Delhi Sultanate- History, Rulers with Maps, and Administration (UPSC Notes)
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate known as one of the India’s rich historical time-period. This empire rulers from the 13th- 16th century, played a pivotal role in shaping the country’s culture, architecture, and society. Delhi Sultanate was a series of Islamic dynasties that ruled over the Indian subcontinent. It began with Ghurid invasion in 1192, establishing first Muslim rule in Delhi. Over the period various dynasties, such as Slave Dynasty, Khilji Dynasty, Tuglaq Dynasty, Sayyid Dynasty and the Lodi Dynasty, left their marks on the region. Lets discuss in detail:
Muizzuddin Muhammad, also known as Muhammad of Ghor, defeated the Chahmana ruler Prithviraj Chauhan in the Second battle of Tarain in 1192 CE. This defeat paved the way for further Ghurid expansion into India. The Rajputs failed miserably in forging any alliance to recover the lost territories.
In 1206, Qutubuddin Aibak established the Delhi Sultanate after declaring his independence from the Ghurids. The establishment of the Delhi sultanate resulted in profound changes in India’s society, administration, and cultural life.
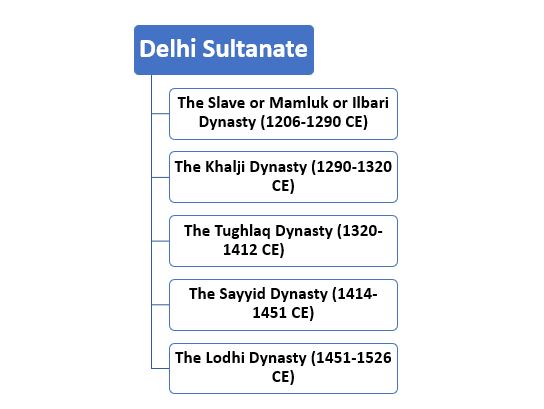
Dynasties in Delhi Sultanate
As we have discussed above that Delhi Sultanate was a series of Islamic dynasties that ruled over India from Delhi.
1. The Mamluk or Ilbari or Slave Dynasty (1206-1290 CE) of Delhi Sultanate
- Muhammad of Ghor, Sultan of the Ghurid Empire, was killed in 1206 CE. His empire was split into regions led by his former Mamluk (a non-Arab slave soldier who had converted to Islam)
- Qutb-ud-din Aibak was the founder of slave dynasty, also we can say founded the Delhi Sultanate under the Slave dynasty.
| Region | Ruler |
| Ghazni | Taj-ud-Din Yildoz |
| Bengal | Muhammad bin Bakhtiyar Khilji |
| Multan | Nasir-ud-Din Qabacha |
| Delhi | Qutbuddin Aibak |
- The Slave or Mamluk dynasty is also called the Ilbari dynasty, as most of the rulers were of the Ilbari tribe, such as Iltutmish and Ghiasuddin Balban. However, Qutbuddin Aibak was of the Aibak tribe.
- People of Humble origin were often given a high rank in the Slave dynasty.
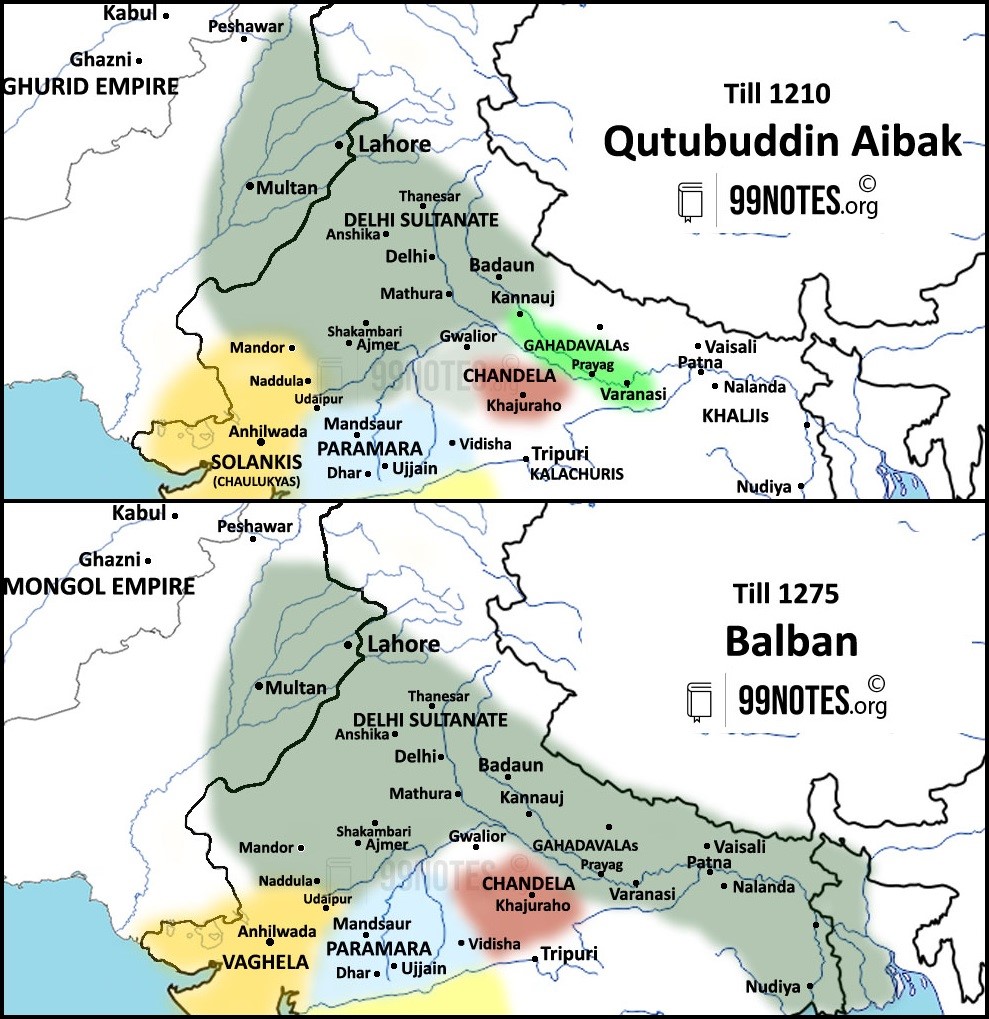
- Qaiqabad (1287-1290 CE) was the last ruler of slave dynasty; he was killed after getting paralysis. After his death, his son Kayumars was killed by a group of nobles led by Arz-i-Mamalik (military head) and Malik Firuz (Later known as Sultan Jalaluddin Firuz Khalji).
