What is a Constitution?
Constitution is a document or set of documents that lays down basic set of rules for the establishment of a state and its governance and is legally enforceable.
A modern state is virtually impossible to be run without such basic sets of rules that defines the powers, responsibilities and limits of the ruling class. Any political system works in a constitutional framework and thus constitution is an essential element of a modern state.
Basic Terminologies
Before understanding the functions of a constitution, a student must be aware of certain terminologies:
State
State is a community of persons permanently occupying a definite territory independent of external control and possessing an organized government.
Article 12 of the Indian constitution defines the term ‘State’ as :
- The Government of India and Parliament of India,
- The Government and the Legislature of each of the States,
- All local bodies, such as municipalities, panchayats, district boards, port and improvement trusts etc.
- Oher authorities within the territory of India or under the control of the Government of India, such as statutory or non-statutory authorities like Lokpal, RBI etc. and Public sector Undertakings like LIC, ONGC, SAIL etc.
Elements of a State
A Political state has 4 essential elements:
- Population: State is the highest association amongst all associations in a society, which consists of a population. Thus, population is the most basic unit of a state.
- Territory: Territory is a geographical boundary of a state. A State has a very well-defined territory within which it is sovereign, i.e. it is legally recognized as supreme.
- Government: People residing in a territory cannot be automatically be termed as a state unless they are organized politically. Government enables the state to exert its political power in an organized way.
- Sovereignty: It is the most important element of a state. A Sovereign is a supreme legal power in the state. If a politically organized nation is controlled by an external power, then it is not sovereign. For example, India before 15th August 1947. A state is impossible without being sovereign.
Difference between a Nation and a State
A state is a political entitiy whereas a nation is a cultural entity. When population in a territory feel a sense of belongingness with the land, this land is referred to as a nation.
The 19th century French Philosopher, Ernst Renan, defiend nation as a culmination of a long past of endeavours, sacrifice and devotion. “A heroic past, great men, glory, that is the social capital upon which one bases a national idea. To have common glories in the past, to have a common will in the present, to have performed great deeds together, to wish to perform still more, these are the essential conditions of being a people.”
A nation is therefore a large-scale solidarity. Its existence is a daily plebiscite.
There are many factors based on which, nation can be established, for example:
- Language: For example, France was formed after the French Revolution, when people of all major French speaking areas struggled together.
- Common Struggles: For example, India has 100s of languages, cultures and belief systems and yet it is together. It is because of the common struggles that has shaped modern India.
- Religion: Nations like Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Vatican etc. are based on religious identities.
Nation State is a nation that has been organised into a political state. It one of the strongest forms of political entities being both culturally celebrated and politically legitimate.
A province is its inhabitants; if anyone has the right to be consulted, it is the inhabitant.
Functions and Role of a Constitution
Why is constitution important?
A Constitution fulfils following function in a society.
- Coordination in society: Set of basic rules that allow for minimal coordination amongst the society.
- Appoints a decision-maker: It decides who will make the decision in the society, i.e. the government.
- Limits the government: It sets some limits on the government about what it can impose on the citizens.
- Facilitates individual aspirations: Enables the government to fulfil the aspirations of the society.
- Fundamental Identity of the People: A constitution expresses the collective identity of the people. The constitution makers of every country select the most noble political ideals of their time in their constitution. Thus, constitution is a reflection of what the political identity of the state.
Functions of a Constitution in a state:
Constitution performs very important political functions in the society.
- Establishes the state: Constitution provides legitimacy to the state by defining its locus and the sovereignty.
- Established the organs of the state – delineates their functions and the inter-relations between them.
- Defines powers as well as the limitations of the state.
- Constiution is the Supreme Law of the Land, which cannot be changed easily even by the government.
- Rights of the citizen: It defines the relationship between the Individual and the state. The constitution ensures that the state should protect rights of the citizen.
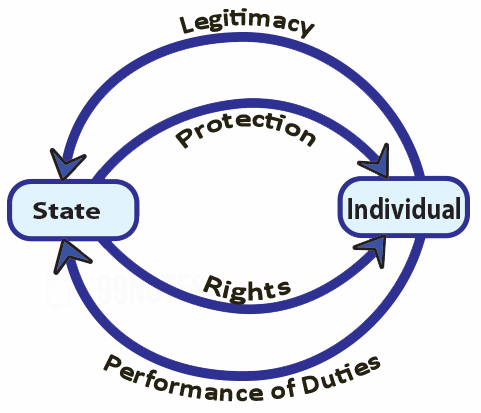
What makes a constitution Legitimate?
Why should we follow Indian Constitution? It has been imposed over us without our individual consent. We just happen to born in this system which already existed.
The Constitution is deemed legitimate because of following reasons:
- Mode of promulgation: The constitution of India, for example, was passed by the elected representatives of various sections of the society, which makes it more legitimate than say the Japanese constitution which was written by S. General Douglas MacArthur.
- Credibility of the Constitution makers: the constitution makers of India were all popular leaders of their time and represented all sections of the society.
- It ensures the powers to be intelligently organized
- It reflects the locus of people’s hope.
- Balanced Institutional design: It ensures checks and balances.
- Flexibility: Should not be very rigid, unable to bear change; If it is too rigid, then it would not be able to stand the changes of the time leading a state towards failure; And if it is too flexible, any despotic ruler can change it easily, again leading a state towards failure.
It is the wisdom of the constitution makers of India that they mentioned the Indian Constitution as a ‘Living Document’. It is neither too rigid nor too flexible.
Types of Constitution
There are two major types of classifications of a constitution:
- Written and unwritten Constitutions:
Written Constitution: Some countries like India and USA have written constition. It has an advantage of bringing clarity in the society about the functions of a state, government and the community.
Unwritten Constitution: Countries like Britain do not have a written constitution. The role of the constitution here is replace by a set of Bills, contract, Legal and Judicial precedents.
- Federal and Unitary States:
Federal Constitution of a State: In some countries like in India and Canada, the functions of not only the central government is defined.
Unitary State: It is the one in which the power of only the union are defined and the federal units either don’t exist or are at the mercy of the central government.






