The Rajput Dynasty/States- UPSC Notes
The Rajput States – Famous Rajput Dynasties
After the fall of the Gurjar-Pratihara Empire, several Rajput states emerged in north India. The most significant of these were the Paramaras of Malwa, Chandellas in Bundelkhand, Chaulukyas (Solankis) of Gujarat, Chauhans of Ajmer and the Gahadavalas of Kanauj.
There were other, smaller dynasties spread throughout the country, such as the Kalachuris of Tripuri (near what is now Jabalpur), the Loharas of Kashmir, the Tomars of Delhi, and the Kachchhapaghats of Gwalior.
The GhaznavidsMahmud of Ghazni(998-1030): Mahmud took the reign from his father, Sabuktigin, the first ruler of the Ghaznavids, who ruled from Ghazna. He brought a large part of Persian and Central Asian territory into his empire. Historians in Ghazni’s courts: · Firdausi, also known as the ‘homer of the east’, wrote Shahnama. · Al-Biruni wrote the famous Kitab-ul-Hind, an account of India. Expedition in India: · Conflict with Hindushahis who dominated the northwest frontier of India – Mahmud fought a fierce battle against Jayapal in 1001 CE in the battle of Waihind/Peshawar. Mahmud’s forces severely routed Jayapal, and his capital of Peshawar was devastated. · He also defeated Jayapal’s successor Anandpal/Anantpal, in the battle of Chach and captured Punjab. ·In 1015 he tried to invade Kashmir but was unsuccessful due to unfavourable weather conditions. · In 1018, he led three expeditions in the Gangetic plains to amass wealth. First, he plundered the city of Mathura, followed by an attack on Kannauj, the capital of Pratiharas and the wealthiest city of Hindustan. · In 1022-23, he raided the Ganga Plains again and received bounties from Indian rulers. · In 1025-26, he raided Somnath temple on the Saurashtra coast of Gujarat twice after crossing the Thar Desert. In the 2nd raid, Jats inflicted heavy losses on Mahmud’s forces. He came again in 1027 for the last time to avenge the Jats. · After his death, Ghaznavid raids continued. For example, in 1033, Varanasi was raided again. Fall of Ghaznavids: · A war of succession broke out after the death of Mahmud, which weakened the empire. · Resistance in Central Asia: The Persian and Central Asian territories were soon lost. Seljuk Turks frequently raided the Afghan territories. · Resistance in India: First, under the Parmara king Bhoja in the 1040s, Ghaznavid governors were removed from Hansi and Thanesar. Then, another resistance started under Gahdavals in the 1090s. · Finally, Ghurids ended the last of Ghaznavids in the late 12th century. |
Chandela dynasty:
The Chandellas of Jejakabhukti
- They ruled over central India (Bundelkhand) between the 10th-13th centuries. Their territory was known as Jejakabhukti (modern Bundelkhand). Khajuraho, Kalanjara and Mahoba were their three capitals.
- Nannuka (831–845 CE), is the founder of the Chandela dynasty, initially ruled a small kingdom centred around Khajuraho as a feudal king under Pratiharas.
Independent rule of the Chandela dynasty:
- Dhanga(950CE-999CE) was the first ruler to formally establish Chandella’s sovereignty. According to the Khajuraho inscription, he ruled in the Chedi region, Kalinjar and Gwalior (Gopadri mountain – ruled by Kachchhapaghata Rajputs) till the banks of Betwa and Yamuna rivers.
- During Vidyadhar’s reign (1003-1035), several invasions of Mahmood of Ghazni took place. Finally, in 1018, after the raid and plunder of Kannauj by Ghaznavids, Vidyadhar took control of the Kannauj, and the Chandella power reached its largest extent.
