6 May 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. T.N. moves top court, accuses Kerala of obstructing work on Mullaperiyar dam
| (Source – The Hindu, Section – Front, Page – 1)
Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity – Federal Structure GS3 – Indian Economy – Issues relating to Planning |
| Context |
| ● Tamil Nadu accuses Kerala of impeding essential maintenance on the Mullaperiyar dam while Kerala advocates for its decommissioning due to safety concerns amidst climate change.
● Kerala’s actions allegedly contradict its stated worries about dam safety. ● The dispute highlights longstanding tensions over water management between the two states. |
Analysis of the news:
- Tamil Nadu accuses Kerala of obstructing essential maintenance work on the over 125-year-old Mullaperiyar dam.
| About Mullaperiyar Dam |
| ● Mullaperiyar Dam is located in Kerala, India.
● Constructed between 1887 and 1895 during British rule. ● Built across the Periyar River, it’s a gravity dam. ● Primary purpose is water supply, irrigation and hydroelectricity generation. ● Managed by the Tamil Nadu government. ● Controversy surrounds its safety due to age and seismic concerns. ● Kerala seeks a new dam citing safety worries, while Tamil Nadu opposes it. ● Dispute between the two states remains unresolved, subject to legal battles and negotiations. |
- Kerala has delayed routine maintenance tasks such as painting, patch works, and repairs for periods ranging from two months to over a year.
- Tamil Nadu claims that Kerala’s actions contradict its concerns about the dam’s safety and comprehensive review.
- The reconstituted supervisory committee, empowered by the Dam Safety Act, 2021, has allegedly failed to ensure Kerala’s cooperation.
- Pending work includes grouting the main dam and cutting 15 trees to strengthen the baby dam, with permission initially granted by Kerala but later withdrawn.
- In 2021, Kerala advocated for decommissioning the Mullaperiyar dam and constructing a new one due to concerns about climate change, heavy rainfall, and floods.
- Kerala referenced the Uttarakhand flood of February 2021 and the decommissioning of the Victoria dam in Australia due to structural issues.
- The suggestion for a new dam has been discussed since 1979, with Kerala citing precedents from around the world to support its argument.
| Dam Safety in India |
| Issues with Dam Safety in India:
● Structural Integrity: Concerns persist regarding the structural integrity of many dams, especially older ones, due to inadequate maintenance and aging infrastructure. ● Monitoring Challenges: Insufficient monitoring systems and outdated technology hinder timely detection of potential risks and vulnerabilities. ● Environmental Impact: Dams can have adverse environmental consequences, including habitat destruction and altered water flow patterns. ● Climate Change: Changing climatic patterns pose challenges to dam safety, with increased frequency of extreme weather events. ● Population Pressure: Growing population and urbanization lead to heightened demand for water resources, straining existing dam infrastructure. ● Interstate Disputes: Conflicts over dam construction and water-sharing agreements among states can delay safety measures. ● Financial Constraints: Limited funding for dam maintenance and safety upgrades impedes effective risk mitigation. ● Capacity Building: Shortage of skilled manpower and technical expertise in dam management hampers safety efforts. ● Policy Gaps: Comprehensive policy reforms and robust regulatory frameworks are needed to address the complex challenges. Way Forward: ● Investment in Maintenance: Allocate sufficient funds for regular maintenance and upgrades of dam infrastructure. ● Enhanced Monitoring: Implement advanced monitoring systems and technologies for early detection of safety issues. ● Environmental Assessment: Conduct comprehensive environmental impact assessments for proposed dam projects and prioritize sustainable solutions. ● Climate Resilience: Incorporate climate resilience measures into dam design and management strategies. ● Collaborative Approach: Foster interstate cooperation and dialogue to resolve disputes and streamline water-sharing agreements. ● Capacity Development: Invest in training programs and capacity building initiatives for dam safety professionals. ● Policy Reforms: Strengthen regulatory frameworks and enact legislation to address gaps in dam safety management. Dam Safety Act, 2021: ● Dam Safety Act, 2021 enacted by the Union Government of India. ● Focuses on surveillance, inspection, operation, and maintenance of specified dams. ● Aims to prevent dam failure-related disasters. ● Establishes an institutional mechanism for safe functioning. ● National Committee on Dam Safety (NCDS) formed at the national level. It is responsible for evolving dam safety policies and recommending regulations. ● National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA) created as a regulatory body. It implements policies of NCDS and offers technical assistance to State Dam Safety Organisations (SDSO). ● State Governments empowered to establish the State Committee on Dam Safety. ● State Dam Safety Organisations enforce dam safety standards and issue crucial instructions to dam owners. |
