7 Feb 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
Daily Current Affairs
7-February-2024- Top News of the Day
1. Southern California Braces for Impact as ‘Pineapple Express’ Atmospheric River Brings Heavy Rainfall and Increased Landslide Risks
| Topic: GS1 – Geography – Climate Change This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of understanding atmospheric rivers and their characteristics. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Understanding Atmospheric Rivers and the Pineapple Express:
- Atmospheric rivers are described as narrow sections of the Earth’s atmosphere that transport moisture from tropical regions near the equator to polar areas.
- Often compared to the flow of the Amazon River, these atmospheric rivers release moisture upon reaching land, resulting in heavy rain or snowfall.
- The current rainfall in California is associated with the Pineapple Express, an atmospheric river originating from subtropical waters around Hawaii.
Positive Effects of Rainfall on California:
- After enduring years of drought, California welcomes the recent rainfall, especially in Southern regions.
- This precipitation is beneficial for replenishing water resources and supporting aquatic life, such as Chinook salmon, which suffered during dry periods.
- However, the uneven distribution of rainfall poses challenges, particularly for areas lacking storage capacity and resources to capture stormwater effectively.
Challenges and Risks Associated with Increased Rainfall:
- While the additional moisture aids in wildfire resistance, it also fosters the growth of vegetation that can serve as fuel for future fires when the weather becomes dry again.
- This phenomenon, known as flashy fuels, poses a significant risk for rapid fire growth during dry seasons.
- The lush greenery resulting from rainfall in the summer months can transform into highly flammable vegetation, exacerbating wildfire risks in the region.
Conclusion:
- The current rainfall in Southern California, driven by atmospheric rivers like the Pineapple Express, brings much-needed relief from drought conditions but also poses challenges such as landslides and increased wildfire risks.
- Understanding the dynamics of atmospheric rivers is essential for effectively managing the impacts of such weather events and ensuring the resilience of communities in the face of changing climate patterns.
| What is the “Pineapple Express” Phenomenon? |
| One particular illustration of the widespread atmospheric phenomena known as atmospheric rivers is “Pineapple Express.” The majority of the water vapour that travels outside of the tropics is carried by these long, narrow zones in the atmosphere, which are also referred to as “rivers in the sky” by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. They are very moist, carrying as much water vapour as the Mississippi River on average, and occasionally even more, at its point of entry into the Gulf of Mexico.
|
| PYQ: ‘Climate Change’ is a global problem. How India will be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India will be affected by climate change? (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2017) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of atmospheric rivers and their impact on regional weather patterns and environmental dynamics, with a focus on the recent inundation in Southern California. (150 words/10 m) |
2. Indian Doctor Defies Cancer Odds with Revolutionary CAR-T Cell Therapy: A Beacon of Hope for Cancer Patients
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology – Biotechnology
This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of understanding the significance of CAR-T cell therapy in cancer treatment. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
What is CAR T-cell Therapy?
- CAR T-cell therapies are a major breakthroughin cancer treatment.
In contrast to drug-based treatments like chemotherapy or immunotherapy, CAR T-cell therapies make use of the patient’s own cells.
- To target tumour cells and activate T-cells, they undergo laboratory modification.
- Leukaemias (cancers originating from white blood cells) and lymphomas (arising from the lymphatic system) are now recognised indications for CAR T-cell treatment.
Procedure:
- The patient’s T cells are isolated, and in the lab, the gene for a unique receptor that attaches to a specific protein on the patient’s cancer cells is added to the T cells.
- A chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) is the name given to this unique receptor. A substantial quantity of CAR T cells are cultured in a lab and administered intravenously to the patient.
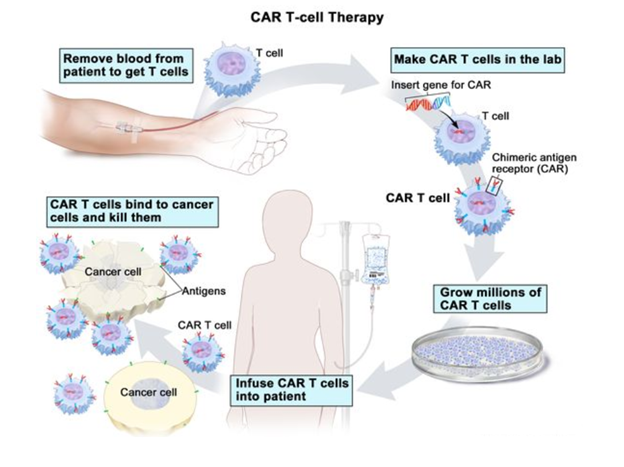
Significance:
- Greater clinical success is achieved by CAR T-cell therapies because they are even more selective than targeted medications and because they directly activate the patient’s immune system to combat cancer.
- This is the reason behind the term “living drugs.”
Challenges:
- Preparation:A significant barrier to the widespread application of CAR T-cell treatments has been the complexity of their preparation.
A decade ago, saw the publication of the first successful clinical trial, and in 2021 India carried out the first homegrown therapeutic development.
- Side Effects:The efficacy in some types of lymphomas and leukaemias can reach 90%, but it is much lower in other cancer types.
Significant adverse effects are also possible; these include neurological symptoms (severe disorientation, seizures, and speech impairment) and cytokine release syndrome, which is characterised by a widespread immune system activation and collateral damage to the body’s normal cells.
