Union Budget 2024 Summary || Highlights of Budget 2024 UPSC
Primary Source: PIB
The Budget document presented by our finance Minister on 23rd July 2024 was the first budget presented in the 18th Lok Sabha after the conduct of recent swearing in. the Previous budget presented in the starting of this year was an interim budget presented by the Previous government.
Stages of a Budget
Budget enactment goes through various processes in the Parliament; these have been discussed below:
Presentation of the Budget
The Budget in Parliament is presented by the Finance Minister on a date fixed by the President. Since 2017, it has been presented on the 1st day of February.
After the speech is concluded in the Lok Sabha, the annual financial statement (Budget) is laid in the Rajya Sabha. It is to be noted that the Rajya Sabha can only discuss the Budget and cannot vote on the demand of grants.
Budget Documents
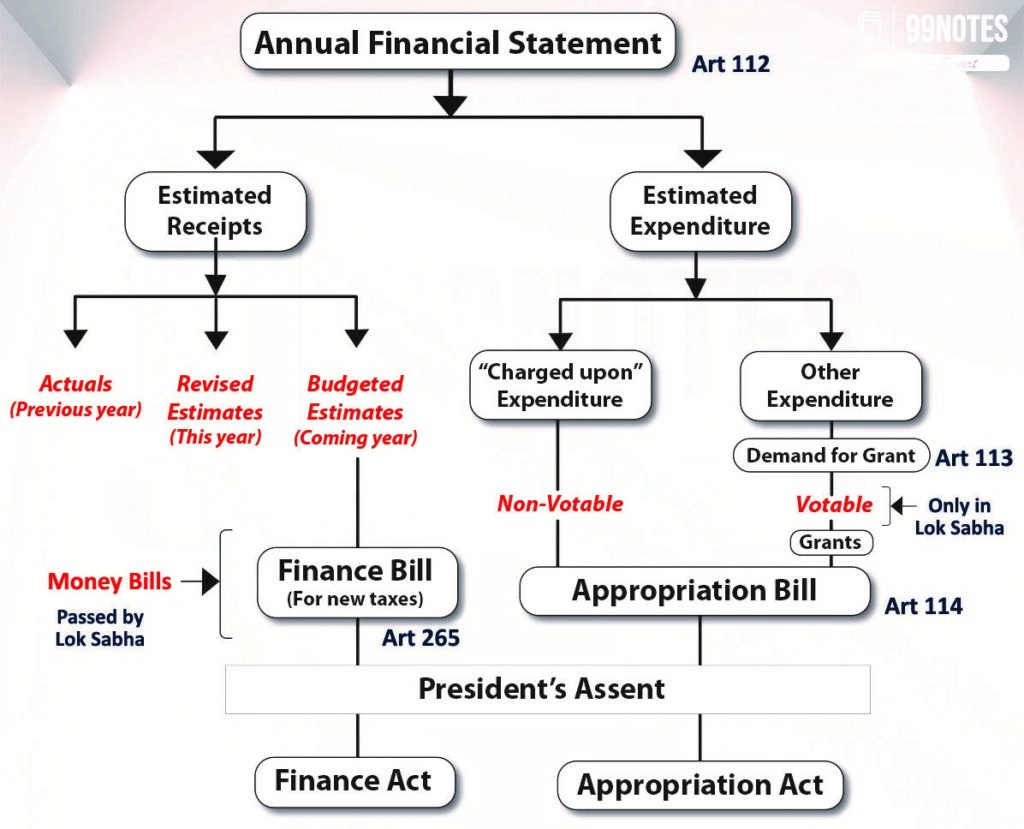
Through annual financial statement (i.e. the Budget), the government presents the following documents:
- Annual Financial statement – Under the provision of Article 112, the government presents an Annual financial statement consisting of estimated expenditure and estimated receipts.
- Demand for grants – It contains ministry-wise demands of various departments of ministries made in front of the Parliament
- Appropriation bill – It authorises the government to withdraw funds from the consolidated fund of India.
- Finance bill – It deals with taxation proposals of the government.
- Outcome Budget – it deals with the performance of ministries in the implementation of policies, schemes and expenditure incurred by them.
- Documents mandated under the FRBM Act –
Phases of the Union Budget
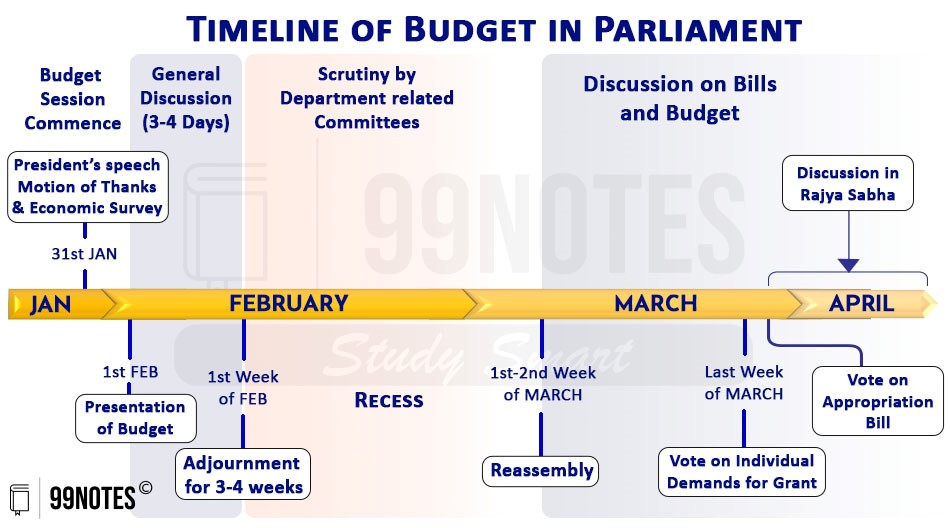
The Budget is discussed in Lok Sabha in two phases;
General Discussion
In the first phase, general discussion takes place. This generally happens on the 1st Week of Feb; currently this is happening in the end of July 2024. The general discussion takes place a few days after the presentation of the Budget and lasts for about 3-4 days.
In general discussion, only the broad outlines of the Budget and underlying principles and policies are discussed. At this stage:
- No cut motion can be moved,
- Nor is the Budget voted by the House.
- At the end of the discussion, the Finance Minister has the right to reply.
Consideration Phase
The Second phase is expected to commence in the end of August 2024. After the general discussion on the Union budget is over, the House is adjourned for a fixed period of time (generally, three to four weeks).
During this period, the demand for grants of ministries is considered by concerned committees. These committees are required to make a report to both Houses within a specified period of time.
- The demands are presented ministry-wise, and each demand is voted on separately; they become grants after they are duly voted. These committees have 31 members (21 from LS and 10 from RS).
- After the standing committees present their report, the Lok Sabha takes up the discussion and votes on the demand of grants. Rajya Sabha only takes part in the general discussion; it does not vote on the demand of grants. At this stage, a detailed discussion of demands takes place.
- The Lok Sabha can criticise the demands, reduce them, or reject them but cannot increase them. It should be noted that demand of grants can only be made on the recommendation of the President.
Passage of Budget
The voting on demand of grants must be completed within a fixed time limit (decided by the Speaker in consultation with the Leader of the House).
On the last day, all the remaining demands are put to vote, even if they have not been adequately discussed. This process is known as ‘Guillotine’.
PART A
Points to be noted:
- Despite global economy remaining under the grip of policy uncertainties, India’s economic growth continues to be the shining exception
- India’s inflation continues to be low, stable and moving towards the 4% target.
- Core inflation (non-food, non-fuel) currently is 3.1% and steps are being taken to ensure supplies of perishable goods reach market adequately.
Interim Budget
The Finance Minister said that as mentioned in the interim budget, the focus is on 4 major castes, namely:
- ‘Garib’ (Poor),
- ‘Mahilayen’ (Women),
- ‘Yuva’ (Youth) and
- ‘Annadata’ (Farmer).
Budget Theme
Announced the Prime Minister’s package of 5 schemes and initiatives to facilitate employment, skilling and other opportunities for 4.1 crore youth over a 5-year period with a central outlay of ₹2 lakh crore.
₹1.48 lakh crore has been allocated for education, employment and skilling.
Budget Priorities
The Finance Minister said, for pursuit of ‘Viksit Bharat’, the budget envisages sustained efforts on the following 9 priorities for generating ample opportunities for all.
- Productivity and resilience in Agriculture
- Employment & Skilling
- Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice
- Manufacturing & Services
- Urban Development
- Energy Security
- Infrastructure
- Innovation, Research & Development and
- Next Generation Reforms