2. The Khalji/ Khilji Dynasty (1290-1320 CE)
The Khalji/ Khilji were of Turk–Afghan. Their rise in power in India ended the monopoly of Turkish nobles and officials. After the
Khilji Dynasty Rulers
1. Jalal-ud-din Khalji (1290-1296 CE)
- Jalal-ud-din Khilji was the Founder of Khilji Dynasty
- He couped against the Slave dynasty rulers at the age of 70, removed some of the harsh rules of Balban and avoided harsh punishments.
- Expeditions under his son-in-law Alauddin Khalji, whom he titled Amir-ul-Tuzuk.
- Alauddin led an expedition to Devagiri, which was ruled by Ramachandra Deva of the Yadava dynasty in 1296. he killed him in Kara (Kaushambi, U.P).
- Rebellions during his regime were –
- Malik Chhajju’s (Governor of Bengal) Revolt was repressed. Chhajju was spared despite the protest from Alauddin.
- Noble Tajuddin Kuchi was humiliated publically for his intention to revolt.
- Sidi Maula(a Sufi saint) was executed on the allegation of conspiracy against the King.
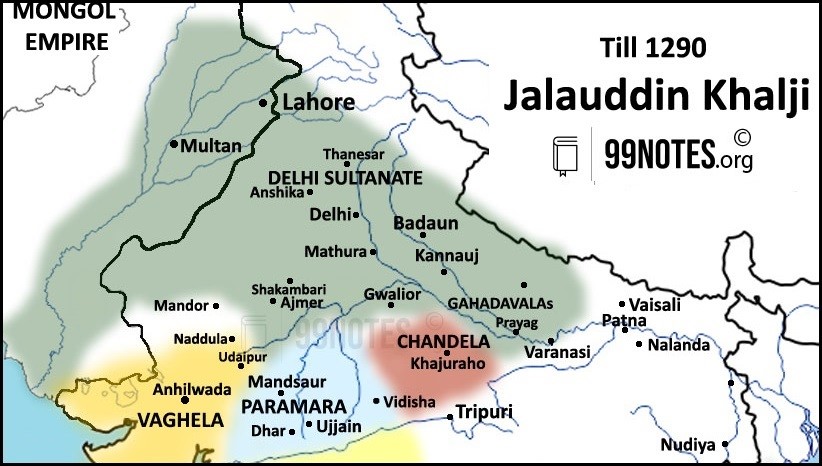
2. Alauddin Khalji (1296-1316 CE) (Early Name: Ali Gurshap)
- Capital: at Siri, a city near Delhi founded by him).
- He proclaimed himself Sultan after killing
- Reintroduced of Blood and Iron policy:
- Nobles were forbidden to hold festivities and marriage alliances without the permission of the Sultan.
- He banned the use of wine and intoxicants.
- Spies were employed against nobles.
- Mongols attacked six times during 1296-1306 during Alauddin’s reign, with the attack of 1303 being particularly fierce. However, he was successful in repulsing the attacks.
- Military reforms introduced to fight Mongols(after 1303 Mongol attack):
- He was the first Sultan to pay the army in cash.
- Introduced the Dagh System (branding of horses) and Chehra System (maintenance of description of each soldier).
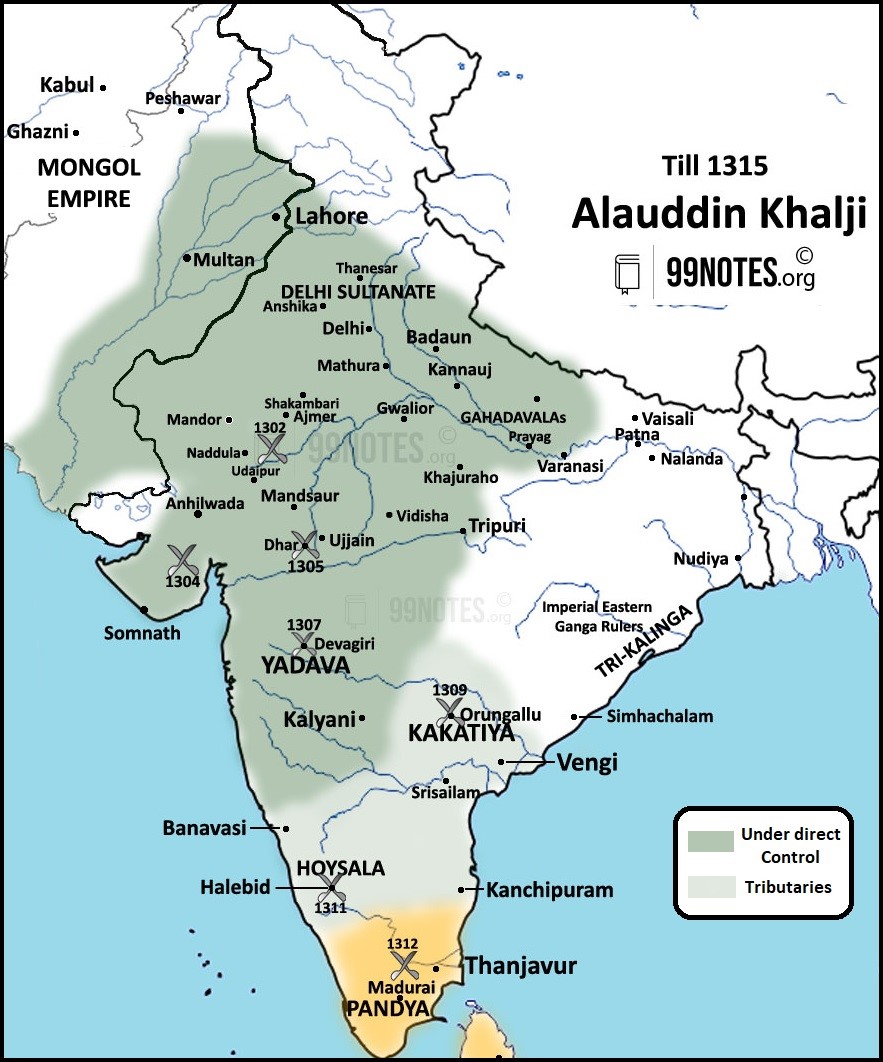
- Conquests in the North (till 1306)
- Made Malik Kafur (captured during the Gujarat expedition) his Malik-Naib (Military general).
