22 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
Daily Current Affairs
22-April -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Global Coral Bleaching Crisis: Urgent Action Needed to Protect Marine Ecosystems
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Environmental pollution and degradation
This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains as this topic provides insights into coral reefs, their significance as ecosystems, and the factors contributing to coral bleaching. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Understanding Corals and Coral Reefs:
- Corals, sessile animals that permanently attach themselves to the ocean floor, form the foundation of coral reefs.
- These intricate ecosystems, comprised of hard and soft corals, host thousands of marine species and provide essential goods and services valued at $2.7 trillion annually.
- Coral reefs play a crucial role in coastal protection, absorbing up to 97% of energy from waves, storms, and floods, thus mitigating loss of life and property damage.
Coral Bleaching: Causes and Consequences:
 Coral bleaching, a stress response triggered by changes in light, temperature, and pollution, results in the expulsion of symbiotic algae from coral tissues, causing them to turn white.
Coral bleaching, a stress response triggered by changes in light, temperature, and pollution, results in the expulsion of symbiotic algae from coral tissues, causing them to turn white.- While bleaching does not always lead to coral death, it compromises their reproductive capacity and increases susceptibility to diseases.
- Global mass bleaching events, characterized by widespread coral bleaching across the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans, have become increasingly frequent and severe due to rising ocean temperatures.
Current Scenario and Drivers:
- The ongoing fourth global bleaching event, confirmed by NOAA, has affected coral reefs in over 54 countries and territories.
- The Great Barrier Reef, the world’s largest, is experiencing its most severe bleaching event to date.
- Higher ocean temperatures, primarily driven by greenhouse gas emissions, have elevated sea surface temperatures, surpassing the threshold for coral bleaching.
- The intensification of the phenomenon has been exacerbated by the El Niño weather pattern, further warming ocean waters.
Future Outlook and Implications:
- While the full impact of the current bleaching event remains to be seen, scientists warn of its severity and long-term consequences.
- With a potential cooling La Niña phase on the horizon, the duration of the bleaching event may be limited.
- However, the ecological and socio-economic ramifications of coral bleaching underscore the urgent need for global action to mitigate climate change and protect coral reef ecosystems.
| Implications of Coral Bleaching |
Ecological Impact:
|
| PYQ: “Biorock technology” is talked about in which one of the following situations?
(a) Restoration of damaged coral reefs (b) Development of building materials using plant residue (c) Identification of areas for exploration/extraction of shale gas (d) Providing salt licks for wild animals in forests/protected areas Ans: (a) |
| Practice Question: Explain the impact of coral bleaching on marine ecosystems and coastal communities. Discuss the measures needed to address coral reef degradation and promote sustainable management practices for marine biodiversity conservation. (250 words/15 m) |
2. Ayushman Bharat Expansion aids elderly healthcare
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies – Interventions for development in various sectors
This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of understanding the intricacies of healthcare policies, especially government-funded schemes like Ayushman Bharat. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Significance of the Initiative:
- The AB-PMJAY scheme, introduced in 2018, is already recognized as the world’s largest government-funded health insurance program, benefiting over 65 crore individuals from deprived backgrounds.
- Expanding its coverage to senior citizens addresses the growing healthcare needs of an aging population, aligning with India’s demographic shift towards an older populace.
Implications of an Aging Population:
- India’s aging population is projected to significantly increase by 2050, with the proportion of individuals over 60 years expected to nearly triple.
- This demographic shift poses challenges such as increased healthcare expenditure, labor force shortages, and public financial strains.
- By targeting senior citizens, the healthcare system can address the rising burden of chronic diseases prevalent in this age group.
Health Challenges Faced by Senior Citizens:
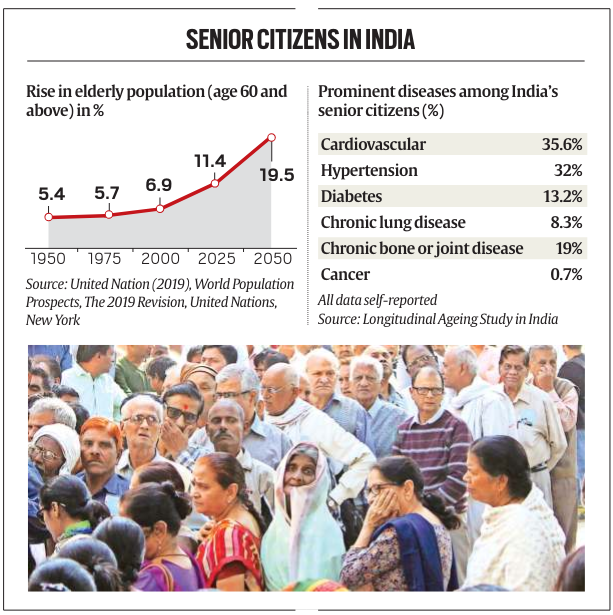 Data from the Longitudinal Ageing Study in India (LASI) reveals a higher prevalence of chronic diseases among the elderly, including cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, diabetes, chronic lung diseases, and cancer.
Data from the Longitudinal Ageing Study in India (LASI) reveals a higher prevalence of chronic diseases among the elderly, including cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, diabetes, chronic lung diseases, and cancer. - These conditions contribute to escalating healthcare costs and underline the urgent need for comprehensive coverage for senior citizens.