| PYQ: Dam failures are always catastrophic, especially on the downstream side, resulting in a colossal loss of life and property. Analyse the various causes of dam failures. Give two examples of large dam failures. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2023) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the ongoing interstate water dispute between Tamil Nadu and Kerala over the Mullaperiyar dam. How do such disputes reflect challenges in cooperative water management and the implications for national development? Suggest measures for resolving such conflicts effectively. (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. Catatumbo lightning: a torrent of current
| (Source – The Hindu, Section – Science, Page – 7)
Topic: GS1 – Geography, GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
| ● Catatumbo lightning, a continuous natural occurrence over Venezuela’s Catatumbo River, arises from a convergence of warm Caribbean air with cooler Andes mountain air.
● Generating up to 160 nights of lightning per year, it earns the area the title “the lightning capital of the world |
Analysis of the news:
- Catatumbo lightning is a continuous natural phenomenon over the Catatumbo River in Venezuela, primarily at its mouth where it meets Lake Maracaibo.
- It is caused by a convergence of warm, moist air from the Caribbean Sea colliding with cooler air from the Andes mountains.
- The collision creates rapidly rising air that cools and condenses, forming towering cumulonimbus clouds.

| Cumulonimbus Clouds |
| ● Cumulonimbus clouds are towering, vertically-developed clouds associated with thunderstorms and severe weather.
● They form due to strong upward atmospheric motion caused by convection. ● These clouds typically have a flat, anvil-shaped top, resulting from the spreading of their upper portion in the stratosphere. ● They can reach impressive heights, often exceeding several miles. ● Lightning, thunder, heavy rain, hail, and tornadoes are common phenomena associated with cumulonimbus clouds. ● They play a crucial role in the Earth’s water cycle by producing precipitation. |
- Strong winds and temperature differences generate electrical charges within these clouds.
- The cumulonimbus clouds, reaching heights of over 5 km, become loaded with static electricity.
- When the electrical potential within the clouds becomes too great, it discharges as lightning.
- Catatumbo lightning occurs for up to 160 nights per year, with an average of 28 lightning strikes per minute at its peak.
- Due to its constant lightning activity, the area is known as “the lightning capital of the world”.
| PYQ: Explain the mechanism and occurrence of cloudburst in the context of the Indian subcontinent. Discuss two recent examples. (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2022) |
3. What is Hubristic bias in investing?
| (Source – The Hindu, Section – Business, Page – 12)
Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
| ● Hubristic bias refers to overconfidence and a false sense of understanding in investing.
● It leads individuals to believe they have a deep grasp of market movements based on limited information, often resulting in speculative behaviour and significant losses, particularly during market downturns. |
Analysis of the news:
- Hubristic bias is a psychological phenomenon commonly observed in investing.
- It involves overconfidence and a false sense of understanding or expertise in market movements.
- Investors affected by hubristic bias often believe they have a deep understanding of market behaviour based on limited or biased information.
- This bias can lead investors to engage in speculative activities, such as day trading, without proper analysis or risk management.
- Hubristic bias becomes more pronounced during bull markets when investors feel invincible due to rising prices.
- However, during market downturns or corrections, the shortcomings of their overconfidence are exposed, resulting in significant losses.
- This bias is fueled by factors like media reports, expert opinions, and discussions with peers, reinforcing the false belief of expertise.
