Advent of Europeans in India in Chronological Order- Complete UPSC Notes
Advent of Europeans in India
The history of modern India can be traced back to the advent of Europeans in India. The trade routes between India and Europe were long and winding, passing through the Oxus Valley, Syria, and Egypt.
We have already seen the advent of Portuguese in the Medieval India. We shall see the advent of Dutch, English, French and other powers in this chapter.
Contemporary European powers in India
The Portuguese were confined basically to the southwest coast of India in the 16th The English expanded their trading networks to include the Coromandel Coast, Bengal and Gujarat.
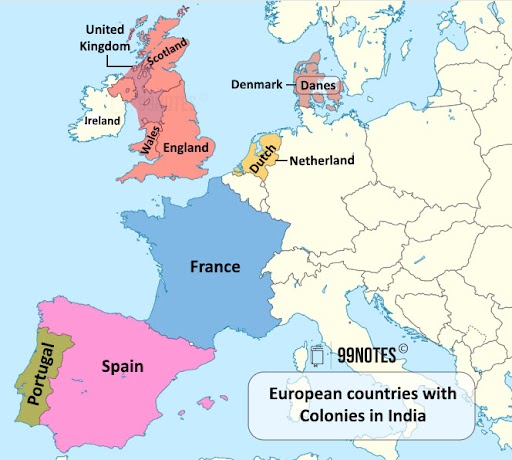
The Dutch
The Dutch are an ethnic group (with a shared history, culture and languages) native to the Netherlands.
Dutch Arrival in India
- Cornelis de Houtman was the first Dutch to reach Bantam and Sumatra in Indonesia in 1596.
- The East India Company of the Netherlands was formed in 1602 by The States-General, the national governing body of the Dutch republic.
- This company was empowered to carry on the war, conclude treaties, take possession of territory, and erect a fortress.
- The Dutch established their first factory in Masulipatnam (Andhra Pradesh) between the Krishna-Godavari basin in 1605.
- They established their capitals at Pulicat (in 1610 and again in 1781), Nagapatnam (in 1690) and Sadras (in 1818).

Dutch East India Company factory in Hugli-Chuchura, Mughal Bengal
Expansion of Dutch in India
The Dutch built factories on the Coromandel coast in Gujarat, Bihar, Bengal, and Uttar Pradesh.
Prelaya Kaveri (Pulicat Lake) was ruled by Queen Eraivi, wife of King Venkata II of the Vijayanagara Empire. In 1608, under her rule, the Dutch East India Company was permitted to construct a fort and engage in trade.
They opened a factory in 1609 and built Fort Geldria in 1613 in Pulicat. Their other vital factories in India were at –
- Surat (1616)
- Bimlipatam (1641)
- Karaikal (1645)
- Chinsura (1653)
- Balasore, Baranagar, Kasimbazar (near Murshidabad), Patna, Nagapatam (1658)
- Cochin (1663).
Dutch Trade in India
Dutch transported various goods and items from India to the islands of the Far East by engaging in trade. Their trade items from India included –
-
- Saltpetre from Bihar
- Indigo from the Yamuna Valley and Central India
- Opium and rice from the Ganga Valley
- Textiles and silk from the Coromandel, Bengal and Gujarat
Later, the Dutch maintained their overall supremacy in the intra-Asian trade, particularly between the Coromandel Coast and the southeast Asian markets.
Dutch Conflict with other European power
1. Dutch Conflict with Portuguese
- In 1658, they took Nagapatam from the Portuguese, where they built Fort Vijf Sinnen in 1690.
- In 1663, with the help of the Dutch, the Raja of Cochin managed to expel the Portuguese from his kingdom. The Dutch then obtained monopoly privileges similar to the Portuguese.
2. Dutch Conflict with the English (The Anglo-Dutch rivalry)
- At this time, the English were also becoming more critical in Eastern trade, which posed a significant threat to the Dutch economy.
- In 1623 the Dutch massacred ten Englishmen and nine Japanese in Amboyna (Indonesia).
- In 1667 there was an agreement between the two sides. According to the settlement British agreed to give up all of their claims to Indonesia. The Dutch withdrew from India to focus on their more profitable trade in Indonesia.
Decline of Dutch power
The Dutch got engrossed in the trade of the Malay Islands. During the 3rd Anglo-Dutch War (1672-74) between Surat and Bombay, communications were cut, resulting in the capture of 3 homebound English ships by the Dutch forces in the Bay of Bengal.
In November 1759, the English retaliated by defeating the Dutch in the battle of Biderra, which dealt the Dutch ambitions in India a fatal blow.
In India, the Dutch were more concerned with trade than empire-building. Their principal commercial interest was in the Spice Islands of Indonesia, where they made huge profits.
The English
Arrival in India
Francis Drake’s world expedition in 1580 and the defeat Spanish Armada in 1588 gave the British a renewed sense of adventure and inspired sailors to explore the east.
