13 September 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. PM announces passing of Delhi Declaration on Civil Aviation
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2054335 )
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
Delhi Declaration (2nd Asia Pacific Ministerial Conference on Civil Aviation)
- Adoption: The Delhi Declaration was formally adopted on September 12, 2024, marking the conclusion of the 2nd Asia Pacific Ministerial Conference on Civil Aviation.
- Purpose: The declaration serves as a comprehensive framework aimed at enhancing regional cooperation, addressing emerging challenges, and fostering sustainable growth in the civil aviation sector within the Asia Pacific region.
- Participants: The conference included delegates from 29 countries, along with 8 international organisations, including the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), celebrating its 80th anniversary.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Regional Cooperation: Emphasises strengthening collaborative efforts among Asia Pacific countries to address common aviation challenges.
- Sustainability: Encourages the adoption of environmentally sustainable practices and technologies in aviation operations to minimise ecological impact.
- Safety and Security: Reinforces the need for high standards of safety and security within the aviation industry.
- Inclusivity: Supports the promotion of diversity and inclusivity within the aviation sector, including efforts to increase the participation of women in aviation.
- Economic Growth: Aims to use aviation as a driver for regional economic development and enhanced connectivity.
Significance: The declaration represents a milestone in advancing the region’s aviation sector through collective and progressive measures, positioning Asia Pacific as a leader in global aviation standards and practices
2. What does dissolution of SCoS entail?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity |
| Context |
|
Dissolution of the Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS)
- The Union Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation dissolved the 14-member SCoS, headed by Pronab Sen, former chief statistician of India.
- The Ministry cited overlapping functions with the Steering Committee for National Sample Surveys, headed by Rajeeva Laxman Karandikar, as the reason for dismantling the SCoS.
- Dr. Sen revealed that SCoS members had questioned delays in conducting the census but were not given specific reasons for the committee’s dissolution.
| Key Responsibilities of Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS) |
|
Role of the New Steering Committee
- The new Steering Committee has 17 members, including retained members from SCoS and additional officials.
- Its responsibilities include reviewing methodologies, sampling designs, and survey instruments for National Sample Surveys.
- The Committee’s role is similar to that of SCoS, but with more official members.
Pressure for a New Census
- Academics and policymakers demand a new census as outdated 2011 data affects schemes like the National Food Security Act.
- The Opposition questions employment and unemployment figures and calls for reliable, up-to-date census data.
- The census provides crucial State and sub-district-level data on education and employment.
Flaws in Administrative Data
- Government data from EPFO, ESIC, and RBI’s KLEMS database is seen as biassed and threshold-based.
- There are concerns that administrative data reflects government intentions and lacks analytical rigour.
- Survey-based data, like the census, has universal coverage and greater reliability.
Urgency of the Next Census
- India’s last census was in 2011, and the 2021 census has been delayed due to COVID-19.
- Economists argue that relying on 2011 data negatively impacts decision-making, urging the government to conduct the next census soon.
