
Environmental and Management Concerns
While the initiative has potential economic benefits, environmentalists and activists highlight pressing concerns:
- Overcrowding and Degradation: Increased footfall risks straining fragile mountain ecosystems, degrading infrastructure, and disrupting the sanctity of sacred sites.
- Wildlife Disturbance: Winter tourism may disturb shy and rare species, like snow leopards and mountain sheep, which migrate to lower altitudes for food.
- Safety and Sustainability: The harsh terrain and weather conditions necessitate robust safety measures and sustainable management practices.
Way Forward
To ensure success and sustainability, the state must address environmental concerns by:
- Conducting a comprehensive carrying capacity study.
- Enforcing strict regulations to prevent ecological harm.
- Promoting eco-friendly infrastructure and responsible tourism practices.
Balanced implementation can help Uttarakhand boost its winter tourism while preserving its ecological and cultural heritage.
4. India’s Biennial Update Report (BUR-4)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Overview of the BUR
- The Biennial Update Report (BUR) is a mandate under the UNFCCC for developing countries to detail their climate action efforts.
- Submitted as part of the Paris Agreement, India’s BUR-4, filed in December 2024, includes GHG emissions data, mitigation measures, and financial and technological support received.
Progress on Emissions Reduction
- India reported a 36% reduction in GDP emissions intensity from 2005 to 2020, advancing toward its 2030 target of a 45% reduction.
- Total GHG emissions in 2020 were 2,959 million tonnes of CO2 equivalent, with net emissions at 2,437 million tonnes after accounting for carbon sinks.
- Notably, emissions fell 7.93% compared to 2019 but rose 98.34% since 1994 due to economic growth.
Sectoral Emissions Breakdown
- Energy Sector: Largest contributor at 75.66%, with electricity production alone accounting for 39%.
- Agriculture: Contributed 13.72%, largely from methane emissions.
- Industrial and Waste Sectors: Accounted for 8.06% and 2.56%, respectively.
CO2 emissions dominated (80.53%), followed by methane (13.32%) and nitrous oxide (5.13%).
Achievements on Climate Goals
India’s updated NDCs (2022) aim for 50% non-fossil fuel-based power capacity by 2030 and an additional carbon sink of 2.5-3 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent. BUR-4 highlighted progress:
- Non-fossil fuel-based power capacity reached 46.52% by October 2024.
- 2.29 billion tonnes of additional CO2 equivalent carbon sink created (2005-2021).
- PAT (Perform, Achieve, and Trade) scheme saved 19.3 Mtoe of energy and reduced 28.74 million tonnes of CO2 equivalent (2012-2022).
Technological Needs for Low-Carbon Growth
India underscored the need for advanced technology to support climate adaptation and low-carbon growth. Barriers include slow technology transfer and intellectual property issues.
- Energy Sector: Ultra-efficient photovoltaic cells, floating wind turbines, geothermal technology.
- Industrial Sector: Carbon capture and storage for cement, iron, and steel.
- Water Sector: Solar and wind-powered desalination for arid regions.
Conclusion
- India’s BUR-4 demonstrates steady progress toward its climate goals while highlighting the challenges of balancing economic growth, emissions reduction, and technology adoption.
- The report underscores the importance of global support to overcome barriers and accelerate climate-conscious development.
| What proactive steps India has taken to combat climate change? |
|
5. A.P. set to hold 3-day Flamingo Festival
| Context |
|

About Flamingo:
- Known for their distinctive pink or reddish coloration, flamingos acquire this from the carotenoid pigments in their diet, mainly from algae and small invertebrates.
- Habitat: Found in tropical and subtropical regions, including parts of Africa, Asia, and the Americas, often in shallow saline or alkaline lakes and mudflats.
- Behavior: Flamingos are social birds, known for living in large colonies, sometimes numbering in the thousands.
- Flamingos migrate to India during the winter season, primarily to coastal wetlands and estuaries for feeding and breeding.
- Feeding: They have specialized beaks designed for filter-feeding, allowing them to consume small organisms from water.
- Ecological Significance: Flamingos help in maintaining ecosystem balance by controlling algae and small invertebrate populations.
- IUCN Red List Status:
- Greater Flamingo: Least Concern
- Lesser Flamingo: Near Threatened
6. Water hyacinth threatens the livelihoods of fishers on Kenyan lake
| Context |
|
Water Hyacinth:
- It is an invasive aquatic plant native to the Amazon Basin in South America.
- Characteristics: Floats on water, has large, glossy green leaves, purple flowers.
- Spread: Grows rapidly, forming dense mats that block sunlight, affecting aquatic life.
