2 July 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. What is on the agenda for the 16th Finance Commission?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity – Constitutional Bodies |
| Context |
|
Introduction
- The 16th Finance Commission (FC) of India, established under Article 280 of the Indian Constitution, has commenced its work focusing on the devolution of the consolidated fund.
- The 73rd and 74th constitutional amendments gave significant recognition to local bodies, introducing sub-clauses 280 (3) (bb) and (c) which require the FC to recommend measures to support panchayats and municipalities by augmenting State consolidated funds.
Cities as Engines of Growth
- Cities contribute around 66% of India’s GDP and about 90% of total government revenues, making them crucial for the country’s development.
- Despite this, the economic scale is insufficient to meet the rising needs of urban areas, with the World Bank estimating a requirement of $840 billion for basic urban infrastructure over the next decade.
Inadequate Financial Devolution
- Despite efforts by five Finance Commissions since the 11th FC, financial devolution to cities remains inadequate.
- Poor fiscal health of municipalities affects both city productivity and quality of life, exacerbated by rapid urbanisation without corresponding fiscal action.
- Intergovernmental transfers (IGTs) to Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) in India are about 0.5% of GDP, much lower than the 2-5% typical of other developing nations such as South Africa, Mexico, the Philippines, and Brazil.
- Although IGTs constitute about 40% of ULBs’ total revenue, issues with predictability, earmarking for vulnerable groups, and horizontal equity persist.
- Stable IGTs are crucial for ULBs, given their financial state and the need for reliable support until their own revenues improve.
Impact of the Goods and Service Tax (GST)
- The introduction of GST has significantly reduced ULBs’ tax revenue (excluding property tax) from about 23% in 2012-13 to around 9% in 2017-18.
- IGTs from States to ULBs are very low, with State Finance Commissions recommending only about 7% of States’ own revenue in 2018-19.
- Increasing the quantum of IGTs as a percentage of GDP is necessary to support ULBs effectively.
- Despite the 74th constitutional amendment’s goal to financially strengthen ULBs, progress over three decades has been inadequate.
Challenges from Parallel Agencies and Programs
- The 13th Finance Commission noted that parallel agencies and bodies are undermining local governments both financially and operationally.
- Local governments require support from Union and State governments through funds, functionaries, and technical aid.
- The proliferation of parallel agencies has distorted the roles of local governments, with programs like the Member of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme and the Member of Legislative Assembly Local Area Development Scheme exacerbating this issue and distorting the federal structure.
Importance of Accurate Census Data
- The absence of the 2021 Census has resulted in reliance on outdated 2011 data, which is inadequate for evidence-based fiscal devolution.
- India has approximately 4,000 statutory towns and an equal number of Census towns, along with an estimated 23,000 villages effectively functioning as urban areas.
- These figures need to be accurately captured by the 16th FC, including significant migration to Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities.
Revisiting the 15th Finance Commission’s Guiding Principles
- The 15th FC’s nine guiding principles need a revisit, with a focus on specific areas such as:
- Enhancement in property tax collection in coordination with the State’s GST.
- Maintenance of accurate accounts by ULBs.
- Allocation of resources for mitigating pollution.
- Emphasis on primary health care, solid waste management, and drinking water.
- The 16th FC must consider the dynamism of India’s urbanisation and ensure IGTs to urban areas are at least doubled to meet rising needs.
Future Outlook and Recommendations
- A McKinsey Global Institute report warns that if India continues to invest in urban infrastructure at current rates, there will be significant shortfalls leading to issues like inadequate water supply and untreated sewage.
- The 16th FC needs to address these challenges by ensuring adequate financial support and empowering ULBs to manage urbanisation effectively.
- Enhancing fiscal devolution and providing robust support to urban areas will be crucial for sustaining growth and improving the quality of life in cities.
Conclusion
Addressing Urban Challenges
- The 16th FC has a critical role in addressing the financial and operational challenges faced by ULBs.
- Reforms should focus on improving fiscal health, ensuring adequate IGTs, and supporting local governments through effective policies and resources.
- Empowering cities with the necessary financial and technical support will be essential for India’s overall development and urban sustainability.
(For more information On finance Commission – https://99notes.in/upsc-notes/general-studies-2/polity/constitutional-bodies/finance-commission/ )
|
PYQ: Q.1 How have the recommendations of the 14th Finance Commission of India enabled the States to improve their fiscal position? (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2021) Q.2 Discuss the recommendations of the 13th Finance Commission which have been a departure from the previous commissions for strengthening the local government finances. (200 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2013) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of intergovernmental transfers to Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) in India and the challenges posed by the current fiscal arrangements. How can the 16th Finance Commission address these challenges to enhance urban infrastructure and governance? (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. Why are scientists looking for the Higgs boson’s best friend?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
Discovery and Significance of the Top Quark
- Measurement Achievement: Scientists have reported the most precise measurement of the top quark’s mass at 172.52 GeV/c², discovered by the Large Hadron Collider.