Current Healthcare Coverage Disparities:
- Despite existing health insurance schemes, only a fraction of India’s elderly population is currently covered, with out-of-pocket expenditures remaining high.
- Factors such as low awareness and financial constraints contribute to the lack of coverage among senior citizens, exacerbating their vulnerability to health-related expenses.
Impact of Ayushman Bharat:
- Government data on AB-PMJAY expenditure highlights significant savings for beneficiaries, particularly for specialized treatments required by senior citizens.
- The scheme has substantially reduced out-of-pocket expenditures, especially in rural areas, where government hospitals offer more affordable healthcare options compared to private facilities.
Conclusion:
- Expanding healthcare coverage under Ayushman Bharat to include senior citizens is a commendable step towards achieving universal health coverage in India.
- By addressing the specific healthcare needs of the elderly population, the initiative can alleviate financial burdens, improve health outcomes, and promote inclusive and equitable access to healthcare services across the country.
| About the Ayushman Bharat Scheme |
|
| Practice Question: With limited resources, a universal healthcare system might face challenges in prioritising treatments and allocating resources fairly. How can ethical guidelines be established to ensure patients receive necessary care while also considering factors like cost-effectiveness and resource constraints? (250 words/15 m) |
3. Marking Democracy: The Enduring Significance of Indelible Ink in Indian Elections
| Important Topic for Prelims |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Purpose of the Ink: Combating Electoral Fraud:
- The indelible ink was developed in the 1950s to address the challenge of fraudulent voting.
- Initially formulated by the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research, it was later patented by the National Research Development Corporation.
- Mysore Paints & Varnish Ltd, established in 1937 by the Maharaja of Mysore, has been licensed to manufacture the ink since 1962.
Historical Usage: Evolution Over Time:
- Mandated by the Representation of the People Act (RoPA) of 1951, the ink has been a staple in Indian elections.
- Initially applied with a glass rod, it was used to mark the base of the forefinger until the 1962 general elections, after which it was moved above the root of the nail on the skin.
Composition and Indelibility: Silver Nitrate and Application:
- Containing silver nitrate, the ink is colorless and becomes visible under ultraviolet light.
- Its indelibility stems from a high concentration of silver nitrate, making removal difficult for at least 72 hours post-application.
- A water-based solvent like alcohol facilitates rapid drying. Sold at Rs 174 per phial, the ink is exported to over 25 countries, each with its unique application method.
Conclusion:
- The indelible ink mark, a hallmark of Indian democracy, remains integral to the electoral process.
- Its evolution, from glass rods to modern-day phials, reflects a commitment to combatting electoral malpractices.
- Despite variations in application methods globally, its efficacy in ensuring free and fair elections endures, symbolizing the strength of Indian democracy on the world stage.
| About Mysore Paints & Varnish Ltd. |
|
4. Net direct tax collections exceed 2023-24 target
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Issues relating to mobilisation of resources
Critical for UPSC to analyse India’s fiscal health, tax revenue trends, and economic performance for policy evaluation and governance. |
| Context |
| ● The news pertains to India’s net direct tax collections for the fiscal year 2023-24, which grew by 17.7% to ₹19.58 lakh crore, exceeding revised estimates. |
Additional information on this news:
- India’s net direct tax collections for 2023-24 grew by 17.7% to reach ₹19.58 lakh crore, slightly surpassing the revised estimates.
- The surge in personal income tax (PIT) contributed significantly, increasing its share of the tax kitty to 53.3%.
- Corporate taxes’ contribution decreased to 46.5% from 49.6% in the previous year.
- Provisional data released by the Finance Ministry indicated that PIT and securities transaction tax (STT) collections drove the uptick in net tax collections during the final fortnight of the financial year.
- PIT and STT receipts grew at almost double the pace of corporate taxes.
- As of March 17, net direct taxes had risen by 19.88% to ₹18.9 lakh crore, with PIT and STT accounting for 51.4% of the receipts.
- By March 31, PIT and STT inflows had increased by ₹73,000 crore, reaching ₹10.44 lakh crore for the full year.
- Gross corporate tax collections increased, but net tax receipts from corporates, after adjusting for refunds, slightly decreased.
- The gross direct tax kitty for 2023-24 stood at ₹23.37 lakh crore, reflecting an 18.5% growth over the previous year.
- Gross PIT and STT receipts accounted for ₹12.01 lakh crore, rising by ₹76,000 crore between March 17 and 31.
| Significance of increase in direct taxes revenue |