- Environmental Impact: Reduces oxygen levels, hampers fish populations, and affects water quality.
- Economic Impact: Disrupts water transport, fishing, and agriculture.
- Control Methods: Mechanical removal, biological control (using insects), chemical treatments.

Lake Naivasha
- Lake Naivasha is a popular freshwater lake in Kenya.
- It has been affected by the invasive water hyacinth for over 10 years.
- The hyacinth has reduced fish populations, impacting the livelihoods of fishermen.
- Previously, fishermen caught up to 90 kg of fish daily, but now it’s only 10-15 kg.
- The lake faces economic losses due to the hyacinth invasion, affecting fishing, transport, and tourism sectors.
7. Spike in Olive Ridley  Turtle Deaths
Turtle Deaths
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
What are Olive Ridley Turtles?
- These turtles are carnivores and get their name from their olive-coloured carapace.
- They are best known for their unique mass nesting called Arribada, where thousands of females come together on the same beach to lay eggs.

-
- Habitat:
- They are found in warm waters of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans.
- Odisha’s Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary is known as the world’s largest rookery (a colony of breeding animals) of sea turtles.
- Habitat:
- Protection Status:
-
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule 1
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
Causes of Turtle Deaths
- The deaths are primarily attributed to bycatch from commercial fishing operations.
- Olive ridley turtles, needing to surface for air, asphyxiate when trapped in fishing nets.
- This year, the spike in deaths may be due to an increased presence of fish near turtle gathering areas, attracting more trawlers.
- Post-mortem reports confirmed signs of suffocation, such as lesions on lungs, bulging eyes, and swollen necks.
Need for Mitigation Measures
- Experts emphasize the urgent need to enforce the use of Turtle Excluder Devices (TEDs) in fishing nets to allow turtles to escape.
- A comparative analysis of fish catch trends could also help identify patterns contributing to the deaths.
- Strict monitoring and regulation of fishing activities near nesting sites are essential to protect these vulnerable turtles.
The Nesting Season and Conservation Efforts
- Olive ridley turtles nest along India’s east and west coasts, with mass nesting sites in Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu.
- Females lay 100-110 eggs per nest, which hatch after 45-60 days. To protect eggs from predation and human disturbance, hatcheries are established by Forest Departments.
- Hatchlings are released safely into the sea, ensuring their survival.
Conclusion
- The alarming deaths of olive ridley turtles in Tamil Nadu underscore the need for stringent conservation measures, including enforcement of TEDs, regulation of fishing practices, and increased public awareness.
- Protecting these turtles is vital for maintaining marine biodiversity and ecological balance.
| Operation Olivia |
|
| PYQ: Which one of the following is the national aquatic animal of India? (2015)(a) Saltwater crocodile
(b) Olive ridley turtle (c) Gangetic dolphin (d) Gharial Ans: C |
8. Ultrablack Brazilian Velvet Ants
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

Velvet Ants: Misnamed but Fascinating Wasps
- Velvet ants, despite their name, are not ants but wasps, recognized for their distinctive fluffy appearance.
- Among them, a species native to Brazil’s tropical savannas and dry shrub deserts, Traumatomutilla bifurca, is noted for its striking black-and-white markings.
- Recent research has revealed that the black parts of female velvet ants are ultrablack, absorbing nearly all visible and ultraviolet light.
Ultrablack: A Rare and Remarkable Shade
- Ultrablack pigmentation, achieved through microstructures that trap light, is uncommon in the animal kingdom.
- Unlike regular black caused by melanin, ultrablack exhibits no sheen and serves multiple purposes, such as camouflage, thermoregulation, and mate attraction.
- In velvet ants, the ultrablack is produced by thin, stacked platelets beneath a dense layer of hair, resembling the pages of a book.
Potential Functions of Ultrablack in Velvet Ants
- Although ultrablack might help camouflage velvet ants from predators with ultraviolet vision, its necessity is unclear.
- Velvet ants are already well-protected by their hard exoskeletons, painful stings, and defensive screeches, which deter most predators.
- Interestingly, only female velvet ants exhibit ultrablack pigmentation, a feature whose purpose remains a mystery.
Scientific Significance
- This discovery marks the first instance of ultrablack pigmentation in Hymenoptera, the insect group that includes bees, wasps, and ants.
- It underscores the diversity of color production mechanisms in nature and highlights the potential adaptive significance of ultrablack coloration in the animal kingdom.
Agriculture
1. Only a radical policy shift can lift farmers from widespread distress
| Context |
|
Budget Cuts and Agrarian Distress
- The last Union Budget reduced food subsidy by ₹7,082 crore and fertilizer subsidy by ₹24,894 crore.
