Types of urban local government
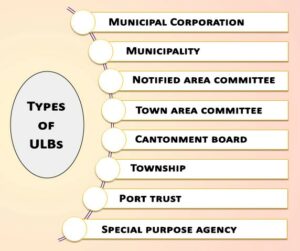 The Government of India Act 1935 brought local government within the purview of the provincial government and granted them enhanced powers. Since that time, local government evolved a lot. Currently, eight types of urban local bodies are visible in India.
The Government of India Act 1935 brought local government within the purview of the provincial government and granted them enhanced powers. Since that time, local government evolved a lot. Currently, eight types of urban local bodies are visible in India.
We shall cover these bodies in this chapter.
Municipal Corporation:
- The Act of state government established Municipal Corporations for the big cities of states, and the Act of Parliament for the big cities of Union Territories.
- A corporation has three authorities.
- First is the corporation council headed by the Mayor (assisted by the Deputy Mayor). The council is a deliberative and legislative organ of the corporation.
- The councillors and Mayor are directly elected by the people.
- The second organ of the corporation is the standing committees that deal with activities like health, education, and public works and are empowered to make decisions in their respective fields.
- The third authority of the corporation is the Municipal Commissioner, a government officer responsible for implementing the decisions taken by the council and standing committees.
Municipalities (Municipal Board/Municipal Council/ Municipal Committee):
- The Acts of the state legislature set them up to administer small cities or towns. It also has three authorities.
- First, the municipal council is the legislative branch of the municipality and is headed by the Chairman, who in turn is assisted by a Deputy Chairman.
- The standing committees facilitate the work of the municipality in various fields, such as health, taxation, etc.
- The third authority of the municipality is the Chief Municipal Officer, appointed by the state government and responsible for the general administration of the municipality.
Notified Area Committee:
- This may be created either in a town that is fast developing or which may not fulfil the conditions for the creation of a municipality.
- It is so called because it is created through a notification of the state government published in the official gazette.
- It is not a statutory body.
- The government nominates all its members and the Chairman. It performs similar functions as performed by a municipality.
Town Area Committee:
- A separate Act of state government creates it for the administration of small towns.
- As provided in the Act, it may be wholly elected or totally nominated or partly elected or partly nominated body.
- It performs limited functions like street lighting, drainage, etc.
Cantonment Boards:
- They are established to perform municipal functions for the civilian population living in cantonment or military areas.
- It is created and works under the Central Act of 1924 under the administrative control of the Ministry of Defence.
- There are three types of Cantonment Boards depending on the civilian population in the Cantonment Area.
- It comprises partly elected and partly nominated members. The members are elected for a three-year term.
- The military officer commanding the cantonment station is the ex officio chairman of the Cantonment Board.
Townships:
- Townships are established by a public sector undertaking as its housing colony to provide civil amenities to its employees.
- It has no elected members, and its affairs are managed by a Town Administrator appointed by the public sector undertaking.
Port Trusts:
- Such urban bodies are established by an Act of Parliament to manage and protect ports and to provide civic amenities to the port area.
- It is headed by an official appointed by the central government.
- It has both elected and nominated members.
Special Purpose Agencies:
- The state governments establish some special purpose agencies to perform some specific functions of municipalities.
- They function as separate bodies and are not under the control of municipalities.
- They may be created either by an act of the State Legislature or by an executive order.
- Some of these agencies are the Housing Board, Water Supply Undertaking, Electricity Supply Undertakings, Urban Development Authorities etc.
Issues associated with urban local government:
Urban governance and management have predominantly been the constitutional domain of state government.
These local institutions of urban government have become weak over the years due to many factors, including encroachment on traditional and legitimate municipal functions by creating parastatals and urban development authorities, a weak executive system, fragile fiscal health, and inadequate staffing and expertise in municipal management.
Issues in decentralisation:
- Under the 74th Constitutional Amendment Act, states have incorporated provisions in their Municipal Acts for transferring additional functions to the municipal body, but the extent of functions transferred differs from state to state and also varies from city to city in the same state.
