19 September 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. India Seeks Renegotiation of Indus Waters Treaty Amidst Rising Tensions with Pakistan
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 18)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
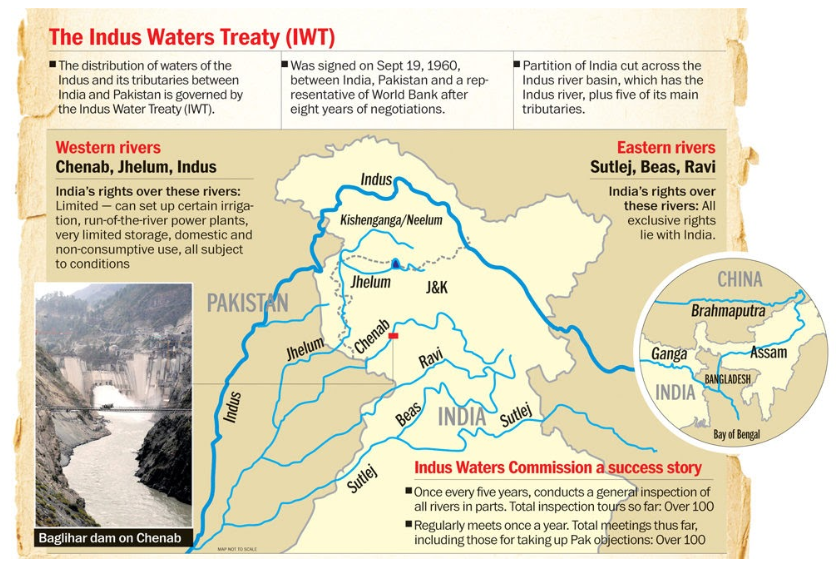
What is the Indus Waters Treaty?
- Signed in 1960 between India and Pakistan, the IWT governs the use of the waters from the Indus River and its tributaries.
- India received unrestricted use of the Eastern Rivers (Beas, Ravi, Sutlej), while Pakistan controls the Western Rivers (Indus, Chenab, Jhelum).
- India is obligated to let the waters of the Western Rivers flow to Pakistan under the treaty.
Reasons for India’s Renegotiation Demand
India cites “fundamental and unforeseen changes in circumstances” for its renegotiation request, including:
- Changes in population demographics
- Environmental concerns and clean energy development
- Cross-border terrorism threats
- The construction of two hydropower projects by India in Jammu and Kashmir has also sparked controversy, with Pakistan claiming that these violate the IWT.
Background to the January 2023 Notice
- India’s earlier notice in January 2023 stemmed from Pakistan’s objections to the hydropower projects and its inconsistent dispute resolution approach.
- Pakistan first sought a “Neutral Expert” for mediation but later shifted to the Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA).
- India rejected the PCA route, citing violation of the treaty’s graded dispute settlement mechanism.
The Role of the World Bank
- The World Bank, a signatory to the IWT, paused the parallel legal processes in 2016, urging both nations to resolve the issue amicably.
- However, Pakistan insisted on moving forward with both dispute mechanisms, which led to India’s notice in 2023.
Key Developments Since January 2023
- April 2023: India held a meeting to assess the modification process of the IWT.
- July 2023: The PCA ruled it had jurisdiction over the hydropower projects, which India refuted.
- September 2023: India participated in Neutral Expert proceedings but continued to reject the PCA’s parallel involvement.
Conclusion
- India’s continued push for renegotiating the IWT reflects a broader effort to adapt the treaty to modern challenges, including environmental concerns and political disputes.
- The renegotiation process, if successful, could reshape water-sharing dynamics between India and Pakistan amidst growing regional tensions.