- To mitigate hubristic bias, investors can focus on diversification, set clear financial goals, and seek professional advice when needed.
- Acknowledging the presence of overconfidence and maintaining a disciplined approach to investing are key strategies to counteract hubristic bias.
4. Unlocking the vast potential of personalisation in banking services
| (Source – The Hindu, Section – Business, Page – 13)
Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
| ● The news encapsulates the significance of personalization in banking, highlighting its role in differentiation amid competition and meeting evolving customer expectations.
● It underscores the need for seamless tailored experiences and investment in advanced technologies for scalable, data-driven personalization efforts. |
Analysis of the news:
- Personalisation is key for banks to differentiate themselves in the competitive financial sector, catering to evolving customer expectations and fending off challenges from traditional and fintech competitors.
| What is personalization in banking services? |
| ● Personalization in banking services refers to tailoring financial products and services to meet the specific needs and preferences of individual customers.
● It involves analysing customer data, such as transaction history, spending patterns, and demographic information, to understand their unique financial behaviours and goals. ● Personalization allows banks to offer customised recommendations, such as personalised investment portfolios, loan options, or savings plans. ● It enhances customer experience by providing relevant and timely offers, advice, and support. ● By delivering more personalised services, banks can improve customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention. ● Advances in technology, such as artificial intelligence and data analytics, have enabled banks to enhance their personalization capabilities and deliver more targeted and effective banking solutions. |
- Tailored experiences must be seamlessly delivered across various touchpoints, including branches, digital platforms, and face-to-face interactions.
- The shift from segment-based offerings to personalised experiences places individual needs and preferences at the forefront.
- Customers expect banks to anticipate their needs and provide proactive recommendations.
- To meet these expectations, banks must reinvent themselves, leveraging advanced technologies and data-driven insights.
- Investment in robust data ecosystems and technological infrastructure is essential to provide personalised experiences at scale.
- A ‘personalisation engine’ is indispensable for successful operation, requiring scalability, flexibility, and integration with existing systems.
- Continuous monitoring and optimisation based on customer responses and data insights are crucial for refining personalisation efforts.
- Cross-functional collaboration and a focus on simplicity and relevance in design are necessary for customer-centric excellence.
- Ultimately, banks must work towards a shared vision of customer-centricity to elevate the overall customer experience.
| Personalisation of banking services |
| Significance of Personalization in Banking Services:
● Enhanced Customer Experience: Personalised recommendations for financial products, services, and investment opportunities based on individual needs and goals. ● Increased Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: Tailored offerings lead to greater satisfaction and a stronger bank-customer relationship. ● Improved Risk Management: Personalised insights can help banks identify and mitigate potential financial risks associated with individual customers. ● Boosted Revenue Generation: Cross-selling and upselling relevant products based on customer profiles can increase profitability. ● Financial Inclusion: Personalised financial solutions can empower unbanked or underbanked populations to manage their finances effectively. Challenges of Personalization in Banking Services: ● Data Privacy Concerns: Balancing personalization with robust data security and customer privacy is crucial. ● Algorithmic Bias: Ensuring algorithms used for personalization are fair and unbiased to avoid discrimination. ● Technological Hurdles: Banks need to invest in sophisticated data analytics tools and infrastructure. ● Customer Trust: Building trust with customers regarding data usage and transparency in personalization practices. ● Digital Divide: Ensuring everyone has access to the technology needed to benefit from personalised banking services. |
| Practice Question: How does personalization in banking services contribute to customer satisfaction, financial inclusion and competitive advantage in the modern financial landscape? Discuss with examples. (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. Maharashtra Forest Department Initiates Tiger Translocation Project to Boost Conservation Efforts in Western Ghats
| (Source: Indian Express; Section: Express network; Page: 12 Topic: GS3 – Environment – Conservation |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of the News:
About Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (STR):
- Location: It is located in the Sahyadri Ranges of the Western Ghats in Maharashtra.