Priority 1: Productivity and resilience in Agriculture
The Finance Minister announced that the government will undertake a comprehensive review of the agriculture research setup to bring the focus on raising productivity.
Budget: ₹1.52 lakh crore has been allotted for agriculture and allied sector.
- New 109 high-yielding and climate-resilient varieties of 32 field and horticulture crops will be released for cultivation by farmers.
- Achievements: From 2014-15 to 2023-24, 2593 high-yielding varieties, including 2177 climate-resilient varieties, were released. Deployment of these technologies has led to increased production even during adverse conditions.
- In the next two years, 1 crore farmers across the country will be initiated into natural farming supported by certification and branding.
- 10,000 need-based bio-input resource centres will be established.
- Government will facilitate the implementation of the Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in agriculture for coverage of farmers and their lands in 3 years.
- For achieving self-sufficiency in pulses and oilseeds, government will strengthen their production, storage and marketing and to achieve ‘atmanirbharta’ for oil seeds such as mustard, groundnut, sesame, soybean, and sunflower.
- Jan Samarth Initiative: Kisan Credit Cards (KCC):
- Objective: Simplify access to credit for farmers through Kisan Credit Cards. As of January 31, 2024, 7.5 crore KCCs have been issued with a limit of ₹9.4 lakh crores.
- Extension: KCCs were extended to support fisheries and animal husbandry, with limits increased for collateral-free loans.
- Strengthening Shrimp Industry:
- Objective: Enhance shrimp breeding and financial support through NABARD. The establishment of Nucleus Breeding Centres (NBCs) will improve the quality and productivity of shrimp brood stocks.
- Impact: India is a major shrimp producer and exporter, with shrimp exports growing to Rs 40,013 crore in 2023-24.
- Further Basic Custom duty on broodstock, polychaete worms, shrimps and fish feed has been reduced to 5%.

