4 September 2023 : Daily Current Affairs
Daily Current Affairs
4-September-2023
Daily Current Affairs For UPSC ,Daily Current affairs of The hIndu and Indian Express.
1) Aditya L1 healthy, spacecraft’s first orbit-raising move successful: ISRO
Topic: GS3-Science and Tech
Context:
- A day after it launched the Aditya-L1 spacecraft, the country’s first mission to study the Sun, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) carried out the first orbit-raising manoeuvre.
- ISRO said the satellite is “healthy and operating nominally”, and the first Earth-bound manoeuvre has been “performed successfully” from ISTRAC, Bengaluru.
Details:
- The Aditya-L1 mission was launched from the Sriharikota spaceport shortly before noon Saturday and placed in an Earth orbit, 235 km x 19,500 km, an hour later.
- Over the next few days, the spacecraft will continue to move around the Earth, progressively raising its orbit and gaining momentum, before embarking on its four-month journey to the Lagrange-1 point of the Earth Sun system.
- It is from this point, about 1.5 million km from Earth, that the Aditya-L1 spacecraft will observe the Sun and carry out experiments.
- The heavier version of the PSLV rocket that had put the satellite in the orbit achieved a milestone of its own. This was the first time that the fourth stage of the PSLV was fired two separate times to insert the space craft in the intended orbit.
- During the firing of the fourth stage of PSLV and the coasting phase in between, there were two instances–one for nearly 25 minutes and another for just over two minutes – when there were no eyes on the satellite. It was only after a ship-based station in the Bay of Bengal and then the Kourou ground station in French Guiana acquired the data that the flight path could be seen.
- A scientist from the space agency said that the mission should ideally have been launched in August. Launching it in September meant that the spacecraft had to travel longer to achieve the specific angle at which it needed to be inserted.
2) First set of infra loans for tier 2, tier 3 cities to be disbursed soon.
Topic: GS3- Economy
Context:
- The First tranche of loans to fund ongoing projects in tier-2 and tier-3 cities under the Urban Infrastructure Development Fund (UIDF) announced in the FY24 Budget will likely be disbursed soon.
- States are also in the process of preparing proposals for new projects.
Details:
- The fund makes low-cost loans available to 459 tier-2 cities with a population between 1 lakh and 9,99,999 and 580 tier 3 towns with a population between 50,000 and 99,999 asper the 2011 Census.
- The National Housing Bank (NHB), in charge of executing the UIDF, had issued guidelines in July and asked states to submit their proposals by September.
- Among the projects set to be funded are sewage treatment plants and sewerage networks.
- The UIDF funding can be combined with funding under other schemes of the Ministry such as Swachh Bharat Mission and AMRUT.
- Among the projects that can be funded under the UIDF are water supply, sanitation, construction of roads, comprehensive area development, local area planning for decongestion, heritage conservation, town-planning schemes and parks with open gyms that do not involve major construction.
- The fund cannot be used for maintenance work, administrative expenses, housing, power, telecom, urban transport, health and education projects, as per the guideline.
3) CORONAVIRUS-PIROLA VARIANT
Topic: GS3- Science and Tech
Context:
- An article published in the Yale Medicine Review on August 31 has noted Covid-19 infections in multiple countries driven by a new Coronavirus variant called BA.2.86, informally termed Pirola
- While the report says that it is too early to know if this strain is more transmissible than other ones, there may be a reason to worry.
- The report says it has “more than 30 mutations to its spike protein compared to XBB.1.5, a variant of Omicron that had been the dominant strain in the United States. The spike protein is how the corona virus enters human cells.
Where have the cases been reported?
- Pirola has been witnessed in the US, the UK, and other countries, in unrelated cases.
- According to Yale Medicine infectious diseases specialist, the high number of mutations is a point of concern here.
- He said in the report that this was similar to the number of mutations that differed between Delta, one of the early strains of the coronavirus, and Omicron (that was dominant in the winter of 2021).
- With every respiratory virus, as it spreads from person to person, it evolves gradually over time. But these massive shifts, which we also saw from Delta to Omicron, are worrisome.
- The other concern is that this strain has been picked up in at least six countries, and the cases are unrelated. This suggests some degree of transmission in the international community that we’re not detecting.
How do viruses mutate?
- It is natural for all viruses to mutate over time and such changes are particularly common in viruses that have RNA as their genetic material, as in the case of coronaviruses and influenza viruses.
- Once a virus enters the human body, its genetic material— RNA or DNA—enters the cells and starts making copies of itself which can infect the other cells.
- Whenever an error occurs during this copying process, it triggers a mutation. Occasionally, the mutation proves to be advantageous for the virus.
- Acc to experts, Pirola is a “much more interesting subvariant”, when compared with the Omicron subvariant, known as XBB.1.9.
4) Black Sea Grain Deal
Topic: GS2- IR
Context:
- Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan will meet Vladimir Putin on Monday, hoping to persuade the Russian leader to rejoin the Black Sea grain deal that Moscow withdrew from in July.
About Black Sea
- The Black Sea is a large inland sea located in southeastern Europe and bordered by six countries: Bulgaria, Romania, Ukraine, Russia, Georgia, and Turkey.
- It is connected to the Mediterranean Sea through the Bosporus Strait and the Sea of Marmara to the south.