- Rajasthan(1302), Gujarat(1304) and Malwa(1305) – under the command of Nusrat Khan and Ulugh Khan, his brother.
- The Rajput rulers were allowed to rule by paying regular tribute and obeying Sultan’s orders.
- Alauddin’s Conquests in the South(1307-1313) –
- In 1296, Devagiri was raided for the first time, and in 1307, the Yadava territory fell to Malik Kafur’s forces almost without a fight.
- In 1303, Kakatiyas bravely defeated Delhi’s forces in the Battle of However, In 1309, Malik Kafur subjugated them.
- In 1310, Yadavas helped Kafur to invade the Hoysala territory.
- In 1311, he tried to invade the Pandyan country, too, when it was dealing with a war of succession, and returned with a great amount of plunder.
- Amir Khusrau (Indo-Persian Sufi singer, musician, poet and scholar) accompanied the sultans on the expeditions.
- Conquests in the North (till 1306)
Constructions under Alauddin’s regime:
- Built Fort of Siri (1302 CE), where the Palace of one thousand pillars (Hazar Satun), Hauz-i-Khas and Huaz-i-Ilahi were also built.
- Alai Darwaza near Qutub Minar.
- Jamayat Khana Masjid near the tomb of Nizamuddin Auliya (who was a famous sufi in his time).

3. Qutb-ud-din Mubarak Shah (1316-1320 CE),
the last ruler, withdrew the blood and iron policy and Introduced the policy of Forgive and Forget. He was killed by Khusrau Khan.
- Qutb-ud-din Mubarak Shah was the last ruler of Khilji dynasty.
- Khusrau Khan was 2 months later defeated by Ghazi Malik (Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq) , the governor of Dipalpur (Punjab, Pakistan), which ended the Khalji Dynasty.
3. The Tughlaq Dynasty (1320-1412 CE)
Origin of Tughlaqs:
- According to Ibn Batuta, the tughlaqs belong to the Qarauna tribe of Turks who lived between Turkistan and
- Ghiyasuddin’mother was a Jatt noble, and his father was likely descended from Indian Turkic
Tughlaq Dynasty Rulers
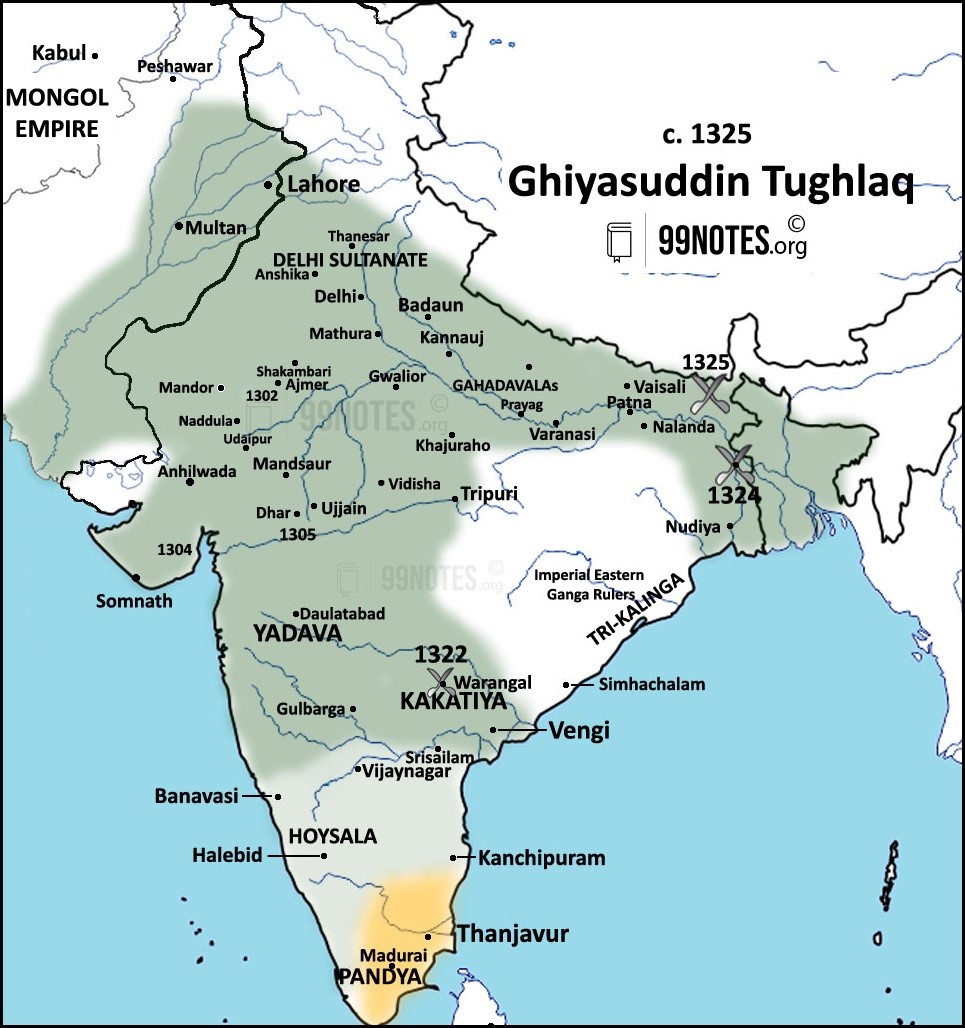
1. Ghiyas-ud-din Tughlaq Shah or Ghazi Malik (1320-1325 CE)
- Ghiyas-ud-din Tughlaq Shah was the founder of Tughlaq Dynasty
- In the five-year period of his rule, he expanded the empire in Bengal and consolidated the territories of Warangal. During his time, the Delhi sultanate reached the peak of its extent.