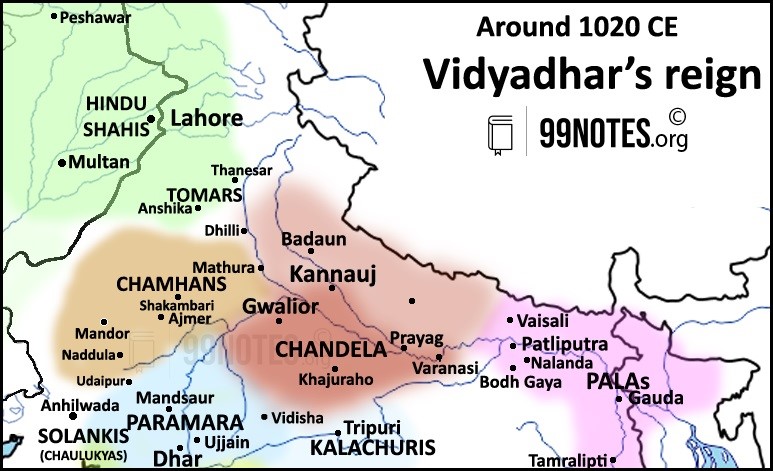
Fall of Chandela Dynasty:
- The Ghaznavids raids in the 1020s could have somewhat weakened the empire. For example, in 1023, Ghaznavids forced the Gwalior fort to pay tribute.
- The Kalachuris occupied the Chandella kingdom for at least 4 decades after the death of Krittivarman(1060-1100) and Sallakshanvarman(1100-1110) defeated the Kalachuris and the Paramars, reviving the Chandella power for some time.
- Parmardi (1165-1203) was the last great Chandella ruler. During the later part of his reign, he lost some of his territories to Prithviraj Chauhan.
- The celebrated legendary fighters Udal and Alha, who were brothers, served as generals under Parmardi. They lost their lives fighting Prithviraj in the Battle of Mahoba, according to Medieval Ballads.
- He also faced the invasion of Qutub-ud-din Aibak at the end of his reign.
- The Chandela Dynasty ruled for 100 more years but with a greatly diminished power.
Cultural Impact of Chandellas:
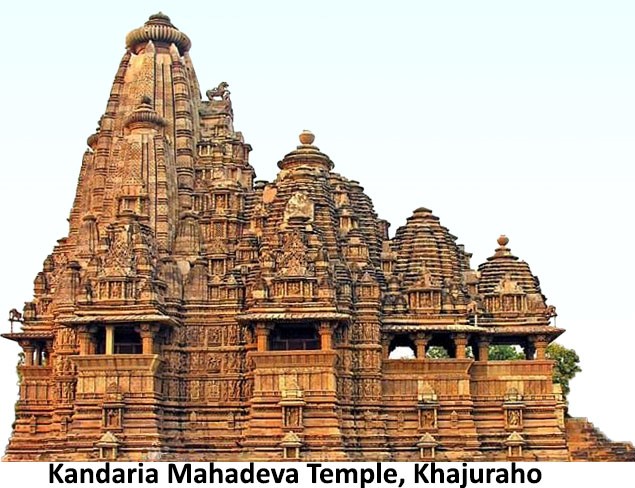
- The Chandelas are renowned for their art and architecture. Most notable among them are the temples at their original capital
- The Kandariya Mahadev Temple is well-known for its aesthetic brilliance. An inscription in the temple Mandapa names king ‘Vrimda’ as the constructor of the temple. Some historians believe him to be king

Parmar Dynasty: The Paramaras of Malwa
- The early Paramaras were established as the vassals by the Rashtrakutas of Manyakheta to counter their common enemy, the Gurjara Pratiharas.
- They mainly ruled over the Malwa region between the 9th and 14th centuries. Their capital was situated in Dharanagar(Dhar district).
- The Udaipur Prashasti and Nagpur Prashasti are two important sources used to reconstruct Parmara History.
Independent rule of Parmara Dynasty:
- Siyaka(940-972CE) was the first Independent ruler of the Paramaras. Harsola Copper Plates suggest that Siyaka was a Rashtrakuta feudatory initially. However, he defeated the Rashtrakutas in 948 CE, declaring their independence.
- Paramaras also sacked the Rashtrakuta capital Manyakheta in 972, which eventually led to the downfall of Rastrakutas, who was replaced by the Western Chalukyas of Kalyani.
- Bhoja (1010-1055 CE), the legendary Parmar ruler, brought the Paramara might to its peak. He was given the title of Parameshwara-Parambhattaraka.
Expansion under King Bhoja
- Against Western Chalukyas: King Bhoja was a part of the triple alliance of the Rajendra Chola with Kalachuris and the Parmaras.
- Against Ghaznavids: He is said to have helped Hindushahis against Ghazni. He could also have been a part of the Hindu alliance in around 1043CE, which was formed to expel the Ghaznavid governors from Hansi and Thanesar.