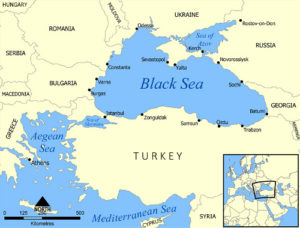
Geographical Features
- The Black Sea covers an area of approximately 436,000 square kilometers, making itone of the largest inland seas in the world.
- The maximum depth reaches about 2,212 meters (7,257 feet) in the central part of the sea.
- The coastline stretches for approximately 2,500 kilometers, offering diverse landscapes and significant cultural and economic importance to the surrounding countries.
Importance and Economic Significance of the Black Sea
Trade and Transport Hub
- The Black Sea serves as a crucial transportation corridor, facilitating trade between Europe, Asia, and the Middle East.
- The sea is home to several significant ports, including Odessa (Ukraine), Constanta (Romania), and Novorossiysk (Russia), which handle substantial cargo volumes and support international shipping.
Energy and Resources
- The Black Sea region contains significant oil and natural gas reserves, attracting interest from energy companies for exploration and production activities.
- The sea supports a thriving fishing industry, providing essential resources for the economies and food security of the surrounding countries.
Ecology and Environmental Concerns
Ecological Importance
- The Black Sea is home to various marine species, including fish, marine mammals, and birds, contributing to the region’s ecological diversity.
- The coastal areas and wetlands around the sea provide essential habitats for migratory birds and other wildlife.
Environmental Challenges
- The Black Sea faces pollution from industrial and agricultural runoff, affecting water quality and marine ecosystems.
- Introductions of non-native species have disrupted the natural balance of the sea’s ecosystems, posing a threat to local biodiversity.
Tourism and Cultural Heritage
Tourism
- The Black Sea coastline is dotted with popular tourist destinations and resorts, attracting visitors with its sandy beaches and warm climate.
- The region boasts a rich history, with ancient ruins and cultural landmarks attracting history enthusiasts.
Cultural Diversity
- The countries bordering the Black Sea have a long history of cultural interaction and exchange, resulting in a diverse and vibrant cultural heritage.
- Each country contributes unique traditions, customs, and culinary delights to the region’s cultural tapestry.
Where will the talks be held?
- The meeting would be held in Sochi on Russia’s southern coast.
Why did Russia quit the deal?
- The deal which was brokered by the United Nations and Turkey in July 2022 had allowed nearly 33 million metric tonnes (36 million tonnes) of grain and other commodities to leave three Ukrainian ports safely despite Russia’s war.
- However, Russia pulled out after claiming that a parallel deal promising to remove obstacles to Russian exports of food and fertilisers hadn’t been honoured.
Why is Turkey a broker?
- Since Putin withdrew from the initiative, Erdogan has repeatedly pledged to renew arrangements that helped avoid a food crisis in parts of Africa, the Middle East and Asia.
- The Turkish president has maintained close ties to Putin during the 18-month war in Ukraine.
- Turkey hasn’t joined Western sanctions against Russia following its invasion, emerging as a main trading partner and logistical hub for Russia’s overseas trade.
- NATO member Turkey, however, has also supported Ukraine, sending arms, meeting Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy and backing Kyiv’s bid to join NATO.
What are Russia’s demands?
- Russia handed over a list of actions that the West would have to take for Ukraine’s Black Sea exports to resume.
- Russia demands eased rules for its own food and fertilizer exports to return to the grain deal.
- Western countries view this as an attempt to leverage food supplies to weaken financial sanctions on Russia.
- The International Monetary Fund highlights the potential negative impact on global food security.
5. Fiscally imprudent policies, populism affect the poor: PM
Topic: GS2 – governance
Context:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi has cautioned against irresponsible financial policies and populism, emphasizing their adverse long-term social and economic consequences.
More information about the news:
- He highlighted the need for financial discipline, urging both national and state governments to be conscious of their fiscal policies.
- PM Modi mentioned India’s sensitivity to neighboring countries facing crises, such as Sri Lanka.
- In response to criticism regarding meetings held in Kashmir and Arunachal Pradesh in the lead-up to the G-20 Summit, PM Modi defended the decisions, citing India’s vast and diverse geography.
- He emphasized India’s stance on energy security, stating that there is no ‘one-size-fits-all’ solution and highlighting the importance of diversity in society and the energy mix.
- PM Modi noted India’s commitment to meeting climate goals despite having a relatively low share of global emissions compared to its population.
Importance of fiscal prudence for governments:
- Ensures financial stability and credibility.
- Maintains investor confidence.
- Reduces inflationary pressures.
- Preserves fiscal space for emergencies.
- Promotes long-term economic sustainability.
- Supports sustainable development and poverty reduction.
- Helps prevent excessive debt accumulation.
Challenges:
- Economic volatility and uncertainty.
- Balancing social welfare with fiscal responsibility.
- Political pressure for populist spending.
- Infrastructure and development needs.
- Addressing income inequality.
- Managing external debt and trade imbalances.
- Responding to unforeseen crises and emergencies.
Mains question: Discuss the challenges and significance of fiscal prudence. How can governments strike a balance between fiscal responsibility and addressing socio-economic needs?
6. Status of the Right to Information Act
Topic: GS2 – governance
Context:
- The Right to Information Act, 2005, provided citizens with access to government information and data for 13 years.
