4 May 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Eta Aquariid Meteor Shower: A Celestial Spectacle Set to Illuminate the Night Skies
| (Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 14)
Topic: GS3 – Science & Technology – Space GS1 – Geography |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of the News:
The Eta Aquariid Meteor Shower:
- The article provides insights into the Eta Aquariid meteor shower.
- It describes the phenomenon as comprising burning space debris entering Earth’s atmosphere at high speeds and explains its visibility from countries such as Indonesia and Australia in the Southern Hemisphere.
Understanding Comets and Meteor Showers:
- Comets, described as frozen remnants from the formation of the solar system, consist of dust, rock, and ice.
- They orbit the Sun in elliptical paths, occasionally coming closer to heat up and emit gases and dust, forming a glowing head and tail.
- Meteor showers are related to comets, occurring when Earth passes through the debris left behind in a comet’s orbital plane.
Mechanism of Meteor Showers:
- Meteors, grains of dust or rock, burn up upon entering Earth’s atmosphere, creating brief tails.
- Most meteors disintegrate completely due to their small size, but occasionally larger meteors, called meteorites upon impact, can cause significant damage upon reaching the ground.
- Meteor showers occur when Earth passes through clouds of dust left behind by comets, resulting in a spectacle of glowing meteor tails in the sky.
Eta Aquariid Meteor Shower and Its Origin:
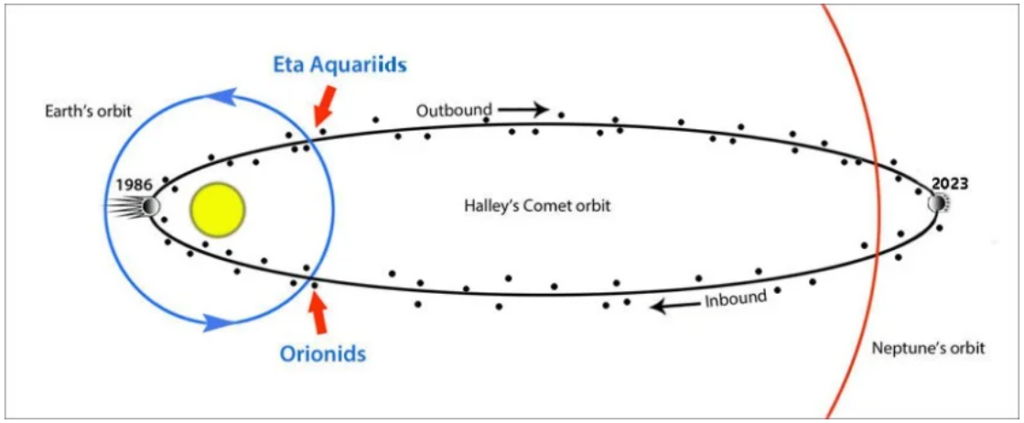
- The Eta Aquariid meteor shower originates from Halley’s Comet’s orbital plane, observed approximately every 76 years.
- Named after astronomer Edmond Halley, who identified its periodic appearances, Halley’s Comet is set to re-enter the inner solar system in 2061.
- The Eta Aquariids, known for their rapid speed, produce long-lasting glowing tails, making them a unique celestial event.
Unique Characteristics and Viewing Tips:
- The Eta Aquariids are characterized by their rapid speed, with approximately 30 to 40 meteors visible per hour during the peak, particularly from the Southern Hemisphere.
- In contrast, viewers in the Northern Hemisphere may observe fewer meteors due to the lower radiant position in the sky.
- Tips for optimal viewing include finding a clear night sky with minimal light pollution, preferably away from artificial lighting sources.
Conclusion:
- The article concludes by encouraging everyone to witness the Eta Aquariid meteor shower, which is likely to be visible across the sky, originating from the Aquarius constellation.
- It emphasizes the significance of clear viewing conditions and suggests using basic telescopes to enhance the experience of this natural nighttime spectacle.
| About Orionid Meteor Shower |
|
| PYQ: What is the difference between asteroids and comets? (2011)
1. Asteroids are small rocky planetoids, while comets are formed of frozen gases held together by rocky and metallic material. 2. Asteroids are found mostly between the orbits of Jupiter and Mars, while comets are found mostly between Venus and mercury. 3. Comets show perceptible glowing tails, while asteroids do not. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 1 and 3 only (c) 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Answer: (b) |
| Practice Question: What is the significance of the Eta Aquariid meteor shower, and how does it relate to comets like Halley’s Comet? Discuss the factors influencing its visibility from different regions and its importance in fostering public interest in astronomy. (250 words/15 m) |
2. Study Reveals Oral Cancer’s $5.6 Billion Productivity Loss in India
| (Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page 1)
Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of the News:
The Study’s Key Findings:
- The study, led by Tata Memorial Hospital (TMH), estimates that premature oral cancer deaths have led to productivity losses of $5.6 billion, equivalent to 0.18% of India’s GDP in 2022.