- Religious discrimination Policy: He lowered the tax rate for Muslims and raised the tax for Hindus.
- He was an effective Administrator:
2. Muhammad bin Tughlaq (1325-1351 CE) (Birth Name: Jauna Khan)
- He got the title of Ulugh Khan and ruled as Muhammad bin Tughlaq.
- Sources of History of his rule:
- Ibn Batuta (a Moroccan traveller) visited India during his rule. He appointed Ibn Batuta as Qazi of Delhi and later sent him to the court of the Chinese ruler as an ambassador. Ibn Batuta wrote a book Qitab-ul-Rihla.
- Had a court historian Ziauddin Barani who wrote Tarikh-i-Firoz Shahi, which covers the Tughlaq dynasty.
- Failed Expeditions under Mohammad bin Tughlaq –
-
- He founded a fortified city called Jahanpanah near Delhi in 1327 to address the threat of Mongol invasions.
- He planned to conquer Khurasan and Iraq in 1329. But later abandoned the plan.
- He attacked Qarachil (Kumaon hills, Himalaya) in 1330 to counter Chinese incursion. He wanted to bring the tribes of the Kumaon-Garhwal region into Delhi Sultanate.
- Rebellions after 1335 –
-
- The Vijayanagara Empire was established in 1336 CE by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I in the Deccan.
- In 1336 Kapaya Nayak recaptured Warangal from the Tughlaq army, establishing the Musunuri Nayaka State.
- In 1338, his nephew rebelled in
- By 1339, the eastern regions under local Muslim governors and southern parts led by Hindu kings had declared independence.
- In 1347, Bahmani Sultanate became independent in the Deccan region.
- Attempt towards Agricultural reforms:
-
- Set up a separate department called Diwan-i-amir-i-kohi for agriculture.
- Gave takkavi loans (loans for cultivation) to cultivators.
- However, this policy also failed, probably due to corruption among officials and the inability of cultivators to repay loans.
-
- Mohammad-bin-Tughlaq took several disastrous decisions for which he is called the “wisest fool in history” or “The Mad King”.
-
-
- Transfer of Capital: He transferred his capital from Delhi to Deogiri in 1327 to consolidate southern territories and protect himself from foreign invasion. He renamed it But after the Bengal revolt, he shifted back in 1329. After his return, rulers of the south declared independence.
- He increased the tax rates in the Ganga-Yamuna Doab region and levied additional cesses called This could have led to famine during his rule.
- He introduced Token coins (fiat currency) of copper and bronze; this failed as the forgery of coins increased.

-
-
- Showed some religious tolerance:
-
- He was the 1st Sultan who visited the tomb of Moinuddin Chishti in
- Built the tomb of Nizamuddin Auliya in Delhi.

- He conversed with Muslim mystics, Hindu yogis and Jain saints (like Jinaprabha Suri), including Muslims of various races as nobles.
- Allowed important offices to Muslim converts and a few Hindus.
- Repaired Shamsi Mosque of Badaun.
-
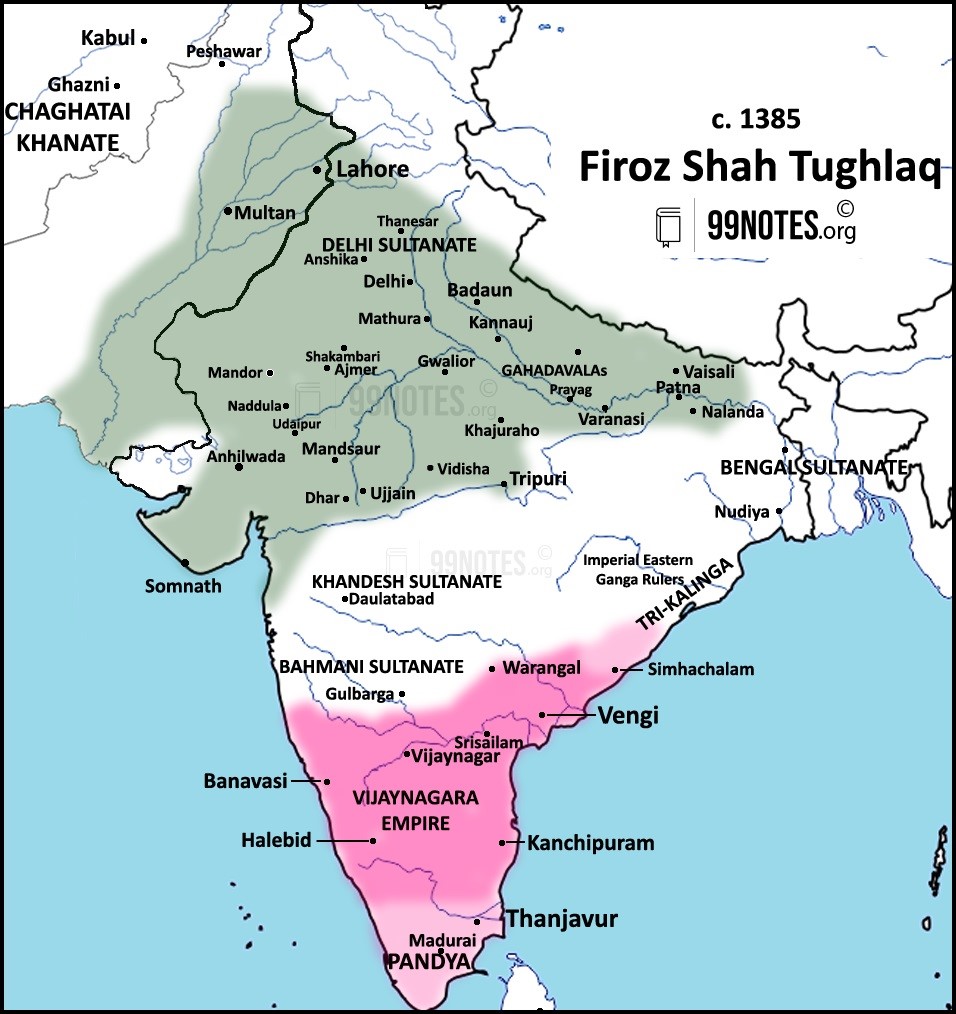
3. Feroz Shah Tughluq (1351-1388 CE)
- Adopted a policy of appeasement of Nobles, theologists and the army.
