23 December 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. In big update, minimum possible mass of dark matter particles revised
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
Dark Matter Distribution
- Dark matter is distributed throughout the universe, but it is not evenly spread.
- In 1922, astronomer Jacobus Kapteyn suggested a dark matter density of 0.0003 solar masses per cubic light year, which equates to two protons per teaspoon.
- However, this measurement applies only to large-scale volumes (like millions of light-years), not smaller scales like inside a house.
- The distribution could either be uniform or in lumps, with varying spacings between dark matter particles depending on their mass.

| Dark Matter and Its Mass Limit |
|
The Impact of Particle Mass
- If dark matter particles are heavy (around 100 proton masses), they would be spaced by around 7 cm, possibly existing within your house.
- Heavier particles (up to 10-19 proton masses) would have spacings of 30 km, with dark matter particles occasionally passing through a house.
- For lighter particles (10-31 proton masses), the wavelength is larger, up to 200 light years, which would affect how dark matter interacts with dwarf galaxies.
Findings from New Research
- A May 2024 study used data from the dwarf galaxy Leo II to infer dark matter density and discovered that particles of 10-31 proton masses could not account for the observed mass in the galaxy’s inner regions.
- This suggests the need for heavier particles to explain the dense mass in those areas.
| Practice Question: Examine the implications of the revised minimum mass of dark matter particles on our understanding of its distribution and role in cosmic structures. How do such findings contribute to advancements in astrophysics and cosmology? (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. The principle behind the working of a speed gun, used for motion tracking
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
What is a Speed Gun?
- A speed gun is a device that measures the speed of a moving object without physical contact.
- It uses electromagnetic radiation, typically radio waves, which bounce off the object to calculate its speed using the Doppler effect.
- Speed guns are commonly used by law enforcement, sports coaches, and various industries to track motion accurately.
The Doppler Effect
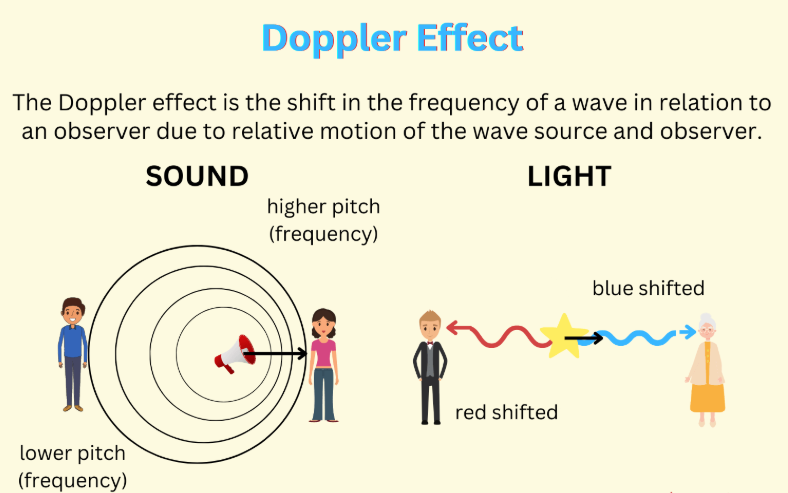
- The Doppler effect, discovered by Christian Doppler, describes the change in frequency of waves due to the relative motion between the source and the observer.
- As a moving object approaches, the frequency of waves (like sound or light) increases, creating a higher pitch; as it moves away, the frequency decreases, resulting in a lower pitch.
- This effect is used in speed guns to calculate the speed of moving objects based on the shift in frequency of the waves.
How Speed Guns Work
- Speed guns emit radio waves, which are reflected by the moving object.
- The frequency difference between the emitted and reflected waves is used to determine the speed of the object.
- The speed is calculated using the formula: (frequency difference * speed of light) / (2 * emitted frequency).
- The speed of light in a medium is constant, allowing for accurate speed measurement over long distances.
Limitations of Speed Guns
- Radio waves emitted by the gun diverge as they travel, potentially causing inaccurate readings if multiple objects are within the radar’s beam.
- Continuous-wave radar can result in errors due to reflections from multiple vehicles.
- LIDAR speed guns, which use laser light instead of radio waves, offer improved accuracy with minimal beam divergence, overcoming these limitations.