Priority 2: Employment & Skilling
Prime Minister’s Package
The Finance Minister said that the government will implement 3 schemes for ‘Employment Linked Incentive’, as part of the Prime Minister’s package.
These will be based on enrolment in the EPFO, and focus on recognition of first-time employees, and support to employees and employers.

Government will also facilitate higher participation of women in the workforce through setting up of working women hostels in collaboration with industry, and establishing creches.
4th scheme for skilling in collaboration with state governments and Industry. 20 lakh youth will be skilled over a 5-year period and 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes will be upgraded in hub and spoke arrangements with outcome orientation.
5th scheme offers internship opportunities for one crore youth in 500 top companies over five years, providing an internship allowance of ₹5,000 per month and a one-time assistance of ₹6,000.

Other Schemes
- Model Skill Loan Scheme will be revised to facilitate loans up to ₹7.5 lakh with a guarantee from a government promoted Fund, which is expected to help 25,000 students every year.
- Increased Loan Limit: The Indian government has relaunched the ‘model skill loan scheme’ with an increased maximum loan limit of Rs 7.5 lakh, up from the previous Rs 1.5 lakh, aiming to make skill development courses more accessible.
- Broader Lending Framework: The scheme now includes non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), NBFC-Microfinance Institutions (MFIs), and small finance banks as eligible lenders, expanding beyond traditional banks.
- Expanded Course Eligibility: The scheme covers more skill development courses, including those not aligned with the National Skill Qualification Framework (NSQF), provided they are listed on the Skill India Digital Hub platform.
- Rationale for Changes: The previous version of the scheme had low uptake, with Rs 115.75 crore in loans extended to 10,077 borrowers by March 31. The limited loan amount and rising course fees were barriers.
- Government’s Vision: The scheme’s revamp aligns with a broader vision for strategic skill development, anticipating future technological advancements and job market changes by 2047.
- Expected Impact: The government expects the revamped scheme to benefit 25,000 students annually, better preparing them for a dynamic job market.
2. Financial support for loans upto ₹10 lakh for higher education in domestic institutions.
- Beneficiaries: youth who have not been eligible for any benefit under government schemes and policies
- E-vouchers for this purpose will be given directly to 1 lakh students every year for annual interest subvention of 3% of the loan amount.