| What is Kishanganga Hydroelectric Project? |
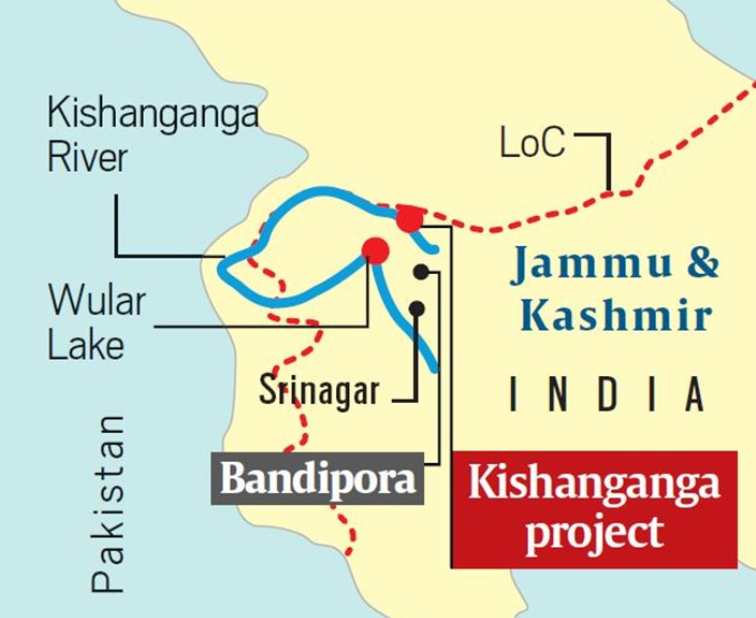
|
| PYQ: Present an account of the Indus Water Treaty and examine its ecological, economic and political implications in the context of changing bilateral relations. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2016) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of India’s recent notification seeking the “review and modification” of the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT). How does this move reflect the changing geopolitical and environmental landscape, and what are the potential consequences for Indo-Pakistani relations and regional water management? (250 words/15 m) |
2. Cabinet Clears Proposal for One Nation, One Election: Constitutional Amendments and Phased Implementation Ahead
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 18)
| Topic: GS2 – Polity |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
What is the Central Idea behind One Nation-One Election (ONOE)?
- The concept talks about a scenario where all State elections will take place simultaneously with the general elections of Lok Sabha, once every five years.
- The idea is to streamline the electoral process and reduce the frequency of elections, thus saving time and resources.
Background:
- The idea has been around since 1983, when the Election Commission first mooted it. However, until 1967, simultaneous elections were the norm in India.
- The first General Elections to the House of People (Lok Sabha) and all State Legislative Assemblies were held simultaneously in 1951-52.
- That practice continued in three subsequent General Elections held in the years 1957, 1962 and 1967.
- However, due to the premature dissolution of some Legislative Assemblies in 1968 and 1969, the cycle got disrupted.
-
- In 1970, the Lok Sabha was itself dissolved prematurely and fresh elections were held in 1971. Thus, till 1970, only the First, Second and Third Lok Sabha enjoyed full five-year terms.
Phased Implementation
- The transition to simultaneous elections will occur in two phases.
- First, Lok Sabha and state Assembly elections will be synchronized, followed by local body elections within 100 days.
- This approach seeks to streamline electoral processes nationwide.
Constitutional Amendments Required
- Two key Constitution Amendment Bills are necessary to bring this initiative to life.
- These require a special majority in both the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha.
- Additionally, at least half of the state legislatures must ratify the amendment regarding local body elections.
State-Level Cooperation
- The states will need to cooperate to ratify the amendments, especially as local governments fall under their jurisdiction.
- As upcoming elections in several states could change political dynamics, the Centre will need broad consensus across parties.
Mid-Term Elections and Unexpired Terms
- In cases where a state Assembly or Lok Sabha dissolves before completing its five-year term, a mid-term election will be held.
- However, these elected bodies will serve only until the next scheduled simultaneous elections.
Election Commission’s Role
- The Election Commission will create a unified electoral roll covering Lok Sabha, state, and local elections.
- This would be done in consultation with state Election Commissions to streamline voter databases across the country.
| What are the Challenges Associated with ONOE? |
Constitutional Concerns and Mid-Tenure Collapse:
Logistical Challenges in Implementing ONOE:
Federalism Concerns and Law Commission’s Findings:
Recurrence of Elections and Democratic Benefits:
Biased Democratic Structure:
Cost Implications and Economic Considerations:
Legal Concerns:
Language Bias in Consultation Process:
Independence of the Election Commission:
|
| PYQ: ‘Simultaneous election to the Lok Sabha and the State Assemblies will limit the amount of time and money spent in electioneering but it will reduce the government’s accountability to the people’ Discuss. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2017) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the potential challenges and implications of implementing the “One Nation, One Election” proposal in India. How would it affect the federal structure, democratic processes, and governance at the central, state, and local levels? (250 words/15 m) |
3. PM-AASHA schemes to continue with additions: Centre
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Topic: GS3 – Agriculture |
| Context |
| ● The Union Cabinet approved the continuation of PM-AASHA schemes to ensure fair prices for farmers and control essential commodity price volatility.