- Further, the devolution of functions to the municipal bodies is also affected because, in some cities, the parastatals (traditionally delivered certain basic functions) have not been dismantled.
- As a result, they continue to perform certain functions that may have legally been passed on to the municipal bodies.
- The continued existence of the parastatals has led to overlaps and often conflicts in the roles and responsibilities of each agency involved in municipal governance.
- In such a scenario, it becomes difficult for the citizens to hold any particular agency responsible for inadequate service delivery.
Parallel Bodies:
- In some states, there is some ambiguity regarding the functional domain of Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) and parastatal bodies, making municipal governance further remote and inaccessible for the citizens.
- The multiplicity of agencies providing various services in the Urban Sector has led to overlapping, ambiguity and wastage of resources.
- Over and above that, the parastatal bodies are not elected Bodies and are not directly answerable to the citizens.
Financial impediments:
- Discussions with stakeholders revealed that municipal bodies’ capacity and resource constraints are the major reasons for this difference in their performance.
- While the larger municipal corporations still have access to funds, the smaller municipal councils are financially weak. The provision to levy and collect adequate usercharges is not fully utilised.
- However, the state budgetary allocations have been drying up for most states, and it is being realised that the traditional system of funding based on plan and budgetary allocations will only be reduced in the future.
Operational capacity issues/ Limited human resources:
- Inadequate training is one of the main impediments to introducing new technologies and management styles in the working of municipal corporations.
- ULBs in India often suffer from a shortage of skilled and qualified personnel, affecting their ability to effectively carry out their duties and functions.
- Also, most ULBs face problems due to lack of capacity, improper staffing patterns, and lack of standardisation.
- They do not have the institutional, operational, educational, and legal capability to develop commercially viable infrastructure projects, mobilise resources for the projects, and implement them.
- In fact, the root cause of the problem of inefficient service delivery is the capacity constraints of ULBs.
Insufficient public participation :
- While there is little effort on the part of the municipal bodies to include people in the process, the problem is compounded by the fact that there is very little awareness among citizens of their role in the governance process.
Issues in transparency and accountability:
- The main impediment towards achieving transparency and accountability is not the lack of understanding of the need for the same but the lack of means to achieve the same.
- As most ULBs are severely capacity-constrained both in terms of funds and manpower, In such a scenario, it becomes hard to put in place systems that would enhance accountability.
Poor infrastructure:
- Many ULBs in India face a shortage of infrastructure, such as water supply, roads, and sewage systems, which limits their ability to provide basic services to the citizens.
Political interference:
- ULBs in India are often subject to political interference, affecting their independence and neutrality in decision-making.
Way forward:
The Planning Commission of India constituted a Working Group on Urban Governance to formulate the 12th Five-Year Plan. Some of the recommendations of the committee for strengthening urban governance are as follows:
Standardising the classification of ULBs:
- The states should adopt standard norms for the classification of ULBs.
- It would be advisable that all the municipalities be reclassified into three categories, viz;
- Municipal Corporation for large urban areas of 5 lahks and more population;
- Municipal Council for urban areas of 1 lakh to 5 lakh population;
- Nagar Panchayat for towns below 1 lakh population.
Strengthening Ward Committees:
- There is wide variation in the functioning of ward committees across the state. Although the legal provisions for the constitution of a Wards Committee have been made in most states, the actual spirit of the amendment is diffused.
- Hence, ward committees’ constitution and functioning need to be incentivised.
- Further, there is a need to establish area sabhas and to link area sabhas and ward committees to ensure that accountability and participatory processes become a reality.
Strengthening Metropolitan Planning Committees:
- The 74th Amendment specific establishment of a Metropolitan Planning Committee (MPC) for preparing development plans at the metropolitan level.
- However, MPCs are yet to evolve as per the spirit of the constitutional amendment. Only a few states have initiated the creation of such entities.