| Practice Question: Discuss the reasons behind the dissolution of the Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS) by the Union Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. How does this change impact the reliability of statistical data and the conduct of the census? (150 Words /10 marks) |
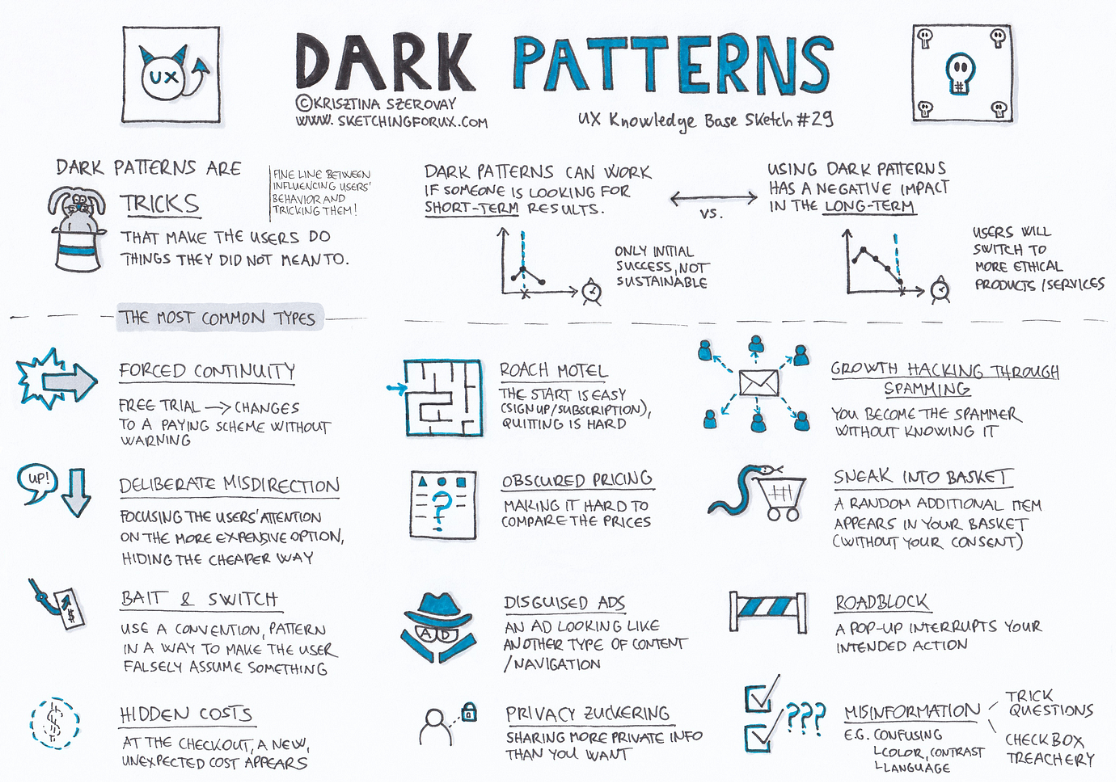
3. Dark patterns pose a growing concern in India’s digital landscape
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 13)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
| What are Dark Patterns? |
|
Dark patterns are deceptive design practices used in websites and apps to manipulate users into making decisions they might not have otherwise made.These tactics exploit psychological tendencies and often involve misleading information, hidden fees, or confusing navigation.Common examples include creating false urgency, making subscription cancellations difficult to find, and using misleading language to trick users. |
Concerns Posed by Dark Patterns
- Consumer Manipulation: Dark patterns exploit psychological biases to push users into actions they did not intend, such as signing up for unwanted services or sharing personal information.
- Undermining Trust: These deceptive practices erode trust in digital platforms and online transactions, potentially leading to lower customer loyalty and increased negative perceptions of businesses.
- Legal and Ethical Risks: Companies using dark patterns face legal risks under consumer protection laws. In India, such practices fall under ‘unfair trade practices’ as per the Consumer Protection Act, 2019.
- Impact on Market Position: Businesses relying on dark patterns risk fines, legal actions, and damage to their reputation, which can affect their market position and competitiveness.
Way Forward
- Adopt Ethical Design Practices: Businesses should prioritise transparency by designing user-friendly interfaces with clear information on subscription terms and easy options for opting out or cancelling services.
- Educate Designers and Developers: Incorporate ethics into design training to ensure professionals consider the broader impact of their work and avoid employing manipulative tactics.
- Strengthen Regulations: Regulatory bodies should enforce guidelines that prevent dark patterns, including mandatory disclosures, penalties for non-compliance, and regular audits to ensure adherence.
- Empower Consumers: Use technological solutions like browser extensions and plug-ins to detect and warn users about potential dark patterns. Consumer advocacy groups should educate users about their rights and encourage reporting of unethical practices.
- International Collaboration: Learn from global regulations such as the EU’s Digital Services Act and GDPR to shape and enhance national guidelines against dark patterns.
| Practice Question: Analyse the impact of dark patterns on consumer trust in e-commerce and evaluate India’s recent guidelines to address these issues. How do these measures compare with international regulations? (150 Words /10 marks) |
Prelims Facts
1. INDIAN ARMY CONTINGENT DEPARTS FOR INDIA- OMAN JOINT MILITARY EXERCISE AL NAJAH V
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2054052 )
| Context |
|

Military Exercise AL NAJAH.:
- The Indian Army contingent departed today for the 5th edition of the India-Oman Joint Military Exercise AL NAJAH.