- Against weaker neighbours: He raided the Chahmana territory and might have even captured their capital Shakambari for some time.
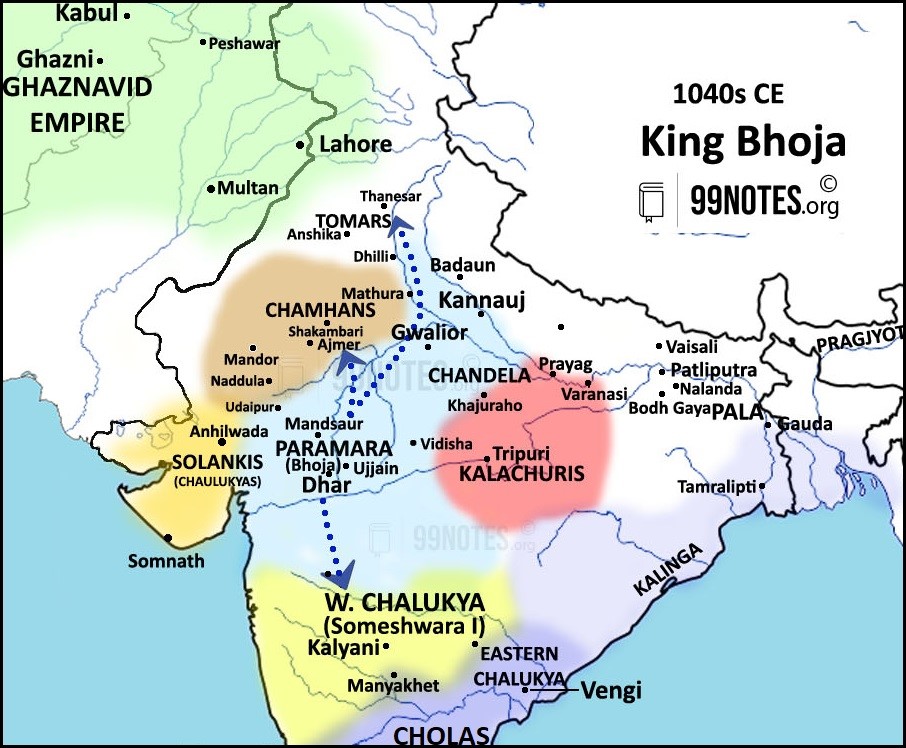
Cultural contributions of King Bhoja
- He founded the city of Bhojapur, where he constructed the Bhojeshwar Temple.
- He is also credited with writing books on philosophy, poetics, yoga and
- Dasabala, who wrote Chintamani-Sarnika(1055 CE), was king Bhoja’s court poet.
Fall of Paramara Power:
- A War of succession broke out after king Bhoja’s death.
- Loss of Independence:
- Kalachuris allied with the Solankis of Gujarat to occupy the Parmara Kingdom in the late 11th century.
- Solanki King Jaysimha occupied it in the late 12th century.
- Regular raids from the south:
- In King Bhoja’s later years, the Western Chalukyan ruler Someshwar I raided Dhara.
- Later, Hoysalas and Yadavas of Devagiri invaded the kingdom.
- From the 13th century, Parmaras faced regular incursions from the rulers of the Delhi Sultanate. It was finally Alauddin Khilji who killed the last Parmara ruler in 1305.
Chaulukya Dynasty: The Chaulukyas/Solankis of Gujarat
- The Chalukyas, then the feudatories of the Gurjara-Pratiharas, possessed the region of Gujarat and Kathiawad in about 950 CE.
- By taking advantage of the disturbance and anarchy in the Pratihara kingdom, they were able to carve out an independent principality of their own in Saraswati valley.
Independent rule of Solankis:
- They reigned over parts of Gujarat and Rajasthan between 940-1244 CE, with their capital at Anhilawada, modern Patan.
- During the reign of Bhimadeva I in 1025 CE, the famous Somanath Temple was plundered by Muhammad of Ghazni.
- In the 11th century, Solankis were first engaged with the Parmaras and then with the Chauhans of Shakambari and the Chauhans of Nadulla.
- King Jaisimha Siddharaja (1092-1142) turned Solankis into an imperial power, greatly expanding the kingdom.