- Experts highlights that 91% of the deaths occurred among patients with a median age of 41.5 years.
- The study tracked 100 patients over three years, revealing that those who succumbed to the disease cumulatively lost 671 productive or working years, with the monetary value of losses exceeding Rs 72 lakh for men and Rs 57 lakh for women.
Significance of the Study:
- Senior Experts from Tata Memorial Centre, emphasizes the significance of the study in shedding light on productivity losses of cancer in low-resource settings like India.
- As per experts the findings will aid policymakers in planning effective resource allocation for oral cancer treatments.
- The study underscores the challenges of late diagnosis, intervention, access to healthcare, and the financial burden of treatment, especially for the middle class.
Causes and Impact of Oral Cancer:
- Oral cancer is primarily caused by factors such as tobacco consumption, excessive alcohol consumption, unhygienic oral conditions, and viral infections like papillomavirus.
- The study analyzed the impact of premature deaths on GDP, revealing substantial income losses per death, particularly in advanced-stage cancer cases.
- Experts from TMH utilized the human capital approach to calculate productivity loss, considering education, training, and health as investments in human capital that enhance productivity and earning potential over time.
Limitations and Underestimation of Impact:
- While the study provides valuable insights, experts acknowledges its limitations, including potential underestimation of the true impact due to disparities in treatment access across the country.
- They highlight the importance of considering individual patient data, including socioeconomic status and education levels, in economic studies to provide a comprehensive understanding of the burden of diseases like oral cancer.
Significance and Implications:
- Oral cavity cancer has become the most prevalent cancer among men in India, contributing to a significant portion of the global incidence and mortality.
- Doctors of Tata Memorial Centre, emphasizes the need for early screening, given the increasing incidence of oral cancers among younger age groups.
- Despite advancements in diagnosis and treatment, financial burdens and late-stage detections continue to pose challenges, impacting both healthcare providers and patients and leading to elevated mortality rates and diminished quality of life.
| More details about Oral Cancer |
|
| Practice Question: What are the economic implications of premature oral cancer deaths in India? Discuss the factors contributing to productivity losses and the significance of early screening in addressing the economic burden of oral cancer.. (250 words/15 m) |
3. End of an Era: Aging NASA Satellites Pose Challenges for Climate Research
| (Source: Indian Express; Section: The World; Page: 12)
Topic: GS3 – Science & Technology – Space |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of the News:
Aging NASA Satellites:
- As three stalwart NASA satellites—Terra, Aqua, and Aura—approach the end of their operational lives, scientists are grappling with the impending loss of invaluable data.
- These satellites have been in orbit for over two decades, providing crucial information for weather forecasting, wildfire management, oil spill monitoring, and more.
- However, as they near their final descent to Earth, researchers face the daunting task of finding alternative sources for the data they have been collecting.
Implications for Climate Research:
- The shutdown of these satellites poses a significant setback for climate research, particularly in monitoring the stratosphere and ozone layer.
- Experts at MIT, laments the loss of irreplaceable data, emphasizing the critical role of these satellites in understanding the dynamics of the ozone layer.
- Data from the microwave limb sounder on Aura has been instrumental in revealing the impact of natural disasters such as wildfires and volcanic eruptions on ozone depletion, highlighting the urgent need for continuous monitoring.
Impact on Climate Modeling:
- Furthermore, the end of Terra and Aqua will disrupt the monitoring of solar radiation and its effects on Earth’s climate.
- These satellites play a crucial role in measuring the balance between incoming solar radiation, absorption, and reflection, which is essential for climate modeling and predicting global temperature changes.
- The data provided by NASA’s Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System (CERES) instruments is indispensable for understanding the Earth’s energy budget and the drivers of climate variability.
Transition to New Technologies:
- Amidst the looming loss of these aging satellites, NASA and other agencies are exploring alternative approaches to Earth observation.
- The future may involve smaller, lighter instruments that can be deployed more cost-effectively and efficiently.
- However, the transition to these new technologies must occur before the existing satellites go dark to ensure continuity in Earth monitoring and climate research.
Conclusion:
- The retirement of NASA’s Terra, Aqua, and Aura satellites marks the end of an era in Earth observation.
- While the loss of these venerable spacecraft poses significant challenges for climate research, it also presents an opportunity for innovation and the development of more agile and versatile Earth observation technologies.
- As scientists brace for the inevitable, the imperative remains to ensure the continuity of data collection and monitoring to address the pressing challenges of climate change and environmental degradation.
| India’s Weather Satellites |
Types of Weather Satellites
|
| Practice Question: What are the implications of the impending shutdown of NASA’s aging satellites—Terra, Aqua, and Aura—for climate research and Earth observation? Discuss the challenges faced by scientists and the importance of transitioning to new technologies for continuous monitoring of environmental changes. (250 words/15 m) |
4. India press freedom score fell over the last year: RSF
| (Source – The Hindu, Section – News, Page – 5)
Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context: |
| ● India’s press freedom declined as per Reporters Without Borders, despite a marginal rise in rank due to global declines.