Priority 3: Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice
PM Vishwakarma, PM SVANidhi, National Livelihood Missions, and Stand-Up India will be stepped up.
| Let’s Revise a Few Schemes |
|
PM Vishwakarma
PM SVANidhi – Pradhan Mantri Street Vendor’s Atmanirbhar Nidhi – a special micro-credit facility scheme for providing affordable loan to street vendors. The scheme is aimed at enabling the street vendors to resume their livelihoods that have been adversely affected due to COVID-19 lockdown. National Livelihood Missions: launched in rural areas, bringing poor families above the poverty line by organising them into SHGs through a mix of bank credit & government subsidy. Stand-up India:
|
Purvodaya
It is a plan for the all-round development of the eastern region of the country covering Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha and Andhra Pradesh. This will cover human resource development, infrastructure, and generation of economic opportunities to make the region an engine to attain Viksit Bharat.
Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan
Aim: improving the socio-economic condition of tribal communities, government by adopting saturation coverage for tribal families in tribal-majority villages and aspirational districts covering 63,000 villages and benefitting 5 crore tribal people.

More than 100 branches of India Post Payment Bank will be set up in the North East region to expand the banking services.
Budget for rural development including rural infrastructure: ₹2.66 lakh crore

Priority 4: Manufacturing & Services
Support for promotion of MSMEs
- A separately constituted self-financing guarantee fund
- Scheme: guarantee cover up to ₹100 crore per applicant, while the loan amount may be larger.
- Public sector banks will enhance their credit assessment capabilities for MSMEs.
- Public sector banks will build their in-house capability to assess MSMEs for credit, instead of relying on external assessment. She also announced a new mechanism for facilitating continuation of bank credit to MSMEs during their stress period.
- Mudra Loans: The limit of Mudra loans will be enhanced to ₹ 20 lakh from the current ₹10 lakh for those entrepreneurs who have availed and successfully repaid previous loans under the ‘Tarun’ category.
| About PM MUDRA Loans |
| Under PM MUDRA Yojana, three categories of interventions have been named which includes: Shishu :- Loan up to ₹50,000. Kishore :- Loan ranging from ₹50,000 to ₹5 lakh. Tarun :- Loan above ₹5 lakh and below ₹10 lakh. |
- Financial support for setting up of 50 multi-product food irradiation units in the MSME sector will be provided.
- Setting up of 100 food quality and safety testing labs with NABL accreditation will also be facilitated. [National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories]
- E-Commerce Export Hubs will be set up in public-private-partnership (PPP) mode for traditional artisan.

Priority 5: Urban Development
- PM AwasYojana Urban 2.0:
- Housing needs of 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families will be addressed with an investment of ₹ 10 lakh crore.
- This will include the central assistance of ₹ 2.2 lakh crore in the next 5 years.
- Water Supply and Sanitation: In partnership with the State Governments and Multilateral Development Banks, government will promote water supply, sewage treatment and solid waste management projects and services for 100 large cities through bankable projects.
- PM SVANidhi: Government envisions a scheme to support each year, over the next five years, the development of 100 weekly ‘haats’ or street food hubs in select cities.

