8 August 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Lok Sabha passes Finance Bill, amends provision on LTCG tax
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity |
| Context |
|
Definition and Purpose
- Introduction: The Finance Bill is introduced in the Lok Sabha following the Union Budget presented by the Finance Minister. It encompasses the financial proposals for the upcoming financial year.
- Once passed by Parliament and assented to by the President, it becomes the Finance Act for that year, effectively giving legal force to the budgetary measures.
- Type (I) – Article 117 (1)
- Scope: Contains matters both related to the Money Bill and general legislation.
- Introduction: Can be introduced only in the Lok Sabha, with a Presidential recommendation.
- Legislative Process:
- Rajya Sabha can suggest amendments, which Lok Sabha may accept or reject.
- In case of a deadlock, a joint sitting of both Houses may be convened by the President.
- The President can assent, withhold assent, or return the bill for reconsideration.
- Type (II) – Article 117 (3)
- Scope: Deals with provisions involving expenditure from the Consolidated Fund of India but does not include Money Bill matters.
- Introduction: Can be introduced in either House of Parliament.
- Legislative Process: Governed by procedures applicable to ordinary bills, requiring Presidential recommendation for consideration.
Difference Between Money Bill and Finance Bill
| Aspect | Money Bill | Finance Bill |
| Definition | Contains provisions related exclusively to taxation, borrowing of money by the government, and expenditure from or receipt to the Consolidated Fund of India. | Covers a broader range of financial matters, including provisions related to taxation but may also include general legislation or expenditure not strictly related to the Consolidated Fund. |
| Introduction | Can only be introduced in the Lok Sabha. | Type (I) can be introduced only in the Lok Sabha. Type (II) can be introduced in either House. |
| Certification | Certified as a Money Bill by the Speaker of Lok Sabha. | Not certified as a Money Bill. |
| Rajya Sabha’s Role | Cannot amend or reject the Money Bill. | Can recommend amendments to Type (I); Type (II) is treated like an ordinary bill. |
| Approval Process | Must be passed by Lok Sabha and can be sent to Rajya Sabha for recommendations. Lok Sabha can reject Rajya Sabha’s recommendations. If not acted upon by Rajya Sabha within 14 days, deemed passed. | Must be passed by both Houses. In case of disagreement, a joint sitting of both Houses can be summoned by the President for Type (I). Type (II) follows ordinary bill procedures. |
| Presidential Recommendation | Required for introduction in Lok Sabha. | Required for Type (I); not necessarily for Type (II). |
| Amendments | No amendments allowed by Rajya Sabha. | Rajya Sabha can suggest amendments for Type (I); Type (II) follows ordinary bill procedures. |
| Deadlock Resolution | No provision for joint sitting; Lok Sabha’s decision is final. | President can summon a joint sitting of both Houses for Type (I). Type (II) is resolved through ordinary legislative procedures. |
| Practice Question: Explain the key differences between a Money Bill and a Finance Bill in the Indian parliamentary system. Discuss their respective roles in the legislative process. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. New Bill removes powers of Waqf Board; non-Muslims and women on board
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity |
| Context |
|

New Bill to Amend the Waqf Act, 1995:
- Objective: The Bill aims to amend the Waqf Act, 1995, focusing on the administration and management of Waqf properties in India.
- Key Proposals:
- Property Declaration: Strips the Waqf Board of its powers to declare a property as Waqf. Introduces the District Collector as the arbiter to determine whether a property is Waqf or government land.
- Representation: Proposes the inclusion of two Muslim women and two non-Muslim members on the Waqf Board.
- Section Omitted: Omits Section 40, which grants the Waqf Board the authority to decide if a property is Waqf.
- Waqf Deed Requirements: Requires the execution of a Waqf deed for the creation of Waqf and ensures it does not affect the inheritance rights of heirs.
- New Name: Renames the Act to “Unified Waqf Management, Empowerment, Efficiency and Development Act, 1995.”
- Controversy:
- The Bill has faced criticism from Muslim bodies and Opposition parties, who argue it may facilitate the usurpation of Waqf properties and create societal divides.