- India’s RTI Act was considered one of the world’s most comprehensive public records access legislations.
- Concerns have emerged that the RTI system is becoming less effective, limiting accountability of public officials.
Amendments to the RTI Act:
- The Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, amended the RTI Act, imposing a total prohibition on disclosing personal data, potentially affecting social audits and public officials’ accountability.
Previous Amendments and Concerns:
- The Right to Information (Amendment) Act, 2019, granted the Union Government unilateral power over information commissioners’ tenures and salaries, raising concerns.
- The RTI Act’s implementation depends on subordinate rules set by Union and State Governments.
- Payment methods for RTI requests vary by state, with some states not accepting convenient methods like Indian Postal Orders (IPOs).
- Delays in appointing information commissioners in Central and State Information Commissions have led to lengthy appeals processes.
Challenges with Online RTIs:
- While online RTI applications simplify the process, not all states have online portals, and many government bodies are not registered on these portals.
- The Union Government’s RTI portal faces usability issues, with applicants having to re-enter personal details each time they file a request.
Growing Dissatisfaction:
- Increasing numbers of first appeals suggest growing dissatisfaction with the information provided by public officials.
- The weakening of the RTI Act is not just due to changes in the law but also how various institutions and websites handle RTI requests and appeals.
Overall Concern:
- The RTI Act in India is facing challenges related to amendments, implementation, online portals, and dissatisfaction among citizens, raising concerns about transparency and accountability in governance.
Way forward:
- Strengthen the RTI Act to ensure its effectiveness and independence.
- Address delays in appointing information commissioners.
- Standardize online RTI portals and improve usability.
- Enhance public awareness of RTI procedures and rights.
- Encourage transparency and accountability in government agencies.
- Monitor and address issues related to data privacy and personal information protection.
- Collaborate with civil society and NGOs to promote RTI awareness and usage.
7. What is the debate around ‘one nation, one election’?
Topic: GS2 – governance
Context:
- The “one nation, one election” (ONOE) plan aims to synchronize the timing of Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections across all Indian states to reduce the frequency of polls.
- The practice of simultaneous elections existed initially from 1951-1952 to 1967 but was disrupted due to various reasons, including the dismissal of state governments and defections among parties.
- Reports suggest that the Law Commission of India (LCI) in August 2018 analyzed the feasibility of simultaneous elections and concluded that it would require constitutional and legal amendments.
Advantages of one nation one election:
- Cost-saving: Reduces the frequent expenditure associated with conducting separate elections at the state and national levels.
- Administrative efficiency: Streamlines election management, reducing the burden on administrative resources and security forces.
- Focus on governance: Allows elected representatives and governments to concentrate on governance and development rather than perpetual election campaigning.
- Predictability: Provides certainty in the election schedule, allowing for better long-term planning and policy implementation.
- Reduces political disruption: Minimizes the impact of political campaigns on government functions and stability.
Challenges:
- Constitutional hurdles: Implementing “one nation, one election” requires amendments to the Constitution and various legal frameworks, which can be a complex and time-consuming process.
- Federalism concerns: The concept may be seen as infringing on the autonomy of states in a federal system, contradicting the principles of federalism.
- Mid-term government collapses: If a central or state government falls mid-term, the plan raises questions about whether elections would be held again in every state or if President’s rule would be imposed.
- Blending of issues: Combining national and state elections could blur the distinction between issues, making it harder for voters to differentiate between state and national concerns.
- Accountability: Frequent elections allow voters to hold governments accountable more often, and ONOE might reduce this level of accountability.
- Unproven benefits: The claimed cost savings of ONOE are disputed, with some arguing that the current election expenditure is not excessive considering India’s status as the world’s largest electoral democracy.
Way forward:
- Comprehensive dialogue: Engage in extensive discussions and consultations with political parties, legal experts, and stakeholders to address constitutional and logistical challenges.
- Pilot projects: Consider conducting pilot projects of simultaneous elections in select states to assess their feasibility and impact on governance and federalism.
- Amendments: If deemed necessary, initiate constitutional and legal amendments to facilitate “one nation, one election” while preserving the federal structure and accountability.
- Public awareness: Raise awareness among citizens about the potential advantages and disadvantages of ONOE to garner public support and ensure informed decision-making.
- Data-driven analysis: Conduct thorough cost-benefit analyses to determine the actual financial implications of ONOE and assess whether the claimed cost savings are achievable.
- Gradual implementation: Implement ONOE in phases, starting with states that are willing to participate, and gradually expand the practice based on the lessons learned from initial experiences.
Mains question: What are the key advantages and challenges associated with implementing ‘one nation, one election’ in India, and how can these challenges be addressed effectively?
For Enquiry

