14 October 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Why precision medicine in India can’t advance without biobank laws
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
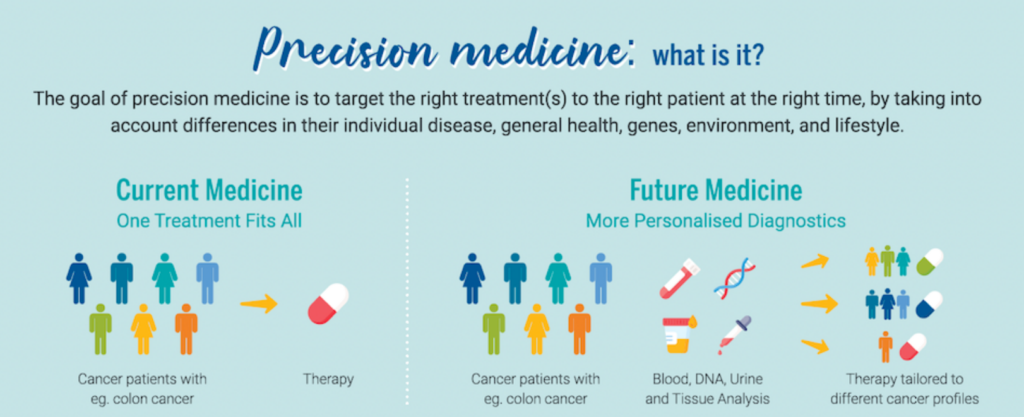
Introduction to Precision Medicine
- Precision medicine is transforming healthcare by offering personalised treatments, especially in fields such as cancer, chronic diseases, and genetic disorders.
- The Human Genome Project laid the groundwork for advancements in genomics, which have enhanced diagnostics and therapies for multiple health conditions.
- Emerging technologies like gene editing, mRNA therapeutics, and organ-on-chips are contributing to the progress of precision medicine.
Technological Advancements in Precision Medicine
- Gene editing and mRNA therapeutics are two key emerging technologies.
- Success stories include restoring vision through gene therapy and reversing diabetes with reengineered stem cells.
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, the mRNA platform played a critical role in the development of vaccines, which led to a Nobel Prize.
- Organ-on-chips offer promising solutions by replicating human organs in laboratories, aiding in more accurate drug testing.
| Precision Medicine in India |
|
Role of Biobanks in Precision Medicine
- Biobanks store biological samples (e.g., blood, DNA, tissues) and are crucial for the success of precision medicine.
- Large and diverse biobanks ensure that research benefits a broad section of society.
- Recent research using biobank data has led to the discovery of rare genetic disorders and the identification of potential sarcoma therapies through organoid-based studies.
Biobanks in India
- India currently has 19 registered biobanks storing various biological specimens, including cancer cell lines.
- Key initiatives like the ‘Genome India’ project, which sequenced 10,000 genomes from 99 ethnic groups, and the ‘Phenome India’ project, focused on cardio-metabolic diseases, are aiding precision medicine research.
- The Paediatric Rare Genetic Disorders (PRaGeD) mission aims to develop therapies for genetic disorders affecting children.
- Despite progress, India’s biobanking regulations are fragmented and hinder the full potential of precision medicine.
Challenges in Biobanking Regulations
- Unlike other countries such as the U.S. and the U.K., India lacks comprehensive regulations on biobanking, leaving gaps in informed consent, data protection, and privacy.
- Current guidelines from the Indian Council for Medical Research and the Department of Biotechnology are inadequate and do not protect individual rights effectively.
- Issues like mishandling of samples, data misuse, and non-consensual sharing pose ethical challenges.
- Without robust laws, Indian citizens risk losing control over their biological samples and the resulting research profits.
The Need for Regulatory Reform
- Stronger regulations, overseen by an expert committee, would encourage public participation in biobanks and ensure ethical practices.
- Proper biobanking laws aligned with global standards would position India as a leader in next-generation therapeutics, enhance trust, and facilitate international collaborations.
- India’s involvement in international organisations like the Quad and BRICS, as well as its leadership in pharmaceuticals, underscores the importance of aligning its biobanking policies with international standards.