- Sources of Feroz Shah’s history:
- He wrote a memoir Futuhat-i Firoz Shah.
- He made Arizuddin Khan translate 100s of Sanskrit manuscripts taken from Nagarkot (Nepal) and elsewhere into Persian under the name Dalail-i-Firozshahi.
- Ziauddin Barani and Shams-i-Siraj lived in his court.
- Reforms in his times:
- Wrote off the loans under Muhammad bin Tughlaq.
- Built free hospitals like Dar-ul-Shafa and marriage bureaus for poor Muslims and ordered the kotwals to make lists of unemployed persons.
- Established Diwan-i-Khairat, an office for charity, and Diwan-i-Bundagan, a department for slaves.
- Established Sarais (rest house) for merchants and travellers.
- Made and repaired canals for irrigation.
- Banned torture as punishment.
- Loosening Grip on Administration and Army:
- He made the position of the army officers and Nobles hereditary, thereby allowing them more power
- He paid the army not in cash but by assignments on the land revenue of villages, which gave birth to powerful feudatories.
- Increased the number of slaves in the rule and posted them in the army and royal workshops (Karkhanas).
- Military Campaigns:
- He did not attempt to reassert the authority in South India and Deccan, which gained independence during Mohammad bin Tughlaq’s times. He, however, crushed the rebellions in Gujarat and Thatta.
- He led two unsuccessful campaigns in Bengal. His armies desecrated the temples in Jajnagar (Orissa) but couldn’t annex the state.
- Led a campaign against Kangra in Punjab Hills.
- His Religious intolerance was aimed at pleasing Muslim orthodoxy, which was a desperate attempt to gain control over his decaying empire.
- He prohibited the practice of Muslim women worshipping at the graves of saints and persecuted several Muslim sects which were considered heretical by the orthodox Muslims.
- For the 1st time, Jaziya (tax on non-Muslim subjects of the rule) became a separate tax; earlier, it was a part of land tax.
- Constructions under him:
4. Nasir-ud-din Mahmud Shah Tughlaq (1394-1412 CE)
- Son of Feroz Shah, Nasiruddin Mahmud, sat on the throne but could not control the rebellious nobles and governors.
- By his time, the army, too, had become inefficient.
- Nasir-ud-din Mahmud Shah Tughlaq was the last ruler of Tughlaq Dynasty
- The invasion of Timur in Delhi in 1398 ended the Tughlaq dynasty, and Nasiruddin Mahmood was displaced in 1412.
4. The Sayyid Dynasty (1414-1451 CE)
- The Sayyid claimed to be the descendant of the Prophet Muhammad.
- After Timur attacked Delhi in 1398, he appointed Khizr Khan as the Governor of Multan. Khizr Khan captured Delhi and established the Sayyid dynasty in 1414.
Rulers of Sayyid Dynasty
| Rulers | Features |
| Khizr Khan (1414-1421) | · He ruled as the Rayat-i-Ala (vassal) of the Timurids.
. Khizr khan was the founder of Sayyid Dynasty. · He didn’t take the title of Sultan but took small titles such as Masnad-i-Aali (Most High Post) and continued to mint coins in the name of previous Tughlaq rulers. |
| Mubarak Shah (1421-34) | · Succeeded in his father’s small kingdom.
· Yahya bin Ahmad Sirhindi wrote Tarikh-i-Mubarakshahi during his rule. · Established a new town Mubarakabad on the banks of the Yamuna River. |
|
Alam Shah (1445-1450) |
· Alam Shah, was the last ruler of Sayyid Dynasty, abdicated his small kingdom and retired to Budaun, U.P.
· Bahlul Khan Lodi (the governor of Sirhind in Punjab) captured Delhi in 1451. |
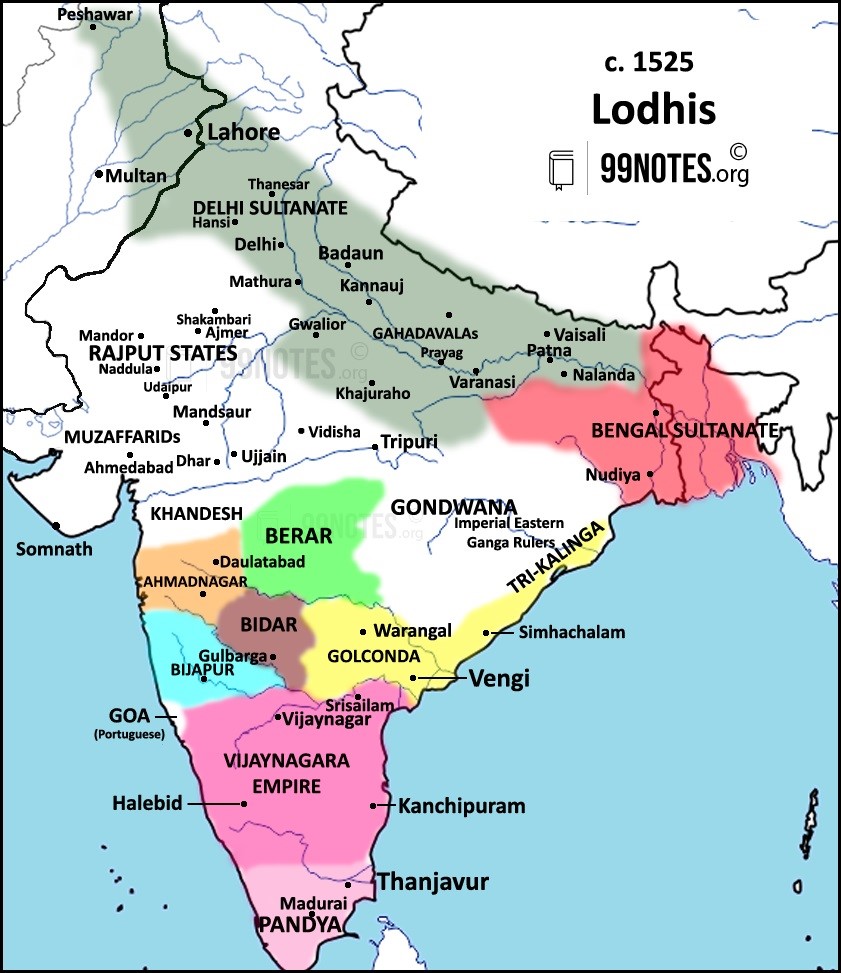
5. The Lodi Dynasty (1451-1526)
- The Lodis were the members of the Pashtun Lodhi tribe.