- The All India Muslim Personal Law Board has condemned the Bill, stating that it could alter the nature of Waqf properties and compromise their protection.
| Waqf Act, 1995: |
|
What is a Waqf Board?
Waqf Act, 1995:
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the key provisions of the proposed amendments to the Waqf Act, 1995. How might these changes impact the management and representation of Waqf properties in India? Critically analyse the concerns raised by various stakeholders regarding this amendment. (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. After artificial intelligence, quantum computing eyes its big breakthrough moment
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 15)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
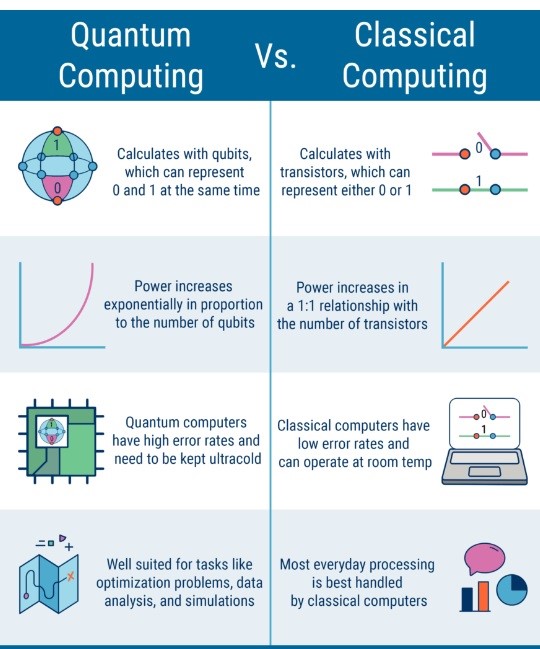
Overview of Quantum Computing:
- Technological Promise:
- Quantum computing is poised to revolutionise fields such as drug development and climate change by performing tasks beyond the capabilities of conventional computers.
- Riverlane, a Cambridge-based company, is at the forefront with its quantum decoder chip, which addresses error correction issues inherent in quantum computing.
Key Components and Concepts
- Quantum Bits (Qubits):
- Unlike classical bits (0 or 1), qubits can represent all values between 0 and 1 simultaneously, similar to dimmer switches versus simple on/off states.
- This capability allows quantum computers to handle a vast amount of information, making them suitable for simulating complex quantum systems.
- Error Correction and Control:
- Quantum systems require precise control over qubits due to their susceptibility to errors and noise.
- Effective error correction is crucial for reliable quantum computing, with ongoing research focusing on shielding hardware and developing algorithms to manage errors.
Current Limitations and Challenges
- Operation Scale:
- Present-day quantum computers can manage approximately 1,000 operations before errors overwhelm them.
- The challenge lies in scaling up the technology while maintaining accuracy and integrating error correction.
- Exponential Growth:
- The benefits of quantum computing increase exponentially with the scale of the machine, allowing it to tackle increasingly complex problems.
- However, the number of components and time required for operations also grows, presenting scalability challenges.
Industry and Regulatory Impact
- Major Investments:
- Leading tech companies, including Google, IBM, Microsoft, and Amazon, are heavily investing in quantum technology, focusing on qubit generation and error reduction.
- This competitive investment underscores the significant potential and importance of quantum computing.
- Regulatory Considerations:
- With quantum computing’s potential to disrupt current cryptographic systems and create new materials, there is a growing need for regulatory frameworks.
- The technology’s implications are prompting regulators to anticipate and address future challenges, learning from past experiences with technologies like AI.
Future Outlook
- Progress and Potential:
- The quality of qubits has improved, making this an exciting time for quantum technology. The primary challenge remains scaling up and integrating effective error correction.
- Quantum computing is expected to solve problems that are currently unsolvable, driving further research and development in the field.
| Practice Question: Evaluate the current challenges faced in scaling up quantum technology and the role of error correction in addressing these challenges. How are major tech companies and regulatory bodies preparing for advancements in quantum computing? (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. Coal Gasification
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2042653 )
| Topic: GS2 – Governance, GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|

Coal/Lignite Gasification:
- Coal and lignite gasification is a process that converts solid coal or lignite into a gaseous mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide.