- Affordability:The introduction of CAR T-cell therapy in India may encounter financial and practical difficulties.
Critics believe that since CAR T-cell therapy will remain out of reach for the majority of people, it may not be cost-effective to develop in India.
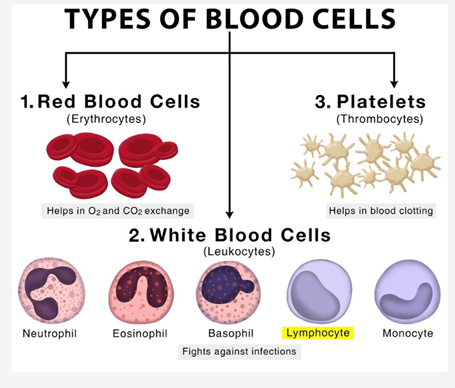
| What are T Cells? |
|
|
PYQ: Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body? (2022)
(a) They protect the environmental allergens. body (b) They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation. (c) They act as immunosuppressants in the body. (d) They protect the body from the diseases caused by pathogens. Ans: (d) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of CAR-T cell therapy in revolutionizing cancer treatment, particularly in the Indian context following its recent approval for commercial use. (150 words/10 m) |
3. Rajya Sabha Passes Water Pollution Control Bill Amendment: Decriminalization and Regulatory Streamlining at Forefront
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies – Interventions for development in various sectors This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of knowing facts about the bill. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Rationalization of Criminal Provisions:
- The amendment seeks to rationalize criminal provisions to ensure that citizens and businesses operate without fear of imprisonment for minor, technical, or procedural defaults.
- It aims to align the penal consequences of offenses with their seriousness, fostering a conducive environment for businesses and promoting ease of living and doing business.
Empowerment of Central Government:
- Under the proposed law, the central government will have the authority to exempt certain categories of industrial plants from restrictions on new outlets and discharges.
- This provision aims to streamline surveillance efforts and alleviate unnecessary burdens on regulatory agencies, facilitating a more efficient regulatory framework.
Enhanced Oversight and Guidelines:
- The bill empowers the central government to prescribe guidelines for the nomination of chairpersons of State Pollution Control Boards and issue directives regarding the grant, refusal, or cancellation of consent for industrial operations.
- These measures aim to ensure fair appointment procedures and alignment with similar provisions in the Air Act, enhancing regulatory consistency and effectiveness.
Conclusion:
- The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Amendment Bill represents an effort to balance environmental protection with the ease of doing business by rationalizing criminal provisions and empowering the central government to oversee regulatory matters.
- While proponents highlight its potential to enhance transparency and reduce regulatory burdens, critics raise concerns about centralization of power and dilution of environmental safeguards, underscoring the complex interplay between economic development and environmental conservation.
| More Details about Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Amendment Bill, 2024 |
|
| PYQ: Enumerate the National Water Policy of India. Taking river Ganges as an example, discuss the strategies which may be adopted for river water pollution control and management. What are the legal provisions for management and handling of hazardous wastes in India? (200 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2013) |
| Practice Question: Examine the significance and implications of the recent amendments to the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974, as passed by the Rajya Sabha. (150 words/10 m) |
4. Rajya Sabha Passes Bills Modifying SC/ST Lists in Odisha and Andhra Pradesh, Focus on Inclusion of Primitive Vulnerable Tribal Groups
|
Topic: GS2 – Social Justice- Vulnerable sections: Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of understanding the significance of these bills in expanding the scope of representation for marginalized communities, particularly Primitive Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs). |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Modification of SC/ST Lists in Andhra Pradesh and Odisha:
- The first bill pertains to the modification of the SC/ST list in Andhra Pradesh, while the second bill focuses on altering the SC/ST list in Odisha.
- Minister Munda highlighted the long-term planning behind these bills, noting the addition of three ethnic groups—Bondo Porja, Khond Porja, Parangiperja—in Andhra Pradesh and four groups in Odisha to the list of Scheduled Tribes.
- These groups are identified as Primitive Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) and have been included in the scheduled list after 75 years of Independence.
Addressing the Needs of Primitive Vulnerable Tribal Groups:
- Minister Munda emphasized the government’s efforts to reach out to the 75 PVTGs spread across various regions, working in mission mode to provide assistance to those residing in far-flung areas.
- He underscored the historical deprivation faced by these groups, leading to the denial of conditional rights and injustices.
- The government has initiated schemes like the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan to uplift the socio-economic conditions of PVTGs and address their needs.
Government Initiatives and Considerations:
- Minister Munda mentioned that the government is considering suggestions from members to add more communities from their respective states to the SC/ST lists.