Conclusion
- To harness the full potential of precision medicine, India must strengthen its biobanking regulations, ensuring ethical practices, data protection, and public trust.
- These reforms will not only benefit domestic healthcare but also enhance India’s position in global medical research and pharmaceutical diplomacy.
| Practice Question: Discuss the potential of precision medicine in transforming healthcare in India. What are the challenges faced by India’s biobanking regulations, and how can they be improved to support research and innovation? (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Delhi High Court Issues Directives to Improve Access to Orphan Drugs for Rare Disease Patients
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 13)
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Classification of Rare Diseases in India
In India, rare diseases are categorized into three groups based on the treatment’s complexity:
- Group 1: Diseases treatable with one-time curative procedures.
- Group 2: Conditions requiring lifelong but relatively affordable treatment.
- Group 3: Diseases requiring lifelong, costly treatment with limited access to effective care.
Financial Assistance and Government Policy
- The National Policy for Rare Diseases (NPRD), launched in 2021, provides financial assistance of up to ₹50 lakh for treatment at designated Centers of Excellence (CoEs).
- These CoEs, such as AIIMS and PGIMER, play a pivotal role in providing care to patients. Additionally, a crowdfunding platform has been created to facilitate voluntary donations for treatment.
High Cost of Orphan Drugs
- Many orphan drugs are patented, making them prohibitively expensive. Pharmaceutical companies are reluctant to manufacture them due to high development costs and a limited market.
- Although patients importing these drugs are exempt from customs duties, companies still face significant taxes.
- The Delhi High Court has emphasized the need for tax exemptions and quicker processing of these medicines to lower costs.
Legal and Policy Interventions
- The government can take steps under the Patents Act to allow third parties to manufacture these medicines, ensuring their availability.
- The High Court has called for more research and negotiations with pharmaceutical companies to lower treatment costs and boost domestic production.
Challenges in Implementation
- The approval process for orphan drugs is often slow, delaying access to essential treatments. The National Rare Diseases Committee highlighted the need for faster regulatory decisions to prevent disruptions in patient care.
Conclusion
- While efforts are being made to address rare diseases in India, significant challenges remain in terms of affordability, availability, and regulatory delays.
- A comprehensive strategy involving government policy reforms, tax incentives, and increased research is essential to improve access to orphan drugs.
| What are the Challenges posed by Rare Diseases in India? |
|
1. Unavailability of treatment- Less than 50% of the 450-odd rare diseases identified in India are treatable. Most patients typically receive only basic treatment that alleviates symptoms. 2. Unaffordable Treatment Costs- Some rare disease’s treatment, requires exorbitantly priced antidotes and supportive medication, which poses the challenge of affordability. 3. Low Focus on R&D for drug development- The rare disease is not considered as a significant market by the drug manufacturers, as the number of persons suffering from individual rare diseases is small. Hence, these diseases are treated as ‘orphan diseases‘ and the drugs are treated as ‘orphan drugs‘ by the pharma giants. 4. Late diagnosis- Rare disease takes on an average of seven years for their diagnosis in India. Delay in diagnosis or a wrong diagnosis increases the suffering of the patients exponentially. 5. Lack of trained healthcare professionals- Lack of trained healthcare professionals to interpret the signs and symptoms of rare diseases in the initial stages, has compounded the challenge posed by rare diseases in India. |
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges faced in the treatment of rare diseases in India, particularly in relation to the high cost of orphan drugs and the role of government policy. What steps can be taken to improve access and affordability for patients? (150 words/10 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. Israeli tanks ram gate of UN facility in Lebanon
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL) – Key Information:

- Established: March 1978 by the UN Security Council.
- Original Mandate: Confirm Israeli withdrawal from Lebanon, restore international peace and security, and assist Lebanon in restoring authority.
- Post-2006 Role: Expanded after the Israel-Hezbollah conflict.
- Monitor the cessation of hostilities.
- Support Lebanese Armed Forces in southern Lebanon deployment.
- Ensure humanitarian access to civilians.
- Facilitate the safe return of displaced persons.
- Troop Strength: Over 10,000 personnel from 50 countries.
- Mandate: Governed by UN Security Council Resolution 1701 (2006).
