Origin and Evolution of Earth
In order to understand earth, which is the prime focus of Geography as a discipline, we must first understand the origin of Earth. However, to understand earth we must understand the origin of our solar system and the Universe in general. There are various theories which gave the basis for the origin of the Universe.
Early Theories:
The earliest hypothesis, which is now rejected, shows the imagination of the early philosophers.
- Nebular Hypothesis: planets were formed out of a cloud of material associated with the youthful sun, which slowly started rotating. It was given by Immanuel Kant, a German Philosopher in 1755. Pierre Simone Laplace, a mathematician revised the Nebular hypothesis in 1796.
- Chamberlain and Mouton (1900) predicted that a wandering star once approached the sun in its initial stages of formation, which created a cigar-shaped extension of material separated from the solar surface. These then formed planets.
- Otto Schmidt, Russia and Carl Weizascar, Germany: They too favoured a Nebular Hypothesis, but a differing in details. According to them, a solar nebula containing Hydrogen and Helium along with ‘dust’ first existed. The friction and collision of particles led to the formation of disk-shaped clouds and planets were formed through a process of accretion.
These hypotheses improved with the better understanding of the structure of the Sun, but never explain the origin of earth satisfactorily.
Modern theories:
The modern theories are based on the scientific understanding of the origin of the Universe.
| The Expanding Universe Hypothesis |
| An astronomer named Edwin Hubble in 1929 studied the Cepheids in Andromeda Galaxy to study their luminosity. Cepheid are pulsating stars that have a constant range of luminosity, which can be used as a standard to measure the luminosity of other celestial objects. With the help of the luminosity of Cepheids, Edwin Hubble could calculate the distance of each Cepheid from Earth. In 1929, he noted that these objects were not emitting their true colour and instead were slightly red-shifted, confirming that the universe was expanding. What is a Red-Shift? When a celestial object moves away from us, its wavelength increases which makes the object appear redder. The wavelength of such objects can even expand so much that the object might be visible only through infrared waves or microwaves the more the object is receding fast, the more the redshift. Not only Expansion but an accelerated expansion Observation of type Ia supernovae allows us to measure the rate of speed of expansion. These observations show us that not only the Universe is expanding, but it is also expanding at an accelerated pace. Hoyle’s Concept of Steady State (a rejected theory): He theorised that the universe is not expanding. However, there is building evidence of accelerated expansion. |
The Big Bang Theory
Given the premise that every celestial object is accelerating away from each other, then, at one point in time, the Universe must have been much smaller, and possibly, it must have an origin point from where it started expanding.
With the help of the rates of expansion of the Universe, its origin has been theorized to have happened around 13.8bn years ago. From this point, a giant explosion took place, after which the expansion is still continuing.
The Stages of development of the Universe:
On the basis of the calculations done based on the theory of relativity and quantum physics, the following picture of the development of the Universe has emerged:
- Beginning: Around 13.8bn years ago in one place as “tiny ball” with unimaginably small volume, infinite temperature and infinite density exploded.
- Explosion which is referred to as “the big bang”continues today. A Particularly rapid expansion happened within fractions of a second after the big bang, which later slowed down a little.
- Sub-atomic particles: A millionth of a second after the Big Bang, the first sub-atomic particles appeared. However, for a few seconds, it was so hot that sub-atomic particles could bind together to form atoms. At this stage, the universe was too bright and opaque.
- Formation of Atoms: within the first 3 minutes, the first atom began to form and for the first-time light could pass through them without scattering. This is the first light that we can observe as the cosmic background radiation even today.
- Atomic matter: Onlyafter 300,000 years the temperature drop below 4,500K, giving rise to stable atomic matter. Before this point electrons and nuclei constantly wiggled. The universe became fully transparent.
Formation of Stars and Galaxies
The initial density of the first formed atomic matter gave rise to differences in gravitational forces. This caused the matter to get drawn together under the influence of their masses. This led to the formation of galaxies and stars.
Galaxies are collections of stars, and nebular clouds and their remnants spread over vast distances that are measured in thousands of light-years. (Typically, 80,000 Light years to 150,0000 Light years.)
Formation of Stars:
- Starts are formed by the accumulation of Hydrogen gas in the form of a very large cloud called a nebula. Such a nebula, by virtue of its mass, attracts nearby gas clouds to grow bigger and denser. Eventually, the growing nebula develops localised clumps of gas, giving rise to the formation of stars.