● Additionally, the Cabinet set Nutrient Based Subsidy rates for fertilisers, ensuring affordability for farmers during the upcoming rabi season. |


Potential Benefits for Farmers under PM-AASHA
- Ensures MSP: Prevents distress sales by guaranteeing minimum support prices for pulses, oilseeds, and copra.
- Expanded Procurement: Increased coverage for procurement from 25% to 40% of state production for oilseeds under the Price Deficit Payment Scheme (PDPS).
- More Direct Payments: Farmers receive differential payments directly into their accounts under the Market Intervention Scheme (MIS).
- Motivation for Cultivation: Promotes the cultivation of pulses and oilseeds, contributing to self-sufficiency and reducing import dependency.
- Buffer Stock Benefits: Stabilises prices, especially for perishable commodities like onion and tomatoes, ensuring fair prices.
- E-platform Integration: Farmers registered on the eSamridhi and eSamyukti portals benefit from MSP even if market prices drop.
- Support for Perishables: Transportation and storage costs for Tomato, Onion, Potato (TOP) crops covered, ensuring better returns.
| Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay SanraksHan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA): |
| ● Objective: PM-AASHA aims to ensure remunerative prices for farmers and mitigate price volatility of essential commodities.
● Components:
● Financial Allocation: ₹35,000 crore allocated during the 15th Finance Commission cycle (up to 2025-26). ● Farmer Protection: Ensures MSP for produce, protecting farmers from fluctuating market prices. ● Consumer Protection: Helps maintain stable supply and affordable prices for agricultural commodities. ● Overall Impact: Supports both producers and consumers by managing price volatility and ensuring price stability. |
| Practice Question: Discuss the objectives and components of the Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay Sanrakshan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA) scheme. How does it aim to stabilise prices for farmers and consumers? (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. Superfast lasers open shortcut to hard drives of the future
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS3 – Science And Technology |
| Context |
| ● Ultrafast lasers have achieved spin currents in just 2 femtoseconds, advancing spintronics technology.
● This breakthrough promises faster, more efficient hard drives by enabling quicker data storage and retrieval, potentially revolutionising future data storage technologies. |
How Ultrafast Lasers Could Revolutionise Future Hard Drives
- Spintronics Basics: Hard drives use electrons’ spin states (up or down) to store data. Faster data storage and retrieval depend on manipulating these spin states quickly.
- Need for Speed: Current technology is limited by how fast we can change these spin states. Faster spin currents can lead to quicker data processing.
- Role of Ultrafast Lasers: Scientists use ultrafast lasers to create spin currents—rapidly changing the spin states of electrons.
- New Achievement: Researchers recently achieved spin currents in just 2 femtoseconds (fs), far faster than previous methods.
- Implications for Hard Drives: This speed allows for more efficient and faster data storage and retrieval. Future hard drives could operate at petahertz rates, vastly improving performance.
- Future Testing: Next steps include testing these methods in real hard drives and pushing for even faster spin currents.
5. Cabinet accepts recommendations of High-Level Committee on Simultaneous Elections
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2056059 )
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity |
| Context |
| ● The Union Cabinet has accepted the recommendations of a High-Level Committee chaired by former President Ram Nath Kovind, advocating for simultaneous elections across India.
● The report proposes phased implementation, aiming to streamline electoral processes and enhance governance stability nationwide. |

Background Of Simultaneous Elections:
- Between 1951 and 1967, simultaneous elections were held for the Lok Sabha and State Assemblies.
- The 170th Law Commission Report (1999) recommended one election every five years for the Lok Sabha and Legislative Assemblies.
- The 79th Parliamentary Committee Report (2015) proposed a two-phase method for implementing simultaneous elections.
High-Level Committee:
- The committee, chaired by former President Shri Ram Nath Kovind, consulted various stakeholders, including political parties and experts.
- The committee received extensive feedback showing widespread support for simultaneous elections.
Key Recommendations of the committee:
- Two-Phase Implementation:
- Phase 1: Conduct Lok Sabha and Legislative Assembly elections together.