On December 31, 1600, Queen Elizabeth I granted the “Governor and Company of Merchants of London trading into the East Indies” a charter with exclusive trading rights. The charter was later extended indefinitely in May 1609. This company also came to be known as East India Company.
This opened doors for English trade with India:
- Captain William Hawkins, an English East India Company representative, arrived in Surat in India, on August 24, 1608.
- In April 1609, Captain William Hawkins reached the court of Jahangir to obtain formal permission to establish an English factory in Surat. Under Portuguese pressure, he was not given permission.
- In 1611, the English started trading on the southeastern coast of India. Masulipatnam was the most prominent.
- In 1616 they established a factory in
Expansions of the English power in India
The British Expansion into India was a result of varieties of factors that worked in various locations.
Expansion in the West
Various factors led to English Expansion into India:
- War with Portuguese: In 1612, in the sea off Surat, Captain Thomas Best defeated the Portuguese. Emperor Jahangir was greatly impressed by the English victory. As a result, permission was granted to the English to establish a factory at Surat.
- Diplomacy:
- In 1615, Sir Thomas Roe (ambassador of King James I ) came to Jahangir’s After various requests, he obtained formal approval to set up factories at Ahmedabad, Broach and Agra.
- In 1662 Bombay was gifted to King Charles II of England as a dowry by the king of Portugal.
In 1668 Bombay was given to the EIC on an annual payment of 10 pounds. This was a more stable base due to its defensive nature. In 1687 headquarter of the East India Company was changed to Bombay from Surat.
Expansion in the South
In 1632 the Sultan of Golconda issued the ‘Golden Farman’ to the English Company. Through this ‘Golden Farman’, they could now trade freely in the ports of Golconda on payment of 500 pagodas a year.
In 1639 the ruler of Chandragiri gave the British merchant Francis Day approval to build a fortified factory at Fort St. George at Madras. In South India, Fort St. George became the English settlements’ headquarters over Masulipatnam.
This enabled the British to its first strong base in the South India.
Expansion in Bengal and Odisha
- In 1633 the English established factories at Hariharpur in the Mahanadi delta and Balasore (Odisha).
- In 1651 Shah Shuja, the subahdar (or governor) of Bengal, permitted the English to trade in Bengal against an annual payment of Rs 3,000 in lieu of all duties.
- In 1651 factory was started in Hooghly and later in other places such as Patna, Kasimbazar and Rajmahal.
Struggle between Mughal and English in Bengal
Despite the farmans’ privileges, the company’s business was obstructed by customs officers who asked them to pay tolls in the check posts. The company wanted to establish a fortified settlement at Hooghly to use force if necessary.
A series of major conflicts, thus, broke off in 1680s:
- In August 1682, Shaista Khan, the Mughal governor of Bengal, received an appeal from William Hedges, the Company’s first agent and governor, requesting that the toll obstructions be removed.
- The appeal failed, and the English and Mughals engaged in hostilities.
- In October 1686, Hooghly was sacked by the Mughals.
- In return, the English captured the imperial forts at Thana (modern Garden Reach) and raided Hijli in east Midnapur and Balasore.
- In February 1690, Job Charnock, a company agent, signed a treaty with the Mughals and returned to Sutanuti.
- On February 1691, a royal Farman was issued allowing the company to “continue their trade contentedly in Bengal” in exchange for a yearly payment of Rs 3,000 in lieu of all dues and an English factory was established.
- In 1696, they fortified their settlement in Sutanuti due to the rebellion of a zamindar Sobha Singh in the Bardhaman district.
- In 1698, for Rs 1200, the English got the zamindari of the three villages of Gobindapur, Sutanuti and Kalikata (Kalighat).
- In 1700 Fort William(fortified settlement ) became the seat of the eastern presidency (Calcutta). Sir Charles Eyre was its first president.
Farrukhsiyar’s Farmans
In 1715, John Surman obtained three Farmans from the Mughal emperor Farrukhsiyar, securing the company with many privileges in Bengal, Gujarat and Hyderabad. These farmans were regarded as the Magna Carta of the Company. Their important terms were –
- In Bengal, on the annual payment of 3,000 rupees, the company’s imports and exports were exempted from additional customs duties.
- The company was allowed to issue dastaks (passes) for the transportation of goods.
- The company was permitted to lease additional lands near Calcutta.
- In Hyderabad, the company was allowed to continue its exemption from trade duties and was only required to pay the prevailing rent for Madras.
- In Surat, the company was freed from the levy of all duties in exchange for an annual payment of 10,000 rupees.
- The company’s coins, minted in Bombay, were now used as legal tender throughout the Mughal empire.
A rival English Company and the amalgamation of the two
- In 1698 a new English Company (“New East India Company“) obtained permission from the British parliament to trade in India.