- These dense gas core, under immense pressure, starts fusing elements, starting a nuclear furnace, where Hydrogen atoms fuse to form higher elements producing immense heat.
Brown Dwarf: [Half Stars/Failed stars] a celestial object intermediates in size between a giant planet and a small star, believed to emit mainly infrared radiation. {70-80 times the mass of Jupiter}
Star Destruction:
A star destroys in one of two ways alone:
- Supernova Explosion: Occurs when a heavy star (greater than 1.4 times the solar mass) dies and explodes.
- White Dwarf: Sun-like stars, when during its end become red giants. When red giants lose energy, they form a planetary nebula, which eventually becomes a white dwarf.
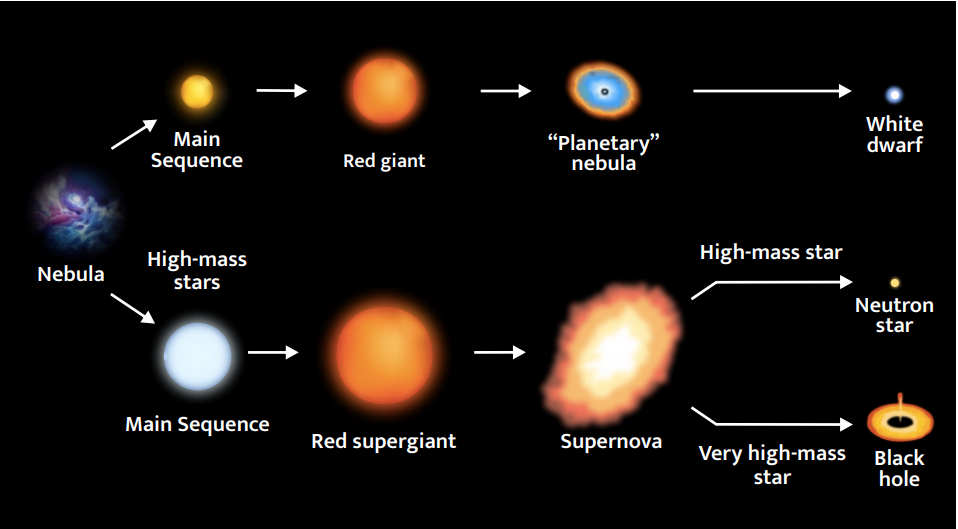
Other important Celestial bodies:
- Neutron Star: What remains after a supernova explosion of a star with a mass comparable to the sun?Its density can be compared to a situation when the mass of the sun is squeezed into one city.
- Black Hole: A region with very strong gravitational effects that not even light can escape. They are formed when very massive stars collapse at the end of their life cycles.
| Did you Know? |
| 10th April 2019: First-ever image of a black hole from observations made by Event Horizon Telescope in 2017 of the supermassive black holes in Messier 87’s galactic centre. Event Horizon Telescope: The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is a large telescope array consisting of a global network of radio telescopes. |
Our Solar System:
Our Sun was formed 5-6 billion years ago from a dust cloud, which we now call Solar Nebula. It consisted of debris from extinct stars and primordial matter, apart from the Hydrogen cloud. The Gravitational forces within this localised nebular lump led to the formation of a core to the gas cloud. This was accompanied by a huge rotating disc of gas and dust.
Gas clouds start being condensed and matter around the core develops into small-rounded objects. They by cohesion develop into a large number of ‘planetesimals‘. Larger bodies start forming by collision, and gravitational attraction causes material to stick together. They accrete to form fewer large bodies in the form of planets.
Formation of Planets:
Solar Nebula started its collapse around 5-5.6bn year followed by the formation of planets at around 4.6bn years ago. OurSolar system consists of eight planets, 63 moons, and millions of smaller bodies – such as asteroids, comets and have huge quantities of dust-grains and gases throughout.