- The reserve spreads over Koyna Wildlife Sanctuary, forming the northern portion, and Chandoli National Park, forming the southern part of the reserve. STR was created by merging the areas of these two forests in 2007.
- The region of the Sahyadri Tiger Reserve includes the area around the Koyna Dam, the Warna River, and many other small rivers and streams originating from the Western Ghats and flowing to the east.
History:
- The history of the area dates back to the Maratha Empire, and many forts built or captured by the first Maratha Emperor Chhatrapati Shivaji Bhonsle can be found here.
- The legendary temple from which Shivaji Maharaj received the Bhavani Sword from divine providence is also said to be among the many ruins in this region.
Habitat:
- The total area of STR is undulating, with steep escarpments along the western boundary.
- The most distinct feature of the Tiger Reserve is the presence of numerous barren rocky and lateritic plateaus, locally called “Sadas”, with less perennial vegetation and overhanging cliffs on the edges, along with numerous fallen boulders with dense thorny bushes.
- STR is the only place where climax and near-climax vegetation are plentiful and prospects of adverse anthropogenic influence in the future are minimal.
Flora:
- The forest cover here is that of moist evergreen, semi-evergreen, moist, and dry deciduous vegetation.
- There are many medicinal and fruit-bearing trees along with the commercial hard wood trees in the reserve.
Fauna:
- The main carnivores are the tiger, leopard, and some lesser cats along with the wolf, jackal, and wild dog.
- The large herbivores are several deer species like Barking Deer, Sambar, and other large and small animals like Indian Bison, Sloth Bear, Mouse Deer, Giant Indian Squirrel and Macaque.
Translocation Plan and Process:
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) approved the translocation plan in October 2023, signaling a significant step towards tiger conservation.
- Initially, a male tiger or a pair of male and female tigers will be tranquilized in TATR and relocated to STR.
- The Maharashtra forest department awaits final clearance from the Union Environment Ministry to commence the translocation process.
About National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA):
- It is a statutory body under the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- It was established in 2006 under Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972.
Objectives:
- Providing statutory authority to Project Tiger so that compliance of its directives become legal.
- Fostering accountability of Center-State in management of Tiger Reserves by providing a basis for MoU with States within the federal structure.
- Providing for an oversight by Parliament.
- Addressing livelihood interests of local people in areas surrounding Tiger Reserves.
NTCA Members:
- Minister in charge of MoEFCC (as Chairperson),
- Minister of State in MoEFCC (as Vice-Chairperson), three members of Parliament, the Secretary (MoEFCC), and other members.
Significance of Translocation for Conservation:
- The translocation project is vital for preserving tiger populations in the northern Western Ghats, a crucial wildlife corridor connecting Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- This corridor facilitates the movement of tigers between various reserves and sanctuaries, ensuring genetic diversity and long-term survival of the species.
Challenges and Threats:
- Despite the importance of the wildlife corridor, the region faces threats from mining activities, road projects, and human settlements, as highlighted in the 2023 tiger population estimation report.
- These factors pose significant risks to the habitat and connectivity of tiger populations, emphasizing the urgency of conservation efforts.
Future Plans and Conservation Strategy:
- Following the translocation from TATR, similar initiatives are planned for the Pench Tiger Reserve landscape in Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh.
- The phase-II of the tiger recovery project aims to translocate a total of eight tigers, comprising three males and five females.
- The process will involve a soft release method, ensuring close monitoring before the tigers are released into their natural habitat within the reserve.
Conclusion:
- The translocation of tigers from TATR to STR represents a crucial step towards tiger conservation in Maharashtra.
- By addressing the challenges and leveraging scientific expertise, the state aims to strengthen its tiger populations and preserve the unique biodiversity of the Western Ghats.
- This collaborative effort underscores the commitment to wildlife conservation and sustainable ecosystem management in the region.
| What is ‘Project Tiger’? |
It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) of the MoEFCC.
