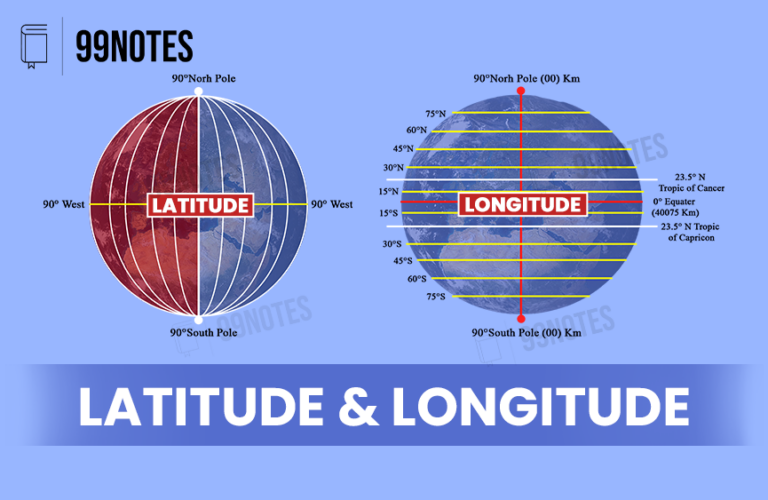
Human Settlements
The human population is highly concentrated in the world. About 90% of the world’s population lives in just 10% of the area. 10 most populous countries contribute 60% to the world’s population. What affects the distribution of population around the earth? Let’s find out. The pattern of population distribution: About 90% of the world’s population…