- He highlighted ongoing efforts to engage with state governments, particularly where the population of PVTGs is declining, and reiterated the government’s commitment to improving the well-being of marginalized tribal communities through targeted schemes and initiatives.
Conclusion:
- The passage of these bills reflects the government’s commitment to empowering tribal communities and addressing historical injustices.
- By modifying the SC/ST lists to include additional ethnic groups, particularly PVTGs, the government aims to ensure their socio-economic upliftment and integration into mainstream society.
- These legislative measures underscore the importance of inclusive governance and targeted interventions to address the specific needs of vulnerable tribal populations across India.
|
How Schedule Tribe is recognized? Lokur Committee, 1965 |
|
The Lokur committee gave the following criteria for the recognition of any community as Scheduled Tribes:
However, the above criteria are not mentioned in the Constitution. |
|
PYQ: Consider the following statements about Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in India: (2019)
Which of the statements given above are correct? (a) 1, 2 and 3 (b) 2, 3 and 4 (c) 1, 2 and 4 (d) 1, 3 and 4 Ans: (c) |
| Practice Question: Evaluate the implications of including Primitive Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in the scheduled lists and analyze the government’s initiatives aimed at addressing historical injustices and socio-economic disparities among tribal communities. (250 words/15 m) |
5. Uttarakhand tables UCC Bill in Assembly
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity – Indian constitution – Significant provisions Crucial for UPSC as it explores the significance of a state implementing a Uniform Civil Code, impacting social and legal aspects. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- Uttarakhand Chief Minister tables Uniform Civil Code (UCC) Bill in the Assembly, calling it a “historic moment.”
- If passed, Uttarakhand will be the first Indian state with uniform laws on marriage, divorce, succession, and live-in relationships.
- Scheduled Tribes, constituting 2.9% of the state’s population, excluded from the UCC.
- BJP legislators support the Bill with chants, while the Opposition criticizes it as a “poll gimmick” with unclear urgency.
- UCC addresses equal rights in divorce, ending practices like ‘Halala’ and ‘Iddat,’ with penalties for offenses.
- Registration of marriages and divorces becomes mandatory, impacting government facilities; custody of children under five goes to the mother.
- Failure to register live-in status results in imprisonment; false information during registration leads to penalties.
- Children from live-in relationships considered legitimate, with equal property inheritance rights for sons and daughters.
- After a person’s death, wife, children, and parents granted equal rights to the deceased’s property, a departure from previous norms.
| Uniform Civil Code |
Introduction:
Key Principles:
Gender Equality:
Social Harmony:
Legal Simplification:
Challenges:
Conclusion:
|
| PYQ: Discuss the possible factors that inhibit India from enacting for its citizens a uniform civil code as provided for in the directive Principles of State Policy. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2015) |
6. Rajya Sabha passes Bills to add PVTGs of Odisha, A.P. in ST lists.
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Vulnerable Sections The amendment bills on Scheduled Tribes in Rajya Sabha hold UPSC importance for governance, social justice, and tribal welfare. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
Bills Passed:
- Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order Amendment Bill, 2024
- Constitution (Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes) Order Amendment Bill, 2024
Objective:
- Addition of new communities to the Scheduled Tribes (ST) list in Odisha.
- Inclusion of synonyms and phonetic variations of existing tribes in the ST lists of Andhra Pradesh and Odisha.
Support and Bipartisanship:
- Both Bills received support from Members of Parliament across party lines.
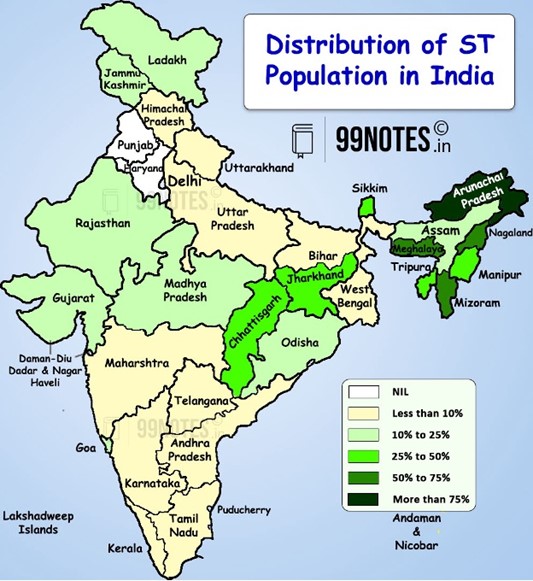
Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs):
- Seven PVTGs, a subset of STs, were notably added—four in Odisha and three in Andhra Pradesh.
- These additions included independent names as synonyms or sub-tribes of existing communities on the ST lists of the respective states.
Union Tribal Affairs Minister’s Comments:
- Arjun Munda, Union Tribal Affairs Minister, criticized previous non-NDA governments for not explicitly including the most vulnerable STs, the PVTGs, in the ST lists.
- Claimed that the current government, led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, is addressing this by bringing legislation for their inclusion.
Specific Additions in Odisha:
- Pauri Bhuyan and Paudi Bhuyan added as synonyms of the Bhuyan tribe.
- Chuktia Bhunjia included as a synonym of the Bhunjia tribe.
- Bondo recognized as a sub-tribe of the Bondo Poraja tribe.
Specific Additions in Andhra Pradesh:
- Bondo Porja and Khond Porja included as synonyms of the Porja tribe.
| Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups |
|
| PYQ: Why are the tribals in India referred to as the Scheduled Tribes? Indicate the major provisions enshrined in the Constitution of India for their upliftment. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2016) |
| Practice Question: Explain the significance of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in the context of India. (150 words/10 m) |
7. Temples and mosques as a marker to study the life and times of Aurangzeb