Priority 6: Energy Security
PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana:
- This scheme was announced in the interim budget 2024, and is now being continued.
- Aim: to install rooftop solar plants to enable 1 crore households obtain free electricity up to 300 units every month.
- Budget: It received an allocation of nearly ₹10,000 crore for the current year, doubling the previous year’s expenditure on solar power.
- Eligibility: Households must pay a minimum of ₹20,000 for the system, which can be financed through a low-interest, collateral-free loan. Eligibility requires a suitable roof and an existing grid connection.
- The scheme has generated remarkable response with more than 1.28 crore registrations and 14 lakh applications.
- Aim: to install rooftop solar plants to enable 1 crore households obtain free electricity up to 300 units every month.
Investment in small modular nuclear reactors (SMRs)
- Investment in SMRs was highlighted, with plans to partner with the private sector for setting up Bharat Small Reactors and advancing nuclear energy technologies.
- What are small modular nuclear reactors (SMRs)? These are small reactors which offer up to 300MW of power.
- These are seen as a significant component of India’s future energy mix.
- In 2024: Government of India and Government of Russian Federation have expressed interest to expand the cooperation in the field of the use of nuclear energy for peaceful purposes including cooperation in the field of Small Modular Reactor.
- Nuclear energy is expected to form a very significant part of the energy mix for Viksit Bharat.
The Budget also restated a 2018 proposal to develop an Advanced Ultra Supercritical (AUSC) thermal power plant through collaboration with NTPC and BHEL, but no specific budget was allocated for this project.

Priority 7: Infrastructure
Capex budget for FY25 is retained at ₹11.1 lakh crore, or 3.4% of GDP. ₹11,11,111 crore
- Pradhan Mantri Gram SadakYojana (PMGSY): Phase IV of PMGSY will be launched to provide all-weather connectivity to 25,000 rural habitations which have become eligible in view of their population increase.
| Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY): |
|
Aim: to provides all-weather road connectivity to all eligible unconnected habitations in rural areas of the country. Ministry responsible: M/o Rural Development. Habitations covered: Plain areas: with population of 500 persons and above (as per 2001 Census); Special Category States and in Select Tribal and Backward Districts: 250 persons. Sub scheme: “Road Connectivity Project for Left Wing Extremism (LWE) Affected Areas” for 44 worst affected LWE districts and adjoining districts, critical from security and communication point of view. It is run by the M/o Home Affairs for unconnected habitations with population of100 and above. Funding pattern: 11 Special Category states = 90:10; Rest all 60:40 b/w centre & state |
| Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP) |
|

- Industrial Node at Gaya.
- 4 Express ways – for road connectivity.

Additionally, special financial support of ₹15,000Cr is provided for Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act.
Priority 8: Innovation, Research & Development
Anusandhan National Research Fund:
It is being institutionalised for basic research and prototype development and set up a mechanism for spurring private sector-driven research and innovation at commercial scale with a financing pool of ₹1 lakh crore in line with the announcement in the interim budget.
Space Economy:
New Aim: The 2024 Budget Aims to expand the space economy by 5 times in the next 10 years, a venture capital fund of ₹1,000 crore will be set up.

Priority 9: Next Generation Reforms

- Economic Policy Framework: The government will formulate an Economic Policy Framework to delineate the overarching approach to economic development and set the scope of the next generation of reforms for facilitating employment opportunities and sustaining high growth.
- Labour related reforms: Government will facilitate the provision of a wide array of services to labour, including those for employment and skilling.
- E-Shram: A comprehensive integration of e-shram portal with other portals will facilitate such one-stop solution. Shram Suvidha and Samadhan portals will be revamped to enhance ease of compliance for industry and trade.

- Green Financing: Government will develop a taxonomy for climate finance for enhancing the availability of capital for climate adaptation and mitigation.
- Foreign Direct Investment and Overseas Investment: The rules and regulations for FDI and Overseas Investments will be simplified to:
- facilitate foreign direct investments,
- nudge prioritization, and
- promote opportunities for using Indian Rupee as a currency for overseas investments.
- NPS Vatsalya: NPS-Vatsalya, a plan for contribution by parents and guardians for minors will be started. On attaining the age of majority, the plan can be converted seamlessly into a normal NPS account.
- New Pension Scheme (NPS): The Committee to review the NPS has made considerable progress in its work and a solution will be evolved which addresses the relevant issues while maintaining fiscal prudence to protect the common citizens.

