Chalcolithic Age Notes for UPSC
What is Chalcolithic age?
Chalcolithic is made from two Greek words, khalkos and lithos, meaning copper and stone, respectively. It is a time period dates from 6,500 years ago to around 3000 years ago. This marks the beginning of the use of metalwork technology. For the first time, people started using metals along with stone tools.
In the Indus valley and the adjoining areas, the Chalcolithic Age started around 6500 years ago for the sites such as Kalibangan, Rajasthan. This early start is attributed to the availability of copper mines in the nearby areas, such as the Khetri mines.
The Chalcolithic age in the Indian subcontinent runs parallel to the Harappan civilisation. However, due to the absence of ‘Tin’, these could not develop into the Bronze culture. Nevertheless, these cultures were no less remarkable than the Harappan culture.
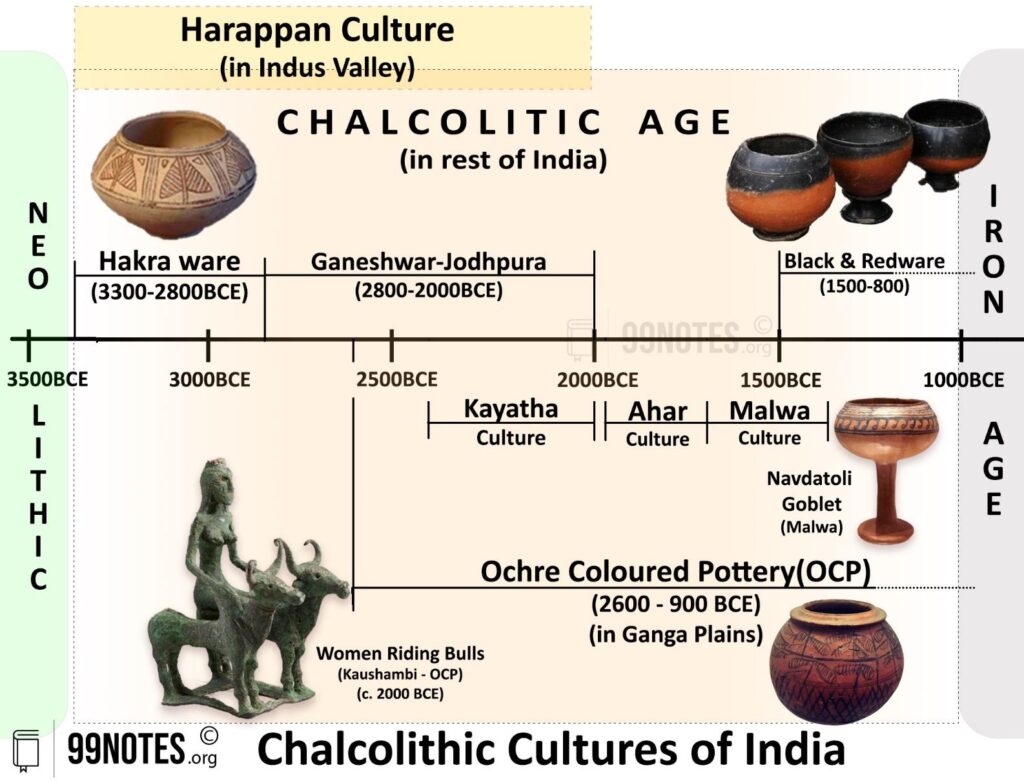
Features of the Chalcolithic Age:
- Introduction of agriculture – People started producing cereals and grains such as rice, wheat, pulses, bajra, and ragi. We find one of the first pieces of evidence of the use of cotton.
- Domestication of Animals – They domesticated many kinds of animals: cows, sheep, goats, buffalo and dogs.
- Shelter – They started to live in rural settlements with mud brick houses.
- Tools – They knew copper smelting. Copper was used for the first time to make tools and other objects.
- Art – The pottery made was black and red pottery and ochre-coloured pottery.