4 September 2023 : Daily Current Affairs

Daily Prelims Quiz : Vegetation

Daily Prelims Quiz : Indian Climate – Monsoon system

Daily Prelims Quiz : Minerals, rocks, landforms and their evolution

Daily Prelims Quiz : Structure of Earth and Plate Tectonics

Daily Prelims Quiz : services relating to Health, Education, Human resources.

Daily Prelims Quiz : Issues relating to the development and management of social sector

Daily Prelims Quiz : Communalism, Regionalism & Secularism.

Daily Prelims Quiz : Social Empowerment,

Daily Prelims Quiz : Effects of Globalization on Indian Society.
Daily Current Affairs 4 September 2023 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
2-September-2023
Daily Current Affairs For UPSC ,Daily Current affairs of The hIndu…
Geography prelims quiz Daily Prelims Quiz : Vegetation Daily Prelims Quiz
Week 9 Day 4
Instructions1. All 5 Questions are Compulsory.2. Each question carries…
Geography prelims quiz Daily Prelims Quiz : Indian Climate – Monsoon system Daily Prelims Quiz
Week 9 Day 3
Instructions1. All 5 Questions are Compulsory.2. Each question carries…
Geography prelims quiz Daily Prelims Quiz : Minerals, rocks, landforms and their evolution Daily Prelims Quiz
Week 8 Day 2
Instructions1. All 5 Questions are Compulsory.2. Each question carries…
Geography prelims quiz Daily Prelims Quiz : Structure of Earth and Plate Tectonics Daily Prelims Quiz
Week 8 Day 1
Instructions1. All 5 Questions are Compulsory.2. Each question carries…
Prelims Quiz Daily Prelims Quiz : services relating to Health, Education, Human resources. Daily Prelims Quiz
Week 7 Day 5
Instructions1. All 5 Questions are Compulsory.2. Each question carries…
Prelims Quiz Daily Prelims Quiz : Issues relating to the development and management of social sector Daily Prelims Quiz
Week 7 Day 4
Instructions1. All 5 Questions are Compulsory.2. Each question carries…
Prelims Quiz Daily Prelims Quiz : Communalism, Regionalism & Secularism. Daily Prelims Quiz
Week 7 Day 3
Instructions1. All 5 Questions are Compulsory.2. Each question carries…
Prelims Quiz Daily Prelims Quiz : Social Empowerment, Daily Prelims Quiz
Week 7 Day 2
Instructions1. All 5 Questions are Compulsory.2. Each question carries…
Prelims Quiz Daily Prelims Quiz : Effects of Globalization on Indian Society. Daily Prelims Quiz
Week 7 Day 1
Instructions1. All 5 Questions are Compulsory.2. Each question carries…

