Union Budget
Union Budget 2023-2024

The term Budget is a generic statement given to a number of documents, which includes the Annual Financial Statement. Article 112 makes it a constitutional obligation upon the Government to lay a statement of the estimated receipts and expenditures in the Parliament. The Government fulfils this duty through its Annual financial statement, which is contained in the Budget.
The Budget also includes the Demand-for-Grants, Appropriation Bill (to authorise the Government to use funds), Finance Bill (to introduce new taxes), Macroeconomic Framework Statement (required under the FRBM Act), Fiscal Policy Strategy Statement and Medium-Term Expenditure Statement apart from the Annual financial statement.
The Summary of the Union Budget of 2023-24 is discussed in this article.
Achievements of India as Stated in the Budget
- India’s economic growth at a rate of 7% is the highest among the major economies. The economy is on the right track after the shocks of the Covid-19 pandemic and the war.
- India has made several achievements that are contributing to its increasing global stature:
- Unique world-class digital public infrastructure, such as, Aadhaar, Co-Win and UPI.
- Covid vaccination drive in unparalleled scale and speed.
- proactive role in frontier areas, such as achieving climate-related goals,
- Mission LiFE, and
- National Hydrogen Mission.
- PM Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY) has been instrumental in ensuring food and ensuring nutritional security during the COVID pandemic. This scheme will continue with the expenditure borne entirely by the Centre.
- G20 Presidency offers a unique opportunity for India to steer an ambitious, people-centric agenda to address global challenges and facilitate sustainable economic development.
- India is now the 5th largest economy in the world, offering an optimal environment for businesses and a vibrant innovation ecosystem. It also has made significant progress in many of the Sustainable Development Goals.
- Indian economy is now more formalised, and several schemes for inclusive development are producing positive outcomes.
Vision for Amrit Kaal – an empowered and inclusive economy
The vision for Amrit Kaal is a technology-driven and knowledge-based economy with strong public finances and a robust financial sector. This vision is anchored upon Jan Bhagidari through Sabka Saath Sabka Prayas and will be realised by:
- facilitating ample opportunities for citizens, especially the youth, to fulfil their aspirations.
- providing strong impetus to growth and job creation and
- strengthening macroeconomic stability.
4 opportunities can be transformative during Amrit Kaal:
- Economic Empowerment of Women
- PM VIshwakarma KAushal Samman (PM VIKAS)
- Tourism
- Green Growth
Economic Empowerment of Women:
- The 81 lakh Women Self Help Groups under Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana National Rural Livelihood Mission will be encouraged to form large producer enterprises or collectives, each having several thousand members and managed professionally.
- These entities will help the rural women with the supply of raw materials, design, quality, packaging, and marketing of their products so that they can cater to large consumer markets.
PM Vishwakarma Kaushal Samman (PM VIKAS)
- A package of assistance has been formulated for traditional artisans and craftspeople, referred to as Vishwakarma, covering areas like quality, scale and reach of their products as well as integrating them with MSMEs value chains.
- The support is multi-dimensional in the form of financial assistance, access to advanced skilling and training, knowledge of modern digital techniques and efficient green technologies, brand promotion, linkage with local and global markets, digital payments, and social security.
Tourism
- The tourism sector holds great employment and entrepreneurship potential for the youth. This can be realised by promoting tourism on a mission mode using the PPP channels and convergence of government initiatives and with the active participation of the states.
Green Growth
- Green growth involves green fuel, green energy, green farming, green mobility, green buildings, and green equipment and energy efficiency. This can create large-scale green job opportunities.
Priorities of the Budget
The Budget adopts 7 priorities called ‘Saptarishi‘, which are supposed to guide us through the Amrit Kal.
- Inclusive Development.
- Reaching the Last Mile.
- Infrastructure and Investment.
- Unleashing the Potential.
- Green Growth.
- Youth Power.
- Financial Sector.

PRIORITY 1: INCLUSIVE DEVELOPMENT
It covers two pillars: 1) Agriculture and Cooperation, and 2) Health, Education and Skilling
Agriculture and Cooperation
- Digital Public Infrastructure for Agriculture
- Agriculture Accelerator Fund
- Atmanirbhar Horticulture Clean Plant Program
- Global Hub for Millets: ‘Shree Anna’
- Cooperation
- Fisheries
- Enhancing the productivity of cotton crop
- Agriculture Credit
Health, Education and Skilling
- Nursing Colleges
- Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission
- Medical Research
- Pharma Innovation
- Multidisciplinary courses for medical devices
- Teachers’ Training
National Digital Library for Children and Adolescents
Agriculture and Cooperation
1. Digital Public Infrastructure for Agriculture
- It will be built as an open source, open standard and interoperable public good.
- Utility:
- Provide farmer-centric solutions in crop planning and health, farm input, credit, and insurance.
- Help in crop estimation.
- Market Intelligence
- Support the growth of the agri-tech industry and start-ups.
2. Agriculture Accelerator Fund
- It will be set up to bring innovative and affordable solutions for farmers’ challenges by:
- Encouraging agri-startups by young entrepreneurs in rural areas.
- Fostering the development of modern technologies for improved agricultural practices for better productivity and profitability.
3. Atmanirbhar Horticulture Clean Plant Program
- It will be launched with an outlay of ₹ 2,200 crores. Aim = to boost the availability of disease-free, quality planting material for high-value horticultural crops.
4. Global Hub for Millets: ‘Shree Anna’
- To make India a Global Hub for Millets, the Indian Institute of Millet Research, Hyderabad, will be supported as the Centre of Excellence for sharing best practices, research, and technologies at the international level.