- The kingship was highly centralised during the rule of the earlier Turkish Sultan of India, and Sultan’s absolute power was absolute.
- But for the Afghans, the King was ‘the first among equals‘.
Rulers of Delhi Sultanate:
| Rulers | Features |
| Bahlul Khan Lodi (1451–1489)
(Capital – Delhi)
|
. Bahlul Khan Lodi was the founder of Lodi Dynasty.
· He annexed Delhi from the Sharqi dynasty of Jaunpur U.P. · He never sat on the throne in front of his fellow Afghan nobles nor organized an open darbar. · Called his Afghan nobles Masnad-i-Ali. |
| Sikandar Shah Lodi (1489–1517)
(Born as Nizam Khan) (Capital Agra) Built by Sikandar Lodi in 1516
|
· He took up the title Sikandar Shah.
· He founded the city Agra and Sikandrabad and made Agra his capital. Administrative Changes: · He demanded obedience from his nobles and held an open durbar, unlike his father. · Started the audit practice to check the accounts of Muqtas and Walis (governors). · Refined the intelligence system. · He banned the use of languages other than Persian in government offices. · Founded a new measurement of a yard called Gazz-i-Sikandari. Social initiatives: · Opened charity houses for impoverished and disabled people and gave financial aid to educational institutions. · During his reign, Ayurvedic books were translated under the title Tibb-i-Sikandari. Military Expeditions: · He annexed Dholpur (Rajasthan); thus, Rajputana and Malwa regions came under his rule. · He also annexed the forts of Narwar and Chanderi of Madhya Pradesh. · Khanzada of Nagaur (Rajasthan) accepted his suzerainty. |
| Ibrahim Lodi (1517-1526) | · Ibrahim Lodi was the last ruler of Lodi Dynasty.
. Babur defeated Ibrahim Lodi in the first Battle of Panipat (April 20, 1526), which ended the Lodi dynasty. · Babur was invited by the governor of Lahore, Daulat Khan Lodi and the governor of Dipalpur Alam Khan Lodi. |
Administration of Delhi Sultanate
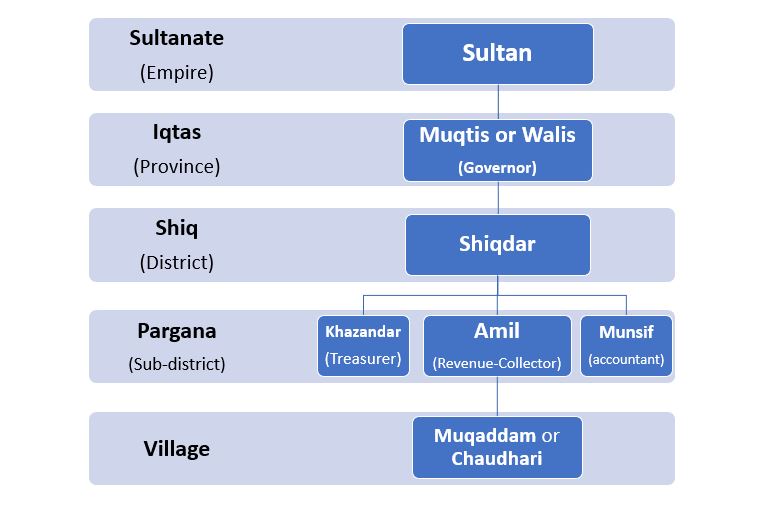
- The empire was divided into Provinces(Iqtas), districts (Shiqs) and Sub-districts(Pargana) for efficient collection of revenue.