Places in Focus:
- Ramyah (South Lebanon): Location of the UN peacekeeping force’s facility attacked by IDF tanks; near the volatile border with Israel.
- Blue Line: Demarcation between Israel and Lebanon, established by the UN to confirm Israeli withdrawal from Lebanon.
- Meiss ej Jebel: Another location in south Lebanon where IDF soldiers halted a UNIFIL logistical movement.
2. Ladakh aurorae validate space weather tracking, scientists say
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Ladakh recently witnessed auroral sightings, marked by reddish or greenish lights, typically seen in northern regions.

- The latest aurora occurred on October 10-11, following previous sightings in May 2023 and November and May 2022.
- The auroras were captured by all-sky cameras operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics at Hanle and Merak in Ladakh.
- These sightings validate advancements in space weather monitoring by astrophysicists, who predicted the event 48-72 hours earlier.
- The occurrence of auroras in Ladakh, a lower-latitude region, signals heightened solar activity and coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
- Solar storms are part of the sun’s 11-year activity cycle, with the current cycle predicted to peak in 2024.
3. What is Wayanad’s new X-band radar?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Context |
|
What Are X-Band Radars:
- The radar operates within the X-band of the electromagnetic spectrum (8-12 GHz, 2-4 cm wavelengths) and provides high-resolution images by using shorter wavelengths to detect smaller particles like rain droplets and soil.
- This technology will help monitor particle movements in the region, including soil shifts, to provide early landslide warnings.
- The radar offers high temporal sampling, meaning it can frequently sample its environment, enabling detection of rapid particle movements.
- X-band radars are limited in range due to faster attenuation of higher frequency signals but are highly effective for localised monitoring.
- It is part of a broader radar infrastructure initiative by the Ministry of Earth Sciences, including the addition of 56 Doppler radars across India.
4. U.S. to send missile defence system and troops to Israel
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 14)
| Context |
|
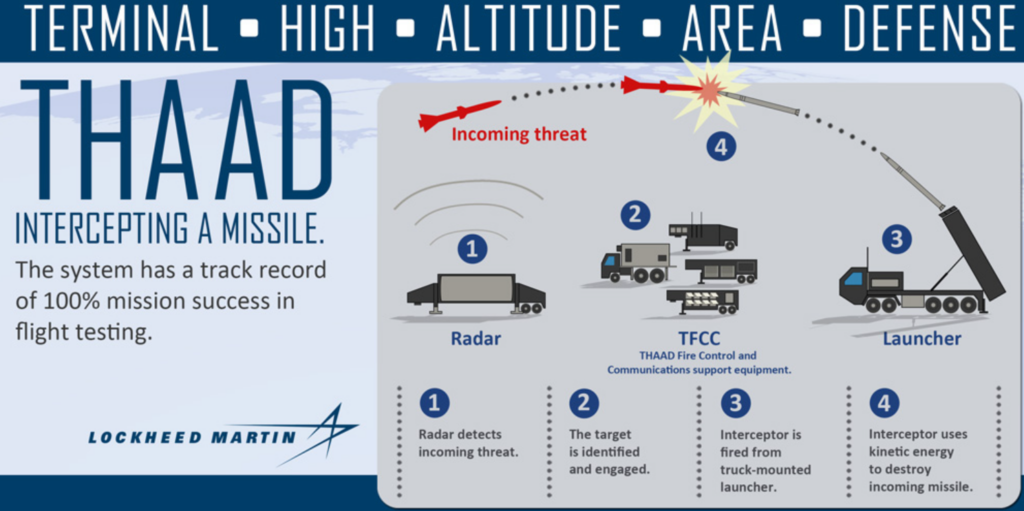
THAAD Missile Defence System:
- The Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) is an advanced missile defence system designed to intercept and destroy short-, medium-, and intermediate-range ballistic missiles during their terminal phase (final stage of descent).
- It uses a hit-to-kill technology, relying on the kinetic energy from impact to destroy incoming missiles, rather than using explosive warheads.
- The system operates at high altitudes, providing wide-area coverage and complementing other missile defence systems like the Patriot, which operates at lower altitudes.
- THAAD consists of four main components: interceptors (missiles), a launcher, a radar system to detect and track targets, and a fire control system for command and control.