- The exercise is scheduled from 13th to 26th September 2024 at the Rabkoot Training Area in Salalah, Oman.
- Exercise AL NAJAH has been held biennially since 2015, alternating between India and Oman.
- The previous edition took place in Mahajan, Rajasthan.
- The exercise aims to enhance joint military capabilities for counter-terrorism operations under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter.
- It will focus on desert environment operations.
- Tactical drills include joint planning, cordon and search operations, and counter-drone measures.
- The exercise will foster interoperability, goodwill, and strengthen bilateral relations between India and Oman.
2. INDIA’S IIP RECORDS A GROWTH OF 4.8% IN THE JULY 2024.
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2054214 )
| Context |
|
What is IIP?
- The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) is a short-term indicator measuring the growth of industrial sectors in the Indian economy, covering mining, manufacturing, and electricity.
- It reflects changes in the volume of production, helping to gauge industrial growth until detailed surveys like the Annual Survey of Industries or GDP figures are available.
- The base year for IIP in India is 2011-12.
- The IIP is published monthly by the Central Statistics Office (CSO), six weeks after the reference month.
- The Indian Index of Industrial Production (IIP) covers three sectors—mining, manufacturing, and electricity—referred to as the broad sectors.
| Broad Sector | Number of Items | Weight (%) |
| Mining | 61 | 14.16 |
| Manufacturing | 620 | 75.53 |
| Electricity | 1 | 10.32 |
3. Beyond the horizon
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
SpaceX Polaris Dawn Mission:
- Mission Overview: SpaceX Polaris Dawn is a private space mission focusing on pioneering advanced spacewalks and high-altitude scientific experiments.
- Crew: The mission is led by Jared Isaacman, a private astronaut and space entrepreneur, along with other non-professional astronauts.

- Historic Achievement: It marks the first spacewalk conducted by non-professional astronauts, showcasing advancements in private space exploration.
- Objectives: Key objectives include conducting scientific research in microgravity, testing new space technologies, and expanding the capabilities of private space missions.
- Spacecraft: The mission uses a SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft, known for its reliability and advanced technology.
- Significance: Polaris Dawn represents a significant milestone in the democratisation of space travel and commercial space exploration.
4. ‘Mission Mausam’ to boost radar network to seed, tweak clouds
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|

Mission Mausam:
- Objective: To upgrade India’s weather forecasting infrastructure and enhance understanding of weather modification techniques.
- Budget: ₹2,000 crore, cleared by the Cabinet.
- Nodal Body: Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- Duration: First tranche until 2026.
- Key Equipment: Plans to install up to 60 weather radars, 15 wind profilers, and 15 radiosondes for monitoring atmospheric conditions.
- Cloud Simulation: A cloud-simulation chamber will be set up at the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune, to improve rain-cloud modelling.
- Weather Modification: The mission aims to conduct research on cloud-seeding and reducing lightning risk by modifying clouds.
- Radar Infrastructure: India currently has 39 weather radars (1 for every 432 km) compared to 160 in the U.S. (1 for every 154 km), highlighting the need for expansion.
- Significance: Improved data collection for more accurate weather forecasts and potential future weather interventions.
5. A 16-point document on judicial values was adopted by SC in 1997
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
16-Point Document on Judicial Values (Restatement of Values of Judicial Life):
- Adopted by the Supreme Court in a Full Court Meeting on May 7, 1997.
- Serves as a guide for the expected conduct of Supreme Court and High Court judges.
- Emphasises impartiality in judicial conduct.
- Judges should maintain a degree of aloofness consistent with the dignity of their office.
- Public confidence must be maintained through probity in interactions with other constitutional functionaries.
- A judge’s behaviour must reaffirm faith in the impartiality of the judiciary.
- Judges are advised to avoid any act that erodes credibility in public perception.
- Judges are to be conscious of being under public scrutiny.
- Avoid actions or omissions that are unbecoming of their high office.
- No official or personal acts should compromise judicial independence.
- Judicial conduct should uphold the separation of powers between the Executive and Judiciary.
- It is an illustrative guide, not exhaustive.
- Highlights the need for public esteem in the judiciary.