- Allocations for agriculture fell from 5.44% in 2019 to 3.15% in 2024, despite 1,00,474 farmer suicides between 2015 and 2022.
- India ranks 105th out of 127 countries on the Global Hunger Index 2024, highlighting severe agrarian distress.
Controversial Farm Policy and Protests
- The draft National Policy Framework on Agricultural Marketing (NPFAM) reintroduces pro-corporate provisions from the repealed farm laws.
- Farmers nationwide are protesting against NPFAM, demanding its withdrawal.
Key Demands for Farmers
- Statutory Minimum Support Price (MSP):
- Farmers demand MSP at C2+50% (1.5 times production cost), as recommended by the Swaminathan Commission.
- Non-implementation of MSP has led to indebtedness, suicides, and distressed land sales.
- Reduction in Production Costs:
- Rising costs of fertilizers, seeds, diesel, and electricity must be reduced.
- The government should regulate corporate input producers and support public sector firms.
- Comprehensive Loan Waiver:
- A one-time loan waiver for farmers and agricultural workers is essential to prevent suicides.
- The government has waived ₹14.46 lakh crore of corporate loans in the last decade.
- Crop Insurance and Climate Change:
- A new, farmer-friendly crop insurance scheme is needed to replace the flawed PMFBY.
- Climate change-induced droughts, floods, and unseasonal rains require robust insurance coverage.
- Investment in Irrigation and Power:
- Public investment in irrigation and power must increase to reduce costs and ensure steady supply.
- Completing stalled irrigation projects can boost yields and employment.
- Expansion of MGNREGA:
- MGNREGA work-days should increase to 200, with wages raised to ₹600.
- The scheme is a lifeline for rural workers and boosts purchasing power.
Funding Solutions
- Impose wealth and inheritance taxes on billionaires, whose numbers doubled from 109 in 2014 to 200 in 2025.
- Restore corporate tax rates to generate ₹1.45 lakh crore annually.
- Increase direct taxes on the rich while reducing indirect taxes and curbing tax evasion.
Conclusion
- Addressing agrarian distress requires MSP implementation, reduced production costs, loan waivers, better insurance, and increased public investment.
- Funding can come from taxing the wealthy and restoring corporate taxes.
Disaster and disaster Management
1. Dam Safety Act, 2021
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
-
- The Supreme Court criticized the Union government for not fully implementing the Dam Safety Act, 2021, nearly five years after its passage.
- The court emphasized that despite the Act being enacted, the National Committee on Dam Safety had not been formed.
- Kerala raised concerns about the safety of the 129-year-old Mullaperiyar dam, requesting a reduction in its permissible water level to prevent potential disasters.
- Section 5 of the Act mandates the formation of the National Committee within 60 days of the Act’s commencement, which has not been done.
- Tamil Nadu informed the court about the establishment of the National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA), but the court questioned the legality of its formation before the National Committee.
| Dam Safety Act, 2021 |
The Dam Safety Act, 2021 is aimed at ensuring the safety of dams in India. Here are some of its key provisions:
The Act also includes provisions for the maintenance and repair of dams, the collection of data on dam safety, and the training of personnel involved in dam operations. |
2. Rat-Hole Mining Issue: Safety and Environmental Challenges
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Coal Mine Tragedy in Assam
- On January 6, several workers were trapped for over 12 hours in a water-flooded coal “rat-hole” mine in Dima Hasao district, Assam.
- The rescue operations, involving the National and State Disaster Relief Forces and the Army, have been progressing slowly due to the challenges posed by the flooded, deep mine.
What is Rat-Hole Mining?
Rat-hole mining is a traditional and hazardous method of coal extraction, prevalent in Northeast India, particularly Meghalaya.
Process:
- Miners dig narrow vertical or horizontal pits, descending using ropes or bamboo ladders.
- Coal is manually extracted using rudimentary tools.
Types:
- Side-Cutting: Narrow tunnels are dug into hill slopes to access thin coal seams.
- Box-Cutting: A vertical pit is dug, leading to horizontal tunnels for coal extraction.
Environmental and Safety Concerns
Rat-hole mining poses severe environmental and safety hazards:
Safety Risks:
- Lack of structural support, ventilation, and safety gear increases risks of accidents, injuries, and fatalities.
- Flooding during rains often leads to worker entrapment and fatalities.
Environmental Impact:
- Causes land degradation, deforestation, and contamination of water sources.
- Polluted water bodies adversely affect local communities and ecosystems.
Legal Status and Ban
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) banned rat-hole mining in 2014 and reaffirmed the ban in 2015.
Reason for Ban:
- Frequent accidents, including fatal flooding incidents, highlighted the unsafe and unregulated nature of these mines.