- The system has a range of up to 200 kilometres and can target missiles at altitudes of up to 150 kilometres.
- Developed by Lockheed Martin, THAAD is a critical part of the U.S. military’s layered missile defence strategy.
- It has been deployed in several regions, including South Korea, the Middle East, and Guam, for defence against missile threats from adversaries.
5. Dragon Drones: A New Thermite Weapon Escalates Destruction in Russia-Ukraine War
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 13)
| Context: |
| The article discusses the emergence of “dragon drones” in the Russia-Ukraine war, which deploy thermite, a highly destructive incendiary substance, raising concerns over their devastating impact and legal implications in warfare. |
Analysis of News:

What are ‘Dragon Drones’?
- Dragon drones are unmanned aerial vehicles that deploy thermite, a mixture of aluminum and iron oxide, which burns at an extreme temperature of 2,427°C. Thermite was originally developed over a century ago to weld railroad tracks.
- When ignited, it triggers a self-sustaining reaction that can burn through most materials, including clothes, trees, military vehicles, and can even burn underwater.
- On humans, it causes severe, potentially fatal burns and damage to bones. The combination of thermite with high-precision drones makes these weapons particularly effective in warfare.
Use in the Russia-Ukraine War
- Dragon drones were first used in the Russia-Ukraine war around September. Reports suggest Ukrainian forces used these drones to ignite vegetation, exposing Russian troops and their equipment to attacks. Soon after, Russian forces also began deploying their own dragon drones. The high-temperature burning of thermite makes it highly destructive and difficult to defend against, as it bypasses traditional defenses.
Historical Use of Thermite in Warfare
Thermite has been used in both World Wars:
- In World War I, German zeppelins dropped thermite bombs.
- In World War II, both the Allies and Axis forces used thermite-laden incendiary explosives extensively. The Allies dropped millions of thermite bombs on Germany and Japan.
- Thermite hand grenades were used to disable artillery without causing explosions.
- In modern warfare, thermite is often utilized by espionage agents or special operations teams due to its intense burning properties without a loud explosion.
Legal Status of Thermite in Warfare
- The use of thermite in warfare is not prohibited under international law. However, under Protocol III of the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons, the use of incendiary weapons like thermite is restricted to military targets.
- The use of such weapons against civilians is prohibited due to the indiscriminate nature of thermite, which can cause severe burns and respiratory injuries.
6. India Launches Groundbreaking Genomic Study to Unravel South Asia’s Ancient Population History
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page: 01)
| Context: |
| For the first time, the Indian government has launched a comprehensive scientific study using ancient and modern genomics to explore the population history of South Asia, addressing conflicting theories about the origins of ancient Indian communities. |
Analysis of News:
Project Details and Collaborators
- The study, titled “Reconstruction of the Population History of South Asia using Ancient and Modern Genomics”, is led by the Anthropological Survey of India (AnSI), under the Ministry of Culture.
- Collaborating with the Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences (Department of Science & Technology), the project will examine 300 ancient skeletal remains collected from archaeological sites across India and Pakistan, including Indus Valley Civilisation sites like Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro, and other key locations.
Objectives of the Study
The project aims to analyze DNA extracted from these ancient remains to uncover insights into:
- The origins of ancient Indian communities
- Diet, living conditions, disease prevalence, and environmental adaptations
- Migration patterns and genetic interactions over time
Revisiting the Aryan Migration Theory
- The study also seeks to clarify historical debates, such as the 19th-century Aryan invasion theory, which proposed that a class of migrants from Central Asia played a key role in shaping Indian civilization.
- Modern scholars, however, argue that the Aryans were indigenous and migrated after the drying of the Saraswati River.
Timeline and Significance
- The research, expected to be completed by December 2025, is seen as a crucial step toward understanding India’s complex migration history and the origins of its ancient civilizations.
7. SpaceX Achieves Milestone as Starship Booster Successfully Caught Mid-Air in Bold Test Flight
(Source: Indian Express; Section: The World; Page: 12)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Successful Launch and Booster Recovery
- The 400-foot (121-meter) Starship launched at sunrise from Texas, successfully arcing over the Gulf of Mexico.