5. Cooperation
- The Government is promoting a cooperative-based economic development model to help farmers, especially small and marginal farmers, and other marginalised sections.
- Steps in this direction:
- A new Ministry of Cooperation was formed to realise the vision of ‘Sahakar Se Samriddhi’.
- Strengthening of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) through computerisation.
- Formulating model bylaws enabling PACS to become multipurpose PACS.
- A national cooperative database is being developed for country-wide mapping of cooperative societies.
- New in the Budget:
- A massive, decentralised storage capacity shall be implemented ‒ to ensure that farmers can store their produce and realise remunerative prices of their produce through the release of their products at an appropriate time.
- The Government will facilitate the setting up a large number of multipurpose cooperative societies, dairy cooperative societies and primary fishery societies in uncovered panchayats and villages in the next 5 years.
6. Others
- Enhanced productivity of cotton crops
- Productivity of extra-long staple cotton will be enhanced:
- By adopting a cluster-based and value chain approach in PPP mode
- Through collaboration between farmers, state and industry for input supplies, extension services, and market linkages
- Productivity of extra-long staple cotton will be enhanced:
- Fisheries
- A new sub-scheme worth an outlay of ₹ 6,000 crores for investments will be launched under PM Matsya Sampada Yojana.
- Aim = To encourage market expansion, improve the efficiency of the value chains and encourage the activities of fish vendors, fishermen, and micro & small enterprises.
- The target for agriculture credit will be enhanced to ₹20 lakh crore, focusing on animal husbandry, dairy, and fisheries.
Health, Education and Skilling
1. Nursing Colleges
- Nursing schools will be established alongside the 157 medical colleges that have been operating since 2014.
2. Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission
- It will be launched. Aim = To eliminate Sickle Cell Anaemia by 2047.
- Pillars = Awareness creation, universal screening with a focus on the age group of 0-40 years in affected tribal areas, counselling, and collaboration of central and state governments.
3. Medical Research Facilities
- To encourage collaborative research and innovation, selected ICMR labs will be provided facilities to enable research by public and private medical college faculty and private sector R&D teams.
4. Pharma Innovation
- A new programme is to be launched to promote R&D in pharmaceuticals through centres of excellence and by encouraging investment by the industry for R&D in specific priority areas.
5. Multidisciplinary courses for medical devices
- To ensure the availability of skilled labour for futuristic medical technologies, high-end manufacturing, and research, dedicated multidisciplinary courses for medical devices will be promoted in existing institutions.
6. Teachers’ Training
- Teacher’s training shall be re-envisioned through:
- Innovative pedagogy, curriculum transaction, continuous professional development,
- Dipstick surveys,
- ICT implementation, and
- Developing District Institutes of Education and Training (DIETs) as vibrant institutes of excellence.
7. National Digital Library for Children and Adolescents
- It will be set up to facilitate the availability of quality books across geographies, languages, genres and levels, and device-agnostic
- Vibrant Physical libraries
- States will be encouraged to provide infrastructure for accessing the National Digital Library resources and open physical libraries for children and adolescents at panchayat and ward levels.
- National Book Trust, Children’s Book Trust and other sources shall be encouraged to contribute noncurricular titles in regional languages and English to the physical libraries to build a culture of reading.
- Financial sector regulators and organisations will be urged to supply these libraries with age-appropriate reading material to foster financial literacy.
- Collaboration with NGOs that work in literacy.
PRIORITY 2: REACHING THE LAST MILE
Extension of existing Initiatives
- Aspirational Districts and Blocks Programme
- Eklavya Model Residential Schools
- PM Awas Yojana
New initiatives:
- Pradhan Mantri PVTG Development Mission
- Upper Bhadra Project
- Bharat Shared Repository of Inscriptions (Bharat SHRI)
Support for poor prisoners
1. Pradhan Mantri PVTG Development Mission
- It shall be launched with a corpus of ₹15,000 crores over 3 years under the Development Action Plan for the Scheduled Tribes.
- Aim: To improve the socio-economic conditions of the particularly vulnerable tribal groups (PVTGs).
- The PVTG families and habitation will be saturated with basic facilities and opportunities for education and sustainable livelihood.
2. Bharat Shared Repository of Inscriptions (Bharat SHRI)
- It will be set up in a digital epigraphy museum. The first phase will involve the digitisation of 1 lakh ancient inscriptions.
3. Others
1. Aspirational Blocks Programme
- Modelled on the Aspirational Districts Programme, it has already been launched, covering 500 blocks for providing essential government services in various areas like health, nutrition, education, water resources, financial inclusion, skill development, and basic infrastructure.
2. EMRS
- Around 39000 teachers and support staff shall be recruited for Eklavya Model Residential Schools over 3 years.
3. Upper Bhadra Project
- The Upper Bhadra Project, serving Karnataka’s central drought-prone central region, will be given central assistance of ₹5,300
4. PM Awas Yojana
- Its outlay is being enhanced by 66% to over ₹79,000 crores.
5. Poor prisoners
- Poor prisoners unable to pay the penalty or bail amount will be given financial assistance.
PRIORITY 3: INFRASTRUCTURE & INVESTMENT
Capital Investments
- Capital Investments – a driver of growth and jobs.
- Effective Capital Expenditure.
Infrastructure
- Enhancing opportunities for private investment in Infrastructure through Infrastructure Finance Secretariat.
- Harmonized Master List of Infrastructure.
Transport and Logistics
- Railways.
- Logistics.
- Regional Connectivity.
Urban Development
- Sustainable Cities of Tomorrow.
- Making Cities ready for Municipal Bonds.