- Significant environmental degradation prompted regulatory action.
Current Scenario:
- Despite the ban, the practice persists due to economic pressures and lack of alternative livelihoods, particularly in Meghalaya and nearby areas.
Conclusion:
- The recent Assam tragedy underscores the persistent issues associated with rat-hole mining despite legal prohibitions.
- Addressing these concerns requires strict enforcement of the ban, sustainable livelihood alternatives for local populations, and a shift towards safer, regulated mining practices to prevent future disasters.
| What are the Current Laws and Regulations Related to Mining in India? |
|
| PYQ: Coastal sand mining, whether legal or illegal, poses one of the biggest threats to our environment. Analyse the impact of sand mining along the Indian coasts, citing specific examples. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2019) |
3. Mahakumbh Mela 2025 Stampede
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

Causes of Stampedes
- Stampedes are caused by structural weaknesses, poor crowd control, unexpected surges, and inadequate security.
- The NDMA report highlights factors such as excessive crowding beyond capacity, lack of proper barricading, poorly planned entry/exit points, and weak coordination among stakeholders.
- Sudden panic or excitement also accelerates crowd movement, leading to crushing and suffocation.
Role of Crowd Behavior
- Crowd psychology plays a critical role in stampedes. Individuals often follow the actions of others, leading to a chain reaction.
- Poorly managed control measures, such as misdirected police actions, can escalate chaos.
- The NDMA suggests that a community-based crowd management approach is more effective than force-based control.
Lessons from Past Stampedes
- Previous incidents, like the 2003 Nashik Kumbh and the 2005 Kalubai Yatra, reveal common failures: inaccurate crowd estimates, inadequate infrastructure, narrow and unsafe pathways, and lack of coordination among authorities.
- The presence of vendors, poor security, and illegal electrical connections also contributed to disasters.
Strategies for Crowd Control
- Effective crowd management requires a balance between controlling inflow, regulating movement, and ensuring safe dispersal.
- Authorities must assess past crowd patterns, enforce mandatory registrations, and use technology for monitoring.
- Infrastructure improvements like staging points, clear pathways, and public announcements can significantly reduce risks.
Need for Proactive Planning
- The NDMA stresses proactive and holistic planning for religious events. Where infrastructure expansion is not possible, improving waiting areas and regulating entry through online registration can help.
- Comprehensive information dissemination and coordination between stakeholders are crucial in preventing future stampedes.
| What are the Impact of these Stampedes? |
Stampedes at religious gatherings in India have significant impacts on local communities. Mentioned below are some of the major impacts.
|
Internal Security
1. India Bolsters Maritime Strength
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
INS Nilgiri: Versatile Stealth Frigate

- INS Nilgiri, the lead ship of the Project 17A frigates, is designed for multi-mission operations in blue-water environments.
- Equipped with supersonic missiles, advanced air defense systems, and rapid-fire weapons, it excels in anti-surface, anti-air, and anti-submarine warfare.
- Built with an “integrated construction” approach, it reduces build time and enhances efficiency.
- The frigate represents a modern upgrade to the Shivalik-class vessels, with six more ships under Project 17A in various construction stages.
INS Surat: AI-Enabled Stealth Destroyer
- The fourth and final destroyer under Project 15B, INS Surat, is India’s first AI-enabled warship.
- Designed for offensive operations, it features advanced sensors, surface-to-air missiles, and anti-ship weaponry.
- With a displacement of 7,400 tonnes and speeds exceeding 30 knots, it integrates seamlessly into network-centric warfare.
- This destroyer underscores India’s focus on combining cutting-edge technology with indigenous design, ensuring high maneuverability and strike capability.
INS Vaghsheer: Silent and Lethal Submarine

- INS Vaghsheer, the final vessel of the Kalvari-class submarines under Project 75, is a diesel-electric “hunter-killer” submarine.
- Renowned for its stealth and versatility, it is equipped with wire-guided torpedoes, anti-ship missiles, and advanced sonar systems.
- The modular construction facilitates future upgrades, including Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) technology, enhancing underwater endurance.
- Vaghsheer is pivotal for missions like surveillance, intelligence gathering, and special operations.
Strategic Significance of the Additions
- The simultaneous commissioning of a frigate, destroyer, and submarine showcases India’s naval prowess and its commitment to bolstering maritime security.
- These platforms enhance India’s capability to deter regional threats, secure maritime trade routes, and maintain strategic influence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Their indigenous origin aligns with India’s Make in India initiative and reinforces global confidence in India’s defense production capabilities.
Miscellaneous Schemes
1. Genome India Project
| Context |
|
Genome India Project:
- Objective: The Genome India project aims to create a comprehensive database of human genomes from various population groups across India, focusing on disease research and drug therapy development.