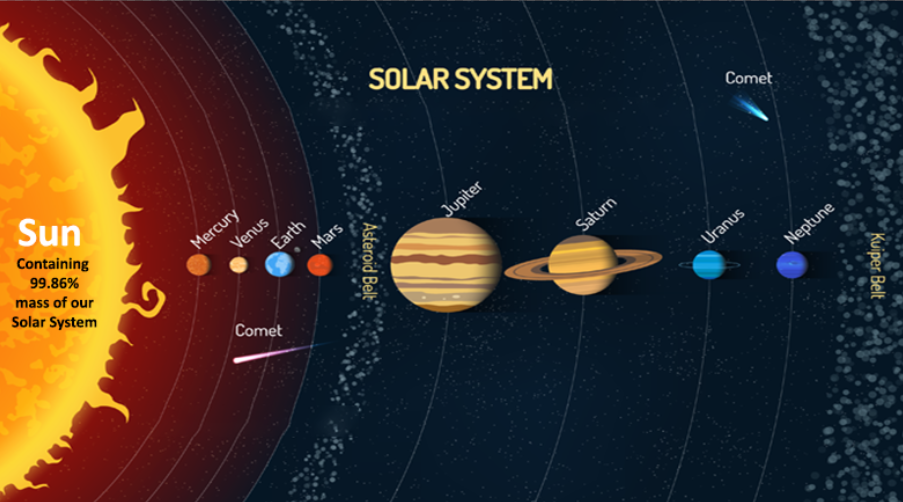
These planets can be classified into two categories:
- Inner planets: The inner planets, or terrestrial planets, are the four planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Terrestrial planets are rocky and have thick atmospheres and mostly Hydrogen (H) and Helium (He).
- Outer planets: Jovian or gas Giants. (‘Jovian’ means Jupiter-like). There are four outer planets in our solar system namely Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
Differences between Inner and outer planets:
- Terrestrial planets were formed in close vicinity of the parent star, where it was too warm for gas to condense to solid particles. Jovian formed at quite a distant location.
- The solar wind has been most intense near the sun. It has blown away almost all of the gaseous atmosphere of these planets. Whereas, the Jovian planets still hold huge amounts of Hydrogen gas.
- Terrestrial planets are small and have low gravity, which again leads to a low capacity for holding air.
Formation of Moon:
In 1838, Sir George Darwin suggested that it was formed by a single rapidly rotating body with the earth. It became dumb-bell-shaped and broke away and depression was occupied by the Pacific Ocean. However, this theory is now rejected.
Modern theories: The Moon formed due to a ‘giant impact’ or ‘the big splat’. A body of 1 to 3 times the size of Mars collided with Earth shortly after it was formed. This blasted-off portion continued to orbit the earth and eventually formed into the present moon 4.4 billion years ago.
Evolution of Earth:
Earth has a layered structure, the atmosphere has low density, and material in different zones has different Characteristics. We shall study the internal structure of the earth in the next chapter. Here we are going to study the evolution of its surface.
Development of Lithosphere:
- Earth formed around 4.6 billion years ago. However, till the formation of the moon (4.4 billion years ago), the history of the earth is relatively unknown. However, after the ‘giant impact’, we know that earth remained in a molten state for millions of years.
- In this primordial age, the materials started getting separated depending on their densities. Heavier metals like Iron sank to the core, and lighter minerals like silicates formed the earth’s mantle and crust.
- Later earth cooled and solidified, condensing into smaller sizes. This led to the development of the outer surface, i.e. crust.
Evolution of Atmosphere and Hydrosphere:
Earth’s Atmosphere formed in three stages:
- Loss of Primordial atmosphere of Hydrogen and Helium; Due to strong solar winds earth’s initial atmosphere (the primordial atmosphere) got stripped off (in the case of all terrestrial planets). It is for this reason that the moon does not have an atmosphere. Only after earth developed its magnetic field, it could hold its atmosphere.
But, howdid we get this atmosphere? It was through degassing.
- Degassing: It is the process of gasses outpouring from the hot interior of the earth. This contributed to the evolution of the atmosphere.
- Continuous volcanic eruption contributed to Water vapour and gases
- During the cooling of the earth, gases and water vapour were released. Early atmosphere contained water vapour, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, methane, ammonia and very little oxygen.
| Formation of Hydrosphere |
| As the earth cooled water vapour condensed, and CO2 got dissolved in rainwater falling on to the surface and being collected in the depressions to give rise to oceans. Oceans were formed within 500 million years of the earth’s formation, i.e. 4000 million years ago.Around 3800 million years ago life began to evolve in the oceans. |
- Photosynthesis: 2500-3000 million years ago photosynthesis evolved. Life was confined to the ocean. They were saturated with O2 and began to flood the atmosphere.