| What are direct taxes?
● Direct taxes are levied directly on individuals and entities by the government. ● These taxes cannot be shifted to another person or entity and are borne by the taxpayer themselves. ● Examples of direct taxes include income tax, corporate tax, capital gains tax, and property tax. ● Direct taxes are imposed based on an individual’s or entity’s income, profits, or assets. ● They are an important source of revenue for the government and play a significant role in funding public services and welfare programs. What are different types of direct taxes? ● Income Tax: Levied on the income earned by individuals, including salaries, wages, interest, dividends, and rental income. ● Corporate Tax: Imposed on the profits earned by companies or corporations from their business activities. ● Capital Gains Tax: Applied on the gains realized from the sale of capital assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, or precious metals. ● Property Tax: Levied on the value of property owned by individuals or entities, including land, buildings, and other real estate. ● Wealth Tax: Tax on the net wealth or assets owned by individuals or entities, including cash, bank deposits, investments, jewelry, and other valuables. ● Inheritance Tax: Tax imposed on the value of inherited assets or property received by heirs or beneficiaries of an estate. ● Gift Tax: Levied on the value of gifts received by individuals or entities, typically above a certain threshold, to prevent tax evasion through gifting assets. Significance of increase in direct taxes revenue: ● Government Revenue: Increase in direct taxes revenue signifies a growth in the government’s primary source of income, providing funds for public expenditure, social welfare programs, and infrastructure development. ● Fiscal Stability: Higher direct taxes revenue contributes to fiscal stability by reducing budget deficits, financing government expenditures, and lowering reliance on borrowings, enhancing macroeconomic stability and investor confidence. ● Progressive Taxation: Direct taxes, such as income tax and corporate tax, are typically progressive, with higher-income individuals and companies paying a larger share of their income as tax, promoting equity and redistributive justice in society. ● Investment in Public Goods: The rise in direct taxes revenue enables governments to invest in public goods and services, including education, healthcare, infrastructure, and social security, enhancing overall welfare and quality of life for citizens. ● Reduction of Indirect Taxes: Increased direct taxes revenue may allow for a reduction in indirect taxes, such as goods and services tax (GST), benefiting consumers by lowering the cost of goods and services and improving affordability. ● Economic Development: Higher direct taxes revenue reflects a growing economy, increased economic activity, higher employment levels, and rising incomes, indicating a positive trajectory of economic development and prosperity. |
| PYQ: Enumerate the indirect taxes which have been subsumed in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. Also, comment on the revenue implications of the GST introduced in India since July 2017. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2019) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the various types of direct taxes prevalent in India, elucidating their significance, impact on taxpayers, and role in government revenue generation. (250 Words /15 marks) |
5. India is a top-tier security partner: Australia
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral Relations
Understanding India – Australia defence cooperation is crucial for UPSC to analyse regional security dynamics and India’s strategic partnerships. |
| Context |
| ● The news highlights Australia’s National Defence Strategy-2024, emphasising India as a key security partner and outlining plans for Indo-Pacific cooperation. |
Additional information on this news:
- Australia released its new National Defence Strategy-2024, highlighting India as a top-tier security partner.
- The Comprehensive Strategic Partnership between Australia and India prioritises cooperation for Indo-Pacific stability.
- The strategy aims to deepen and expand defence cooperation with India through practical and tangible measures.
- The 2024 Integrated Investment Programme (IIP) allocates $330 billion over a decade to enhance defence capabilities.
- Defence funding as a proportion of GDP is projected to rise to around 2.4% by 2033-34 for Australia.
- Australian envoy in India, Philip Green, reaffirmed Australia’s support for India’s regional role and defence cooperation.
- Australia plans to deepen defence relationships with Southeast Asia, the Pacific, Indian Ocean, and North Asia regions.
- Partnerships with Japan and India will be expanded, along with collaboration with like-minded European nations.
- The NDS acknowledges increasing conflict risks, including on the border with India.
| India – Australia Defence Partnership |
| ● Strategic Alignment: India and Australia share strategic interests in maintaining peace, stability, and security in the Indo-Pacific region, fostering closer defence cooperation and partnership.