- Importance: The top quark is the most massive subatomic particle, significantly influencing our understanding of particle physics and the universe.
Top Quark Characteristics
- Mass and Energy: The top quark is 10-times heavier than a water molecule and about three-times as much as a copper atom.
- Instability: Due to its mass, it decays rapidly in less than 10⁻²⁵ seconds into lighter particles.
- Interaction with Higgs Field: The top quark’s mass is crucial for understanding the Higgs boson, as they interact strongly.
Implications for the Universe
- Higgs Boson and Field: The Higgs boson, which interacts with the top quark, has a mass that affects the universe’s energy levels.
- Potential Energy and Stability: The Higgs field’s potential energy could lead to quantum tunnelling, potentially altering the universe drastically, although this event is highly improbable in the near future.
Historical Context and Measurement Techniques
- Discovery: The top quark was discovered in 1995 at the Tevatron accelerator in the US.
- Measurement Evolution: Initial mass measurements ranged from 151-197 GeV/c², refined over time to 174.98 GeV/c², and the latest precision value of 172.52 GeV/c².
- Detection Process: Particle accelerators produce a particle soup where top quark decays are tracked and analysed to determine its mass.
Future Research and Applications
- Researchers aim to further refine the top quark’s mass measurement for deeper insights.
- Precise measurements could reveal other particles with masses close to the top quark, hidden in existing data.
| PYQ: Discuss the work of ‘Bose-Einstein Statistics’ done by Prof. Satyendra Nath Bose and show how it revolutionised the field of Physics. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2018) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the recent precise measurement of the top quark’s mass by the Large Hadron Collider and its implications for our understanding of the Higgs boson and the fundamental structure of the universe. (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. Unchecked Urban Expansion Leads to Chronic Flooding in Delhi: A Call for Comprehensive Water Management
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
| Topic: GS3 – Infrastructure |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Rapid Urban Growth:
- Delhi is experiencing one of the world’s fastest urban expansions. NASA data indicates that Delhi’s geographic size nearly doubled from 1991 to 2011, primarily on the peripheries of New Delhi, where rural areas have been absorbed into urban sprawl.
- Cities within the NCR—Bahadurgarh, Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Noida, and Gurugram—have also seen rapid urbanization.
- According to the UN’s “The World’s Cities in 2018” data booklet, Delhi is projected to overtake Tokyo as the world’s most populous city by 2030, with an estimated population of nearly 39 million, up from around 16 million in 2000.
Ignoring Natural Topography:
- This urban expansion has largely ignored Delhi’s natural topography, which is crucial for drainage.
- Historically, cities and villages in Delhi were strategically built on higher ground to allow for natural drainage.
- However, as the city expanded, the land’s drainage capacities were overlooked.
- High-intensity rains now cause significant run-off, and existing drainage systems are inadequate to manage the excess water.
Concrete Overload:
- Urbanization has led to excessive concretization, preventing natural water absorption and causing significant run-off.
- The natural slope from the Ridge to the Yamuna River, which facilitates drainage, has been obstructed by concrete structures.
- For example, low-lying areas like Sarai Kale Khan, where multiple drains converge, experience intense flooding annually due to poor planning.
- Construction on floodplains, such as the building of railway lines, roads, and other infrastructure, has further exacerbated the problem.
Lack of Water Management Planning:
- Urban planners have consistently neglected water management as a critical resource.
- The absence of a comprehensive water masterplan has led to frequent flooding in areas like the Pragati Maidan Tunnel.
- Many water bodies, which could help manage floodwaters, have been converted into real estate, significantly reducing Delhi’s capacity to handle heavy rains.
Environmental and Infrastructure Challenges:
- The conversion of storm drains into sewers and the extensive concretization of land leave no room for rainwater to percolate into the soil.
- Environmentalists emphasize the need to de-concretize lawns and pavements, stop blocking drains with solid waste, and avoid construction in low-lying areas.
- Properly designed filtration pits and reliance on gravitational flow are suggested solutions to improve water absorption and reduce flooding.
Conclusion
- To address the chronic flooding issues, Delhi needs a paradigm shift in urban planning, emphasizing natural topography and effective water management.