- The central government needs to support the state government in this regard.
Improved financial management:
- Urban local bodies should be provided with adequate resources and financial support to deliver essential services to their citizens. This could include grants, loans, and other forms of financial assistance.
Convergence of functions of parastatals/state bodies with Local Bodies:
- Historically, due to poor staffing and technical capabilities of the Local Bodies, a number of Parastatal Bodies were created to provide services listed in the 12th Schedule.
- The multiplicity of agencies providing various services in the Urban Sector has led to overlapping, ambiguity and wastage of resources.
- There is a need for activity mapping for these bodies.
- Urban local bodies should be given greater autonomy and decision-making powers to effectively address their citizens’ needs. This can include powers related to planning, financing, and delivering services.
Empowerment of political office bearers:
- The Mayors or Chairpersons of the ULBs should be accountable to the people and have power and tenure commensurate with this objective.
- In addition, there is a critical need for building the capacity of the political executive, specifically in areas such as sensitisation vis-a-vis the need for reforms, service level benchmarks, etc.
Strengthening the Organisational Capacities:
- There is an urgent need for increased investment, financial management and audits in local bodies. Thus, the creation of a municipal cadre is essential.
- Urban local bodies should be supported in building the necessary skills and knowledge to manage their affairs effectively. This could include training in financial management, planning, and service delivery.
Regulatory mechanisms for delivery of basic urban services:
- An Independent Urban service Regulator is needed as the current paradigm of service providers deciding service levels and tariffs is outdated. The regulator would monitor the provision of service and the tariff regime and ensure transparency and efficiency.
Improved infrastructure and services:
- Investments in public transportation, water and sanitation, infrastructure and other essential services by providing ULBs with the resources and support can help to address some of the challenges faced by citizens and make urban areas more livable and attractive.
Public-Private Partnership (PPP):
- PPPs, structured around a robust revenue model (including user charges, targeted subsidies, and viability gap funding) and offer a good prospect of return on investment, can contribute to systemic gains and better management of urban services.
- The State governments should bring out a legislative framework to address the entire gamut of issues in the implementation of PPP Projects and develop clear policies about the identification of projects that can be developed and implemented on a PPP basis, delivery processes, project development, approval and implementation process, guiding principles of contract management etc.
Accountability and Citizen Participation:
- A more interactive and participative framework (like open data initiatives or citizen engagement platforms) should be followed by ULBs to ensure greater accountability to the citizens.
- This can be achieved through citizen advisory boards, town hall meetings, and other mechanisms for public input.
- Citizen Report cards, like the one prepared by the Public Affairs Centre in Bengaluru, need to be replicated across all cities.
Use of E-Governance and Technology for improvement of the delivery of services and need for the database:
- Information Technology (IT) can be important in improving governance.
- With municipal administration becoming increasingly complex, the benefits of IT adoption are becoming more and more visible across several municipalities.
- The tools of IT and E-Governance should be strengthened and adopted in all the ULBs; for this, whatever skill upgradation is required should be done.
Enhanced collaboration:
- Urban local bodies should work closely with other levels of government, as well as with civil society and the private sector, to effectively address the challenges facing their communities.
- The Principle of PANCHASHEELAS can be a unique solution in this regard.
Conclusion
Good Urban governance demands that Local Self Government be a vibrant entity with sufficient autonomy to respond to the residents’ needs and aspirations. However, reluctance to share power stifled their growth during the post-independence era. The 74th CAA attempted to correct the situation. However, the real power transfer has not occurred despite being passed more than three decades back. As urbanisation is increasing and cities are experiencing widening gaps in infrastructure and services, the government, especially the Central Government, has created conditions for the State governments to undertake reforms to strengthen the ULBs. It is high time necessary steps are taken at the earliest, as cities are the engines of economic growth. Smart Cities Mission and Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)are important programmes of the government of India, which emphasise the central role of the ULBs in planning for the vision of the cities with particular emphasis on citizen participation.