| Topic: GS1 – Indian History The Gyanvapi Masjid controversy sheds light on historical events, governance, and communal tensions, relevant for UPSC exam preparation. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- The Gyanvapi Masjid in Varanasi has become a point of contention, with Muslims gathering in large numbers for prayers amid increasing pressure from Hindutva forces.
- The mosque was built by Mughal emperor Aurangzeb in the 17th century after demolishing a temple on the land occupied by defiant zamindars (landlords).
- Initially, Aurangzeb showed respect towards Brahmins and requested their prayers for the well-being of the Mughal empire after ascending the throne.
- However, political motives led Aurangzeb to authorize the destruction of certain Hindu and Jain temples, with historian Audrey Truschke citing around 12 such instances.
- In 1659, Aurangzeb issued a farman asking officials not to disturb the Brahmins of Benares, emphasizing their importance for the well-being of the empire.
- The destruction of the Vishvanath Temple in Benares was seen as a warning to anti-Mughal factions, including troublesome zamindars and influential Hindu religious leaders.
- The Vishvanath Temple was built during Akbar’s reign, later demolished during Aurangzeb’s rule in 1669, and a new temple was constructed in the 18th century by Maratha ruler Ahilyabai Holkar.
- Historian Satish Chandra suggests that Aurangzeb viewed temples as centers spreading subversive ideas, leading to strict actions against them.
- Architectural historian Madhuri Desai argues that the Vishvanath Temple was built in the 18th century, while others believe it existed before Muslim invaders, possibly in the 12th century.
- The Gyanvapi Masjid, also known as Masjid Alamgiri or Jama Masjid, is embroiled in legal and social controversies today, representing a medieval monument reflecting the era of Aurangzeb.
8. ‘Tax-to-GDP ratio to hit all-time high of 11.7% of GDP in FY25’
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Issues relating to growth Crucial for UPSC: India’s rising tax-to-GDP ratio, government’s tax reforms, and fiscal policies contribute to economic development and governance. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- India’s tax-to-GDP ratio is projected to reach a record high of 11.7% in 2024-25, driven by increased direct tax collection.
- Revenue Secretary Sanjay Malhotra emphasizes the government’s focus on simplifying and rationalizing the tax regime to minimize disputes and enforcement intrusiveness.
- Corporate and personal income tax rates have been reduced to encourage adoption of the new tax regime, which offers a higher tax-free income threshold.
- Personal Income Tax collections have seen a 28% growth so far this year, with expectations of moderating to 20%-22% by March.
- A Group of Ministers has been reconstituted to review GST rates, aiming for periodic adjustments to rationalize rates on different items.
- The tax-to-GDP ratio is expected to increase due to a rise in direct taxes, reaching 6.7% in 2024-25, contributing to a more equitable distribution.
- Government anticipates a 1.1 buoyancy in revenue growth for 2024-25, with tax revenues projected to grow at 11.5% as nominal GDP is expected to rise by 10.5%.
| Tax-to-GDP ratio |
|
| Practice Question: How does the Tax-to-GDP ratio impact a nation’s fiscal health? Discuss key factors influencing this ratio and its implications for economic sustainability. (150 words/10 m) |
9. Understanding the delimitation exercise
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity – Elections Critical for UPSC: Delimitation process, constitutional provisions, and balancing democracy and federalism are key governance aspects for examination. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
Delimitation Process: Constitutional Provisions
- Delimitation involves fixing seats and boundaries of constituencies for Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies.
- Article 82 and 170 of the Constitution mandate readjustment after each Census.
- Delimitation Commission, appointed by Parliament, conducts the process.
Frozen Seats and Constitutional Requirements
- Seats frozen as per 1971 Census to encourage population control measures.
- The 42nd Amendment Act (till 2000) and 84th Amendment Act (till 2026) maintained seat allocation based on 1971 Census.
- Boundaries adjusted, but the number of seats and reserved seats for SC/ST based on 2001 Census.
Issues and Implications
- Population growth disparities among states raise concerns about the delimitation exercise.
- Two proposed scenarios: Continue with 543 seats or increase to 848 with proportionate distribution.
- Potential disadvantages for southern and smaller states may contradict federal principles and population control philosophy.
International Practices and Ideal Solution
- In the U.S., seats capped at 435 since 1913, redistributed after each Census using the “method of equal proportion.”
- EU Parliament uses “degressive proportionality” based on population size.
- Proposed solution: Cap Lok Sabha seats at 543, maintaining federal principles, while increasing MLAs to address democratic representation at the state level.
- Emphasizes empowering local bodies for grassroots democracy.
| Delimitation Commission |
|
| Practice Question: How does the Delimitation Commission enhance democratic representation in India? Explain its role in adjusting electoral boundaries and ensuring fair and equitable representation in parliamentary and assembly constituencies. (150 words/10 m) |
For Enquiry