3. Will satellite broadband services truly be a game-changer?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 13)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
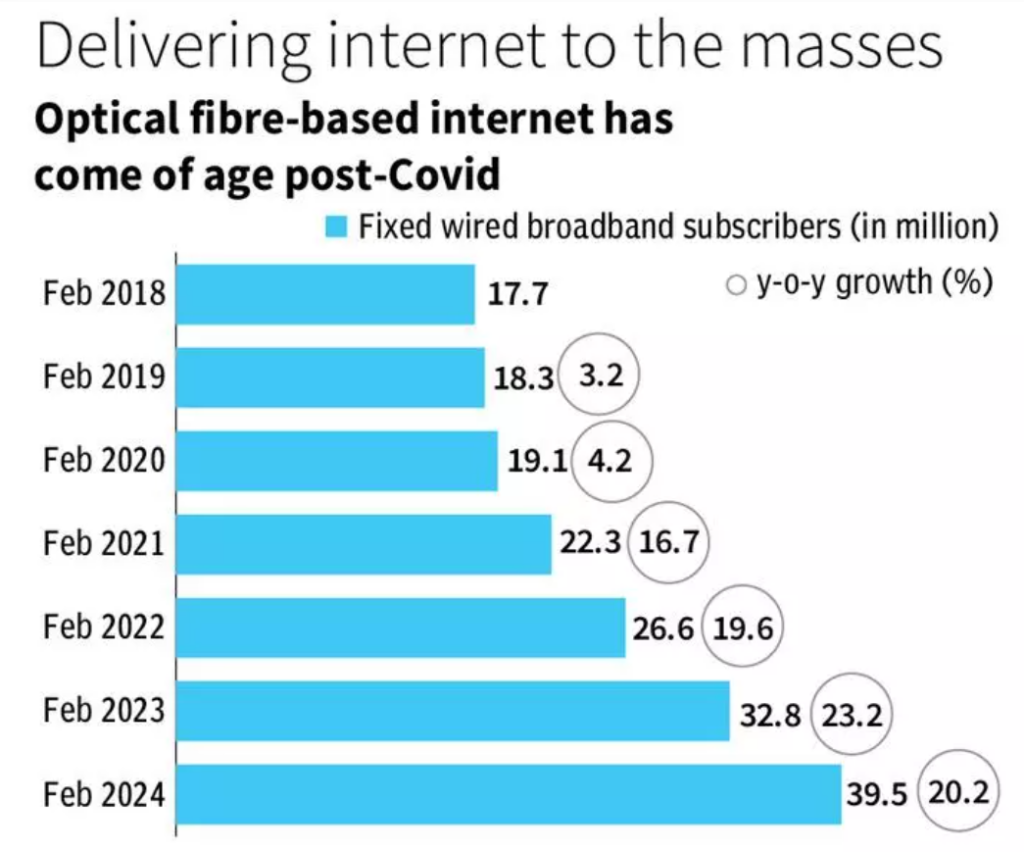
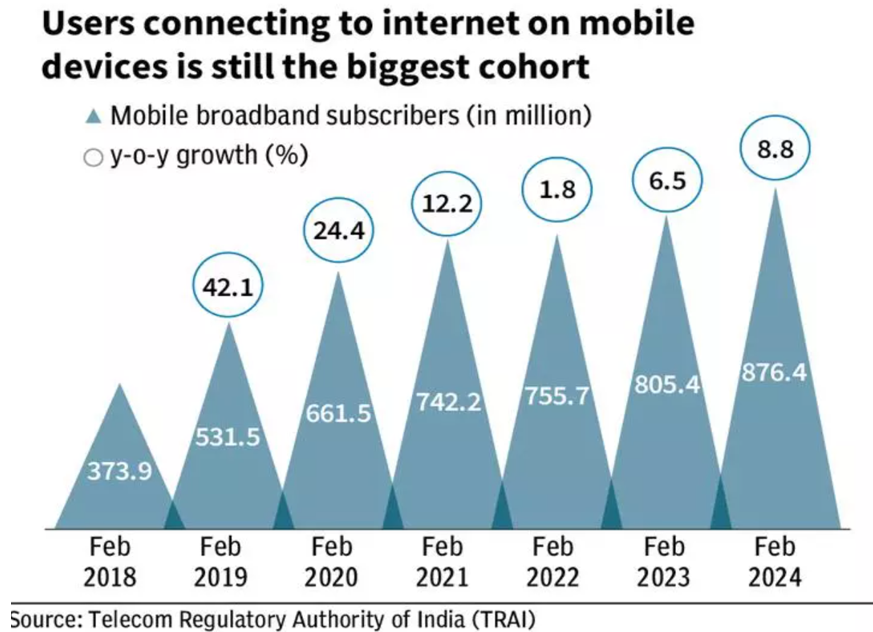
Current State of Broadband Penetration in India
- India is currently facing a broadband penetration gap of 48%, despite 25 years of terrestrial mobile services.