- Urban Infrastructure Development Fund
Urban Sanitation
Capital Expenditure
1. Steep rise in capital investment
- Capital investment has been increased steeply by 33% to ₹10 lakh crores (~ 3.3% of the GDP) for the current year. This rise is almost thrice the outlay of 2019/20.
- The steep rise in capital expenditure in recent years is a key strategy of the Government for crowding-in private investments, job creation, enhancing growth potential, and providing a buffer against global headwinds.
2. Effective Capital Expenditure
- It is a sum of the central Government’s direct capital investment and the indirect capital investment in the form of Grants-in-Aid to States for the creation of capital assets.
- This total amount is budgeted at ₹13.7 lakh crore (~ 4.5% of GDP).
3. Support to State Governments for Capital Investment
- The central Government’s plan to grant state governments a 50-year interest-free loan will continue for another year to promote infrastructure investment and provide them with incentives for complementary policy initiatives.
Infrastructure
1. Infrastructure Finance Secretariat
- The recently created Infrastructure Finance Secretariat will support all stakeholders in attracting more private investment in infrastructure, such as roads, railways, urban infrastructure, and power, which are primarily reliant on public funds.
2. Harmonized Master List of Infrastructure
- An expert committee will review the list recommending the classification and financing framework suitable for Amrit Kaal.
Urban development
1. Sustainable Cities of Tomorrow
- To make our cities the “sustainable cities of tomorrow,” the states and cities will be encouraged to implement urban planning reforms and initiatives.
2. Making Cities ready for Municipal Bonds
- The creditworthiness of municipal bonds shall be increased through reforms in the property tax governance and ring-fencing user charges on urban infrastructure.
3. Urban Infrastructure Development Fund (UIDF)
- UIDF will be established using priority sector lending shortfall.
- Public agencies will use the UIDF to create urban infrastructure in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
- It is to be managed by the National Housing Bank.
- States will be urged to use funds from grants from the 15th Finance Commission and already-existing programmes to adopt reasonable user fees while accessing the UIDF.
4. Urban Sanitation
- The goal is to shift from manhole to machine-hole mode by 100% mechanical desludging of septic tanks and sewers.
- The dry and wet waste will be scientifically managed through a more focused approach.
Transport and logistics
1. Railways: It has received a capital outlay of ₹2.40 lakh crores.
2. Logistics
-
- For ports, the coal, steel, fertiliser, and food grain sectors, 100 essential transportation infrastructure projects have been identified towards first and last-mile connectivity. These projects will be implemented on a priority basis with an investment of ₹75,000 crores, with private sources contributing ₹15,000 crores.
3. Regional Connectivity
-
- To increase regional air connectivity, 50 additional airports, heliports, water aerodromes, and advance landing grounds will be revived.
PRIORITY 4: UNLEASHING THE POTENTIAL
Governance Reforms
- Mission Karmayogi
- E-Courts
- One-stop solution for identity and address updating.
- Simplification of the Know Your Customer (KYC) process.
Business facilitation
- Ease of Doing Business
- Common Business Identifier
- Unified Filing Process
- Vivad se Vishwas I – Relief for MSMEs
- Vivad se Vishwas II – Settling Contractual Disputes
- Entity DigiLocker
Innovation and Technology
- Centres of Excellence for Artificial Intelligence
- National Data Governance Policy
- Fintech Services
- 5G Services
- Lab Grown Diamonds
Planning
- State Support Mission
Result Based Financing
Governance Reforms
1. Mission Karmayogi
- It is a capacity-building program for civil servants of the Centre, States and Union Territories.
- iGOT Karmayogi (Integrated Online Training Platform) – is an online training platform for continuous learning opportunities for civil servants to upgrade their skills and facilitate a people-centric approach.
2. E-Courts
- Phase 3 of the E-Courts project will be launched with an outlay of ₹7,000 crores.
3. One-stop solution for identity and address updating.
- Using the DigiLocker service and Aadhaar as the foundational identity, a one-stop solution will be established to reconcile and update the identity and address of individuals with various governmental entities, regulators, and regulated entities.
4. Simplification of the Know Your Customer (KYC) process.
- The KYC process will become simpler by using a “risk-based” approach rather than a “one size fits all” one.
Business facilitation
1. Ease of Doing Business
- Above 39000 compliances have been reduced, and more than 3,400 legal provisions have been decriminalised.
- Jan Vishwas Bill was introduced to amend 42 Central Acts.
2. Common Business Identifier.
- All digital systems of the designated government agencies will use PAN as their common identifier.
3. Unified Filing Process.
- It will be set up to avoid the need for separate submission of the same information to various government agencies.
4. Vivad se Vishwas I – Relief for MSMEs
- The Government and its undertakings will return 95% of the forfeited amount relating to bid or performance security to those MSMEs that failed to execute contracts during the Covid period.
5. Vivad se Vishwas II – Settling Contractual Disputes
- A voluntary settlement scheme with standardised terms will be introduced to resolve contractual disputes involving the government and government undertakings where an arbitral award is being challenged in court.
6. Entity DigiLocker
- It will be set up for use by MSMEs, large businesses and charitable trusts, enabling them to securely share their documents online with specified authorities and entities.
Innovation and Technology
1. Centres of Excellence for Artificial Intelligence
- 3 such centres will be set up in top educational institutions.
- Aim = To realise the vision of “Make AI in India and Make AI work for India” by galvanising an effective AI ecosystem and nurturing quality human resources.
- A partnership will be set up with leading industry players to conduct interdisciplinary research, create cutting-edge applications, and find scalable solutions to issues in the fields of agriculture, health, and sustainable cities.