Central Administration
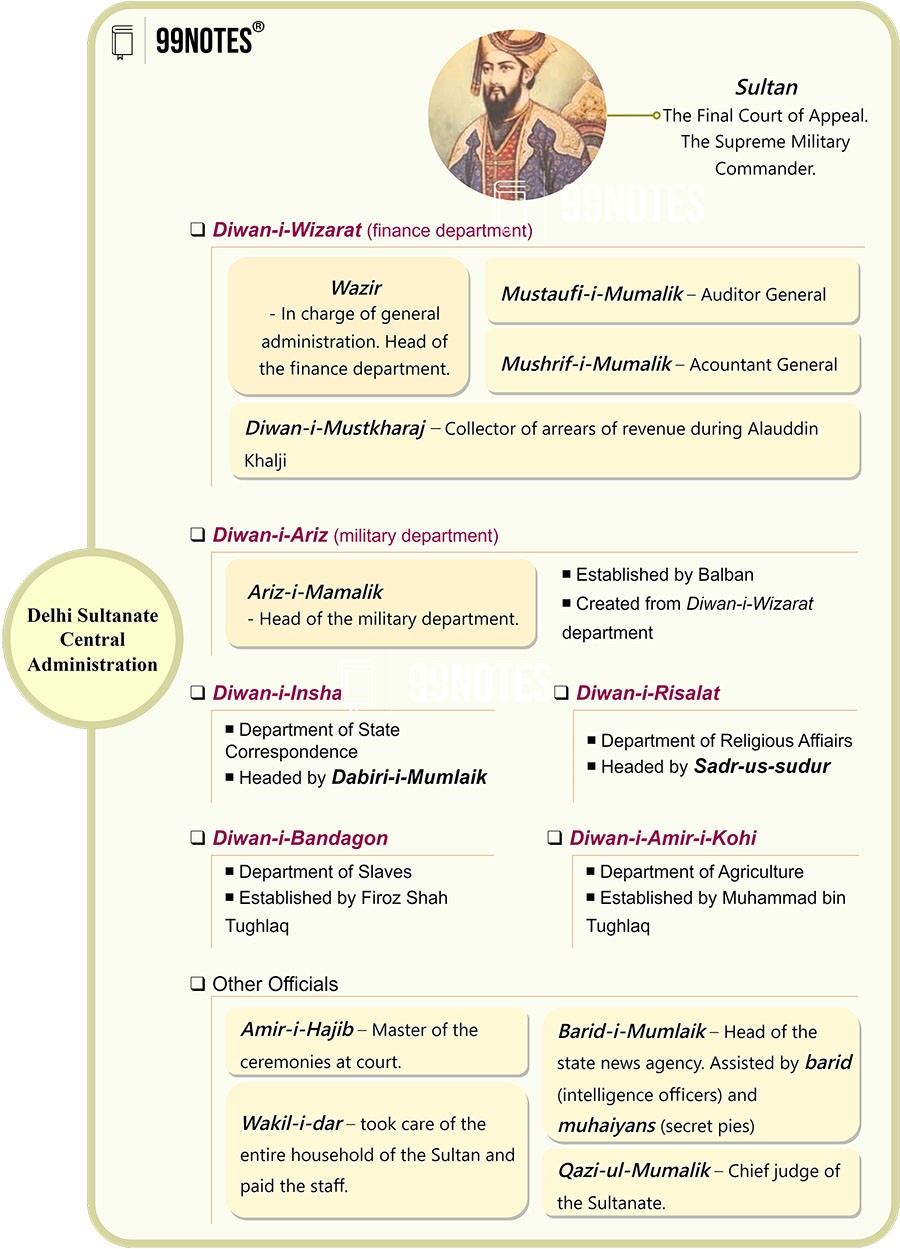
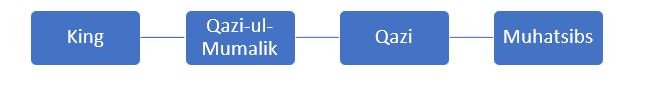
- King or Sultan – Sultan was the head of the Delhi sultanate.
- He was the supreme commander of the army and the highest Judicial authority.
- Caliph recognised him by granting robes of honour, letters of investiture and titles.
- Sikka or coins were inscribed with King’s name, and Khutba (sermons at mosques) were read in his name.
- Wazir – He looked after general administration and was head of the finance department Diwan-i-Wazarat.
- After the Sultan, he was the most influential member in the central government and had wide supervisory authority over other officials.
- Khwaja Jahan was a very powerful Wazir who tried to play the role of Kingmaker after the death of Firoz Shah. After this incident, no Sultan allowed the concentration of power in Wazir’s hands.
- The following officials helped him –
| Mushrif-i mumalik | Accountant-general |
| Mustaufi-i mumalik | Auditor-general |
| Diwan-i mustakhraj | Collector of arrears of revenue during the reign of Alauddin Khalji |
- Arz-i-Mamalik – He was the head of the Diwan-i-Arz (Military Department).
- Balban introduced this department.
- His function was to inspect the troops maintained by the Iqta-holders and supervise the supply and transport of the Sultan’s army.
- Important officials
| Officials | In Charge of |
| Barid-i mumalik | Head of the State news agency. Under him, barids(Intelligence officer) and munhiyan(secret spies) worked and sent news to him. |
| Wakil-i-dar | Took care of the entire household and paid Sultan’s staff. |
| Amir-i-hajib
|
Master of ceremonies at the court. Through him, all petitions to the Sultan were submitted. |
- Important Departments at the Central level:
| Department | Work |
| Diwan-i bandagan | The department of slaves was established by Firoz Shah Tughlaq. |
| Diwan-i-amir-i-kohi | Department for agriculture, which Muhammad bin Tughlaq set up. |
| Diwan-i insha | State correspondence and was headed by Dabir-i mumalik. |
| Diwan-i rasalat | The highest religious office, it was headed by Sadr-us sudur. |
- The Judiciary
Provincial Administration

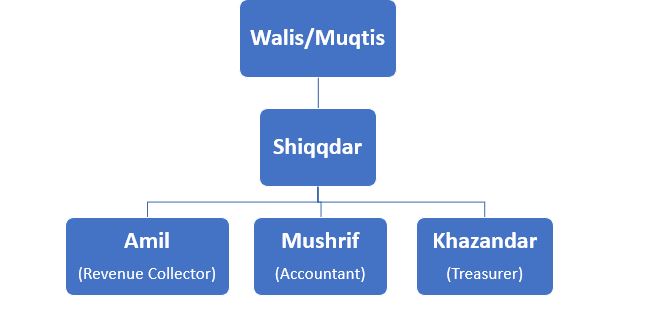
- The whole empire was divided into Iqtas (provinces). The Iqta System originated from the Caliphate Administration of Western Asia. Iltutmish introduced this system in the Delhi sultanate.
- Iqtas were actually the revenue assignments given to high-ranking nobles (Walis/Muqtis) instead of cash payments for their services to the Sultan.
- However, this posed a challenge:
- As the noble could become a virtual lord of the land.
- There was not enough land to be awarded to all nobles. Those nobles with an Iqta were known as
- The Sultans could not solve this problem:
- Alauddin Khalji had to abolish the whole Iqta system during his rule to subdue his nobles. But since nobles were important to maintain the empire, later, sultans revived it.
- Initially, the revenue assignments were non-hereditary and transferable. But during Feroz Shah Tughlaq’s rule, the Iqta assignment was made hereditary to appease the nobles, which ultimately caused the downfall of the Tughlaqs.
- Functioning of the system:
- Iqtadars collected revenue for their expenses and the expenses of their troops and sent the surplus (Fawazil) to
- They were helped at the Pargana level by Amil, Mushrif and Khazandar.