- In 1701 Sir William Norris met Aurangzeb unsuccessfully to gain trading privileges for the company.
- In 1708 the two companies were amalgamated and named as “United Company of Merchants of England Trading to the East Indies”. This company was the East India Company from 1708 to 1873, which was to establish British political power in India.
British Capitals in India
- Calcutta (1858-1911)
- Shimla became the Summer Capital in
- Delhi (from 1911)
The French
French Arrival in India
The last Europeans to arrive in India were French traders. Attracted by the immensely profitable Indian trade, during Louis XIV’s reign in 1664, minister Colbert founded the Compagnie des Indes Orientales (French East India Company).
- First Expedition: In 1667, Francois Caron and Mercara (a Persian) headed an expedition to India and settled a factory in Surat (1668).
- First Factory: In 1669, Mercara obtained a patent from the Sultan of Golconda and founded the factory in Masulipatnam.
- First Colony: In 1673, the Mughal subahdar of Bengal, Shaista Khan, permitted the French to build a township at Chandernagore, close to Calcutta.
Pondicherry – establishment of a French colony
In 1673, the governor of Valikondapuram (during the reign of the Bijapur Sultan), Sher Khan Lodi, granted Francois Martin, the head of the Masulipatnam factory, permission to build a settlement there. As a result, in 1674, Pondicherry was founded. It acted as their base for the trade from South India.
They acquired Yanam in 1723, Mahe on Malabar Coast in 1725 and Karaikal in 1739. They also built factories at Balasore and Qasim Bazar.
Early setbacks of the French
The French entry into India started a strategic struggle between the British, Dutch and French for global dominance. As a result, the French colonies were captured several times during their occupation:
In Pondicherry
-
- In 1693 the Dutch captured Pondicherry, encouraged by their alliance with the English in 1688.
- In September 1697, The Treaty of Ryswick restored Pondicherry to the French.
In other parts of India
-
- The French had lost their factories at Masulipatam, Surat and Bantam to the East India Company by the early 18th Century.
By the early 18th century, the French East India company was one of least impactful out of all the European powers.
In 1720, the French Company was restructured as the Perpetual Company of the Indies, reviving its strength. The French in India further revived under the governorship of Lenoir (1720) and Dumas (1742).
The Anglo-French Rivalry – The Carnatic wars
Carnatic was the name the Europeans gave to the Coromandel coast and its nearby areas. Carnatic war was the result of the Anglo- French rivalry. The wars were started with the vision of establishing a regional political power.
These wars were also an extension of the customary rivalry of England and France throughout their histories; it began with the Austrian War of Succession. It ended with the decisive Seven Years’ War (1756-1763).
The political situation in south India in the 18th century
- Nizam Asaf Jah of Hyderabad was fully drawn in the battle against the Marathas in the western Deccan.
- Coromandel coast, which was in the south of his kingdom, was the without any strong ruler to maintain a balance of power.
- There were the remains of the old Vijayanagara empire in Travancore on the Malabar coast, interior Cochin and Mysore, and in the east, the small states of Tanjore (Thanjavur), Madura (Madurai) and Trichinopoly (Thiruchirapally).
- Hyderabad’s decline signalled the end of Muslim expansionism.
First Carnatic War (1740-1748)
Immediate Causes
- English navy under Barnet captured some French ships, which provoked France.
- In 1746 France retaliated and seized Madras with the help of the navy from Mauritius under the French governor of Mauritius, Admiral La Bourdonnais.
- Battle of St. Thome (in Madras) in 1746
- It was fought between the French forces under the French governor Joseph Francis Dupleix and the troops of Anwar-ud-din (Nawab of Carnatic).
- A small French army led by Captain Paradise vanquished the strong Indian army under Mahfuz Khan on the banks of the river Adyar.
- Treaty of Aix-La Chapelle: In 1748 the Treaty of Aix-La Chapelle was signed. With this treaty, the Austrian War of Succession
- Under this treaty, the English returned back Madras, and the French gained territories in North America.

Significance
- This war pointed out the that even a tiny, efficient, disciplined army could easily defeat a larger Indian army.
- It emphasised the importance of naval forces in wars.
Second Carnatic War (1749-1754)
Emboldened by the successes in the first Carnatic War, Dupleix wanted to increase the political power of the French in South India. Thus, he started interfering in local dynasty disputes to defeat the English.
Immediate Causes
- In 1748, Nizam-ul-Mulk, the founder of the independent kingdom of Hyderabad, died, which caused a struggle for the inheritance of the kingdom.
- While the English supported Nasir Jang and Anwar-ud-din, the French supported the assertion of Chanda Sahib and Muzaffar Jang in the Carnatic and Deccan, respectively.
The war
- Battle of Ambur (near Vellore) in 1749
- The combined armies of the French, Chanda Sahib and the Muzaffar Jang defeated Anwar-ud-din.