Kurukshetra Magazine Summary: September 2023

7 Feb 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

7 Feb 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

7 February 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC

7 Feb 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

7 Feb 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis

7 February 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

6 Feb 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

6 Feb 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

6 Feb 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz
Kurukshetra Summary Kurukshetra Magazine Summary: September 2023 1. MAKE IN INDIA: CATALYSING GROWTH OF STUDENTS AND YOUTH
Introduction:
India’s economic landscape,…
Daily Quiz 7 Feb 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 7 Feb 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 7 Feb 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
7-February-2024
Q1) What are the locational factors for textile industry? Why have…
feb 2024 PIB 7 February 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
7-February -2024
1. MICRO IRRIGATION
Topic: GS3 – Agriculture – Irrigation…
Daily Current Affairs 7 Feb 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
7-February-2024- Top News of the Day
Stay updated with the Latest 7th February…
Indian Express 7 Feb 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
7-February-2023
1. Policy must address growth gap
Topic: GS3 – Indian…
Feb 2024 The Hindu 7 February 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu Editorial
7-February-2024
1. Union government’s reins on financial transfers to States.
Topic:…
mains answer writing 6 Feb 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
6-February-2024
Q1) Heat waves are a silent natural disaster. Describe the criteria…
Daily Current Affairs 6 Feb 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
6-February-2024- Top News of the Day
Stay updated with the Latest 6th February…
Daily Quiz 6 Feb 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 6 Feb 2024 : Daily Quiz…