- Without significant changes, including the protection of natural water bodies and the implementation of a comprehensive water masterplan, the city will continue to suffer the consequences of unchecked and ill-planned urban expansion.
| The economic geography of Delhi-NCR and its implications for urban planning |
|
| PYQ: The frequency of urban floods due to high intensity rainfall is increasing over the years. Discussing the reasons for urban floods. highlight the mechanisms for preparedness to reduce the risk during such events. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2016) |
| Practice Question: Examine the impact of unchecked urban expansion on chronic urban flooding in Delhi and the larger National Capital Region (NCR). Discuss the underlying causes and suggest comprehensive measures to address these challenges, focusing on sustainable urban planning and effective water management. (250 words/15 m) |
2. UK Teenager Becomes World’s First to Receive Brain Implant for Epilepsy, Achieving 80% Reduction in Seizures
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology – Developing new technology |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
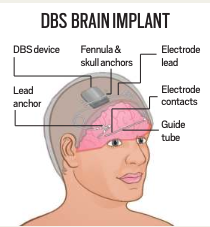
What is Epilepsy?
- Epilepsy is a neurological condition characterized by recurrent seizures, which can manifest as jerking movements of the arms and legs, temporary confusion, staring spells, or stiff muscles.
- These seizures are caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The cause of epilepsy is unknown in nearly 50% of cases, but it can be triggered by head trauma, brain tumors, infections like meningitis, or genetic factors.
- The condition increases the risk of accidents, drownings, and falls. In India, the prevalence of epilepsy ranges from 3 to 11.9 per 1,000 people, according to a 2022 Lancet study.
- Despite the availability of several anti-seizure medications, about 30% of patients are resistant to treatment.
How Does the Device Work?
- The neurostimulator device delivers continuous electrical impulses to the brain to disrupt or block abnormal seizure-causing signals.
- The device, which is 3.5 cm square and 0.6 cm thick, was surgically implanted in Knowlson’s skull and anchored with screws.
- Electrodes were inserted deep into his brain, reaching the thalamus, a relay station for motor and sensory information.
- The electrodes were connected to the neurostimulator, which was activated after Knowlson recovered from surgery. The device can be recharged wirelessly.
What is DBS?
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a technique used to treat movement disorders associated with Parkinson’s disease and other neurological conditions.
- While DBS has been used for childhood epilepsy before, the neurostimulators were typically placed in the chest, with wires running to the brain. In Knowlson’s case, the device is implanted directly in the brain.
- Expert at AIIMS, New Delhi, explains that while DBS for epilepsy is not new and there are new devices entering the market, it is not a miracle cure. It is not the first line of treatment for epilepsy, which usually involves anti-seizure medications and a ketogenic diet.
- If these do not work, brain surgery may be an option to remove the portion of the brain where seizures originate. Other surgical options include corpus callosotomy, where the part connecting the brain’s two halves is removed to prevent abnormal electrical signals from traveling between them.
How Expensive is DBS?
- Neurostimulators cost approximately Rs 12 lakh, with additional surgical costs in private hospitals bringing the total to about Rs 17 lakh. In contrast, brain surgery costs between Rs 20,000 and Rs 30,000.
- As per Experts DBS devices should be considered for patients whose epilepsy originates from multiple brain regions, making surgery less viable, or when medications and diet fail to control seizures.
- At AIIMS, among the thousands of epilepsy patients treated, only seven have undergone DBS therapy, averaging about one patient per year.
| Practice Question: What are the benefits and limitations of using deep brain stimulation (DBS) as a treatment for epilepsy, and how does it compare to other treatment options in terms of effectiveness, cost, and patient suitability? (250 words/15 m) |
3. Project Cheetah to Relocate Surplus Cheetahs from Kuno to Gandhi Sagar Amid Declining Chital Population
(Source: Indian Express; Section: The Second Page; Page: 02)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Conservation |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Decline in Chital Population:
- Kuno National Park has witnessed a significant decline in its prime cheetah prey base, the chital population, which has decreased by over 25% since 2022.
- An estimated 2,250 chital have been lost within a year, perplexing the project team as the seven cheetahs hunting in the wild only accounted for about 50 chital kills during this period.
- The authorities have ruled out large-scale poaching due to the extensive presence of surveillance and monitoring, suspecting instead the park’s 90-strong leopard population.
Leopard Predation and Prey Base Challenges:
- Leopards have been identified as a significant factor in the decline of the chital population and are also disrupting efforts to establish a cheetah prey base in Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary by infiltrating a 60 sq km enclosure meant for chital.
- Madhya Pradesh is working on replenishing Kuno’s chital population by bringing in 1,500 chitals and dispatching another batch to Gandhi Sagar.