Budget Estimates 2024-25
Total receipts other than borrowings: ₹32.07 lakh crore
- The net tax receipts are estimated at: ₹25.83 lakh crore
Borrowings:
2. Gross market borrowings through dated securities: ₹14.01 lakh crore
3. Net market borrowings through dated securities: ₹11.63 lakh crore
Total expenditure is estimated at: ₹48.21 lakh crore.
Fiscal Path:
- Fiscal deficit is estimated at: 4.9% of GDP for FY 2024-25. In the Interim budget, the target for fiscal deficit was 5.1%. The government has lowered this target.
- Fiscal consolidation path announced by her in 2021 has served economy very well, and the government will aim to reach a deficit below 4.5% next year.
| Fiscal Deficit % | 9.5 % | 6.9% | 5.8% | 4.9% | 4.5 % |
| Financial Year | 2021-22 | 2022-23 | 2023-24 | 2024-25 | 2025-26 |
PART B
Apart from giving relief to four crore salaried individuals and pensioners of the country in the direct taxes,
4 Reforms Proposed:
- Union Budget 2024-25 seeks to comprehensively review the direct and indirect taxes in the next six months, simplifying them, reducing tax incidence and compliance burdens and broadening the tax nets.
- The Budget proposes comprehensive rationalization of GST tax structure along with review of the Custom Duty rate structure to improve the tax base and support domestic manufacturing.
- A comprehensive review of Income – Tax Act is targeted at reducing disputes and litigations and to make the act lucid, concise and easy to read. Minister of Finance and Corporate Affairs Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman said that
- Simplification of tax regimes without exemptions and deductions for corporate and personal income tax has been appreciated by tax payers as over 58% of corporate tax came from simplified tax regime in 2022-23 and more than two third tax payers have switched over to the new personal income tax regime.

