Ghurid Dynasty: Time Period, Founder, Rulers & Impact on India
Ghurid Dynasty
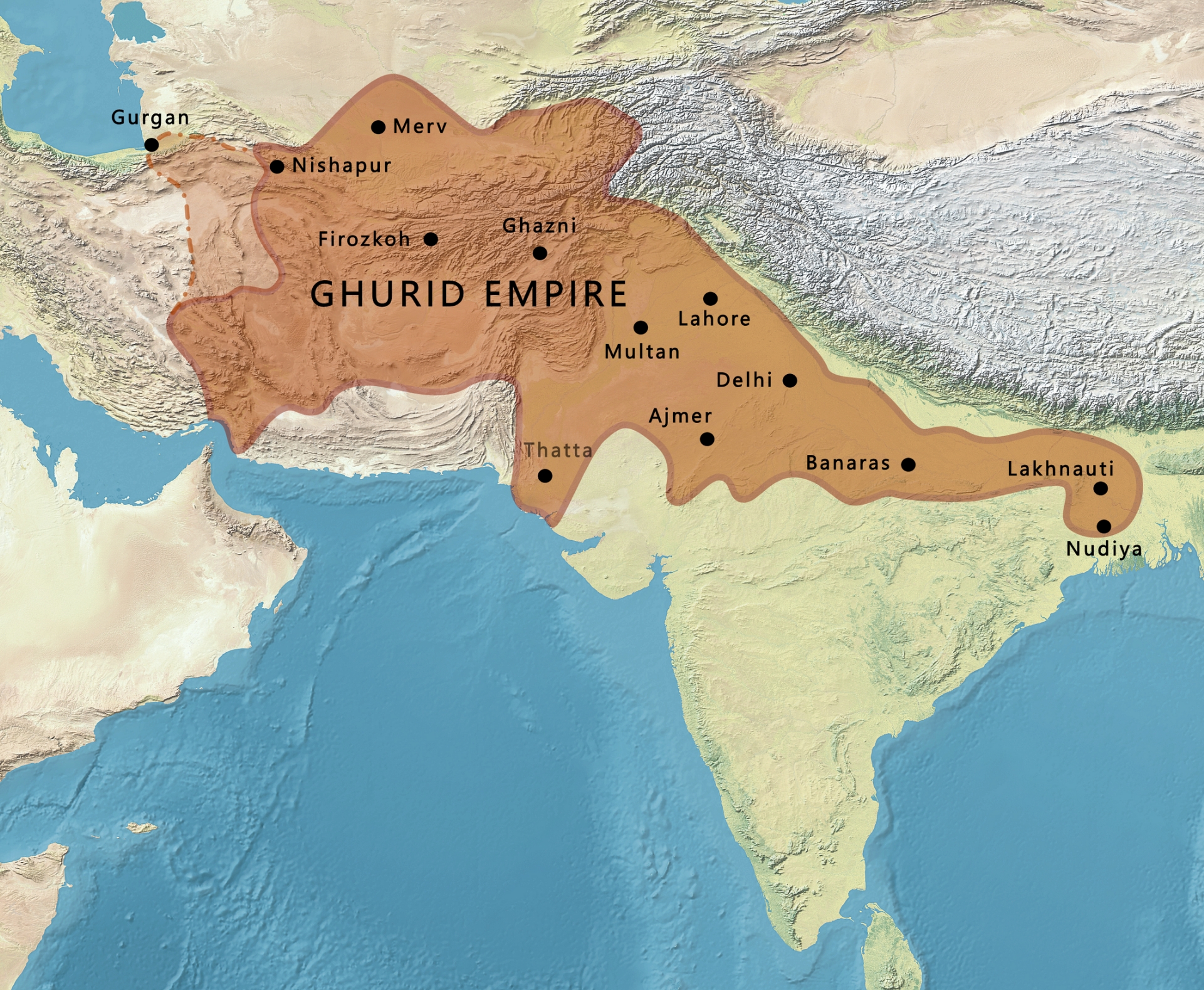
The Ghurid Dynasty, a significant chapter in medieval Islamic history, flourished as a powerful empire in Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent. Let’s delve into the history of its rise, reign, important rulers, and its enduring impact on India.
Introduction to the Ghurid Dynasty
The Ghurids were local chiefs from the Ghor region of central Afghanistan. They were a vassal state of the Ghaznavids and later the Seljuks. The Ghurids capitalized on the Seljuk-Ghaznavid power struggle in the Khorasan region and expanded into a vast empire.
The Ghurid Dynasty, spanning from the 12th to the 13th century, emerged as a dominant force in the region of Ghur present-day Afghanistan. Founded by Alp-Tegin in the late 11th century, the dynasty rose to prominence under his successors, Sultan Mahmud of Ghazni.





![Bhakti Movement: Origin, Main Principles, Causes, And Its Effect [Upsc Medieval History Notes] | Updated April 12, 2025 Bhakti Movement: Origin, Main Principles, Causes, And Its Effect [Upsc Medieval History Notes]](https://www.99notes.in/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/the-bhakti-momvement-banner-99notes-upsc-768x480.webp)

![Maratha Empire: History, Rulers, War &Amp; Administration [Upsc Notes] | Updated April 12, 2025 Maratha Empire: History, Rulers, War & Administration [Upsc Notes]](https://www.99notes.in/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/maratha-empire-featured-768x500.webp)