- Phase 2: Hold local body elections (panchayat and municipal) within 100 days of general elections.
- Common Electoral Roll: Implement a common voter roll for all elections to avoid duplication of electoral processes.
- Wider Discussions: Encourage comprehensive discussions on simultaneous elections across the country.
Way Forward:
- Implementation Group: A specialised group should be formed to oversee the rollout of simultaneous elections.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Broad consultations should continue with political parties and electoral experts.
- Phased Rollout: The committee suggested a gradual transition to simultaneous elections to manage logistical challenges.
This approach aims to streamline the election process, reduce costs, and enhance governance stability.
| PYQ: ‘Simultaneous election to the Lok Sabha and the State Assemblies will limit the amount of time and money spent in electioneering but it will reduce the government’s accountability to the people’ Discuss. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2017) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the advantages and challenges of implementing simultaneous elections in India as recommended by the High-Level Committee chaired by Shri Ram Nath Kovind. (150 Words /10 marks) |
Prelims Facts
1. Madras High Court junks plea to declare Tamil saint-poet’s birthday on Vaikasi Anusham
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 2)
| Context |
| ● The Madras High Court dismissed a petition seeking to declare Vaikasi Anusham as the official birthday of Tamil poet Tiruvalluvar, instead of the current celebration on the second day of Thai.
● The court upheld the Tamil Nadu government’s decision, stating that ‘Tiruvalluvar day’ is meant to honour his literary works, not a specific birth date. |
More About Tiruvalluvar:
- Tiruvalluvar is a renowned Tamil poet and philosopher, best known for his work, the Tirukkural, a classic collection of 1,330 couplets.
- The Tirukkural addresses universal themes such as ethics, politics, economics, and love, and is considered one of the greatest works of Tamil literature.
- Though his exact birth date and place are uncertain, he is believed to have lived between the 4th and 5th century CE.
- Tiruvalluvar is revered as a moral guide and social reformer in Tamil Nadu, with his work promoting non-violence, justice, and the welfare of all.
- His teachings transcend religious boundaries, appealing to people from all walks of life and faiths.
- The Tirukkural has been translated into numerous languages, symbolising its global appeal.
- A 133-foot statue of Tiruvalluvar stands in Kanyakumari, symbolising the significance of his work.
2. We are sharing state-of-the-art expertise with ISRO for Gaganyaan’
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Context |
| ● The news highlights India’s space collaboration with France, focusing on the Gaganyaan mission.
● France is assisting with astronaut training, space medicine, and knowledge exchange, while both nations plan future cooperation in space exploration and satellite launches, including the TRISHNA mission. |
Analysis of the news:
- France is actively supporting India’s Gaganyaan mission, leveraging its extensive experience in human spaceflight.
- Focus on space medicine: French space experts are sharing knowledge on space physiology and medicine, helping India understand the physical effects of space travel on astronauts.
- Astronaut training: French expertise is aiding in training Indian astronauts, ensuring they are prepared for the physical and psychological challenges of space missions.
- State-of-the-art technologies: France is providing access to cutting-edge technologies and latest advancements in human spaceflight.
- Knowledge exchange programs: Both countries are engaged in continuous collaboration, focusing on key areas like space exploration and human space physiology, thus enhancing India’s capabilities in manned space missions.
| TRISHNA Mission |
| ● TRISHNA (Thermal Infra-Red Imaging Satellite for High-resolution Natural Resource Assessment) is a joint mission between India and France.
● The satellite will be launched in 2026. ● It uses thermal infrared imaging to provide high-resolution data for monitoring natural resources. ● Applications include climate change assessment, agricultural management, drought forecasting, and urban heat island monitoring. ● The mission will enhance Earth observation capabilities by analysing temperature variations on land and water. ● The data collected will support sustainable resource management and help address global environmental challenges, including climate change. |
3. Earth to Temporarily Capture Asteroid 2024 PT5 as Rare ‘Mini-Moon
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page 18)

| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
What is a ‘Mini-Moon’?
- A mini-moon refers to an asteroid that becomes temporarily trapped by Earth’s gravity and orbits the planet for a short period.
- Mini-moons are small and difficult to detect, with only four confirmed mini-moons ever discovered.