- Religion – The discovery of earth goddess clay images in chalcolithic sites suggests some form of religion.
- Jewellery – The discovery of jewelry in sites shows that they were fond of ornaments and decorations.
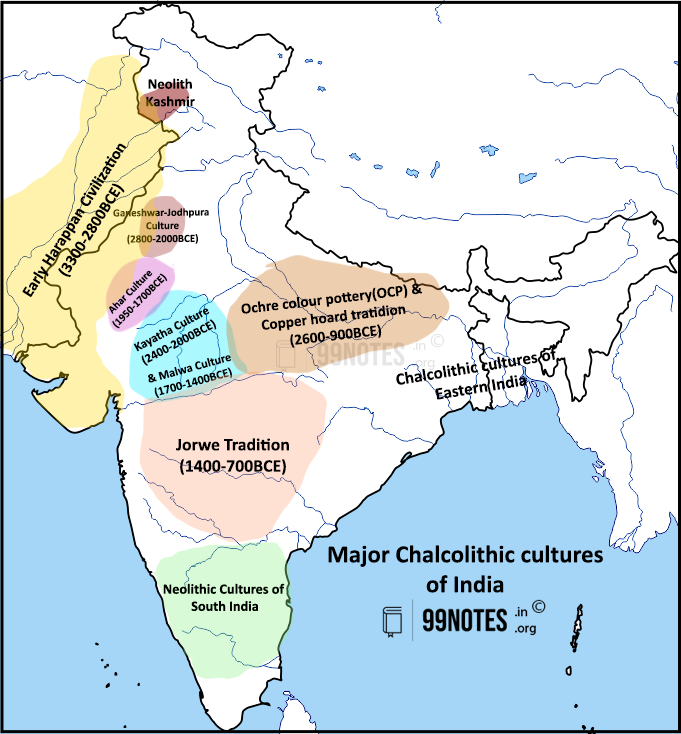
Major cultures of the Chalcolithic age in India
1. Ahar culture (or banas culture, 1950-1700 BC)
This is one of the earliest chalcolithic age cultures of that age in India. The culture is named after Ahar, in District Udaipur, which was the first site excavated in 1961-62 by H.D. Sankalia.
-
- Major sites – More than sixty sites of the Ahar culture have been discovered so far, such as Gilund, Bogor, Balathal and Ojiyana (all in Rajasthan).
- Shelter – People lived in mud brick houses with hearths in some, and in the later part of the culture, they also lived in homes made of stone.
- Industry – There was mass production of ceramics, metal works, and the development of bead industries.
2. Kayatha culture (Madhya Pradesh, 2450-2000 BC)
This site is around Chambal River, Madhya Pradesh. Horse remains have been found at Kayatha.
-
- Shelter – They have mud plastered on their floor.
- Industry – There was a specialised blade industry which produced chalcedony blades.
- Economy – A mixed economy was practised, as seen from the evidence of subsistence farming, stock raising and hunting-fishing.
3. Malwa culture (1700-1400 BC)
This site is around the river Narmada. It is the most predominant culture of chalcolithic age in central India.
-
- Other sites – Nagda, Kayatha, Eran etc
- Shelters – the houses are laid in rows along the road and by lanes. Houses are made of mud bricks and fired bricks at Nagda. It is significant as they are absent at other Malwa sites.
- Industry – large number of ceramic objects have been found.
- Religion – Some terracotta female figurines have been found, and, in some houses, sacrificial altars have been found. Some painted male figures have been found in some wares.
4. Jorwe culture (1700-700 BC)
This culture is Maharashtra’s most important and characteristic chalcolithic culture.
-
- Other sites – Jorwe in Ahmadnagar district, Gujrat; Prakash in the Tapi valley, Daimabad in the Pravara Godavari valley and Inamgaon in the Bhima valley(Maharashtra)
- Shelters – Early Jorwe culture had rectangular houses and a sedentary lifestyle. Late Jorwe culture had circular houses and a semi-nomadic lifestyle.