- The lack of progress in expanding broadband services could persist for another 25 years if the regulatory environment remains unchanged.
Debate on Spectrum Allocation for Satcom
- The allocation of spectrum for satellite broadband services has sparked heated debates.
- Legacy telecom operators are opposing new players, like satellite broadband companies, receiving preferential treatment regarding spectrum access.
- Some industry players argue for the auctioning of spectrum to ensure fair competition, given the substantial investments made by existing telecom companies over the years.
- Others suggest that spectrum should be allocated administratively, as is the common practice globally.
Satcom as a Solution to the Digital Divide
- Satellite communication (satcom) is seen as a potential solution to bridge the digital divide, especially in remote areas where the cost of laying fibre is prohibitive.
- Satcom can complement urban services by providing additional capacity for backhaul services.
- Satellites offer connectivity in areas that terrestrial networks cannot reach, making them particularly valuable for remote locations in India.
Global Perspective on Satcom
- Internationally, companies like AT&T view satellites as a complementary service to existing terrestrial services rather than a replacement.
- A significant number of satellites and a robust infrastructure are necessary to deliver consistent satellite service.
- The cost per bit for satellite-based services remains high, making them less viable for standalone use.
- AT&T plans to integrate satellite services with fiber and wireless services to offer customers a comprehensive connectivity solution.
| Satcom in India |
Challenges for Satcom in India
|
Potential for Satcom in India
- Despite challenges, there is potential for satcom to play a role in India’s digital ecosystem.
- Satcom could offer substantial improvements in availability and network utilization, especially in rural and remote areas.
- It will likely coexist with other technologies, such as fibre and wireless, providing more options for customers.
- However, the success of satcom depends on spectrum allocation rules and the ability to address the cost challenges.
Conclusion
- The future of satcom in India remains uncertain but promising.
- Regulatory decisions on spectrum allocation will determine whether satellite broadband can contribute to expanding India’s digital infrastructure, particularly in underserved regions.
- While challenges remain, satcom is expected to complement existing services rather than replace them, contributing to a more connected India in the long term.
| Practice Question: Evaluate the role of satellite communication in bridging India’s digital divide. How should spectrum allocation policies be framed to ensure fair competition between existing telecom operators and new satellite broadband services? (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. Understanding the Rupee’s Depreciation: Causes, Dynamics, and Implications
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Understanding the Exchange Rate
- The exchange rate refers to the price of one currency in terms of another.
- For example, the current exchange rate of the Indian rupee against the US dollar stands at Rs 85 per dollar, compared to Rs 83 in April and Rs 61 a decade ago.
- This rate reflects the relative value of currencies and fluctuates based on the dynamics of demand and supply in the currency market.
- A depreciating rupee means it takes more rupees to buy one US dollar.
Factors Influencing Exchange Rates
Trade of Goods
- The trade balance significantly affects currency demand. If India imports more goods from the US than it exports, the demand for US dollars increases while demand for the rupee decreases.
- This imbalance weakens the rupee relative to the dollar.
Trade in Services
- A similar dynamic occurs in services trade. If Indians purchase more US services, such as tourism, than Americans consume Indian services, the rupee loses value as demand for dollars grows.
Investments
- Investment flows also play a critical role. If Americans invest more in India, the rupee appreciates due to higher demand.
- Conversely, reduced or negative investments, such as capital outflows during global uncertainty, weaken the rupee.
Underlying Drivers of Demand Shifts
Trade Policies
- Protectionist measures, such as US-imposed tariffs or import restrictions on Indian goods, reduce the demand for rupees, causing depreciation.
Inflation Differential
- Higher inflation in India relative to the US diminishes the rupee’s value. Inflation erodes purchasing power and makes Indian investments less attractive to foreign investors, leading to reduced inflows and weakening of the currency.
Investor Behavior
- Economic uncertainty, policy shifts, or better returns in US markets prompt foreign investors to withdraw capital from India, reducing rupee demand and pushing its value down further.
Implications of Rupee Depreciation

- A weakening rupee makes imports like crude oil and foreign goods more expensive, leading to higher inflation domestically.
- It also increases the burden of servicing external debt. However, it can benefit exporters, as Indian goods become cheaper and more competitive globally.
