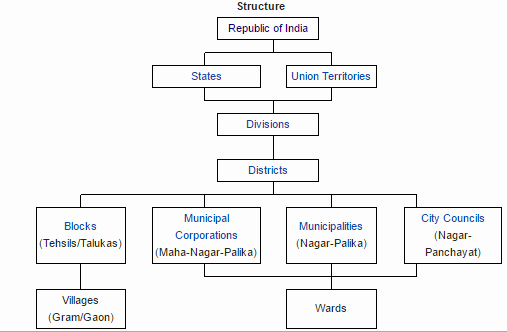
Urban local governments
The system of urban government was constitutionalised through the 74th Constitutional Amendment Act of 1992. Before this, a variety to systems existed in various locations.
Evolution of urban local bodies:
 Pre-British Era:
Pre-British Era:
- The origin of local self-government was deeply rooted in ancient India.
- Texts like Vedas, Manusmriti, Arthasastra and records of some travellers like Megasthenes also mention the origin of local self-government.
- In the Epic era, texts like Ramayana and Mahabharata also pointed to several forms of local self-government, such as Paura (guild), Nigama, Gana, etc. They used to perform various administrative and legislative functions.
British Era:
- Urban local government institutions developed in modern India during the British era. Some major events in this context are as follows:
- Municipal governance in India in its current form has existed since 1664.
Post-independence Era / Way to constitutionalisation:
- Urban local bodies received consistent policy attention from various committees that were set up to suggest ways to improve the urban local bodies.PK Wattal, John Mathai, AP Jain, Rafiq Zakaria, KN Sahaya are prominent among them.
- In August 1989, the Rajiv Gandhi government introduced the 65th constitutional amendment or Nagarpalika Bill in the Lok Sabha. The bill aimed at strengthening and revamping the municipal bodies by conferring a constitutional status on them. The bill was passed by the Lok Sabha but was defeated in the Rajya Sabha in October 1989 and lapsed.
- The National Front Government, under the prime ministership of V P Singh, introduced the revised Nagarpalika Bill in the Lok Sabha again in September 1990. However, the bill was not passed and finally lapsed due to the premature dissolution of the Lok Sabha.
- In September 1991, P V Narasimha Rao’s Government introduced the modified Municipalities Bill in the Lok Sabha, which emerged as the 74th Constitutional Amendment Act of 1992 and came into force on 1 June 1993.
74th Constitutional Amendment Act of 1992:
- Through this act, a constitutional status was given to the municipalities, and from now state governments are under constitutional liability to adopt the new system following the act’s provisions.
- This act added A new Part IX-A to the Constitution of India. This part consists of provisions from Articles 243-P to 243-ZG.
- The act has also added a new Twelfth Schedule to the Constitution, which contains eighteen functional items of municipalities. It deals with Article 243-W.
Articles Related to Municipalities at a Glance
| Article No. | Subject-matter |
| 243P | Definitions |
| 243Q | Constitution of municipalities |
| 243R | Composition of municipalities |
| 243S | Constitution and composition of wards committees, and so on |
| 243T | Reservation of seats |
| 243U | Duration of municipalities |
| 243V | Disqualifications for membership |
| 243W | Powers, authority and responsibilities of municipalities |
| 243X | Powers to impose taxes, and funds, of the municipalities |
| 243Y | Finance Commission |
| 243Z | Audit of accounts of municipalities |
| 243ZA | Elections to the municipalities |
| 243ZB | Application to union territories |
| 243ZC | Part not to apply to certain areas |
| 243ZD | Committee for District Planning |
| 243ZE | Committee for Metropolitan Planning |
| 243ZF | Continuance of existing laws and municipalities |
| 243ZG | Bar to interference by courts in electoral matters |
City Administration in India:
Just like in the case of village administration, an urban local body is is divided into different wards. From each ward, a ward councillor gets elected.
- Municipalities & Municipal corporations are controlled by elected bodies consisting of Councillors.
- Municipal chairperson is head of Municipality.
- The complicated decisions that affect the entire city are taken by groups of councillors who form committees to decide and debate issues. Ex:
- District Planning Committee
- Area Development Committee
- The Commissioner and the administrative staff implement these. These are appointed members.
- Funding:
- Property taxes form only 25-30% of the money that a Municipal Corporation earns.
- Rest comes from Grants from State as per State Finance commission recommendations.
District Administration: For managing matters relating to land these districts are sub-divided. These subdivisions of a district are known by different names such as tehsil, taluka, etc.
- At the head is the District Collector and under her are the revenue officers, also known as tehsildars.
- They have to hear disputes. They also supervise the work of the Patwaris and ensure that records are properly kept and land revenue is collected.
- They make sure that the farmers can easily obtain a copy of their record, students can obtain their caste certificates etc.
- The Tehsildar’s office is where land disputes are also heard.
New districts are carved: The power to create new districts or alter or abolish existing districts rests with the State governments. This can either be done through an executive order or by passing a law in the State Assembly. Many States prefer the executive route by simply issuing a notification in the official gazette.
- States are free to decide on new district boundaries. The Home Ministry comes into the picture when a State wants to change the name of a district or a railway station.
- The trend
- According to the 2011 Census, there were 593 districts in the country. 46 districts were created by States.
- Though the 2021 Census is yet to happen, Know India, a website run by the Govt, says currently there are 718 districts in the country.
- The surge in number is also due to bifurcation of Andhra Pradesh into A.P and Telangana in 2014.





