12 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
Daily Current Affairs
12-March -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Controversy Surrounds Implementation of Citizenship (Amendment) Act as Rules Notified: Legal Challenges and Constitutional Questions Remain
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies – Issues arising out of their design & implementation This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of understanding the constitutional provisions, particularly Article 14, which guarantees equality before the law. The analysis on the potential violation of this fundamental right in the context of the CAA provides insights into constitutional law and governance. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
The Citizenship Law:
- The Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019, introduced an amendment to The Citizenship Act, 1955, allowing for the grant of citizenship to migrants belonging to specified religious communities from Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Bangladesh who entered India before December 31, 2014.
- The amendment, relaxing eligibility criteria based on religious lines, exempts certain areas, including tribal areas and those protected by the Inner Line Permit (ILP) system, from its purview.
Legal Challenge:
- The amendment faced legal challenges before the Supreme Court, primarily on the grounds of violating Article 14 of the Constitution, which guarantees equality before the law.
- The petitioners argue that using religion as a qualifier for citizenship violates the fundamental right to equality.
- The court must determine whether the special treatment of persecuted minorities from specific countries constitutes a reasonable classification and whether it discriminates against Muslims.
The Right to Equality:
- The Supreme Court has held that any differentiation between groups of persons must be founded on an intelligible differentia and have a rational nexus to the object sought to be achieved by the act.
- The government’s argument for excluding Muslims from persecuted minorities due to their majority status in Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Bangladesh will be scrutinized, particularly regarding the selection of these countries and the exclusion of other persecuted minorities.
CAA and Assam:
- In addition to the equality argument, part of the challenge to the CAA rests on the fate of Section 6A of The Citizenship Act, 1955, which is under challenge before the Supreme Court.
- This section, introduced after the signing of the Assam Accord in 1985, determines the base cut-off date for detecting and deleting foreigners in Assam.
- The potential conflict between Section 6A and the CAA regarding the timeline for citizenship regularization in Assam adds another layer of complexity to the legal challenge.
Conclusion:
- The Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019, remains a contentious issue, with legal challenges revolving around its potential violations of constitutional provisions and conflicts with existing agreements such as the Assam Accord.
- The outcome of the legal proceedings will have significant implications for citizenship policies and secularism in India, underscoring the importance of addressing complex legal and constitutional questions surrounding the CAA.
| The Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA) 2019 |
About:
Who is eligible?
|
| PYQ: With reference to India, consider the following statements: (UPSC Prelims 2021) 1. There is only one citizenship and one domicile. 2. A citizen by birth only can become the Head of State. 3. A foreigner once granted citizenship cannot be deprived of it under any circumstances. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 (d) 2 and 3 Ans: (a) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the constitutional and legal complexities surrounding the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019 (CAA), and its potential implications for citizenship policies and secularism in India. (250 words/15 m) |
2. India Successfully Tests Agni-V Missile with MIRV Technology, Enhancing Strategic Deterrence Capability
| Topic: GS3 – Science & Technology – Achievements of Indian S&T; Indigenization of technology This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of understanding advancements in India’s missile technology and defense capabilities. The integration of MIRV technology enhances India’s strategic deterrent and its ability to counter potential threats, which are significant aspects of India’s defense strategy. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Understanding MIRV Technology: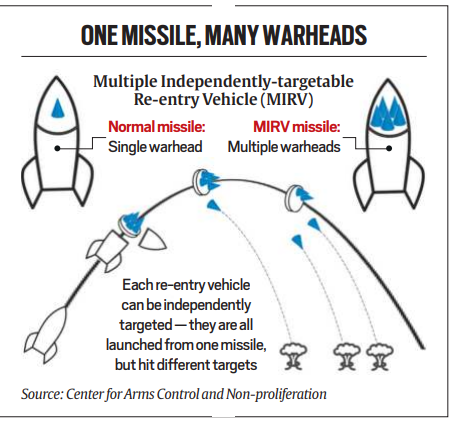
- MIRV technology enables missiles to carry multiple warheads, each independently targetable to strike separate locations or converge on a single target sequentially.
- Developed in the 1960s and first deployed in the 1970s by major nuclear powers, MIRV-equipped missiles require miniaturized warheads with independent guidance and navigation controls, enhancing their effectiveness in strategic warfare scenarios.
Strategic Implications:
- The development of MIRV capability enhances India’s strategic deterrence posture by expanding its nuclear options and increasing the potency of its missile systems.
- MIRV-equipped missiles can inflict devastating damage by striking multiple targets simultaneously, posing significant challenges to enemy defenses and complicating interception efforts.
Advantages of MIRV Technology:
- Apart from its destructive potential, MIRV technology offers strategic advantages, including its ability to penetrate missile defense systems effectively.
- Unlike traditional missiles, MIRV-equipped missiles can overwhelm defense systems with multiple warheads and decoys, making interception more challenging.
- Additionally, MIRV capability enables a credible second-strike capability, deterring potential adversaries from initiating conflict.
Integration with Agni Missile Systems:
- The integration of MIRV technology with the Agni-V missile represents a significant upgrade to India’s indigenous ballistic missile program.
- Agni missiles, developed by the Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO), serve as vital land-based delivery systems for India’s nuclear arsenal.
- Agni-V, with its extended range and MIRV capability, strengthens India’s strategic deterrent against regional and global threats.
Strategic Significance:
- India’s acquisition of MIRV technology reflects its evolving strategic priorities and its commitment to maintaining a credible deterrence posture.