- While Dupleix was appointed as governor of territories to the south of the river Krishna and Muzaffar Jang became the subahdar of Deccan
- In Hyderabad, a French army led by Bussy was stationed to secure French interests.
- Territories near Pondicherry and a few areas on the coastal Orissa (including Masulipatnam) were ceded to the French.
- The siege of Arcot in 1751
- Battle at Trichinopoly in 1752
- Earlier, Chanda Sahib, with the help of the French, had sieged Trichinopoly from Muhammed Ali Khan Wallajah.
- Robert Clive and Stringer Lawrence, with Mysore, Tanjore and the Maratha chief, Morari Rao, relieved Trichinopoly of its siege.
Result
- In 1754, Dupleix was recalled from India.
- Godeheu (the French governor-general after Dupleix) concluded a treaty with the English.
- The French and the English decided that they would not interfere further in the disputes of native princes.
Significance
- Indian authority was becoming dependent on European support rather than vice-versa.
- Salabat Jang in Hyderabad and Muhammad Ali in the Carnatic became clients of the British rather than patrons.
Third Carnatic War (1758-1763)
Background
In Europe, Austria’s effort to recover Silesia started the Seven Years’ War (1756-63), in which Britain and France were on opposite sides.
The war
- In 1758, the French army led by Count de Lally seized the English forts of David and Vizianagaram.
- In retaliation, the English inflicted losses on the French fleet under Admiral D’Ache at Masulipatnam.
- Battle of Wandiwash (1760)
- On January 22 at Wandiwash (Modern Tamil Nadu), the English army led by General Eyre Coote defeated the French army under Count Thomas Arthur de Lally and took Bussy as a prisoner.
- Pondicherry was surrendered by Lally on January 16, 1761.
Result
In 1763, under the Treaty of Peace of Paris, the Indian factories were restored to the French. France recognised sovereignty of Britain over Canada, Saint Vincent and Tobago.
Significance
- After the war, French political influence disappeared.
- Like the Portuguese and Dutch, the French confined themselves to their small enclaves and trades.
- The English became the most dominant European power in the Indian subcontinent.
Reasons for the British Success and the French Failure
- Government control – The English Company was a private enterprise; thus, the company could take instant decisions without waiting for the government’s approval. The French government-controlled and regulated the French Company; hence, decision-making delays.
- The Navy – The English navy was much superior to the French one, which helped break the vital sea link between France and the French possessions in India.
- Strategic possessions – The English held three critical places: Bombay, Madras and Calcutta, whereas the French had only Pondicherry.
- Commercial interest vs territorial ambition – The French priority of territorial ambition led to the shortage of funds. While the British never neglected their commercial interests.
- Commanders – English had outstanding commanders like Major Stringer Lawrence, Sir Eyre Coote, Robert Clive etc. On the other side, only Dupleix was prominent on the French side.

Reasons for the success of English over other European powers
- An efficient structure of the trading company – The English East India Company was well organised. An annually elected board of directors controlled it. The company’s shareholders took an interest in promoting the company’s prosperity. The State primarily owned the trading companies of France and Portugal, and their nature was feudalistic.
- Naval Superiority – Britain’s Royal Navy was the largest and most advanced then.
- Industrial Revolution – In the early 18th century, the Industrial Revolution started in England. But it reached other European nations late. This helped England to maintain its dominance.
- Military Skill and Discipline – The British soldiers were well-trained. The British commanders experimented with new military tactics. Moreover, technological developments equipped the military well. All this combined enabled smaller groups of English fighters to defeat larger armies.
- Stable Government – Britain had a stable government with efficient monarchs. However, other European nations like France saw a violent revolution in 1789. Further, Napoleon’s defeat in 1815 significantly weakened France’s position, forcing it to side with Britain.
- Lesser Zeal for Religion – Britain was less zealous about religion and less interested in spreading Christianity than Portugal, Spain or the Dutch. This made the English rule more acceptable to the subjects.
- Use of Debt Market – The Bank of England (the world’s first central bank) sold government debt to the money markets with the assurance of a competent return on Britain’s defeating rival countries like France and Spain. This financed their wars. Other European powers could not match the expenditure of the British.





![Early Political Activities: 1858-1905 [Complete Notes For Upsc] | Updated March 14, 2026 Early Political Activities: 1858-1905 [Complete Notes For Upsc]](https://99notes.in/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/early-politics-featured-66698a6014484-768x500.webp)
![Home Rule Movement (1916-1918): India'S Fight For Self-Governance [Upsc Notes] | Updated March 14, 2026 Home Rule Movement (1916-1918): India’S Fight For Self-Governance [Upsc Notes]](https://99notes.in/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/home-rule-featured-66698a5b2a805-768x500.webp)