Local/Village Administration
- Rural aristocracy included Khut, Muqaddam and Chaudhri, who collected land revenues (Kharaj) from the peasants and deposited them with the officials of Diwan-i-Nizarat (Revenue department)
- Muqaddam, or Chaudhri, headed the village, and Khut was the revenue collector. Patwaris were the village accountant.
- The revenue collectors were allowed to have remuneration called Haqq-i-Khuti or Haqq-i-Muqaddam, which was the exemption from the revenue of a portion of land they held.
- They also took some share of the revenue from the peasants, called Qismat-i Khoti or Qismat-i-Muqaddam.
Military of Delhi Sultanate
- Sultan was the commander-in-chief of the army.
- Balban introduced a separate military department – Diwan-i-Arz, headed by Arz-i-Mamalik.
- The army consisted of cavalry, infantry and elephant
- Infantry:
- The Sultans often purchased slaves (Bandagan) for military service.
- The infantry was recruited from slaves or people of humble origin, and even Hindus.
- These foot soldiers (Payaks) also consisted of some archers (Dhanuks).
- Cavalry:
- The cavalry was the most important unit of the army since it enhanced its manoeuvrability.
- Alauddin Khalji introduced three levels of soldiers –
-
-
- Murattab – They had no horse of their own.
- Sawar – Persons having one horse each.
- Do-aspa – A person having two horses. Such a system was introduced to increase the speed of the army.
-
-
- Supply Horses:
- Horses were brought from Arabia, Turkistan and Russia. This import dependence made Indian rulers vulnerable.
- Thus, Sultans like Firuz Tughlaq established breeding centres (Paigahs) for horses.
- The Officer-Incharge of the Horse Stables (Qurkhana) was called
- The Turks introduced the saddle and These had given the Turks an edge over the Indians as these helped the mounted archer strike with speed without fear of falling.
- Supply Horses:
- Elephants came from Bengal.
- Shahna-i-Pil looked after elephants and was superintended for elephants.
- Firearms
- The Alauddin’s army had rudimentary artillery, as evident from the word Sang-i maghribi as midfa (canon) in the Sultanate literature. They also used catapults. The southern kingdoms faced such technologies for the first time and had no defence against them.
- Tughlaqs used fireworks and rockets against Timur, but he had better firearms, which led to his victory.
- Army Logistics:
- Zarradkhana supplied the arrows and catapults. It also replaced broken weapons.
- The food was supplied to the army on the march through
- The Intelligence system:
- The Talaiah/Yazkis was a wing of the army that moved ahead of the main army to bring the news of the enemy army.
- Sahib-i-barid-i lashkar (news writer) sent reports of the army expedition to the centre.
- The military court was known as Qazi-i Lashkar.

Maintenance of the Army in Delhi Sultanate:
- The Sultan kept a standing army, while Nobles were expected to maintain a fixed number of soldiers in exchange for payments (or revenue assignments).
- Soldiers could be assigned 3 types of services:
- Hashm-i-Qalb or Afwaj-i qalb, which consisted of Khasa Khel (royal slaves and guards), was posted in the capital
- Hashm-i atraf were those posted outside the capital.
- Mufrads were other unattached soldiers.
- Payments:
- Wajhi were the soldiers who were paid regularly.
- Ghair-Wajhi were the soldiers recruited on an irregular basis who were paid by way of drafts (Itlaq, Barat). These drafts could be encashed by the Sultan’s revenue officers of the Khalisa (Crown or reserve land).
- Royal Security
- The most loyal slaves were appointed as Royal Bodyguards (Jandar), who were headed by Sar–
- During public appearances, Sultans were protected by fully armed soldiers called Silahdars, who were under the charge of Sar-silahdar.
- They were paid a hefty salary.
Reforms were introduced by Various rulers of Delhi Sultanate in the army.
- Balban: separated the military department as Diwan-i-Arz.
- Alauddin Khalji started payment in cash for the first time in Delhi Sultanate. This reduced the dependence on feudal lords.
- He introduced the Dagh (branding of horses) and Chehra or Huliya (maintaining the description of every soldier) system in the army.
- He introduced three levels of soldiers – foot soldiers, ek-apsa (one horse) and do-apsa.
- Firoz Shah Tughlaq started paying the Wajh soldiers by the grants of villages which was hereditary.
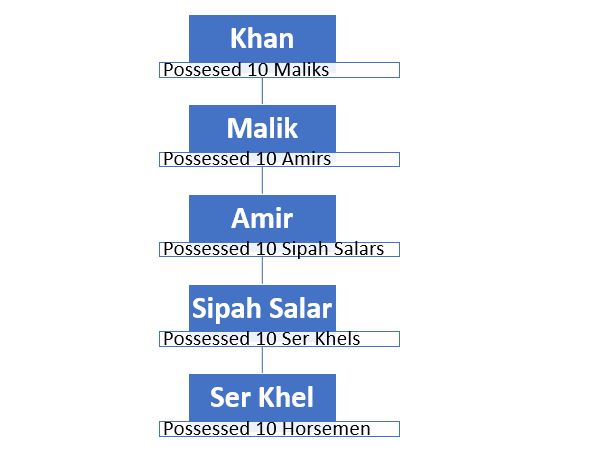
The Decimal System of the Army
- The Sultanate army adopted the Mongol decimal system of the military hierarchy, in which a Khan (a military general) had more than ten thousand horsemen under his command.
- The Sultan was placed above all the Khans.
Conclusion
After the Ghurid Invasion of North India, various Sultanates got established in India, of these Delhi Sultanate proved to be the strongest and ruled over large part of India for many years. They were eventually displaced by the Mughals. Their socio-cultural impact is discussed in the next article.














![Tripartite Struggle (790-1162Ad) History, Cause &Amp; Consequences [Upsc Notes] | Updated February 23, 2026 Tripartite Struggle (790-1162Ad) History, Cause & Consequences [Upsc Notes]](https://99notes.in/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/tripartite-struggle-featured-768x500.webp)