- Scope: It includes 10,000 human genomes representing 83 population groups, covering about 2% of India’s 4,600 population groups.
- Database Availability: The database is housed at the Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC) in Faridabad, Haryana, and is accessible to researchers globally.
- Genomic Insights: The project reveals around 27 million low-frequency variants, including 7 million not found in other global databases.
- Precision Medicine: Genome India focuses on enabling targeted clinical interventions for better healthcare and advancing precision medicine.
- Privacy Measures: Data is anonymized with numeric codes, and access requires proposals vetted by an independent panel.
- Future Potential: While it currently covers a small portion of India’s genetic diversity, plans exist to expand it to a million genomes.

2. SVAMITVA Scheme
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
The SVAMITVA Scheme

- The SVAMITVA scheme (Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas) is an initiative launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in 2020.
- It aims to provide a legal property record to rural households, empowering them with property cards for their homes and land.
- The scheme utilizes advanced technologies like drones and GIS-based mapping to survey rural properties, benefiting rural residents by enabling access to financial services, facilitating land taxation, and aiding rural planning.
Benefits of the SVAMITVA Property Cards
- The primary advantage of the property cards is that they provide rural families with a recognized legal document for their property, which they can use to access financial services like loans.
- This has enabled many villagers to start small businesses, securing economic growth.
- Additionally, these cards assist in property tax determination, enhancing financial flows to Gram Panchayats and improving land market liquidity.
- The cards also support rural land record creation, helping in planning, addressing land disputes, and eliminating encroachments.
Implementation Process
- The SVAMITVA scheme is implemented through a multi-stage process that begins with an agreement between the Survey of India (SoI) and state governments.
- Drones and satellite images are employed for accurate mapping of rural properties.
- After the collection of data, a ground verification process ensures the accuracy of the maps.
- The final property cards are issued digitally or physically to property owners.
- The whole process includes community awareness programs, conflict resolution, and detailed mapping of abadi areas (inhabited land).
Progress and Coverage of the Scheme
- The scheme, initially rolled out as a pilot in 2020, has made significant progress.
- As of now, drone surveys have been completed in over 3.17 lakh villages, covering 92% of the targeted villages.
- States such as Haryana, Goa, and Uttarakhand have achieved full saturation.
- The scheme’s reach extends over 67,000 sq.km of rural land, valued at an estimated Rs. 132 lakh crore.
- With the target to cover all 6.62 lakh villages by the end of FY 2023-24, the scheme is steadily advancing towards its goal.
3. National Critical Minerals Mission
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
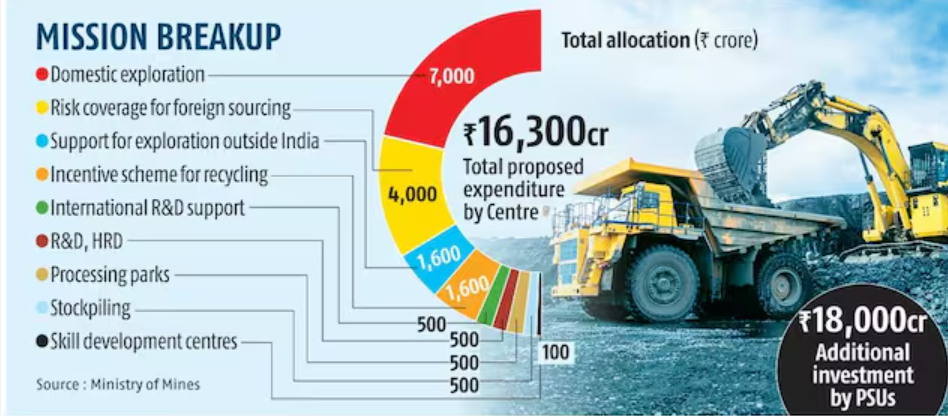
National Critical Minerals Mission (NCMM) Approved
- The mission aims to reduce India’s dependence on imports and secure a stable supply of these essential resources, which are vital for industries like renewable energy, electronics, and defense.

Comprehensive Value Chain Approach
- The NCMM will cover the entire value chain, from exploration and mining to processing and recycling.
- It focuses on intensifying domestic and offshore exploration, streamlining regulatory approvals for mining projects, and offering financial incentives for exploration.
- The mission also emphasizes recovering critical minerals from overburden, tailings, and end-of-life products, promoting sustainable resource utilization.
Global Engagement and Stockpiling
- The mission encourages Indian public and private sector companies to acquire critical mineral assets abroad and strengthen trade ties with resource-rich nations.