- Unlike its four previous attempts that ended in destruction, this test flight achieved controlled recovery.
- For the first time, the first-stage booster returned to the launch pad and was caught by the launch tower’s mechanical arms, known as “chopsticks.”
SpaceX’s Achievement and Future Goals
- The empty spacecraft launched atop the booster also made a controlled landing in the Indian Ocean, marking a significant milestone for the Starship, which is intended for future missions to the moon and Mars.
8. Tele MANAS: Revolutionizing Mental Health Care in India
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2064548®=3&lang=1 )
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health |
| Context |
|
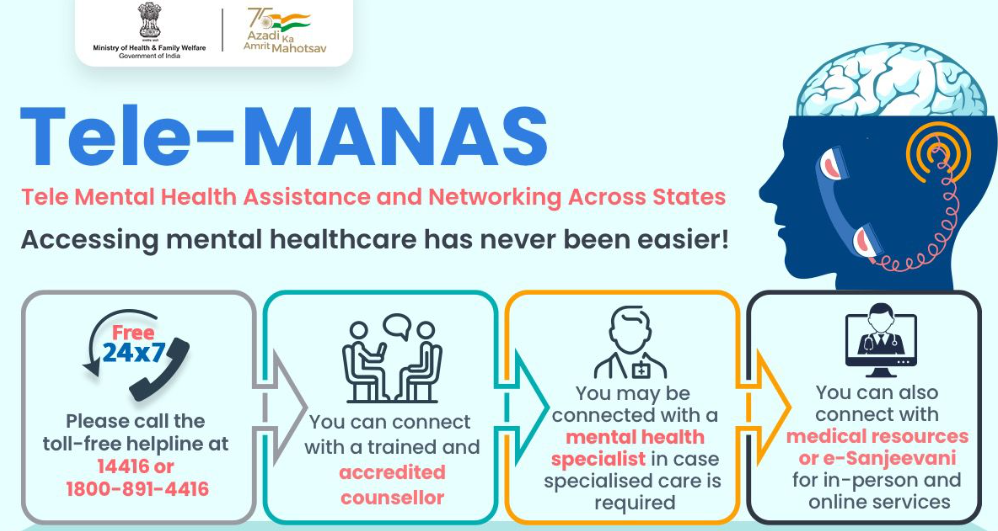
National Tele Mental Health Programme (NTMHP)
- Launched on October 10, 2022, by the Government of India, NTMHP significantly contributed to the nation’s mental healthcare system.
- Tele MANAS, a toll-free helpline (14416), offers accessible mental health services including counselling, psychotherapy, psychiatric consultations, and urgent care across the country.
Tele MANAS Impact
- Tele MANAS made mental healthcare more accessible, especially in remote areas.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) praised Tele MANAS as an effective model for mental healthcare.
- WHO’s review acknowledged Tele MANAS’s potential to improve mental health outcomes in India, emphasising its integration with primary healthcare centres.
Need for Tele MANAS
- Mental health disorders are a significant issue in India, with a 70-92% treatment gap, affecting millions.
- Despite the Mental Healthcare Act of 2017, over 80% of people with mental health disorders do not seek help.
- Tele MANAS was introduced to bridge this gap by providing essential mental healthcare services via phone, addressing both specialised and general mental health issues.
Aim and Objectives
- The aim is to provide universal access to affordable and quality mental healthcare through a 24×7 service.
- Key objectives include:
- Expanding access to mental health services nationwide.
- Building an integrated mental health network that offers a range of interventions.
- Prioritising vulnerable populations to ensure no one is left without care.
Key Achievements
- Tele MANAS has successfully handled over 14.7 lakh calls.
- Established 52 Tele MANAS Cells, collaborated with 23 Mentoring Institutes, and created 5 Regional Coordinating Centers.
Conclusion
- The NTMHP, through Tele MANAS, has revolutionised mental healthcare access in India, breaking barriers of distance and cost.
- The program continues to evolve, with a commitment to making mental health care a fundamental right for all.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the National Tele Mental Health Programme (NTMHP) in addressing India’s mental health crisis. How can digital health platforms like Tele MANAS improve access to mental healthcare in remote and underserved regions? (150 Words /10 marks) |