- However, the project authorities recognize the limitations of this approach without addressing leopard predation.
Proposal for Larger Predators:
- To mitigate leopard predation and ease the pressure on the prey base, the Cheetah Project Steering Committee is considering introducing larger cats, such as tigers, into Kuno.
- The introduction of tigers aims to create an ecological balance by dominating the space densely packed with leopards, thereby reducing their predation and breeding activities.
- Committee chairperson Rajesh Gopal suggested this biological approach, noting that Kuno has one of India’s highest densities of leopards and that tigers are a natural choice given the landscape’s history with tiger presence.
Challenges at Gandhi Sagar:
- Introducing larger predators like tigers is not currently an option for Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Instead, the focus is on removing leopards from the prey enclosure.
- Authorities plan to divide the area and secure one compartment at a time, similar to the approach taken in Kuno in 2022.
Controversy and Estimation Inconsistencies:
- The hypothesis that leopards are the primary cause of the chital population decline has faced skepticism.
- Some officials and a retired forest officer question whether Kuno’s leopards are selectively preying on chitals or if the impact of bushmeat poaching is being underestimated.
- Additionally, there are concerns about the consistency of chital population estimation methods.
- Over the years, reported chital densities have fluctuated significantly, leading to discrepancies in population estimates. For instance, in 2021, two methods yielded densities of 38 and 23 chitals per sq km, with the lower density estimate suggesting over 8,000 chitals in Kuno.
- Despite the state’s efforts to release additional chitals, the population has continued to decline, with no reversal in sight since the introduction of cheetahs in September 2022.
| What is the Cheetah Reintroduction Project? |
|
|
PYQ: Consider the following: (2012) 1) Black-necked crane 2) Cheetah 3) Flying squirrel 4) Snow leopard Which of the above are naturally found in India? (a) 1, 2 and 3 only (b) 1, 3 and 4 only (c) 2 and 4 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 Ans: (b) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the challenges and strategies involved in the relocation of surplus cheetahs from Kuno National Park to Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary, considering the significant decline in the chital population and the impact of leopard predation. Evaluate the potential ecological and management implications of introducing larger predators, such as tigers, to mitigate these challenges. (250 words/15 m) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. Bangladesh Navy Signs Major Deal with India’s GRSE for 800-Tonne Ocean-Going Tug under $500 Million Line of Credit
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 11)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Details of the Deal
- The agreement was signed in Dhaka in the presence of representatives from GRSE and the Bangladesh Navy’s directorate general of defense purchases.
- The deal coincided with a four-day visit to Bangladesh by Indian Navy Chief Admiral Dinesh K. Tripathi, aimed at enhancing bilateral defense relations.
- The 800-tonne ocean-going tug, valued at approximately USD 21 million, is expected to be delivered to Bangladesh within 24 months.
- The tug will assist in towing ships at sea and will also be equipped for rescue operations.
Strategic Implications:
- The development is significant given the increasing Chinese footprint in Bangladesh’s defense market.
- The Bangladesh Navy currently operates several warships of Chinese origin and purchased two submarines from China in 2016.
- This deal with GRSE marks an important step in expanding India-Bangladesh maritime engagement beyond joint exercises and training between the two navies.
- A senior defense official highlighted that this deal is critical as it encourages Bangladesh to consider Indian shipyards for the repair and refit of its naval assets, thereby fostering closer defense ties between the two countries.
2. Kozhikode secures ‘City of Literature’ status at annual UCCN conference held in Portugal
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Context |
|
UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN):
- UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN): An initiative launched by UNESCO in 2004 to promote cooperation among cities that recognize creativity as a major factor in their sustainable urban development.
- Membership Categories: Cities can join the network in various categories such as Literature, Music, Film, Design, Gastronomy, Media Arts, and Crafts & Folk Art.
- Objectives:
- Strengthen international cooperation between cities.
- Promote cultural diversity and sustainable urban development.
- Share best practices and develop partnerships involving the public and private sectors, as well as civil society.
- Current Membership: The network includes 350 cities from around the world, each selected based on their cultural contributions and commitment to placing creativity at the core of their development.
- Annual Conference: Provides a platform for member cities to share knowledge, experiences, and good practices. The 2024 conference in Braga, Portugal, focuses on “Bringing youth to the table for the next decade.”
- Recent Additions: In 2024, Kozhikode (City of Literature) and Gwalior (City of Music) were among the new members integrated into the network.
- Benefits: Member cities gain international visibility, access to UNESCO’s expertise, and opportunities for collaboration and cultural exchange.