- Economy – The economy started deteriorating as in late Jorwe culture climate became dry and arid.
- Agriculture – Crop rotation was used. We find the use of barley, wheat, jowar, rice, ragi, green pea, grass pea and lentils here. The late Jorwe culture, however, saw a decline in agriculture.
- Industry – Stone blade industry was present, as evident from the excavations from Inamgaon. Lime making was also an important industry in this culture.
- Religion – Many terracotta figurines were found here.
- Distinct feature – A large number of burials were found here. Children were buried in urns laid in pits. Adults were buried with their ankles chopped off. A four-legged urn burial with an adult skeleton was found here.
5. Ochre Colored Pottery (OCP) culture (2600 to 900 BCE)
It is named after a ceramic type which is highly rolled and fragile. This pottery is red, but when archaeologists excavate it, it leaves an ochre colour on the fingers. Therefore, it is known as Ochre Coloured Pottery.
- It was first excavated at Bisauli and Rajpur Parsu (Uttar Pradesh)
- Other sites – Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana and western Uttar Pradesh, and some sites in the upper Ganga-Yamuna doab, namely, Bahadarabad, Manpur, Bhatpura, Ambkheri and Bargaon.
-
- Shelters-Settlements with well-made floors, mud huts and hearths show their sedentary lifestyle.
- Agriculture– Remains of domesticated animals like cattle and evidence of cultivated crops like rice and barley further provide information on their subsistence practices.
- Distinct feature– Artefacts of this culture are similar to the Late Harappan and Vedic cultures.

Eventually, the Chalcolithic age transformed into the Bronze age in the areas where tin was available. In other areas, it gave way to the Iron age directly. For example, the painted grey-ware (PGW) age is often marked as the Iron Age’s arrival in North India. Although in the initial stages of this age, copper is much more prevalent than Iron.
Conclusion
The Chalcolithic Age, marking the transition from the Stone Age to the Bronze Age, was a pivotal period in human history, characterized by the innovation of metal tools. notably copper, alongside stone tools. This era witnessed significant advancements in agriculture, settlement patterns, and social organization, laying the foundation for future civilization. The Chalcolithic Age represents a crucial phase of cultural and technological evolution, leading to the establishment of urban centers and the eventual advent of more sophisticated metal works in the Bronze Age.
FAQ Related to Chalcolithic Age
1. Which age is known as the chalcolithic age?
Chalcolithic age is a time period date from 6,500 years ago to around 3000 years ago. The chalcolithic Age also know as the Copper Age, just after the stone age, where early humans used both stone and copper tools.
2. What are the main features of the Chalcolithic age?
The main features of the Chalcolithic age include the use of copper tools, the establishment of small villages, agriculture, and the beginning of animal domestication.
3. Who discovered Chalcolithic age in India?
Each chalcolithic site was discovered by different archeologist during various excavations throughout India, but no single individual is credited with this discovery.
4. What time period was the Chalcolithic era?
The Chalcolithic Era in India is generally dated from around 4500 BCE to 1000 BCE, varying regionally and overlapping the later stages of the Indus Valley Civilization.
5. What is the difference between Chalcolithic Age and Mesolithic Age?
The Chalcolithic Age marks the use of metal (copper) and more advanced agriculture, while the Mesolithic Age was known by microlithic tools and a hunter-gatherer lifestyle transitioning towards food production.
Explore additional significant articles on Ancient Indian History listed in the table below:
| Age of Satvahanas | Stone Age |
| Harappan Civilisation | Vedic Culture |
| The Mahajanapadas | Persian and Greek Invasions |
| Mauryan Empire | Gupta Empire |






![Complete Vedic Period Upsc Notes [1500 Bce-500 Bce] | Updated March 7, 2026 Complete Vedic Period Upsc Notes [1500 Bce-500 Bce]](https://99notes.in/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/vedic-culture-99notes-upsc-1-768x495.webp)