In conclusion, the exchange rate dynamics hinge on the interplay of trade, investments, inflation, and policies. Addressing these factors systematically is crucial to stabilizing the rupee and minimizing the adverse economic impact of currency fluctuations.
| Reasons for falling rupee |
|
| PYQ: Consider the following statements: The effect of devaluation of a currency is that it necessarily 1) improves the competitiveness of the domestic exports in the foreign markets 2) increases the foreign value of domestic currency 3) improves the trade balance Which of the above statements is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2 (c) 3 only (d) 2 and 3 Ans: (a) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the factors contributing to the depreciation of the Indian rupee against the US dollar. Analyze its economic implications and suggest measures to stabilize the exchange rate. (250 words/15 m) |
5. India and Kuwait Elevate Ties to Strategic Partnership, Strengthening Trade, Defence, and Regional Cooperation
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page: 01)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Defence and Security Cooperation
- A significant outcome of the visit was the institutionalization of defence cooperation.
- An overarching agreement was signed, covering joint exercises, personnel training, exchange of expertise, supply of defence equipment, and research and development.
- Both sides also condemned terrorism and called for dismantling terror networks, underscoring mutual interest in regional security.
Expansion of Trade and Economic Ties
- Discussions emphasized the importance of trade and investment, with Modi inviting Kuwaiti stakeholders to explore opportunities in India, particularly in energy, pharma, and infrastructure.
- Both sides stressed the need to finalize the India-GCC Free Trade Agreement to enhance economic engagement further.
Recognition and People-to-People Ties
- Kuwait conferred its highest honour, ‘The Order of Mubarak Al-Kabeer’, on PM Modi for his contributions to bilateral relations. Modi acknowledged the well-being of over one million Indians in Kuwait and their significant role in the Gulf nation’s development.
Shared Vision for Regional Stability
- The leaders discussed peace and prosperity in West Asia, a region of shared strategic interest.
- They expressed optimism about the partnership’s potential to foster regional stability and align with Kuwait’s Vision 2035, which India pledged to support through enhanced collaboration.
Strengthening Multilateral Cooperation
- India expressed interest in intensifying ties with the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) through Kuwait’s presidency.
- The visit reinforced cooperation in multilateral fora, with both nations advocating for global peace and economic stability.
Conclusion
- The visit to Kuwait, the first by an Indian Prime Minister in 43 years, marked a turning point in bilateral relations.
- With agreements spanning defence, trade, and people-to-people ties, the strategic partnership lays the groundwork for a mutually beneficial relationship poised to contribute to regional and global stability.
| About kuwait |
|
| Practice Question: Analyze the significance of Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Kuwait and the elevation of bilateral relations to a strategic partnership. Discuss the key areas of cooperation and their potential impact on regional stability and global affairs. (250 words/10 m) |
6. Key Health Indicators reflect India’s Progress
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2087048®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
India’s Commitment to Universal Health Coverage
- India has made significant progress in healthcare access, equity, and outcomes, with transformative policies aimed at achieving Universal Health Coverage (UHC).
- The launch of Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY) has been a key milestone. The scheme offers health cover of Rs. 5 lakh per eligible family for secondary and tertiary care hospitalizations.
- As of December 17, 2024, over 36.28 crore Ayushman Cards have been issued.
- Women account for nearly 50% of the cardholders and hospital admissions, promoting gender equity in healthcare.
- AB PM-JAY has also empaneled 30,932 hospitals across India.
Advancements in Digital Health Infrastructure
- The Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA) initiative has advanced India’s digital health infrastructure, enabling hassle-free access and sharing of health records.
- As of December 22, 2024, over 71.81 crore ABHA numbers have been generated, and 46.53 crore health records are linked with ABHA.
- Additionally, over 3.55 lakh health facilities and more than 5.38 lakh healthcare professionals have been registered on the Health Facility Registry (HFR) and Health Professional Registry (HPR), respectively.
Mission Indradhanush and Immunization Efforts
- Mission Indradhanush has expanded immunization under the Universal Immunization Programme, focusing on areas with low immunization rates.
- The campaign has successfully vaccinated 5.46 crore children and 1.32 crore pregnant women against preventable diseases.
Improvements in Key Health Indicators
- Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) in India reduced from 103 per 100,000 live births (2017-2019) to 97 per 100,000 live births (2018-2020).
- Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) decreased from 32 per 1,000 live births (2018) to 28 per 1,000 live births (2020).
- These improvements reflect the effectiveness of targeted healthcare interventions and policies aimed at improving maternal and child health outcomes in India.