- Additionally, it proposes the development of a domestic stockpile of critical minerals to ensure supply security and mitigate global market volatility.
Strategic Importance
- Critical minerals like lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements are essential for clean energy technologies, electric vehicles, and advanced electronics.
- By securing these resources, the NCMM aims to support India’s energy transition, industrial growth, and strategic autonomy.
- The mission aligns with global trends, as countries increasingly focus on securing critical mineral supplies to drive economic and technological advancement.
Reports/indexes
1. Annual Ground Water Quality Report, 2024
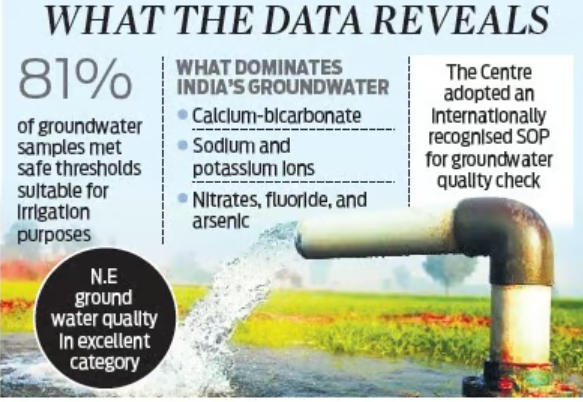
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Key Highlights
- Groundwater Extraction: The report states that the degree of groundwater extraction across India is 60.4%.
- Safe Blocks: Approximately 73% of the analysed blocks fall within the ‘safe’ category, indicating adequate replenishment of groundwater resources.
- Nitrate Pollution: There are 440 districts with excessive nitrates in their groundwater as of 2023.
- Rajasthan (49%), Karnataka (48%), and Tamil Nadu (37%) reported the highest levels of nitrate contamination.
- The report identifies uranium contamination, particularly in Rajasthan and Punjab, where the highest numbers of samples exceeded 100 ppb (parts per billion).
- Fluoride contamination is a major concern in states such as Rajasthan, Haryana, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
Reasons for groundwater contamination
- Excessive Use of Fertilizers: Over-reliance on nitrogen-based synthetic fertilizers in agriculture leads to nitrate leaching into groundwater.
- Industrial Effluents: Discharge of untreated or inadequately treated industrial waste introduces heavy metals and other toxic substances into groundwater.
- Geological formations in some regions release naturally occurring contaminants like arsenic, fluoride, and uranium into groundwater.
- Excessive extraction lowers water tables, concentrating naturally occurring contaminants like arsenic, uranium, and fluoride.
Government Initiatives
- National Aquifer Mapping Programme (NAQUIM) to delineate and characterize the aquifer system in the country.
- National Rural Drinking Water Programme (NRDWP): Addressing contaminants such as fluoride and arsenic through water treatment plants and alternate water supply solutions.
- Jal Kranti Abhiyan, aimed at consolidating water conservation and management initiatives in the country through a holistic and integrated approach involving all stakeholders.
- Atal Bhujal Yojana, was launched to improve groundwater management in priority areas with critical and overexploited blocks.
- Namami Gange Program: Clean and rejuvenate the Ganga River Basin, including the mitigation of groundwater contamination in adjacent regions.
2. QS World Future Skills Index
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
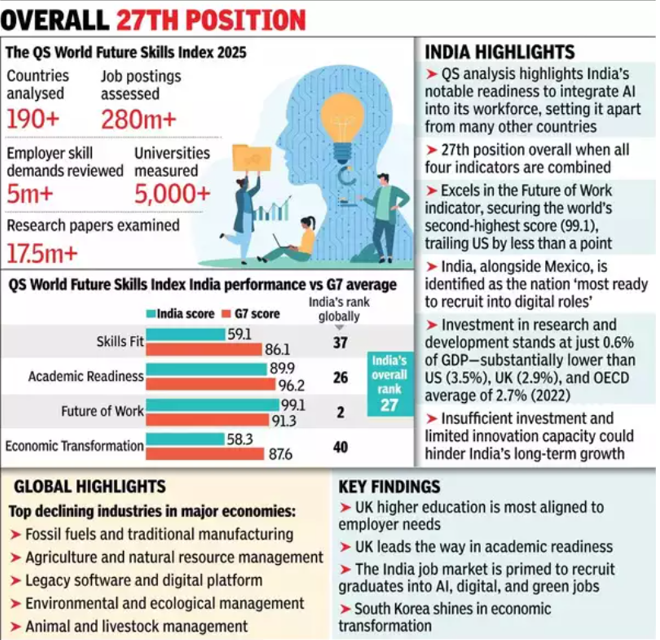
What is the QS World Future Skills Index?