- Some objects initially thought to be mini-moons turned out to be space debris.
Characteristics of 2024 PT5
- 2024 PT5 was discovered using NASA’s Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) on August 7.
- The asteroid is about 33 feet long and is too small to be seen with the naked eye or amateur telescopes.
- It likely originates from the Arjuna asteroid belt, which has orbits similar to Earth’s. There is also a possibility that 2024 PT5 is a fragment of the Moon.
Classification Debate
- While 2024 PT5 is being considered as a potential mini-moon, it may not fully qualify.
- To be classified as a mini-moon, an asteroid must complete at least one full orbit around Earth.
- Instead, 2024 PT5 will perform a horseshoe-shaped orbit, meaning it will not complete a full revolution around Earth this fall.
Scientific Significance
- The observations of 2024 PT5 will help scientists better understand asteroids that pass close to Earth or collide with it.
- This knowledge is crucial for future endeavors, including asteroid mining, where companies aim to extract valuable minerals and water for use in space missions, such as producing rocket fuel.
4. Air pollution a risk factor for brain strokes, similar to smoking: Study
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 09)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Key Findings from the Study
- Link Between Air Pollution and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH): Air pollution, particularly particulate matter (PM2.5), has emerged as a significant risk factor for subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), a type of brain stroke caused by ruptured blood vessels between the brain and its covering tissues.
- Global Impact: In 2021, around 14% of deaths and disabilities from SAH were attributed to particulate matter pollution, a risk factor comparable to smoking.
Types of Brain Strokes
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH): Bleeding occurs between the brain and the tissues covering it.
- Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Bleeding within brain tissue due to ruptured blood vessels.
- Ischaemic Stroke: The most common type, caused by a blood clot or blockage in brain vessels.
Role of Particulate Matter (PM2.5)
- Impact on Arteries: PM2.5 particles, about 30 times thinner than human hair, can damage arterial cells either directly or indirectly through inflammation, increasing the chances of rupture and leading to SAH.
Climate Change and Stroke Risk
- Rising Risk from Heat: The risk of strokes linked to high temperatures has increased by more than 70% from 1990 to 2021, emphasizing the role of climate change in stroke incidents.
Decline in Stroke Mortality
- Reduction in Deaths: Between 1990 and 2021, deaths from SAH decreased by 34%, intracerebral hemorrhage deaths fell by 29%, and ischaemic stroke deaths reduced by 13%.
Modifiable Risk Factors
- Preventable Risks: The study found that 84% of strokes in 2021 were connected to 23 modifiable risk factors, including air pollution, smoking, diet, body mass index (BMI), blood pressure, and cholesterol.
Increasing Stroke Risk Factors
- Rising Health Risks: Key stroke risks such as high BMI increased by 88%, while high blood sugar levels rose by 32% from 1990 to 2021.
5. India Launches First Integrated Ocean Energy Atlas to Harness Blue Renewable Energy Potential
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 09)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Key Findings
Mapping Blue Renewable Energy Sites:
- Indian oceanographers have identified potential sites along India’s coastline for generating energy from blue renewable sources like tidal waves and ocean currents.
Integrated Ocean Energy Atlas:
- The Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) has developed an “Integrated Ocean Energy Atlas” to estimate the renewable energy potential from various blue energy sources along India’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), covering up to 220 km from the coast.
Energy Potential
Estimated Energy Output:
- India’s EEZ is estimated to hold a potential of about 9.2 lakh Terawatt hours (TWh) from blue renewable energy sources.
Importance of Blue Energy
Untapped Energy Resources:
- Offshore renewable energy sources such as sun, wind, tides, waves, and ocean thermals have been underutilized, and harnessing them can play a vital role in India’s transition to a blue economy and achieving net-zero energy goals.
Assessment Approach
Data and Methodology:
- The atlas was created using 20-30 years of data from weather models, in-situ data, and satellite observations, providing a comprehensive assessment of potential energy generation across various oceanic renewable sources.
Applications
Utility for Renewable Energy Sector:
- The atlas will serve as a valuable tool for industries involved in renewable energy for better planning and decision-making in tapping blue energy resources.
6. Cabinet approves ‘Bio-RIDE’ scheme to support cutting edge research and development in Biotechnology
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2056001 )
| Context |
| ● The Bio-RIDE Scheme, approved by the Union Cabinet, aims to accelerate biotechnology innovation and entrepreneurship in India.
