Persian and Greek Invasion of India Notes for UPSC
Persian and Greek Invasion of India
In the 6th century BCE, India’s northwest was a site of conflict between various principalities. Kambojas, Gandharas and Madras fought with each other. Since there was an absence of a powerful overarching kingdom, the principalities of the northwest could not be organized into one kingdom. This area was also wealthy and easily entered through passes in the Hindukush. Due to these reasons, foreign rulers invaded India.
Persian invasion of India
Achaemenid Empire, also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC.

Persian Rulers and their invasions
1. Darius (reign from522 BC until his death in 486 BC)
- He was the 3rd king of the Achaemenid Empire.
- He penetrated northwest India in 516 BC.
- He annexed Punjab, west of the Indus, and Sindh.
- The conquered part was the 12th province (called Satrapy) of Iran. It was the most populated and fertile region of the empire.
- Three hundred sixty talents (a unit of weight) of gold tribute were paid, representing one-third of Iran’s total income from its Asian provinces.
- The Iranian army enrolled Indian subjects.
2. Xerxes (486 to 465 BC)
- He continued to rule over the Indian Satrapy.
- He employed Indian subjects in the long war against the Greeks.
Effect of Persian invasion on India
-
Trade and commerce –
- Persian Royal road: The Indo-Iranian trade flourished due to the establishment of the Persian Royal road, which acted as a precursor to the silk route.
- Iranian coins were used in the conquered part.
-
Cultural –
- Kharosthi script was introduced. It was written right to left like Arabic. Some Ashokan inscriptions of the 3rd century BC in Northwestern India were written in Kharosthi script.
- Mauryan sculptures were greatly influenced by Iranian art. For example – The bell-shaped capitals of Ashokan pillars were similar to the Iranian capitals.
- The preamble of Ashokan edicts had Iranian influence. For example – the Iranian term dipi was used as lipi in Ashokan edicts.
- Further invasion – Iranian invasion paved the way for other attacks on India. For example – Greeks came to know about Indian wealth through Iranian sources.
Greek Invasion of India
Ancient Greece was a Northeastern Mediterranean civilization that spanned the period of the Greek Dark Ages in the 12th and 9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (around AD 600). However, it was only ever united once, for 13 years, under the rule of Alexander the Great’s empire (336-323 BC).
Alexander’s Invasion (336 to 323 BC) of India
After defeating the Persian empire in the 4th century BC, he invaded the Indus valley in 326B.C through the Khyber Pass.
Reasons for Alexander’s invasion of India
- He was attracted to the immense wealth of India. Herodotus and other Greek authors had portrayed India as a magnificent country.
- Further, he had a strong regard for natural history and geographic research.
- He was also inspired by the past conquerors and wanted to emulate and surpass them.
The polity of India during Alexander’s invasion
- The northwestern part of India was divided into many independent monarchies and tribal republics and not organized into one kingdom.
- Taxila, whose ruler was Ambhi, was situated between the rivers of Indus and Jhelum.
- Porus was the ruler of a kingdom between the Jhelum and Chenab rivers. He is believed to be a king from the ancient Vedic tribe named Puru.
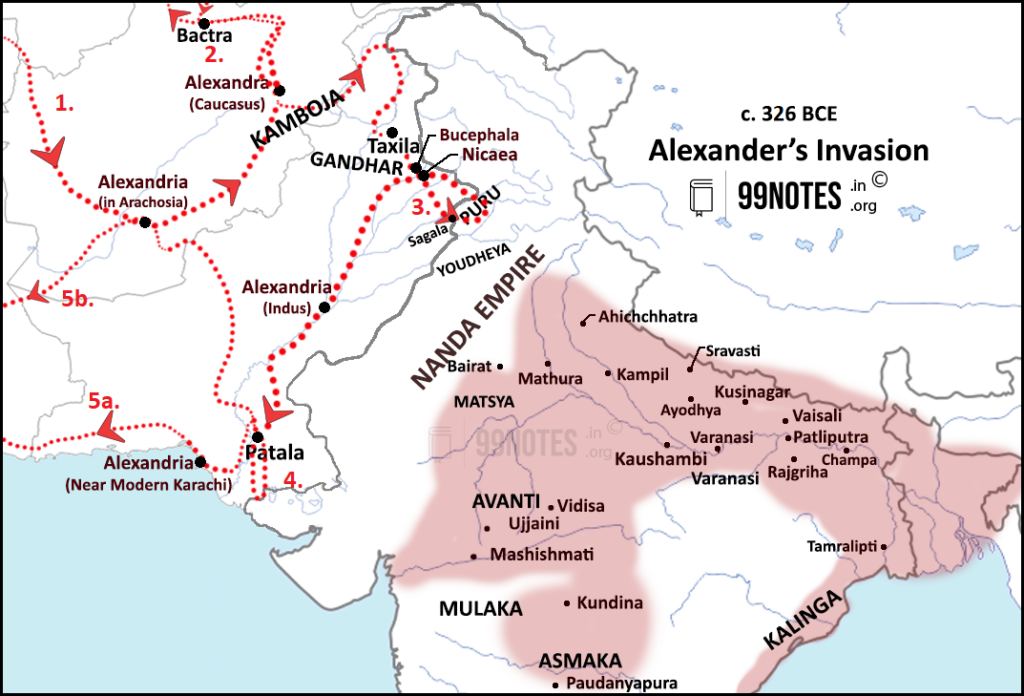
The invasion of Alexander’s of India:
- After entering India in 326 BC, he met Ambhi of Taxila. Ambhi submitted his kingdom. In return, it appears that Alexander made him the governor of Taxila under his kingdom.
- Battle of Hydapses –
- After Taxila, he proceeded to a Battle of Hydaspes against Porus, wherein Ambhi of Taxila contributed with 5000 men at Alexander’s disposal. Ambhi and Porus were already hostile to each other before the arrival of Alexander.
- Despite Porus’ defeat, Alexander was moved by his bravery. He thus gave him back his kingdom and made him an ally.
- He then reached the Beas River.
- Avoided conflict against Nandas
- He wanted to advance eastward, but his army refused to accompany him.
- They learned about a formidable power on the Ganga – the Nanda dynasty, which outnumbered Alexander’s army.
- The retreat
- Alexander defeated numerous small republics during his return march, including Agalassoi (a tribe that lived in modern Pakistan in the lower Indus Valley), until he reached the end of the Indian frontier.
- Most defeated states were restored to their rulers who submitted to his authority, which were eventually lost to Mauryan rulers.
- However, his lands were divided into three sections and given to three Greek governors, and one such governor was Seleucus Nikator of Northwestern India.
- His new fleet was sent out under the command of his close friend Nearchus to scout the coastline and look for harbours between the Euphrates and Indus River mouth.
- He stayed in India for 19 months (326-325 BC.)
Effect of Alexander’s Invasion
- He founded several cities in North West India.
| Name of the city | Region |
| Alexandria | Fergana Valley, near Kabul |
| Boukephela(on the name of his horse) | Near Jhelum River |
| Nicaea | Near Chenab |
| Alexandria | On river Indus |
| Alexandria | Near modern Karachi |
| Alexandria | Near Arachosia |
- Trade with Europe: India came into contact with Europe. Alexander’s ships campaign opened up distinct routes by land and sea for Greek merchants for trade, which later developed as silk and spice routes, respectively. This eventually made India an export hub under Kushans.
Greek sources of history
- Alexander’s historian gave a detailed version of India’s social, economic and political conditions at that time. The societal needs were: –
- Prevalence of sati system
- Sale of girl child in the market places by poor parents.
- A good breed of oxen was available in northwest India.
- The most popular craft in India was carpentry, where artisans constructed chariots, boats, and ships.
- His invasions weakened Northwestern India, which paved the way for the expansion of the Mauryan empire into northwest India.