- The successful test of the Agni-V missile underscores India’s indigenous technological prowess and its ability to develop advanced defense capabilities.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s acknowledgment of the achievement highlights its strategic significance for India’s national security.
Conclusion:
- The successful test of the Agni-V missile equipped with MIRV technology represents a significant milestone in India’s defense capabilities.
- By enhancing its strategic deterrent and expanding its nuclear options, India reinforces its position as a formidable regional power.
- The integration of MIRV technology with indigenous missile systems underscores India’s commitment to self-reliance in defense and its readiness to address evolving security challenges effectively.
| PYQ: Consider the following statements: (UPSC Prelims 2023) 1) Ballistic missiles are jet-propelled at subsonic speeds throughout their flights, while cruise missiles are rocket-powered only in the initial phase of flight. 2) Agni-V is a medium-range supersonic cruise missile, while BrahMos is a solid-fuelled intercontinental ballistic missile. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? 1) 1 only 2) 2 only 3) Both 1 and 2 4) Neither 1 nor 2 Answer: (d) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the strategic significance and implications of India’s successful test of the Agni-V missile equipped with Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle (MIRV) technology. Evaluate how this technological advancement enhances India’s national security posture and defense capabilities. (250 words/15 m) |
3. Mumps Outbreak Surges in Kerala: Health Authorities on High Alert
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of understanding the transmission dynamics of infectious diseases, their clinical manifestations, and potential complications. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Confirmation and Response:
- Health officials from the Union Health Ministry have confirmed the outbreak and have alerted the National Centre for Disease Control in the state.
- This acknowledgment signifies the severity of the situation and the necessity for immediate response measures to curb the spread of the infection.
Nature of Mumps and Its Transmission:
- Mumps is caused by the paramyxovirus and is typically transmitted through direct contact or airborne droplets from the upper respiratory tract of an infected individual.
- The incubation period ranges from two to four weeks, with initial symptoms including low-grade fever, headache, body ache, and malaise.
- A distinctive symptom of mumps is the swelling of the salivary glands. While it predominantly affects young children, adolescents, and adults can also contract the infection.
Epidemiological Distribution:
- The majority of cases are concentrated in Malappuram district and other parts of north Kerala, according to health officials.
- This concentration highlights the need for targeted interventions and heightened surveillance in these areas to contain the outbreak effectively.
Vaccination Status and Challenges:
- Although a vaccine for mumps exists as part of the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, it is not included in the government’s universal immunization program.
- Public health experts emphasize that while children can receive the MMR vaccine against all three diseases at private centers, its exclusion from the government program is attributed to its relatively lower efficacy against mumps compared to measles and rubella.
- Additionally, vaccine hesitancy, particularly prevalent in Malappuram district, poses a challenge to vaccination efforts in the region.
Clinical Course and Complications:
- In most cases, mumps is a self-limiting disease; however, in rare instances, it can lead to complications such as brain swelling, hearing loss, and painful inflammation of the testis in adult males.
- These potential complications underscore the importance of timely diagnosis, treatment, and preventive measures.
Conclusion:
- The mumps outbreak in Kerala underscores the significance of robust surveillance, prompt response measures, and the need for broader vaccination coverage to mitigate the spread of infectious diseases and safeguard public health.
| PYQ: Consider the following statements: (UPSC Prelims 2021) 1) Adenoviruses have single-stranded DNA genomes whereas retroviruses have double-stranded DNA genomes. 2) Common cold is sometimes caused by an adenovirus whereas AIDS is caused by a retrovirus. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Ans: (b) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the recent mumps outbreak in Kerala, highlighting its epidemiology, transmission dynamics, and impact on public health infrastructure. Evaluate the effectiveness of vaccination strategies in mitigating the spread of mumps and analyze the challenges faced in implementing universal immunization programs. (250 words/15 m) |
4.Multiple re-entry vehicle technology successfully tested on Agni-5 missile
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology – Achievements of Indian S&T The successful test of Agni-5 with MIRV technology showcases India’s strategic capabilities, crucial for UPSC aspirants studying defense and geopolitics. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- Prime Minister announced the successful test-firing of Agni-5 ballistic missile with Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle (MIRV) technology by DRDO under Mission Divyastra.
- The test was conducted from Dr A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Island in Odisha, marking a significant technological breakthrough.
- MIRV technology allows a single missile to carry multiple warheads, enabling deployment at different locations.
- India, with this test, joins a select group of nations possessing MIRV capability, according to government sources.
- The DRDO statement highlighted that telemetry and radar stations tracked multiple re-entry vehicles, achieving the designed parameters.
- The system features indigenous avionics systems and high-accuracy sensor packages, ensuring the re-entry vehicles reach target points with precision.
- The successful test underscores India’s growing technological prowess in the field of ballistic missiles.
- The Agni series remains integral to India’s nuclear weapons delivery capabilities
| Significance of Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle (MIRV) technology for India |