- The QS World Future Skills Index evaluates how well countries are equipped to meet the evolving demands of the international job market.
- It aims to empower governments to align education and skills with future demand, fostering innovation, sustainable global competition and talent development.
India’s Position in the QS World Future Skills Index 2025
- India ranks second globally for preparedness for future job skills, including AI and green competencies, just behind the United States, as per the QS World Future Skills Index 2025.
- This positions India as a “future skills contender,” reflecting its readiness to meet the demands of the rapidly evolving global job market, particularly in digital, AI, and green skills.
- The country’s commitment to technological innovation and youth empowerment is highlighted by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, who acknowledges the role of the government in equipping youth with the necessary skills for economic prosperity.
India’s Strength in ‘Future of Work’ Readiness
- India scored highly, particularly in the ‘future of work’ category, where it ranked second.
- This indicator evaluates a country’s ability to meet the growing demand for digital, AI, and green competencies in job markets, reflecting India’s preparedness for future employment trends.
- The assessment, based on over 280 million job postings worldwide, shows India’s strong positioning in preparing its workforce for technological and sustainable industries, critical for the evolving economic landscape.
Areas of Weakness: Skills Fit and Innovation in Sustainability
- Despite India’s strong showing in future skills preparedness, the country struggles with critical gaps in other areas.
- India’s ‘skills fit’ score was the lowest among the top 30 countries, particularly in adapting its workforce to rapidly changing economic demands.
- This gap underscores challenges in aligning India’s higher education system with evolving industry needs. Moreover, India’s performance in future-oriented innovation in sustainability is concerning.
- Scoring only 15.6 out of 100, India lags behind other nations in fostering innovation for sustainability, an area where improvement is necessary to support long-term economic transformation.
Economic Transformation and the Need for Education Reform
- India’s economic transformation, driven by growth and workforce efficiency, faces challenges in terms of innovation and investment.
- The report suggests that India must invest in aligning its economic momentum with higher education reforms to remain competitive globally.
- To address the skills gap, the report recommends that Indian universities focus on creativity, problem-solving, and entrepreneurial skills within their curricula.
- Stronger collaboration with industries is also essential to ensure that education aligns better with the evolving workforce demands, ensuring a more dynamic and competitive position in the global economy.
Places In news
1. India ‘protests’ new Chinese counties in Ladakh
| Context |
|
Places in Focus
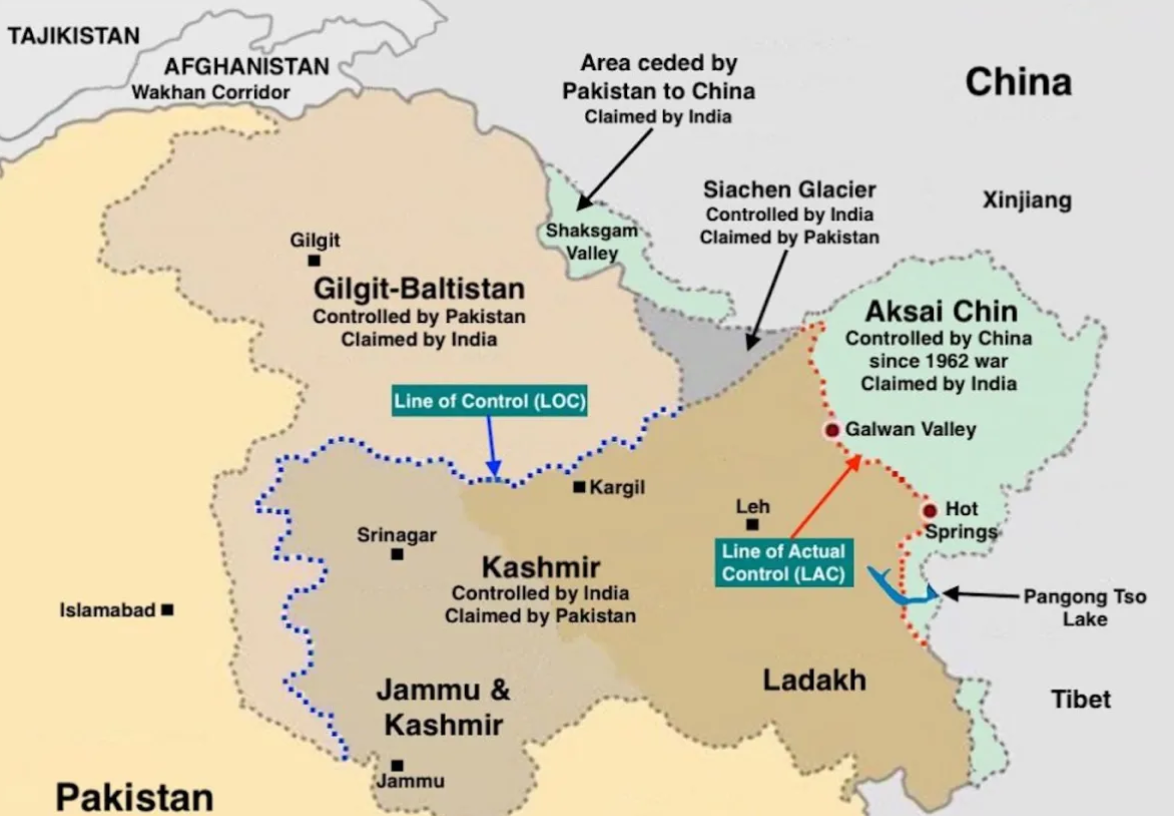
Hotan Prefecture (Xinjiang, China)
- Located in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of China.