- He defeated and annexed the Parmara kingdom of Malwa.
- He also waged wars with Chandellas but could not succeed.
- He made the Chauhans of the Nadulla, his vassal.
- He also defeated the Chauhans of Shakambari and later turned them into an ally by marrying his daughter to the Chauhan king Arnoraj.
- He also defeated the Soorma ruler of Sindh.
- He might have also checked the advance of Western Chalukyan ruler Vikramaditya VI.
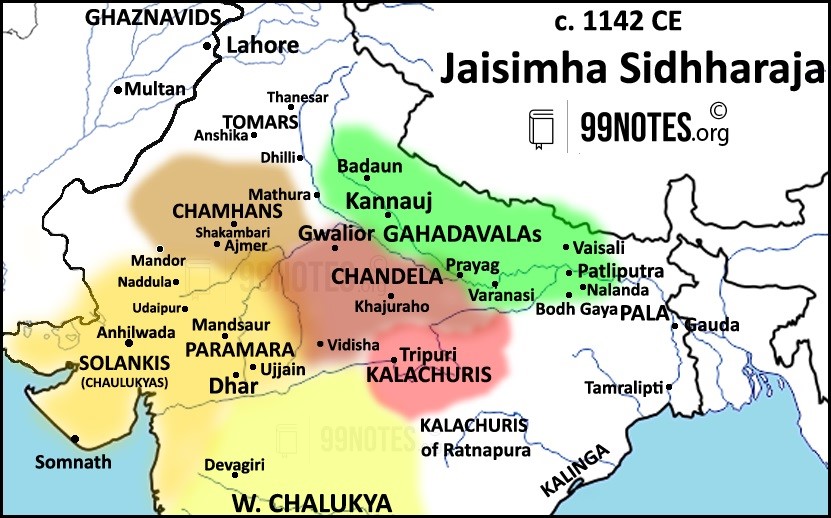
- King Kumarpala (1143-72) continued his stronghold on the empire despite many rebellions. He remained quite fierce in dealing with rebels despite his adoption of Jainism.
Fall of Chaulukya Dynasty:
- Ghurid Invasions: In 1178, Mohammad of Ghor tried to invade Chaulukyan territory but was defeated by the Chalukyas. But, after the fall of Chauhans, Ghurids invaded the Chaulukyan capital Naharwala in 1197.
- Paramaras gained independence after the Ghurid invasions. They captured the Lata region and also raided the Chaulukyan capital.
- Solankis also faced strong Yadava incursions from the south several times.
- Northern feudatories declared their independence twice whenever Bhima II(1178-1240) was busy in the south.
- The power was usurped by Vaghelas in the 1240s, who were practically managing the kingdom’s affairs much before actually declaring their rule.
Māru-Gurjara architecture:
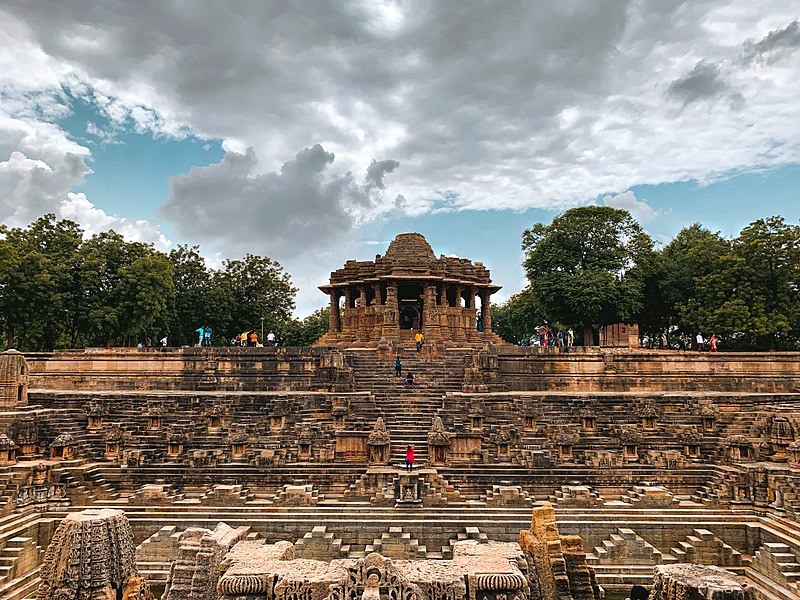
- Māru-Gurjara architecture or Solanki architecture is a style of north Indian temple (both Hindu and Jain) architecture that originated in Gujarat and Rajasthan from the 11th to 13th centuries under them.