|
| PYQ: Consider the following statements: (2023) 1. Ballistic missiles are jet-propelled at subsonic speeds throughout their flights, while cruise missiles are rocket-powered only in the initial phase of flight. 2. Agni-V is a medium-range supersonic cruise missile, while BrahMos is a solid-fuelled intercontinental ballistic missile. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? a) 1 only b) 2 only c) Both 1 and 2 d) Neither 1 nor 2 Answer: (d) |
| Practice Question: How does the recent successful test-firing of Agni-5 with MIRV technology enhance India’s strategic capabilities? Discuss its implications for national security. (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. Drones handed over to 1,000 women
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government Policies – Interventions for development in various sectors The Namo Drone Didi scheme showcases women’s role in technology, aligning with UPSC candidates’ studies on socio-economic initiatives and empowerment. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- Women from Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka showcased drone flying skills under the Namo Drone Didi scheme.
- The event, held at 10 locations nationwide, featured a demonstration of agricultural drones for women beneficiaries.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi handed over drones to 1,000 women selected for operating drones in agriculture.
- 108 women received certificates, enabling them to legally fly drones for agricultural and related purposes.
- PM emphasized the role of “Nari Shakti” in leading India’s technological revolution, citing achievements in IT, space, and science sectors by women.
| Namo Drone Didi scheme |
● Empowering Rural Women: Launched in March 2024, the Namo Drone Didi scheme aims to provide economic opportunities for women in rural areas.
○ Distributes 15,000 drones to women-led Self-Help Groups (SHGs) over three years.
○ Crop monitoring: Assessing crop health and identifying potential issues.
○ SHG members will receive training to operate drones safely and efficiently.
○ Women can rent out the drones to farmers for a fee, generating income and becoming financially self-sufficient.
○ Drone technology can improve efficiency and precision in farming practices, potentially leading to increased crop yields And helping women farmers. |
| PYQ: Consider the following activities: (2020) 1. Spraying pesticides on a crop field 2. Inspecting the craters of active volcanoes 3. Collecting breath samples from spouting whales for DNA analysis At the present level of technology, which of the above activities can be successfully carried out by using drones? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Answer: (d) |
| Practice Question: How does the Namo Drone Didi scheme contribute to women’s empowerment in agriculture and technology? Discuss its socio-economic implications. (150 Words /10 marks) |
6.Liberal democracy has declined significantly in India: Report
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity The V-Dem report on India’s democratic decline is crucial for UPSC aspirants studying governance, democracy, and human rights. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- India, classified as an “electoral autocracy” in 2018, has further declined to become one of the worst autocratisers, according to the “Democracy Report 2024” by the V-Dem Institute.
- The report categorizes countries based on the Liberal Democratic Index (LDI), placing India in the category of autocratising countries, with almost half of the population in such nations.
- Components of democracy, including freedom of expression, clean elections, and freedom of association/civil society, are worsening in autocratising countries.
- South and Central Asia witnessed significant regression, bringing India’s level of liberal democracy to that of 1975, during the state of emergency declared by Indira Gandhi.
- The report highlights the Modi-led government’s suppression of freedom of religion, intimidation of political opponents, and silencing dissent in academia.
- The possibility of further autocratisation is noted, especially with a potential third consecutive term for the BJP and Prime Minister Modi.
- V-Dem’s Democracy Report involves 4,200 scholars worldwide, analyzing 31 million datasets covering 202 countries from 1789 to 2023.
| Practice Question: How does the V-Dem report on India’s democratic decline raise concerns about governance and human rights? Analyze the implications. (150 Words /10 marks) |
7. Oldest ‘dead galaxy’ yet is spotted by James Webb Telescope
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology – Space The discovery of an early “dead” galaxy by the James Webb Space Telescope enhances UPSC aspirants’ understanding of astrophysics and cosmic evolution. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- The James Webb Space Telescope, operational since 2022, revealed a surprising discovery of a “dead” galaxy.
- The galaxy ceased star formation approximately 13.1 billion years ago, only 700 million years after the Big Bang.
- This is the earliest observed “dead” galaxy, raising questions about its rapid cessation of star formation.
- The small galaxy, with 100 million to one billion stars, experienced a brief burst of star formation lasting 30 to 90 million years.
- After star formation stops, the galaxy becomes a stellar graveyard as existing stars die without replacement.
- Researchers, led by astrophysicist Tobias Looser, are intrigued by the puzzling and early halt of star formation.
- The hierarchical death of stars changes the galaxy’s color from blue to yellow to red over time.
- NASA’s Webb telescope, surpassing Hubble in distance and time observation, allows insights into the universe’s early stages.
- The study suggests the possibility that the galaxy may have later resumed star formation, adding complexity to its history.
| The James Webb Space Telescope |
|
| PYQ: Launched on 25th December, 2021, James Webb Space Telescope has been much in the news since then. What are its unique features which make it superior to its predecessor Space Telescopes? What are the key goals of this mission? What potential benefits does it hold for the human race? (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2022) |
| Practice Question: How does the James Webb Space Telescope’s discovery of an early ‘dead’ galaxy contribute to our understanding of cosmic evolution? Discuss the implications. (150 Words /10 marks) |
For Enquiry