● Maritime Security: Both countries are maritime powers with a focus on safeguarding maritime routes, ensuring freedom of navigation, and countering piracy, illegal fishing, and maritime threats in the Indian Ocean and South China Sea. ● Military Exercises: India and Australia regularly conduct joint military exercises, such as Exercise AUSINDEX and Exercise Malabar, to enhance interoperability, exchange best practices, and strengthen bilateral defence capabilities. ● Information Sharing: Defense partnership includes intelligence sharing, defence technology cooperation, and cybersecurity collaboration to address shared security challenges, counter-terrorism, and combat emerging threats. ● Defense Trade: Growing defence trade and technology transfer between India and Australia involve procurement of defence equipment, weapons systems, and platforms, promoting defence industrial cooperation, and enhancing defence preparedness. ● Strategic Dialogues: High-level strategic dialogues and defence consultations between India and Australia facilitate policy coordination, strategic alignment, and mutual understanding on regional security issues, including China’s assertiveness and maritime disputes. ● Quad Engagement: Both countries are members of the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad), along with the United States and Japan, advocating for a free, open, and rules-based Indo-Pacific, promoting stability, prosperity, and security in the region. ● People-to-People Ties: Defense partnership strengthens people-to-people ties, military-to-military exchanges, and defence personnel training, fostering trust, friendship, and cooperation between the armed forces of India and Australia. |
| PYQ: ‘Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad)’ is transforming itself into a trade bloc from a military alliance, in present Smes – Discuss. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2020) |
| Practice Question: Examine the significance of Australia’s National Defence Strategy-2024 in the context of Indo-Pacific security and India’s strategic partnerships. (150 Words /10 marks) |
6. The mpox virus uses a ‘genomic accordion’ to evolve and infect humans.
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology
Understanding genomic dynamics of mpox outbreaks aids in public health strategies and strengthens global disease surveillance. |
| ● The news discusses the recent mpox outbreak, its genomic analysis, and the implications for public health and global disease surveillance efforts. |
Additional information on this news:
- Poxviruses, including smallpox and mpox, have been significant threats to public health, causing widespread mortality.
- The smallpox vaccine led to its eradication, showcasing the power of global public health initiatives.
- The recent mpox outbreak, stemming from a 1958 spillover event, gained global attention and posed a public health emergency.
- The outbreak highlighted the virus’s ability to evolve and adapt, with one clade showing high human-to-human transmission.
- Researchers sequenced the mpox genome, identifying genomic sections influencing transmissibility and evolutionary dynamics.
- Genome sequencing aids in understanding the virus’s evolution and potential for outbreaks.
- The outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) involved a distinct lineage of mpox clade I.
- Genome data suggests a recent zoonotic spillover, emphasizing the importance of genomic surveillance in outbreak management.
- Vigilant genomic investigations and coordinated public health efforts are crucial for mitigating the threat of emerging pathogens.
| What is genomic accordion? |
| ●Genomic accordion refers to rhythmic expansions and contractions in the genome size of viruses, particularly poxviruses like mpox.
● It involves the duplication or deletion of gene stretches within the virus’s genome. ● These expansions and contractions are influenced by evolutionary pressures and can occur over relatively short periods. ● Genomic accordion allows viruses to adapt to different hosts and environmental conditions. ● In the context of mpox, researchers have observed expansions and contractions in the virus’s genome, influencing its virulence and transmissibility. ● Understanding genomic accordion provides insights into how viruses evolve and spread, aiding in the development of effective countermeasures and public health interventions. ● It highlights the dynamic nature of viral genomes and the importance of genomic surveillance in monitoring disease outbreaks. |
| PYQ: (UPSC civil services prelims 2017)
Q With reference to agriculture in India, how can the technique of ‘genome sequencing’, often seen in the news, be used in the immediate future? 1. Genome sequencing can be used to identify genetic markers for disease resistance and drought tolerance in various crop plants. 2. This technique helps in reducing the time required to develop new varieties of crop plants. 3. It can be used to decipher the host-pathogen relationships in crops. Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only Ans: Option D |
| Practice Question: How does genomic analysis of the mpox virus contribute to public health strategies and global disease surveillance efforts? Discuss. (150 Words /10 marks) |
For Enquiry