- The famous Sun temple at Modhera and Rani-ki-vav, built by Queen Udayamati, are exquisite examples of this type of architecture.

Tomar Dynasty: The Tomars of Delhi
- Little is known about the early Tomars of Haryana. However, according to the Bardic traditions, they formed a sovereign territory around Dhillika (Delhi), possibly around the 10th century CE. They ruled between Delhi and Hansi (Anshika).
- Anangpal Tomar (1051-1081) was the most famous ruler of the Tomars.
- He could have received help from Paramara King Bhoja when an alliance of Hindu kings repelled Ghaznavid Governors from Anshika (Hansi) and
- He is believed to have built fort Lal Kot in Dhillika (Delhi) and fort Aligarh in Anshika (Hansi). Later, Fort Asigarh became a manufacturing centre for high-quality swords in India.
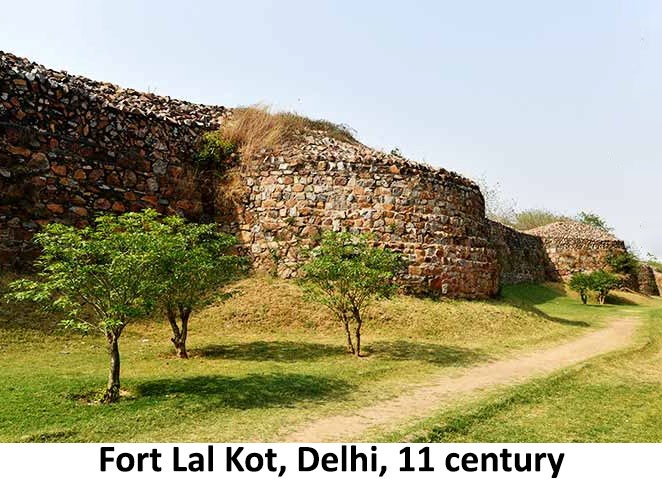

- Conquests with Chahmanas: A number of Chahman inscriptions mention their fierce conquests with the Tomars or Tamvars. The fort Lal Kot in Delhi was attacked and captured several times by the Chahmans, according to these inscriptions. In 1152, a powerful Chahmana invasion led by Vigrahraja annexed the Tomar territory.
- Reconstruction of Tomar History is done with huge difficulty using indirect sources of other rulers. We have only three conflicting manuscripts that tell about the Tomar dynasty lineage. One is the Gwalior manuscript of Khadag Rai, the second is Abul Fazl’s Ain-e-Akbari, and the third is one Kumaon manuscript.
Chauhan Dynasty: The Chauhans/Chahmanas of Ajmer
- The Chauhans of Shakambari (Sambhar) were initially the most important feudatory of the Gurjara Pratiharas.
- Durlabha Chauhan was the legendary commander of the Pratiharas king Vatsaraja’s campaign in the Ganga valley during the Tripartite struggle for Kannauj in the 8th century CE.
- Chahamanas rose to power after the decline of the Gurjara-Pratiharas.
Independent rule of Chauhan Dynasty:
- In the mid-10th century, king Lakshmana established their second branch at Nadulla (today’s Nadol), now referred to as the Chauhans of Nadol, which was independent of the Pratiharas.
- Then, his elder brother Simharaja(944-971), the king of Shakambari, declared his independence by adopting the title Maharajadhiraja.
- Then king Ajayaraja (1110-1135) founded the city of Ajayameru (modern Ajmer) as the political centre and seat of power.
- Till the time of king Vigrahraj(1150-64), Tomar territory was annexed by the Chauhans.
Chamhana Conflict with the Solankis:
- Till the early 11th century, Parmaras were the common threat to the Solankis as well as the Chauhans. After their fall, Solankis and Chauhans got into fierce conflict with each other.
- The Chauhans of Nadulla were subjugated by the Solankis.
- The Shakambari Chauhans faced regular aggression from Solankis. Nevertheless, several attempts for peace were made by the Solankis.