12 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

12 March 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

12 March 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC

12 March 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis

11 Mar 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

11 Mar 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

11 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

11 March 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

11 March 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC

11 March 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis
Daily Current Affairs 12 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
12-March -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Controversy Surrounds Implementation of…
March – The Hindu Editorial 12 March 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu Editorial
12-March-2024
1. Central transfers and the issue of shares of some States
Topic:…
March 2024 PIB 12 March 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
12-March -2024
1. FIRST TRAINING SQUADRON PARTICIPATES IN CUTLASS EXPRESS 24
Topic:…
Indian Express 12 March 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
12-March-2024
1. EC’s hour of reckoning
Topic: GS2 – Polity – Constitutional…
Daily Quiz 11 Mar 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 11 Mar 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 11 Mar 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
11-March-2024
Q1) The interconnectedness of environmental, social, and governance…
Daily Current Affairs 11 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
11-March -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Debating Tiger Safaris: Balancing Conservation…
March – The Hindu Editorial 11 March 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu Editorial
11-March-2024
1. We need limits on election campaign spending
Topic: GS2 –…
March 2024 PIB 11 March 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
11-March -2024
1. India EFTA- Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement
Topic:…
Indian Express 11 March 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
11-March-2024
1. A dialogue among healers
Topic: GS2 – Governance…