Income Tax rates
The tax slab of ₹3-6 lakh has been revised to ₹3-7 lakh, with the 5% tax rate unchanged.
| Income Slabs | Tax Rate |
| 0 – 3 Lakh rupees | NIL |
| 3 – 7 Lakh rupees (limit revised) | 5% |
| 7 – 10 Lakh rupees | 10% |
| 10 – 12 Lakh rupees | 15% |
| 12 – 15 Lakh rupees | 20% |
| Above 15 Lakh rupees | 30% |
Standard Deduction
Budget 2024-25 increased standard deduction in the income tax for a host of individuals:
- For salaried employees from ₹ 50,000/- to ₹ 75,000/- for those opting for new tax regime.
- Deduction on family pension for pensioners enhanced from ₹ 15,000/- to ₹ 25,000/-.
These measures aim to provide relief to around 4 crore salaried individuals and pensioners.
Assessments now, can be reopened beyond three years up to 5 years from end of year of assessment, only if, the escaped income is more than ₹ 50 Lakh. The new tax regime rate structure is also revised to give a salaried employee benefits up to ₹ 17,500/- in income tax.
Tax Reforms for Industries
Angel Tax
- Removing angel tax for all classes of investors and simplified rules and recognition for FDIs aim to facilitate inflow and promote the Rupee for overseas investments.
- This will boost the start-up morale.
- About Angel Tax: It was introduced in 2013 Budget. It is an income tax levied at the rate of 30.6% when an unlisted company issues shares to an investor at a price higher than its fair market value. It taxed the difference between amount received by a start-up against dilution of their equity/asset and fair market value of that asset. This was done to curb money laundering.
Other Reforms:
Aim: To promote investment and foster employment, Budget has given boost to entrepreneurial spirit and start-up ecosystem, abolishing angel tax.
- For Foreign Shipping companies: a simpler tax regime for foreign shipping companies operating domestic cruises is proposed looking at the tremendous potential of cruise tourism.
- Foreign miningcompanies selling raw diamonds in the country can now benefit from safe harbor rates which will benefit the diamond industry.
- Corporate tax rate on foreign companies reduced from 40 to 35% to attract foreign capital.
Rationalisation of Tax rate Structures
Tax regime for charities
Simplified the direct tax regime for charities: The two tax exemption regimes for charities will be merged into one.
TDS rate structure
- Rationalisation of TDS: 5% TDS on many payments to be merged into 2% TDS and 20% TDS on repurchase of units by mutual funds or UTI stands withdrawn.
- TDS rate on e-commerce operators reduced from 1% to 0.1%.
- Now credit of TCS will be given on TDS deducted from salary.
- Decriminalized delay of payment of TDS up to the due date of filing of TDS statement.
- Standard Operating Procedure soon for simplified and rationalized compounding guidelines for TDS defaults.
Capital gains taxation.
- Short term capital gains (STCG) tax increased to 20% from 15% on certain financial assets, including shares, bonds etc.
- Long term Capital Gains (LTCG) Tax rationalisation: LTCG tax on all financial and non-financial assets to attract 12.5% rate.
- Definition: Listed financial assets held for more than a year and unlisted assets (financial and non-financial) held for more than two years to be classified as long-term assets. Unlisted bonds and debentures, debt mutual funds and market linked debentures will continue to attract applicable capital gains tax.
- For equity share/equity-based fund of Limit of exemption on Long term capital gains has been increased to ₹1.25 Lakh per year. The LTCG Tax rate has been increased from 10% to 12.5%.
- For all other Capital Gains:
- In line with other LTCG assets, the LTCG tax rate has been lowered from 20% to 12.5% for fixed assets too (i.e. mainly property).
- The indexation benefit has been eliminated for Fixed capital assets from the calculation of LTCG.
- What is Indexation? Indexation offsets accrued capital gains against inflation rate during the holding period, lowering the effective tax rate.
- Exception: Properties purchased or inherited prior to the year 2001 will continue to enjoy the indexation benefit.
Custom Duties
The Government envisages further simplifying and rationalizing the tax structure to expand it to remaining sectors. Further digitalisation of remaining services of Customs and Income Tax including rectification and order giving effect to appellate orders over the next two years.
Custom duties have been revised to rationalize and revise them for ease of trade and reduction of disputes.
- Giving relief to cancer patients, Budget fully exempted three more cancer treating medicines from custom duties, namely, Trastuzumab Deruxtecan, Osimertinib and Durvalumab.
- Reduction in Basic Customs Duty (BCD) on X-ray machines tubes and flat panel detectors.
- BCD on mobile phones, Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) and mobile chargers reduced to 15%. However, to incentivize domestic manufacturing, BCD on PCBA of specific telecom equipment increased from 10 to 15%.
- To give a fillip to processing and refining of critical minerals, full exemption of custom duties on 25 rare earth minerals like lithium and reduced BCD on two of them.
- Budget proposed to exempt capital goods for manufacturing of solar panels.
- To boost India’s seafood exports, BCD on broodstock, polychaete worms, shrimps and fish feed reduced to 5%.
- To foster competitiveness of Indian leather and textiles articles of export, BCD reduced from 7.5% to 5% in Methylene Diphenyl Diisocyanate (MDI) used for manufacture of spandex yarn.
- Custom duties on gold and silver reduced to 6% and on platinum to 6.4%.
- BCD on ferro nickel and blister copper removed, while, BCD on ammonium nitrate increased from 7.5 to 10% to support existing and new capacities in pipeline. Similarly, BCD on PVC flex banners increased from 10 to 25% considering the hazard to environment.
Vivad Se Vishwas
For dispute resolution and dispose-off backlogs, Vivad se Vishwas Scheme – 2024 for resolution of certain income tax disputes pending in appeal.
The monetary limits for filing appeals related to direct taxes, excise and service tax in High Courts, Supreme Courts and tribunals has been increased to ₹ 60 Lakh, ₹ 2 Crore and ₹ 5 Crore, respectively.
Further to reduce litigation and provide certainty in international taxation, scope of safe harbour rules to be expanded and transfer pricing assessment procedure to be streamlined.
| About Vivad se Vishwas Scheme |
|
This is an umbrella scheme which aims to provide a mechanism to the taxpayers amicably resolve their cases/conflict with the income tax department. Various provisions have been launched under the Vivad se Vishwas over the years:
|