- Solanki ruler Jaisimha married his daughter to the Chauhans in the early 12th
- Further, a peace treaty appears to have existed between Solankis and Chauhans in the 1180s.
Prithviraj Chauhan:
- Prithviraj III, also known as Rai Pithora in folklore, was the most well-known of the Chauhan kings. He was only eleven when he assumed the throne in the period about 1177, but he assumed full control of the kingdom at the age of sixteen.
- He immediately embarked on a vigorous policy of expansion, bringing many of the smaller Rajput states under his sway.
- Prithviraj Chauhan defeated Muhammad Ghori in the first battle of Tarain or Thaneshwar in 1191.
- However, in 1192 Muhammad Ghori invaded again and defeated the 25-year-old Prithviraj in the second battle of Tarain. There is no clear consensus on whether Prithviraja died in the battle or was captured.
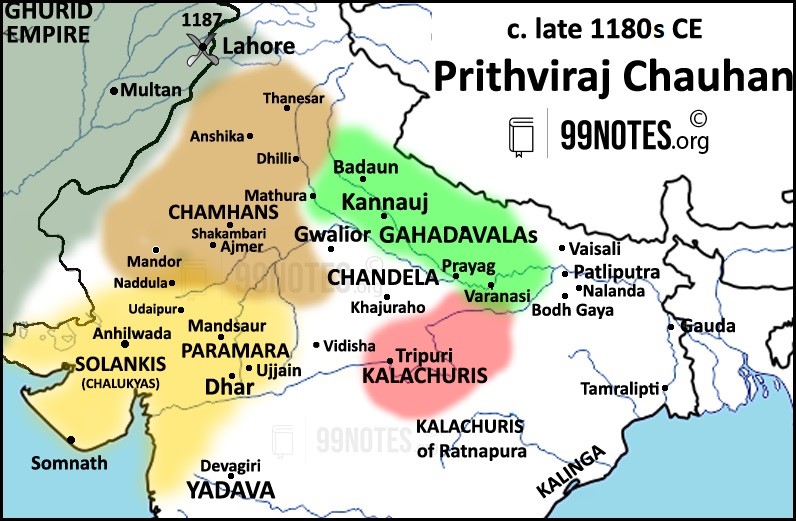
Reasons for the fall of Chahman Dynasty:
- Fratricidal wars with Neighbours: Prithviraj Chauhan led an expedition against Chandelas in their capital, Mahoba, where legendary warriors Alha and Udal lost their lives.
- In addition to the Gahadawalas, the Chalukyas (Solankis) and the Chandelles were the Chahamanas’ greatest rivals.
- Division within Chauhan Clan: Chahmans of Nadol, for example, remained loyal feudatories of the Solankis for a long time.
- Prithviraj became a legend in folklore, and his heroism has been written in books like Prithviraj Raso and Prithviraj.
Literary sources on Prithviraj:
- “Prithviraj Vijaya” is a eulogistic poem written in Sanskrit by the court poet of Prithviraj, Jayanaka.
- He could have been a Kashmiri Brahmin as his language matches the famous Kashmiri poets Bilhana and Kalhana.
- Prithviraj Vijaya gives the complete lineage of the Chahmans and lists his battles. It covers the 1st battle of Tarain and abruptly ends without covering the 2nd
- Its accuracy is corroborated by Chahman inscriptions.
- “Prithviraj Raso” is written by Chand Bardai.
- The language of Apabhramsa used in the poem points out that it was written much later than the events it mentions.
- It gives a highly conflicting view that the Gahadaval ruler Jaichandra/Jaichand invited Mohammad Ghori due to personal animosity with Chauhans.
- However, neither of the dozens of inscriptions of both the Chahmans and Gahadavals hint at this aspect, nor the Jayanka’s Prithviraj Vijaya tell about it.
The Gahadavalas of Kannauj
- The Gahadawalas occupied Kannauj in the 11th century. They ruled over the major portions of the Gangetic doab during 1090-1193 from Kannauj. Little is known about their origin.
- Independent rule of Gahadavals:
- Chandradeva(1089-1103), who ruled from Kannauj after the end of the last Pratihara ruler, established the Gahadava power. Chandradeva captured Banaras and made it his second capital. He brought stability to the middle Ganga plain after the fall of Parmara king Bhoja and Kalachuri King Lakshmikarna.