- Includes parts of Aksai Chin, a disputed area claimed by India.
- Strategically important due to its location along the ancient Silk Road.
- Known for its jade production and historical significance in trade routes.
Aksai Chin (Ladakh, India)
- A high-altitude plateau in the northeastern part of the Indian Union Territory of Ladakh.
- Administered by China but claimed by India as part of Ladakh.
- A significant flashpoint in India-China territorial disputes, including during the 1962 war.
- Sparsely populated due to its harsh, arid climate.
Yarlung Tsangpo (Tibet, China)
- The upper course of the Brahmaputra River, originating in Tibet.
- Flows through deep gorges in the Himalayas before entering India and Bangladesh.
- Site of China’s proposed $137 billion mega dam project.
- Critical for regional hydrology and ecosystems in downstream areas.
2.Saydnaya prison
| Context |
|
Saydnaya Prison:

- Location: Saydnaya prison is located north of Damascus, Syria.
- Purpose: Originally built in the 1980s to house political prisoners, including Islamist and Kurdish militants.
- Operations: Became a symbol of brutal state control, used for extrajudicial executions, torture, and forced disappearances.
- Human Rights Violations: Reports include mass executions, torture, rape, and enforced disappearances.
- Infamous Incidents: In 2016, the UN commission found crimes against humanity committed at Saydnaya. Amnesty International labeled it a “human slaughterhouse.”
- Crematorium: A crematorium was found to burn the remains of executed prisoners.
- Liberation: In 2024, rebels seized the prison and freed over 4,000 prisoners.
3. Grampians Park Bushfire Alert
| Context |
|

Places in news:
- Grampians National Park is located in the state of Victoria, Australia.
- The park has been affected by bushfires in late December 2024.
- The bushfires were exacerbated by extreme heat conditions in the region.
- Australia’s southeast, including Victoria, experienced a severe heatwave, raising the risk of fires.
- Temperatures in some areas were reported to be up to 14°C above average, intensifying fire hazards.
- Authorities and emergency services are actively working to control the fires and ensure public safety.
4. Ukraine struggles to protect its last coal reserves from Russia’s grasp
| Context |
|
Places in news:
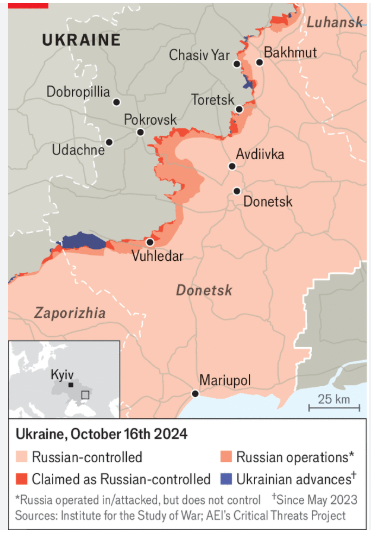
- Pokrovsk: Once a thriving mining hub in Ukraine, Pokrovsk is located above the country’s largest coal reserves. It is now under threat from Russian advances, with its strategic mines vital to Ukraine’s economy. The area has suffered extensive destruction, and its population has dwindled from 82,000 to about 10,000 due to the ongoing war.
- Udachne: A village near Pokrovsk, once home to many miners working in the Pokrovsk Coal mines. With the mines shut down, many workers have relocated, while others remain in limbo in largely deserted areas.
- Donetsk Region: A historically significant industrial area in eastern Ukraine, Donetsk is a focal point of the ongoing conflict. The region, rich in coal mines, is at the center of Russia’s attempts to annex Ukrainian territory. The capture of key mining cities like Pokrovsk would deal a heavy blow to Ukraine’s economy and military.