3. Field evaluation trials of submarine bids under Project-75I complete
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
Project-75I:
- Project-75 (I) Overview: Project-75 (I) aims to construct six Kalvari Class Diesel-Electric Attack submarines in India.
- Objective: It focuses on enhancing indigenous submarine construction capabilities with advanced technologies and weaponry.
- AIP System: The key enhancement over its predecessor is the introduction of a Fuel-cell-based Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) system.
- Stealth and Technology: Submarines under this project feature advanced stealth capabilities, low radiated noise levels, and modern sensor suites.
- Indigenisation: Each submarine in Project-75 (I) is mandated to achieve a minimum of 45% indigenous content, reaching up to 60% by the sixth submarine.
- MSME Development: The project aims to boost the submarine building industry and support MSMEs in manufacturing associated equipment.
- Size and Capacity: These submarines may be larger than those built under Project-75, enhancing operational capabilities.
- Implementation Challenges: Delays and challenges in technology adoption and infrastructure development have affected the overall progress of the project.
- Strategic Importance: Project-75 (I) plays a crucial role in India’s naval modernization and self-reliance goals under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
4. Chinese rocket engine goes Awol during hot testing
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Tianlong-3 (Heavenly Dragon 3) is a medium-lift rocket by Chinese private company Space Pioneer.
- Designed to be partially reusable with a first stage that can land itself and be used again (up to 10 times).
- Aims to compete in the commercial launch market for medium-sized payloads to low Earth orbit (LEO) and sun-synchronous orbit (SSO).
- Tianlong-3 is a partly reusable, two-stage rocket aimed at cutting mission costs, comparable in performance to SpaceX’s Falcon 9.
- Space Pioneer is among several Chinese private-sector firms rapidly growing in the commercial space sector since 2014, focusing on developing reusable rockets and launching satellites.
5. Bolivia’s economic crisis fuels distrust in govt. amid debates over ‘failed’ coup
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 15)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Currency Dependence: Bolivia’s economy heavily relies on the U.S. dollar, leading to shortages exacerbated by draining international reserves and mounting debt.
- Import Economy: The nation imports a significant portion of its goods, creating a dependency on foreign currencies like the dollar, which is in short supply.
- Inflation and Price Gouging: The shortage of dollars has fueled inflation, leading to inflated prices for essential goods like food, clothing, and car parts.
- Political Instability: Internal political conflicts, including disputes between President Luis Arce and former President Evo Morales, have contributed to economic uncertainty and policy paralysis.
- Impact on Livelihoods: The economic crisis has deepened poverty levels among the working class, with job losses and inadequate wages exacerbating social unrest.
- Long-term Challenges: Despite Bolivia’s significant natural resources, including vast lithium reserves, economic diversification efforts face long-term hurdles due to governance failures and investment challenges.
6. Lack of reliable energy burdens businesses and public services in Nigeria
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 15)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- Grid Reliability Issues: Nigeria’s national electricity grid struggles to provide sufficient and reliable power, with frequent outages affecting both urban and rural areas.
- Many rural and poor communities lack access to the national grid altogether, relying on unreliable local generators or going without electricity entirely.
- Solar Potential: Nigeria has significant solar energy potential due to abundant sunshine, but large-scale solar projects face challenges in funding and implementation.
- Investment Barriers: High interest rates for borrowing in Nigeria, often two to three times higher than in advanced economies, deter investment in solar projects despite their potential to meet the country’s energy needs.
- Tariff Issues: Electricity tariffs in Nigeria are not cost-reflective, leading to financial instability in the power sector. Distribution companies struggle to pay producers, impacting infrastructure development and maintenance.
- Petroleum Dependency: Removal of long-standing petroleum subsidies has increased costs for backup generators, further straining households, schools, hospitals, and businesses reliant on alternative power sources.
Value addition/Mains Fodder points:
Term in the news:
-
AI Washing:
- AI washing is a term derived from greenwashing, where companies exaggerate their environmental friendliness to appeal to more customers. Similarly, businesses can be accused of AI washing that claim to have integrated AI into their products, when they are actually using less sophisticated technology.
- In simple terms, AI washing refers to the practice of exaggerating or misrepresenting the capabilities of artificial intelligence in a product, service, or company.
- For Examples:
McDonalds recently decided to ditch its AI technology at drive-thru restaurants in the United States after customers complained that their orders had been incorrectly taken down. Meanwhile, Coca Cola attempted to jump on the AI hype train in 2023 by introducing a limited edition, AI-generated flavour of the cold drink which ultimately failed to impress many customers.
Important Quotes for UPSC Mains:
“Information is the oil of the 21st century and analytics is the combustion engine.”