22 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

22 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC Copy

22 April 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis

20 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

20 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

20 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

20 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC

20 April 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

20 April 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis

SCIENCE REPORTER SUMMARY: JANUARY 2024
April 2024 Daily Current Affairs 22 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
22-April -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Global Coral Bleaching Crisis: Urgent Action…
April 2024 PIB 22 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC Copy PIB Summary for UPSC
22-April-2024
1. PM inaugurates 2550th Bhagwan Mahaveer Nirvan Mahotsav on occasion…
April 2024 Indian Express 22 April 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
22-April-2024
1. Cures, care, competition
Topic: GS2 – Governance…
Daily Quiz 20 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 20- April 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 20 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
20-April-2024
Q1) Assess the present computational methodology for Gross Domestic…
April 2024 Daily Current Affairs 20 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
20-April -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Israeli Military Strikes Iran in Apparent…
April 2024 PIB 20 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
20-April-2024
1. High turnout in Phase 1 of Lok Sabha Elections 2024 despite heat…
April 2024 The Hindu Editorial 20 April 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu EDITORIAL
20-April-2024
1. Israel, a two-state solution, some recent perceptions.
Topic:…
April 2024 Indian Express 20 April 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
20-April-2024
1. A BITTER SWEET
Topic: GS2 – Social Justice –…
Science Reporter SCIENCE REPORTER SUMMARY: JANUARY 2024 ARTICLE 1: India-born Prof. Arogyaswami Paulraj Receives Faraday Medal for Pioneering MIMO Technology
Awards…