Prelims Facts
1. SpaDeX: meeting in space
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
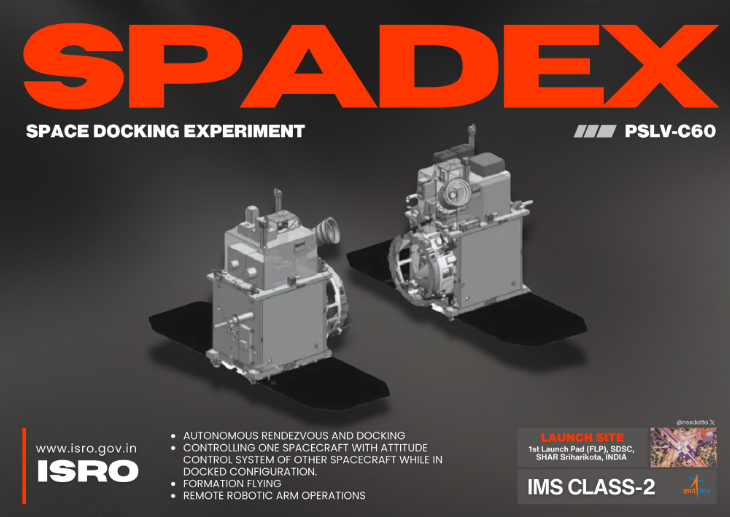
SpaDeX Mission:
- SpaDeX is a mission by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) focused on mastering in-space docking technology.
- The mission involves launching two satellites into orbit, where they will demonstrate docking and undocking while in motion.
- This technology is crucial for future space operations, enabling satellites launched separately to link up and perform complex tasks.
- The SpaDeX mission is a key step towards the development of the ‘Bharatiya Antariksh Station,’ India’s upcoming space station.
- Upon successful completion, India will join the select group of countries capable of performing space docking, becoming the fourth country globally.
- The two spacecraft, each weighing 220 kg, will be launched together on the PSLV C60 mission, scheduled for December 30, 2024.
- They will be placed in a 470-km-wide circular orbit at a 55° inclination.
- The mission’s primary goal is to demonstrate the docking maneuver, with secondary objectives including power transfer between the spacecraft.
2. Panama Canal
(Source: Indian Express; Section: The World; Page: 14)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
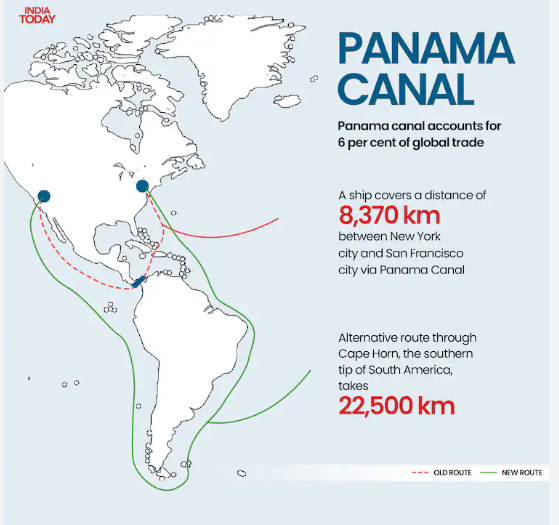
About Panama Canal:
- It is a constructed waterway that connects the Atlantic and Pacific oceans across the Isthmus of Panama.
- It is one of the two most strategic artificial waterways in the world, the other being the Suez Canal.
- It is approximately 80 kilometers long.
- The canal was built by the United States between 1904 and 1914, and it was officially opened on August 15, 1914.
- It is owned and administered by the Republic of Panama since the oversight of the Canal was transferred from the United States to Panama in 1999.
- The Panama Canal consists of a series of locks that raise and lower the water level to facilitate the passage of ships through the continental divide.
Significance of the Panama Canal
- The Panama Canal, completed in 1914 after a decade of US-led construction, is a vital artificial waterway connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
- It significantly reduces shipping costs and travel time by bypassing the southern tip of South America.
- Handling about 6% of global trade annually, the canal remains crucial for international commerce, particularly for US shipping and defense.
US Role in Canal Construction
- The US was instrumental in constructing the canal after France abandoned earlier efforts.
- President Theodore Roosevelt prioritized the project, navigating engineering challenges with innovative “lock” systems to facilitate ship passage.
- However, construction came at a high cost, including over $300 million and thousands of workers’ lives.
- The canal’s creation involved controversial treaties with Panama, following its US-backed independence from Colombia in 1903.
Transfer of the Canal to Panama
- Tensions over US control of the canal led to the Torrijos-Carter Treaties of 1977.
- These agreements established Panamanian sovereignty over the canal by 1999 while preserving its neutrality under US defense oversight.
- The decision to relinquish control stemmed from rising operational costs, inefficiencies, and diminishing strategic value for the US.
For more such UPSC related Current Affairs, Check Out-21 December 2024: Daily Current Affairs