2. National Data Governance Policy
- It will be formulated to enable access to anonymised data by start-ups and academia to unleash innovation and research.
3. Lab Grown Diamonds (LGD)
- LGD is a technology- and innovation-driven emerging sector with high employment potential.
- LGDs are environment-friendly and possess the same optical and chemical properties as natural diamonds.
- To promote the indigenous production of LGD seeds and machines, an R&D grant will be extended to one of the IITs for 5 years.
- A review of the custom duty rate on LGD seeds has been proposed to reduce production costs.
4. 5G Services
- 100 labs for developing 5G-based apps will be set up in engineering institutions. There will be apps for precision farming, intelligent transport systems, smart classrooms, health care applications, etc.
5. Fintech Services
- The scope of documents stored in DigiLocker will be expanded to facilitate more innovative Fintech services.
Planning
1. State Support Mission of NITI Aayog
- To work collectively towards national priorities, this mission will continue for 3 more years.
2. Result Based Financing
- A shift to a ‘result-based’ from an ‘input-based’ mode of financing select schemes would be carried out on a pilot basis for enhanced fiscal efficiency.
PRIORITY 5: GREEN GROWTH
- Green Hydrogen Mission
- Energy Transition
- Energy Storage Projects
- Renewable Energy Evacuation
- Green Credit Programme
- PM-PRANAM
- GOBARdhan scheme
- Bhartiya Prakritik Kheti Bio-Input Resource Centres
- MISHTI
- Amrit Dharohar
- Coastal Shipping
Vehicle Replacement
1. Green Hydrogen Mission
- It has been recently launched. It targets to achieve an annual production of 5 MMT of green hydrogen by 2030. The mission has an outlay of ₹19,700 crores.
2. Energy Transition
- The Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas has been allocated a ₹35,000 crore sum to make priority capital investments to achieve the objective of net zero and for energy transition and energy security.
3. Energy Storage Projects
- A Viability Gap Funding will support a 4000 MWH Battery Energy Storage Systems.
- A detailed framework will be formulated for Pumped Storage Projects.
4. Renewable Energy Evacuation
- With a total investment of ₹20,700 crores, including the Centre’s support of ₹8,300 crores, the inter-state transmission system will be constructed for the evacuation and grid integration of 13 GW of renewable energy from Ladakh.
5. Green Credit Programme
- Green Credit Programme will be launched under the Environment (Protection) Act 1986 to induce behavioural changes.
- Under this, incentives will be provided to companies, individuals and local bodies for their environmentally sustainable and responsive actions.
- It will also help mobilise additional resources for such activities.
6. PRANAM
- PM Programme for Restoration, Awareness, Nourishment and Amelioration of Mother Earth (PRANAM) will be launched to incentivise States and UTs to promote alternative fertilisers and balanced use of chemical fertilisers.
7. GOBARdhan scheme
- With the circular economy in mind, new plants under GOBARdhan scheme will be launched, including:
- 200 compressed biogas (CBG) plants,
- 300 community or cluster-based plants
- A 5% CBG mandate will be introduced for all organisations marketing natural and biogas.
- Fiscal support will be provided for the collection of bio-mass and distribution of bio-manure.
8. Bhartiya Prakritik Kheti Bio-Input Resource Centres
- These centres will be set up to create a national-level distributed micro-fertiliser and pesticide manufacturing network to facilitate 1 crore farmers to adopt natural farming in 3 years.
9. MISHTI
- ‘Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes’ (MISHTI) will be launched to promote mangrove plantation along the coastline and on salt pans through convergence between MGNREGS, CAMPA Fund and other sources.
10.Amrit Dharohar
- This programme will be introduced to promote the best possible use of wetlands and improve biodiversity, carbon storage, ecotourism opportunities, and local communities’ ability to generate income.
11.Coastal Shipping
- Coastal shipping will be promoted through PPP mode with viability gap funding as the cheap and energy-efficient mode of transportation, for passengers as well as freight.
12.Vehicle Replacement
- States will be supported for replacing old vehicles and ambulances.
PRIORITY 6: YOUTH POWER
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0
- Skill India Digital Platform
- National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme
- Tourism
Unity Mall
1. Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikash Yojana 4.0 (PMKVY 4.0)
- PMKVY 4.0 will be launched with an emphasis on on-job training, partnership with the industry, and alignment of the curriculum with industry requirements. It will also focus on new-age courses for Industry 4.0, like coding, AI, robotics, mechatronics, IOT, 3D printing, drones, and soft skills.
- 30 Skill India International Centres will be set up in various states to prepare youth for international opportunities.
2. Skill India Development Platform
- Skill India Development Platform will be a unified platform that will cater to aspects like:
- demand-based formal skilling,
- linking with employers, including MSMEs
- facilitating access to entrepreneurship schemes.
3. National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS)
- DBT (Direct Benefit Transfer) under NAPS will be launched to transfer stipends to support 47 lakh youth in 3 years.
4. Tourism
- At least 50 sites will be selected through challenge mode to develop them as tourist destinations with an integrated and innovative approach. Each destination would be developed as a full package, with both the domestic and foreign tourists in mind.
- An App will be launched to enhance the tourist experience by making available aspects like physical connectivity, virtual connectivity, tourist guides, high standards for food streets and tourists’ security.
- Sector-specific skilling and entrepreneurship development will be dovetailed to achieve the objectives of the ‘Dekho Apna Desh’ initiative.
- Infrastructure and amenities for tourism will also be made available in border villages under the Vibrant Villages Programme.
5. Unity Mall
- The states will be encouraged to set up Unity Mall as spaces to promote the sale of their ODOPs (one district, one product), GI products and other handicraft products and to provide space for such products of all other states.