- King Madanapala(1104-1113) defended his territory against the Ghaznavids, whose ruler Masud III had declared a holy war to capture the doab region. His son Prince Govind Chandra played a major role in these campaigns.
- Gahadaval power reached its peak during the reign of Govind Chandra (1114-1155). Under him, the Gahadvar kingdom extended from Mongyr in Bihar to Delhi.
Fall of Gahadavals:
- Jai Chandra (1170-1193), who ruled from Varanasi, was the last prominent Gahadaval ruler.
- He had the largest empire of all Rajputs in his time, according to Ibn Athir‘s Kamil ut Tawarikh.
- Although Prithviraj Raso mentions his conflict with Prithviraj, No Gahadaval inscription or the inscriptions of the neighbouring Rajputs mention any such conflict.
- He lost his life in 1193 while fighting with the Ghurids.
- Harishchandra (d. 1197) continued to control Kannauj and Varanasi after his father, Jai Chandra’s death. In the Kotwa inscription, he assumes the sovereign titles of Maharajadhiraja, Parmeshwar and Parambhattaraka.
- It was only during the reign of Iltutmish that Kannauj was captured. He celebrated this victory by issuing coins.
The Ghurids· The Ghurids were centred in the Ghor (in central Afghanistan) as local chiefs. · In 1163, Muhammad Ghori became king and immediately started rapid expansion. · In 1173, he captured Ghazni and threatened to capture Punjab, which was under the Later Ghaznavids.
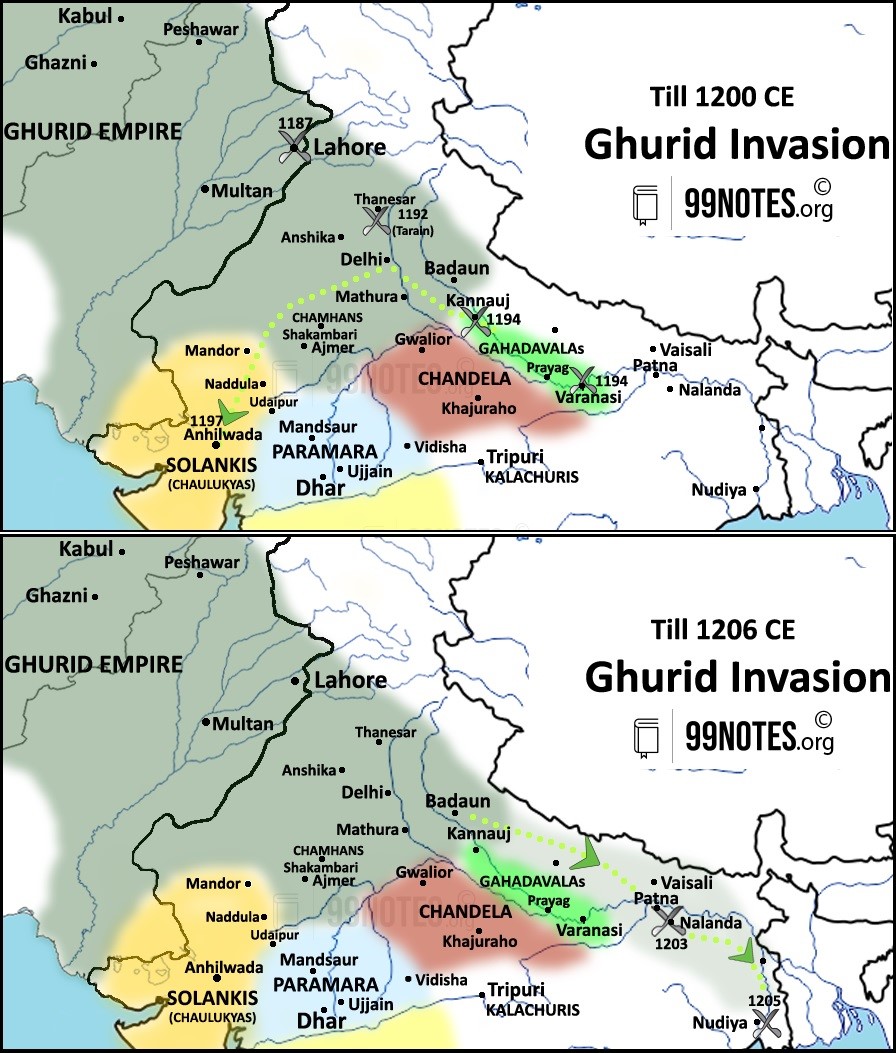
Ghurid Conquest of India: 1. Attack on Solankis: o Ghurids first tried to attack Rajputana in 1178 by crossing the Thar Desert. They faced Chalukyas/Solankis in the battle of Kayadara/Kasaharad in 1178 under the leadership of Nayiki Devi, the Queen regent of infant king Mularaja. o The joint forces of Solankis and their feudatories, Parmaras of Abu, Chahmans of Nadol & Jalor, defeated the Ghurids badly. In this battle, the Shakambari Chauhans(under Prithviraj) declined to help since they saw the Chalukyas as much arch-rival as the Ghurids. 2. Conquest of Punjab: He attacked Peshawar in 1179-80 CE and marched towards Lahore in order to the Ghaznavid ruler Khusrau Malik in 1181 CE. He overthrew the last Ghaznavid principality of Lahore under Khusrau Malik in 1186 CE. 3. The first battle of Tarain 1191 CE o Ghori took control of Punjab’s Tabarhinda (Bhatinda) fortress, which was strategically vital to the security and defence of Delhi. Perhaps this was why Prithviraj Chauhan reached Tabarhinda without wasting any time to reverse the situation. o In the battle fought in 1191 CE, Prithviraj won and left Ghori badly wounded. 4. The second battle of Tarain 1192 CE: In 1192 CE, Turkish forces attacked for the second time, and Prithviraj maintained complacency for some reason. This time Ghori came with good preparation and a carefully planned strategy to defeat the Chauhans. o Prithviraj Chauhan was badly defeated in this war and was caught by the Turkish forces. 