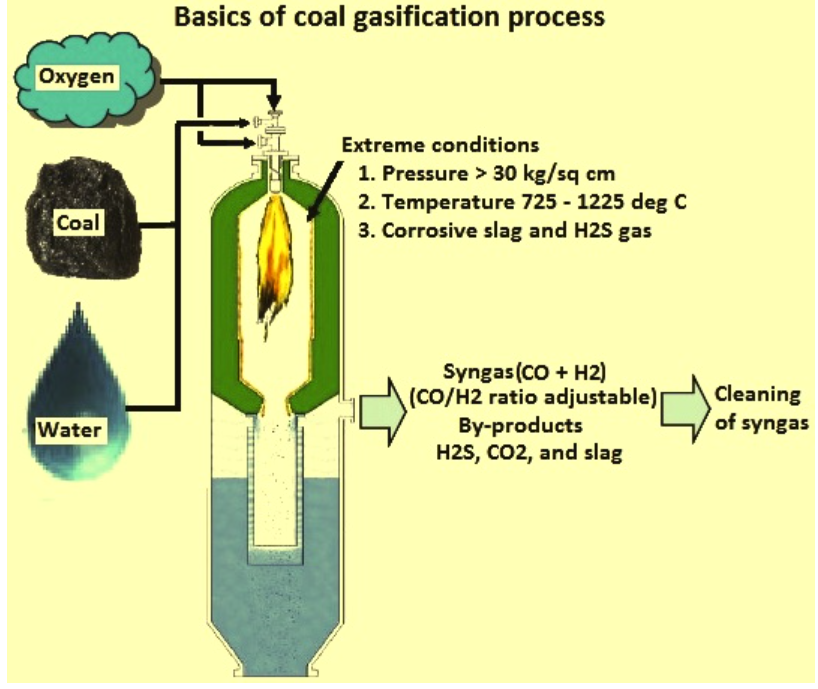
- This is achieved through a high-temperature reaction with oxygen and steam in a gasifier.
- The resulting gas mixture, known as syngas (synthesis gas), can be used as a fuel for power generation, chemical synthesis, or as a feedstock for producing synthetic fuels and chemicals.
- Gasification offers a cleaner alternative to direct combustion of coal, with the potential to reduce emissions of sulphur dioxide and particulates.
- It also enables the capture of carbon dioxide, which can be sequestered to mitigate climate change.
- This technology supports the transition to a more sustainable energy system by utilising abundant coal resources more efficiently and with fewer environmental impacts.
5. Nandini Sahakar Yojana
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2042682 )
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies |
| Context |
|

Nandini Sahakar Scheme:
- Objective: The Nandini Sahakar Scheme aims to support women cooperatives in alignment with the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative, enhancing the socio-economic status of women.
- Focus: It provides financial assistance, project formulation, hand-holding, and capacity development specifically for women cooperatives engaged in business activities.
- Financial Assistance: There is no minimum or maximum limit on the financial assistance provided for projects by women cooperatives.
- Support: The scheme includes inputs for enterprise development, business plan formulation, credit, subsidy, and interest subvention from other schemes.
- Implementation: National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) funding is project-based. As of March 31, 2024, no proposals have been received from women cooperatives in Bihar.
- Disbursement: NCDC has cumulatively disbursed ₹6,426.36 crore for developing women-promoted cooperative societies across India.
6. LEFT WING EXTREMISM
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2042680 )
| Topic: GS3 – Internal Security |
| Context |
|
National Policy and Action Plan (2015):
- Seeks to address Left Wing Extremism (LWE) with a multi-pronged strategy including security measures, development interventions, and community rights.
Achievements of the policy:
Security Measures:
Funds for modernization, training, equipment, intelligence sharing, and Fortified Police Stations provided Central Armed Police Forces battalions.
- Rs. 6908 crore allocated for capacity building under Special Infrastructure Scheme (SIS), Security Related Expenditure (SRE), and Special Central Assistance (SCA).
- Rs. 1000 crore allocated for helicopters and critical infrastructure under Assistance to Central Agencies for LWE Management (ACALWEM).
Development Initiatives:
- Road Network: 14395 km roads constructed; 11474 km in the last 10 years.