Success Story of the Project Tiger
|
| PYQ: Among the following Tiger Reserves, which one has the largest area under “Critical Tiger Habitat”? (2020) (a) Corbett (b) Ranthambore (c) Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam (d) Sundarbans Ans: (c) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the various steps taken by India for Tiger conservation. (150 words/10 m) |
6. Dengue Devastates Latin America: Over 6 Million Cases Reported in First Four Months of 2024
| (Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 13)
Topic: GS3 – Science & Technology |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of the News:
About Dengue:
- It is caused by the dengue virus (DENV).
- It is transmitted to humans through the bites of infected female mosquitoes, primarily the Aedes aegypti mosquito.
- The severe form of dengue fever, also called dengue hemorrhagic fever, can cause serious bleeding, a sudden drop in blood pressure (shock) and death.
- It is more common in tropical and subtropical climates.
Symptoms:
- The most common symptoms are high fever, headache, body aches, nausea and rash.
- Most will also get better in 1–2 weeks but in severe cases it can be fatal.
Treatment:
- There is no specific treatment for dengue.
- Early detection of disease progression associated with severe dengue, and access to proper medical care lowers fatality rates of severe dengue to below 1%.
- The dengue vaccine CYD-TDV or Dengvaxia was approved by the US Food & Drug Administration in 2019, the first dengue vaccine to get the regulatory nod in the US.
Magnitude of the Outbreak:
- Dengue, a mosquito-borne viral infection, is rapidly spreading throughout Latin America, affecting countries in South America, Central America, Mexico, and the Caribbean.
- Within the first four months of 2024, the region has reported over 6 million cases, marking a significant increase from the 4.4 million cases reported in the entirety of 2023.
- This surge in cases is occurring both before the typical peak season for dengue and in regions experiencing severe outbreaks for the first time.
- The escalation of dengue cases in Latin America coincides with global temperature rises, which create conducive environments for the proliferation of the Aedes mosquito, the vector responsible for transmitting dengue.
Rising Case Numbers:
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has documented a concerning trend of increasing dengue cases globally, with a ten-fold rise from 500,000 to 5.2 million cases between 2000 and 2019.
- While reporting declined during the COVID-19 pandemic years of 2020-2022, 2023 witnessed a resurgence, characterized by a significant increase in the number, scale, and geographic spread of outbreaks.
- As of April 23, 2024, reported dengue cases have exceeded 6.5 million worldwide, with over 7,300 deaths. In 2023, the Americas reported 4.5 million cases and 2,300 deaths.
Latin American Surge:
- Brazil, the largest country in Latin America, bears the brunt of the dengue outbreak, with over 4.2 million reported cases and more than 2,000 deaths between January and April 2024.
- Several states in Brazil have declared a state of emergency, and makeshift field hospitals have been set up to accommodate the influx of patients. The scarcity of mosquito repellents exacerbates the crisis, with uncertain timelines for replenishment.
- Peru and Puerto Rico have also declared states of emergency, with significant increases in cases and deaths compared to previous years.
- Additionally, Argentina, Central American countries, and Mexico are experiencing unseasonal spikes in dengue cases, while Uruguay and Chile face dengue outbreaks for the first time in a century.
Factors Contributing to the Outbreak:
The escalation of dengue in Latin America is influenced by multiple factors.
- Over the past three decades, the region has experienced an average warming of 0.2 degrees Celsius per decade, leading to expanded mosquito habitats and prolonged transmission seasons.
- The 2023 El Niño phenomenon intensified these effects, exacerbating temperature rises across the region.
- Rising temperatures also correlate with an increase in extreme weather events such as untimely rainfall, storms, flooding, and rising sea levels, which create stagnant water pools ideal for mosquito breeding.
- Rapid urbanization, coupled with ineffective garbage collection in shantytowns, further exacerbates the problem by providing additional breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
Conclusion:
- Dengue’s rapid spread in Latin America presents a multifaceted challenge exacerbated by climatic factors, urbanization, and inadequate public health infrastructure.