5. Battle of Chandawar: In 1194 CE, a big Ghurid cavalry marched towards Kannauj and Benaras, where Gahadvalas under Jaichand was defeated. 6. Muhammad-bin-Bakhtiyar Khilji, a general of Ghori, led expeditions in Bengal and Bihar between 1203-1206, where he attacked Odantapuri, a prominent Buddhist monastery and destroyed the University of Nalanda and Vikramasila. Ghori appointed one of his loyal slaves Qutubuddin Aibak as his governor of the Indian territories captured by him after the 1st Battle of Tarain. o He initiated the Slave Dynasty in India, the first Muslim rule. o Much of the attacked Ganga plains retained its independence even after these initial attacks. |
Nature of Turkic Conquest:
- Nature of Ghaznavid raids in the 11th century:
- The aim was to gather wealth: In medieval times, plunder was a means that kings deployed to gather wealth. Such was the nature of Ghaznavid raids too. It seems that Mahmud had no intention of extending territory beyond Punjab. However, in the 12th century, several attempts were made to capture the Ganga plains.
- Religious Motivation: Again, in medieval times, religion often motivated alliances and attacks, such as Rajendra Chola’s alliance with the Khmer kingdom. Ghaznavid kings, too, wanted to portray themselves as the Champion of Islam.
- Difference from Raids of Indian kings: Indian kings plundered temples but respected the deities of other kings. However, Mahmud’s aim was the total annihilation of temples. In the 7th year of his reign, he issued coins from Lahore naming him Mahmud But-Shikan (Mahmood, the breaker of idols).

- Nature of Ghurid attacks at the end of the 12th century:
- The aim was to establish a territory in India: In fact, the loyal slaves of Ghurids conquered more territories in India after Ghori’s death to extend their rule in India, thereby establishing the Delhi Sultanate, the first Muslim state in India.
- Religious Motivation: Ghurids account mention that Aibak destroyed thousands of temples during his campaign for Kashi and Chandella territory.
Conclusion: The power of the Rajput kings declined significantly after the Ghurid invasion of India, even though their rule continued in their respective city-states as feudal lords of their region. Nevertheless, the cultural impact of the Rajputs was significant, as seen in the next article.




![Tripartite Struggle (790-1162Ad) History, Cause &Amp; Consequences [Upsc Notes] | Updated March 13, 2026 Tripartite Struggle (790-1162Ad) History, Cause & Consequences [Upsc Notes]](https://99notes.in/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/tripartite-struggle-featured-768x500.webp)