- This modified the composition of the atmosphere.
- Thus, Oxygen from CO2 was ejected in the Atmosphere and Carbon from CO2 was converted into Organic matter.
| Magnetism of Earth |
| The Geomagnetic poles (dipole poles) are the intersections of the Earth’s surface and the axis of a bar magnet hypothetically placed at the centre of the Earth by which we approximate the geomagnetic field. There is such a pole in each hemisphere, and the poles are called as “the geomagnetic north pole” and “the geomagnetic south pole”, respectively. 80.7N 72.7W 80.7S 107.3E On the other hand, the magnetic poles are the points at which magnetic needles become vertical. There also are “the magnetic north pole” and “the magnetic south pole”. 86.5N 162.9E 64.1S 135.9E |
Origin of Life:
Modern scientists refer to the origin of life as a kind of chemical reaction, which first generated complex organic molecules and assembled them.
- The record of life that existed on the planet in different periods is found in rocks in the form of fossils.
- The microscopic structure is closely related to the present form of blue algae that have been found in geological formations that are much older than 3,000 million years ago.
- It can be assumed that life began 3,800 million years ago.
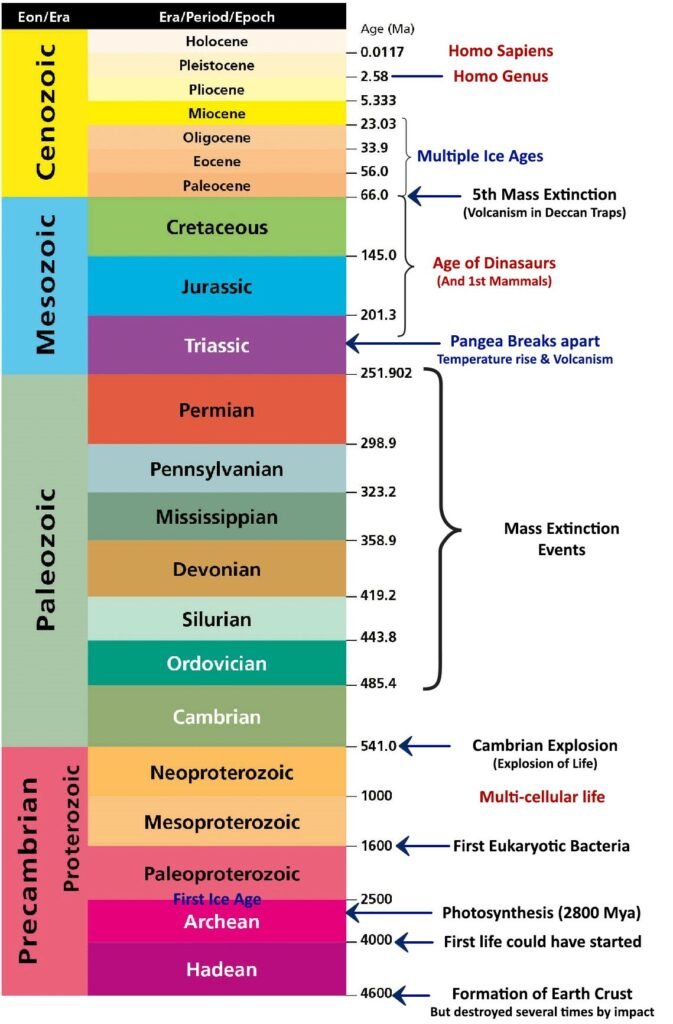
Different stages of the formation of life can be studied from a geological time scale:
| Stanley Miller’s first primordial soup Hypothesis: |
| In 1953, Stanley Miller, an American scientist performed an experiment, in which he mixed Ammonia, Methane & Hydrogen (roughly the initial concentration of the atmosphere), and passed electricity through it. After a few days, he found Amino acids, the building blocks of protein, DNA and life in general. Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: To make protein modern cells follow 3 steps: Transcription: copy genes from DNA to RNA; Translation: use this RNA as a blue-print to make proteins.Replication, i.e. these proteins can produce its DNA replica; |