● With a focus on sustainable bio-manufacturing, the scheme supports research, startups, and industry-academia collaboration to strengthen India’s bioeconomy. |
Bio-RIDE Scheme: Key Highlights

- Unified Scheme: The Bio-RIDE Scheme merges two umbrella schemes under the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) into one comprehensive framework with a new focus on Biomanufacturing and Biofoundry.
- Proposed Outlay: Rs. 9,197 crore for the 15th Finance Commission period (2021-22 to 2025-26).
- Three Broad Components:
- Biotechnology Research & Development (R&D): Support for advanced research in biotechnology fields like healthcare, agriculture, and bioenergy.
- Industrial & Entrepreneurship Development (I&ED): Fostering bio-entrepreneurship through seed funding, incubation, and mentorship for startups.
- Biomanufacturing & Biofoundry: Promoting environmentally sustainable biomanufacturing aligned with India’s green goals under the ‘Lifestyle for the Environment (LiFE)’ initiative.
- Goals:
- Innovation & Entrepreneurship: Nurture startups and scale-up bio-based products.
- Industry-Academia Collaboration: Enhance commercialization of biotechnology products through partnerships between academic institutions and industry.
- Sustainable Practices: Focus on green biomanufacturing to tackle global challenges like climate change.
- Human Resource Development: Support students and researchers in biotechnology for capacity building and skilling.
- Circular Bioeconomy: Promote indigenous solutions for healthcare, agriculture, and environmental sustainability with a vision to make India a global leader in biotechnology and a $300 billion bioeconomy by 2030.
7. New Re-usable Low-cost launch vehicle for Bharat
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2055979 )
| Context |
| ● The Indian Union Cabinet has approved the Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV), featuring high payload capacity, cost efficiency, and reusability.
● With a Rs. 8,240 Crore budget, it aims to enhance space capabilities for national and commercial missions, including lunar exploration. |
Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV):

- Payload Capacity: NGLV will have a payload capability of 30 tonnes to Low Earth Orbit (LEO), three times more than current capabilities.
- Cost Efficiency: It will be 1.5 times more cost-effective than the LVM3, offering lower-cost access to space.
- Reusability: Features a reusable first stage, promoting sustainable space operations and reducing overall mission costs.
- Modular Propulsion: Equipped with modular green propulsion systems, enhancing efficiency and environmental sustainability.
- Development Timeline: The project is set for completion within 96 months (8 years), including three developmental flights (D1, D2, D3).
- Budget: Rs. 8,240 Crore approved for development, testing, facility establishment, and program management.
- Commercial and National Missions: Aims to support national and commercial missions, including human spaceflight, lunar exploration, and satellite constellations.
- Industry Involvement: Significant Indian industry participation is expected in the project, facilitating a smooth transition to operational use.
8.After Moon and Mars, India sights science goals on Venus
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2055982 )
| Context |
| ● The Union Cabinet has approved India’s Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM) to study Venus’s surface, atmosphere, and transformation.
● Scheduled for a March 2028 launch, the mission aims to advance scientific knowledge, foster technological innovation, and create economic and educational benefits. |
India’s Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM):

- Mission Overview: The Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM) is designed to deploy a spacecraft to orbit Venus for detailed scientific study.
- Development and Launch: ISRO will handle the spacecraft development and launch, with a target launch window in March 2028.
- Funding: The total cost is Rs. 1236 crore, including Rs. 824 crore for spacecraft development, payloads, global ground station support, and launch vehicle.
- Objectives:
- Explore Venus’s surface and subsurface structures.
- Investigate atmospheric processes and the impact of solar activity.
- Examine the evolution of Venus, including its transformation from potentially habitable conditions.
- Advantages:
- Scientific Insight: Provides valuable data on Venus’s atmospheric and geological processes, helping to understand planetary evolution.
- Technological Advancement: Enhances India’s capabilities in spacecraft and launch vehicle technology.
- Economic Benefits: Stimulates job creation and technology transfer across industries.
- Educational Impact: Involves academic institutions and offers training opportunities for students in aerospace and related fields.
- Future Missions: Lays groundwork for future planetary explorations with advanced payloads and orbital techniques.