PRIORITY 7: FINANCIAL SECTOR
- Credit Guarantee for MSMEs
- National Financial Information Registry
- Financial Sector Regulations
- GIFT IFSC
- Data Embassy
- Improving Governance and Investor Protection in Banking Sector
- Capacity Building in Securities Market
- Central Data Processing Centre
- Reclaiming of shares and dividends
- Digital Payments
- Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav Mahila Samman Bachat Patra
- Senior Citizens
- Fiscal Management
- 50-year interest-free loan to States
- Fiscal Deficit of States
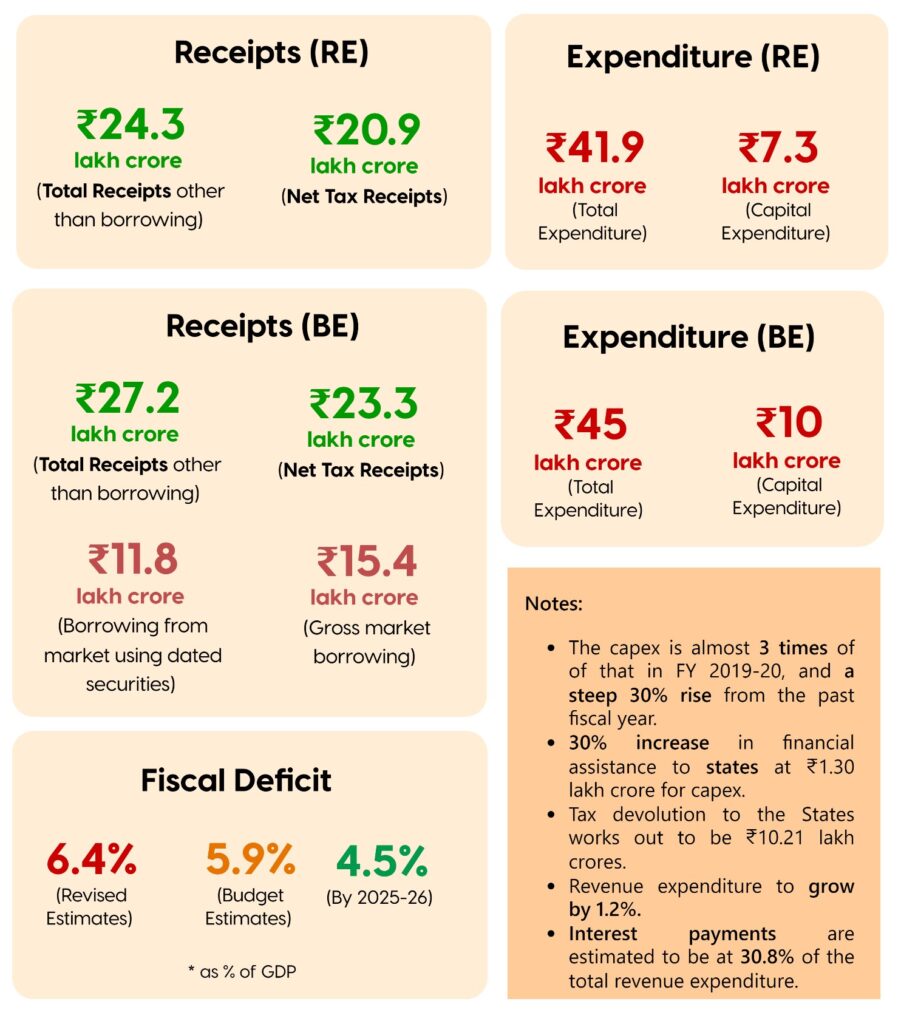
- Revised Estimates 2022-23
Budget Estimates 2023-24
1. Credit Guarantee for MSMEs
- The credit guarantee scheme for financing MSMEs has been revamped and will take effect from 1st April 2023. The scheme involves an infusion of ₹9,000 crores in the corpus, which will enable an additional collateral-free guaranteed credit of ₹2 lakh crore and a 1% fall in the cost of credit.
2. National Financial Information Registry (NFIR)
- NFIR is a proposed public infrastructure under a new legislative framework and will be designed in consultation with the RBI. It will serve as the central repository of financial and ancillary information. It will enable an efficient flow of credit, promote financial inclusion, and foster financial stability.
3. Financial Sector Regulations
- Public consultation would become an important pillar to enable optimum regulation in the financial sector. The public will be involved in the process of making regulations and issuing subsidiary directions.
- The financial sector regulators will conduct a comprehensive review of existing regulations by involving the public and the regulated entities to simplify, ease and reduce the cost of compliance.
- A deadline would be set for considering applications under various regulations.
4. GIFT IFSC
- The following steps will be taken to enhance business operations in GIFT IFSC:
- Powers under the SEZ Act will be delegated to IFSCA to avoid dual regulation,
- A single-window IT system will be set up for registration and approval from IFSCA, SEZ authorities, GSTN, RBI, SEBI and IRDAI.
- Acquisition financing by IFSC Banking Units of foreign banks will be permitted,
- A subsidiary of EXIM Bank will be established for trade re-financing,
- IFSCA Act will be amended to include statutory provisions for arbitration, ancillary services, avoiding dual regulation under SEZ Act, and
- Offshore derivative instruments will be recognised as valid
5. Data Embassy
- Data Embassies in GIFT IFSC will be set up for countries looking for digital continuity solutions.
6. Improving Governance and Investor Protection in Banking Sector
- Some amendments to the Banking Regulation Act, the Banking Companies Act, and the RBI Act are proposed to improve bank governance and strengthen investor protection.