● RSF highlighted India’s media under an “unofficial state of emergency” since present government’s tenure. |
Analysis of the news:
- India’s World Press Freedom Index score dropped from 36.62 to 31.28, with a rank improvement from 161 to 159 due to other countries’ declines.
| About World Press Freedom Index |
|
- Norway and Denmark topped the index, while Eritrea ranked lowest, with Syria just above.
- RSF attributed global press freedom threats to political authorities, with a 7.6-point average decline globally.
- India’s media is described as under an “unofficial state of emergency” since Modi’s 2014 tenure, with criticism of BJP leading to harassment campaigns.
- The U.S. also saw a decline in press freedom score from 71.22 to 66.59 and a rank drop from 45 to 55, partly attributed to Trump’s presidency.
- RSF raised concerns about press freedoms in countries like the U.S., especially during election periods.
| Impacts of Threat To Press Freedom |
Threats to Press Freedom in India:
Impact:
Way Forward:
|
PYQ: What do you understand about the concept “freedom of speech and expression”? Does it cover hate speech also? Why do the films in India stand on a slightly different plane from other forms of expression? Discuss. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2014)
| Practice Question: Analysing the recent findings by Reporters Without Borders (RSF), discuss the challenges posed to press freedom in India. Examine the factors contributing to the decline in India’s press freedom index score and evaluate the implications of such threats on democratic principles and governance. (250 Words /15 marks) |
5. India, Indonesia agree to enhance defence industry collaboration
| (Source – The Hindu, Section – News, Page – 5)
Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral Relations |
| Context |
| ● India and Indonesia reaffirmed their commitment to strengthening defence ties during the seventh India-Indonesia Joint Defence Cooperation Committee meeting in New Delhi.
● Discussions focused on enhancing collaboration in defense industry, maritime security, and multilateral cooperation. |
Analysis of the news:
- India and Indonesia held the seventh India-Indonesia Joint Defence Cooperation Committee meeting in New Delhi.
- Chaired by Defence Secretary Giridhar Aramane and Secretary-General of Indonesia’s Ministry of Defence Air Marshal Donny Ermawan Taufanto.
- Both sides agreed to enhance collaboration in defence industry, maritime security, and multilateral cooperation.
- They expressed satisfaction at the expanding scope of defence cooperation between the two countries.
- Progress on various bilateral initiatives discussed in working groups on defence cooperation and defence industries cooperation was reviewed.
- Air Marshal Taufanto visited DRDO headquarters, TATA Advanced Systems, and Larsen & Toubro defence facilities in Pune.
- He also met with Indian defence industry partners like Bharat Forge, Mahindra Defence, and Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited to discuss cooperation in research and joint production.
- The visit aimed to strengthen defence ties and enhance defence industrial capabilities through collaboration and exchanges.
| India – Indonesia Relations |
| India – Indonesia Complementary Relations:
● Strategic Location: Both countries are strategically located in the Indo-Pacific region, enhancing regional stability and security. ● Economic Cooperation: Bilateral trade and investment relations are robust, with potential for further growth, particularly in sectors like energy, infrastructure, and agriculture. ● Cultural Ties: Historical and cultural connections, including shared traditions and heritage, foster strong people-to-people relations. ● Maritime Collaboration: Cooperation in maritime security and navigation promotes safety and stability in the Indian Ocean and beyond. ● Strategic Partnerships: Engagement in regional forums like ASEAN strengthens diplomatic ties and regional cooperation. ● Defence Cooperation: Collaboration in defence and security initiatives enhances mutual capabilities and addresses common security challenges. ● Development Assistance: India provides development assistance to Indonesia, supporting infrastructure projects and capacity-building initiatives. Challenges: ● Trade Barriers: Tariffs and non-tariff barriers hinder smooth trade relations. ● Infrastructure Gaps: Lack of robust infrastructure affects connectivity and trade facilitation. ● Security Concerns: Maritime disputes and security challenges in the region pose risks. Way Forward: ● Enhanced Trade Relations: Address trade barriers through negotiations and agreements. ● Infrastructure Development: Invest in infrastructure projects to improve connectivity. ● Security Cooperation: Strengthen maritime security cooperation to address common challenges. ● Cultural Exchanges: Promote cultural exchanges and people-to-people ties to deepen understanding. ● Diplomatic Engagement: Continue diplomatic dialogue and collaboration in regional forums to foster mutual interests. |
| PYQ: Explain the formation of thousands of islands in Indonesian and Philippines archipelagos. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2014) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the recent developments in India-Indonesia defence cooperation and their significance in strengthening bilateral ties. How can enhanced collaboration in the defence industry and maritime security contribute to regional stability and multilateral cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region? (250 Words /15 marks) |