FAQ’s Related to Persian and Greek Invasion of India
Who was the first Persian invader of India?
Cyrus the Great was the first Persian invader of India, extending his empire into the northwest regions around 550 BC.
How long did Persians rule India?
Persian rule in the northwest parts of India lasted until around 326 BCE, when Alexander the Great defeated the Persian satraps.
When was Persian introduced in India?
Persian was introduced in India during the Delhi Sultanate, becoming the administrative and cultural language by the 13th century.
Explore additional significant articles on Ancient Indian History listed in the table below:
| Harappan Civilisation | Various Aspects of Harappan Civilisation |
| Stone Age | Decline of Harappan Culture |
| Vedic Period | Religious Traditions in Ancient India |
| Mauryan Empire | Gupta Empire |



![Sangam Age: Literature, Map, &Amp; Dynasties [Upsc Exam Notes] | Updated June 30, 2024 Sangam Age: Literature, Map, &Amp; Dynasties [Upsc Exam Notes]](https://99notes.in/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/megalith-sangam-age-99notes-upsc-768x495.webp)


![Post Mauryan Period: Shunga, Kanva Dynasties &Amp; More [Upsc Notes] | Updated June 30, 2024 Post Mauryan Period: Shunga, Kanva Dynasties & More [Upsc Notes]](https://99notes.in/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/post-mauryan-age-99notes-upsc-1-768x495.webp)