7. Capacity Building in Securities Market
- SEBI will be empowered to oversee and regulate the capacity-building of security market functionaries and professionals.
8. Central Data Processing Centre
- A Central Data Processing Centre will be established to handle various forms submitted to field offices under the Companies Act, allowing for faster response times to companies.
9. Reclaiming of shares and dividends
- An integrated IT portal will enable investors to easily reclaim unclaimed shares and unpaid dividends from the Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority.
10.Digital Payments
- Fiscal support for the digital public infrastructure to continue in 2023-24.
11.Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav Mahila Samman Bachat Patra
- Mahila Samman Savings Certificate will be a one-time new small savings scheme valid for 2 years up to March 2025. It is a deposit facility of up to ₹2 lakhs in the name of women or girls for a tenor of 2 years at a fixed interest rate of 7.5% with a partial withdrawal option.
12.Senior Citizens
- Enhanced maximum deposit limit for Senior Citizen Savings Scheme: from ₹15 lakh to ₹30 lakh.
- Enhanced maximum deposit limit for Monthly Income Account Scheme:
- From ₹4.5 lakhs to ₹9 lakhs for single accounts and
- From ₹9 lakhs to ₹15 lakhs for joint accounts.
13.Fiscal Management
- 50-year interest-free loan to States
The entire 50-year loan to states must be spent on capital expenditure within 2023-24. The conditional part of the loan will cover new areas like:
- Scrapping old govt. vehicles,
- Urban planning reforms and actions,
- Financing reforms in ULB to make them creditworthy for municipal bonds,
- Housing for police personnel above or as part of police stations,
- Constructing Unity Malls,
- Children and adolescents’ libraries and digital infrastructure, and
- State share of capital expenditure of central schemes.
- Fiscal Deficit of States
- A fiscal deficit of 5% of the GSDP will be permitted for each state, of which 0.5% must be used for power sector reforms.

PART-B
Revised Estimates and Budget Estimates
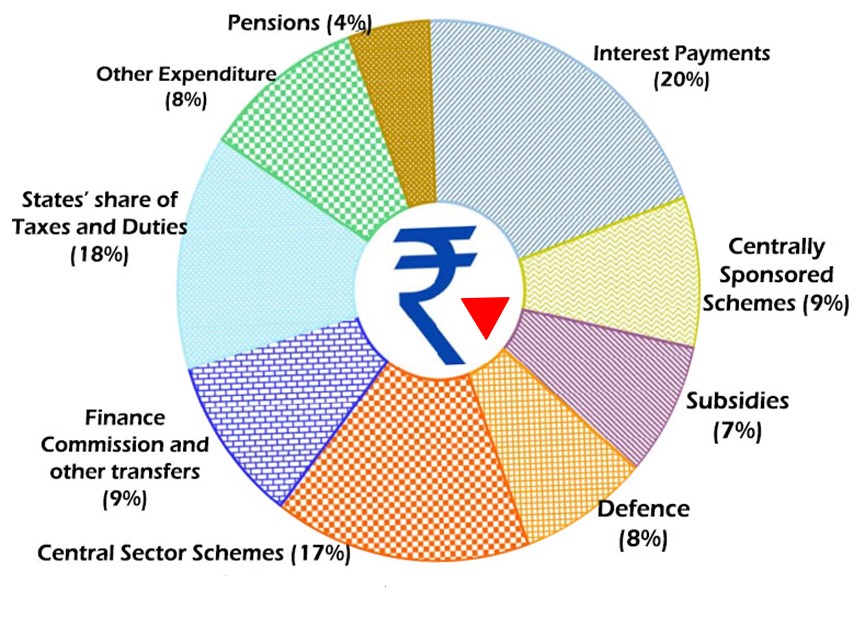
₹ Goes To
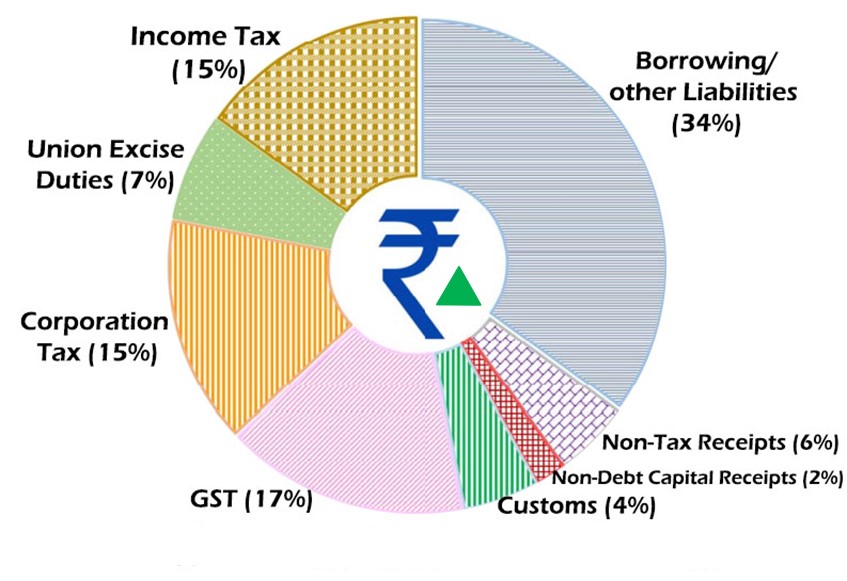
₹ Comes From
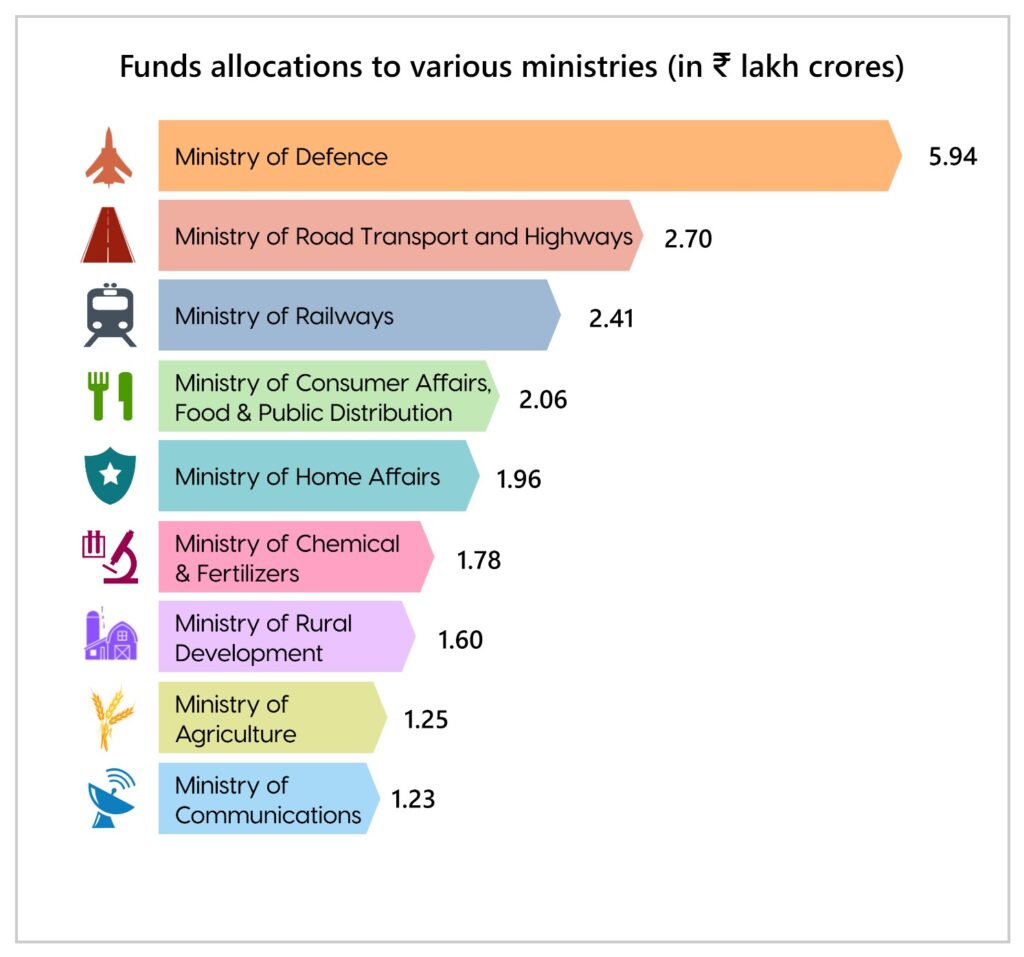
Ministry-wise Allocation of Funds
Direct Tax Proposals
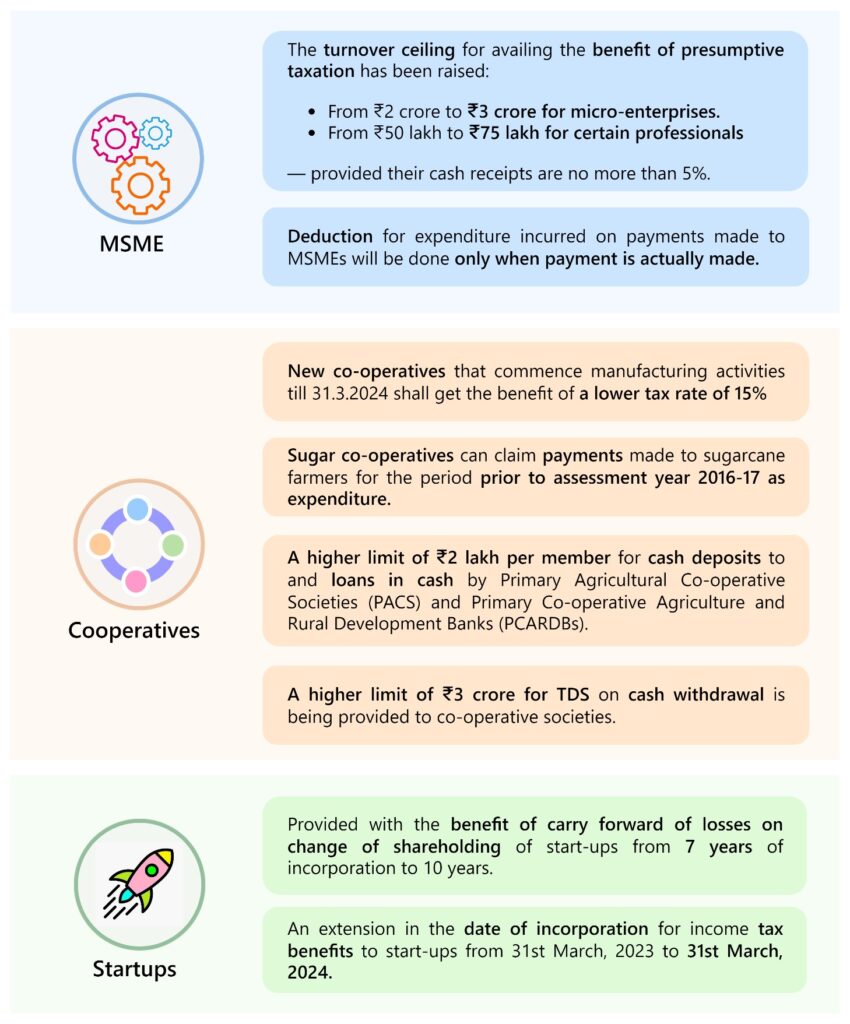
MSME, Cooperatives, and Startups
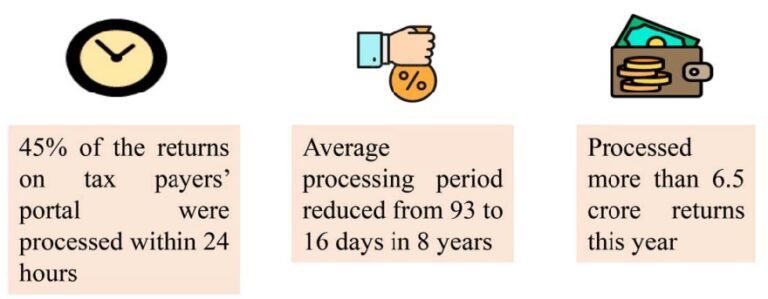
- Tax Appeals: About 100 Joint Commissioners to be deployed for disposal of small appeals.