- Urgent measures are needed to mitigate the current outbreak and prevent future epidemics.
- This requires coordinated efforts at local, national, and international levels to improve vector control strategies, strengthen healthcare systems, and address the socio-economic factors contributing to the spread of the disease.
| Dengue Vaccine Development |
Challenges in Vaccine Development:
Existing Vaccines:Qdenga (Takeda Pharmaceuticals):
Dengvaxia (Sanofi Pasteur):
Recent Developments:New Dengue Vaccine by National Institutes of Health (NIH):
Serum Institute of India (SII):
|
| PYQ: ‘Wolbachia method’ is sometimes talked about with reference to which one of the following? (2023)
(a) Controlling the viral diseases spread by mosquitoes (b) Converting crop residues into packing material (c) Producing biodegradable plastics (d) Producing biochar from thermo-chemical conversion of biomass Ans: (a) |
| Practice Question: What are the contributing factors to the rapid spread of dengue throughout Latin America in 2024, and how do they correlate with the increase in reported cases compared to previous years? (250 words/15 m) |
7. Scientists Achieve Breakthrough: Create Ultra-Thin Goldene Sheets, Paving the Way for Revolutionary Applications
| (Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 13)
Topic: GS3 – Science & Technology – Developing new technology |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of the News:
What is Goldene?
- It is the world’s thinnest gold leaf: a gossamer sheet of gold just one atom thick.
- Researchers have synthesized the long-sought material, known as goldene, which is expected to capture light in ways that could be useful in applications such as sensing and catalysis.
- Goldene is a gilded cousin of graphene, the iconic atom-thin material made of carbon that was discovered in 2004.
- Since then, scientists have identified hundreds more of these 2D materials. But it has been particularly difficult to produce 2D sheets of metals, because their atoms have always tended to cluster together to make nanoparticles instead.
Challenges in Creating Goldene:
- Developing goldene presented a considerable challenge for the scientists from Sweden’s Linköping University.
- While 2D materials have been previously synthesized since the advent of graphene in 2004, metallic sheets have proven elusive due to metals’ tendency to cluster together into nanoparticles.
- Despite previous efforts resulting in gold sheets sandwiched between other materials, goldene stands out as the first free-standing 2D metal, offering unique properties and potential applications.
Synthesis of Goldene:
- To create goldene, researchers employed a sophisticated process involving the deposition of gold atoms onto an atomic monolayer of silicon sandwiched between layers of titanium carbide.
- Through a carefully controlled deposition process, gold atoms diffused into the material, replacing the silicon atoms and forming a trapped monolayer of gold atoms.
- Subsequent etching away of the titanium carbide layers using Murakami’s reagent, a chemical inspired by ancient Japanese metallurgical techniques, yielded a free-standing, one atom thick layer of gold.
Properties and Potential Applications:
- Goldene possesses unique properties that make it highly promising for various applications, particularly in the electronics industry.
- Its super-thin and lightweight nature offers economic advantages over thicker, three-dimensional gold, making it an attractive option for catalysis and electronic components.
- Additionally, the synthesis technique used for goldene can potentially be extended to other metallic objects, expanding the scope of 2D material research.
Future Prospects and Applications:
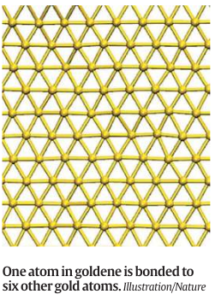
- The potential applications of goldene are diverse and far-reaching. Its unique structure, with each gold atom having only six neighboring atoms, opens up possibilities for applications such as carbon dioxide conversion, hydrogen-generating catalysis, selective production of value-added chemicals, hydrogen production, and water purification.
- The development of goldene represents a significant advancement in material science, with implications for various industries and technologies.
| Practice Question: What are the innovative methods and potential applications of goldene, the newly synthesized one-atom-thick sheet of gold, and how does its creation mark a significant breakthrough in material science and technology? (250 words/15 m) |