Personal Income Tax
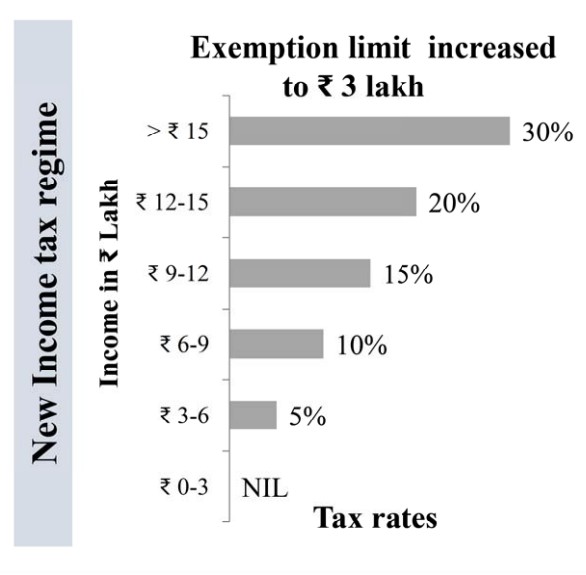
- The rebate limit in the new tax regime has been increased to ₹ 7 lakh.
- This means that individuals in the recent tax regime with income up to ₹ 7 lakhs are exempted from paying tax.
- Reduction in number of slabs in the new personal tax regime to 5.
- Increased tax exemption limit to ₹ 3 lakh.
- The highest surcharge rate has been reduced from 37% to 25%.
Indirect Tax Proposals

- Customs Duty
- The number of basic customs duty rates on goods other than textiles and agriculture has been reduced from 21 to 13.
- National Calamity Contingent Duty on specified cigarettes has been revised upwards by about 16%.
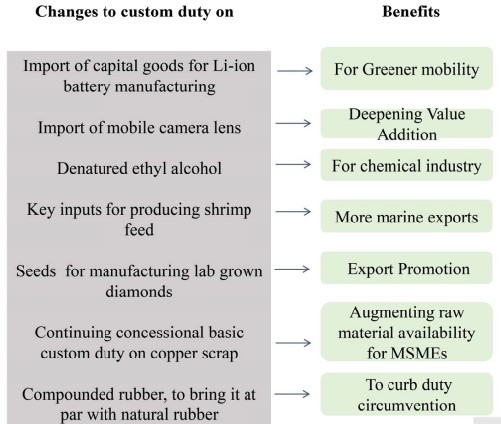
- Exemption from Customs Duty
- Green Mobility: Import of capital goods and machinery required to manufacture lithium-ion cells for batteries used in electric vehicles.
- Electronics:
- Import of certain parts and inputs like a camera lens.
- Concessional duty on lithium-ion cells for batteries to continue for another year.
- Reduced duty (2.5%) on parts of open cells of TV panels.
- Electrical:
- Reduced duty on heat coils.
- Chemical and Petroleum:
- Denatured ethyl alcohol.
- Acid-grade fluorspar and
- crude glycerine.
- Marine Products: Domestic manufacture of shrimp feed.
- Seeds used in the manufacture of Lab Grown Diamonds.
- Increase in Customs Duty
- Electrical – Electric kitchen chimney
- Precious metals: silver dore, bars and articles to align them.
- Compounded rubber.
- Exemption from excise duty
- GST-paid compressed biogas contained in blended CNG.
- What are the benefits of such an Exemption?
Other Tax Proposals
- Important amendments in CGST Act
- The CGST Act will be amended to increase the minimum ambit of tax amount for launching prosecution under GST from ₹ 1 crore to ₹ 2 crores.
- Better targeting of tax concessions
- Deduction from capital gains on investment in the residential buildings has been capped at ₹10 crores for better targeting of tax concessions and exemptions.
- Extending the period of tax benefits to funds relocating to IFSC, GIFT City.
- Providing EEE status to Agniveer Fund.
- Decriminalisation under section 276A of the Income Tax Act.
- Allowing carry forward of losses on strategic disinvestment including that of IDBI Bank.
- What are the implications of tax changes?
- The revenue of about ₹ 38,000 crores will be foregone, while revenue of about ₹3,000 crores will be additionally mobilised due to the changes in the direct and indirect taxes.