- Telecom Connectivity: 5139 mobile towers installed.
- Financial Inclusion: 1007 bank branches, 937 ATMs, 5731 new post offices opened.
- Skill Development: 46 ITIs and 49 Skill Development Centres established.
- Education: 130 Eklavya Model Residential Schools operational.
Impact:
- LWE violence incidents reduced by 73% from 2010; deaths decreased by 86% from 1005 in 2010 to 138 in 2023.
- 32% reduction in LWE incidents and 17% reduction in deaths in 2024 (up to June).
- Reduction in LWE affected districts from 126 in 2013 to 38 in 2024.
- Police stations reporting LWE violence dropped from 465 in 2010 to 89 in 2024 (up to June).
| PYQ: Naxalism is a social, economic and developmental issue manifesting as a violent internal security threat. In this context, discuss the emerging issues and suggest a multilayered strategy to tackle the menace of Naxalism. (250 Words /15 marks)(UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2022) |
| Practice Question: Assess the effectiveness of the National Policy and Action Plan (2015) in mitigating Left Wing Extremism (LWE) in India. What additional measures could enhance the strategy to address LWE? (150 Words /10 marks) |
7. India Launches Portal to Expedite Business Visas for Chinese Technicians, Easing PLI Scheme Production
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 13)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
What is the Production Linked Incentive Scheme (PLI)?
The PLI scheme was conceived to scale up domestic manufacturing capability, accompanied by higher import substitution and employment generation. Launched in March 2020, the scheme initially targeted three industries.
- Mobile and allied Component Manufacturing
- Electrical Component Manufacturing and
- Medical Devices.
- Later, it was extended to 14 sectors.
- In the PLI scheme, Domestic and Foreign companies receive financial rewards for manufacturing in India, based on a percentage of their revenue over up to five years.
Targeted Sectors: The 14 sectors are mobile manufacturing, manufacturing of medical devices, automobiles and auto components, pharmaceuticals, drugs, specialty steel, telecom & networking products, electronic products, white goods (ACs and LEDs), food products, textile products, solar PV modules, advanced chemistry cell (ACC) battery, and drones and drone components.
Industry Concerns and Delays:
- Domestic industries have raised concerns about delays in fulfilling export orders due to visa hold-ups for Chinese technicians.
- These delays began after the 2020 Galwan clash, affecting companies that rely on Chinese machinery.
Government Initiatives
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has initiated interactions with different departments to train them on using the portal.
- This portal aims to facilitate quicker visa approvals, essential for industries dependent on Chinese parts, especially in electrical and electronic segments.
Economic Dependence and Impact
- China accounts for a significant portion of India’s imports, particularly engineering and electronic items.
- Delays in granting visas have forced some manufacturers to consider alternative locations without such restrictions.
- Chinese technicians are preferred due to their cost-effectiveness compared to Western or Southeast Asian counterparts.
Policy Changes Post-Galwan Clash
- Post-Galwan clash, India introduced measures to limit Chinese influence, including changes to the FDI policy under Press Note 3 (PN3).
- This policy brought investments from land-bordering countries under the government route, resulting in only a quarter of Chinese FDI applications being approved up to June last year.
Economic Survey Insights
- The recent Economic Survey suggested attracting Chinese investments to boost exports.
- The Survey highlighted that countries like Mexico, Vietnam, Taiwan, and Korea benefit from the China-plus-one strategy pursued by Western firms.
- It emphasized that India should integrate into China’s supply chain, either through imports or Chinese investments, to boost manufacturing and global supply chain integration.
| Practice Question: How does the new portal for approving short-term business visas for Chinese technicians aim to address production delays in Indian industries, and what are the broader implications for India’s economic strategy in relation to Chinese investments and the global supply chain? (250 words/15 m) |
8. Chhattisgarh Approves Third Largest Tiger Reserve Amid Declining Population
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
Topic: GS3 – Environment – Conservation
| Context: |
| Chhattisgarh has approved the creation of the Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve, the third largest in India, spanning 2,829.387 square kilometers across four northern districts. This is Chhattisgarh’s fourth tiger reserve, integrating an existing national park with a wildlife sanctuary. |
Analysis of News:
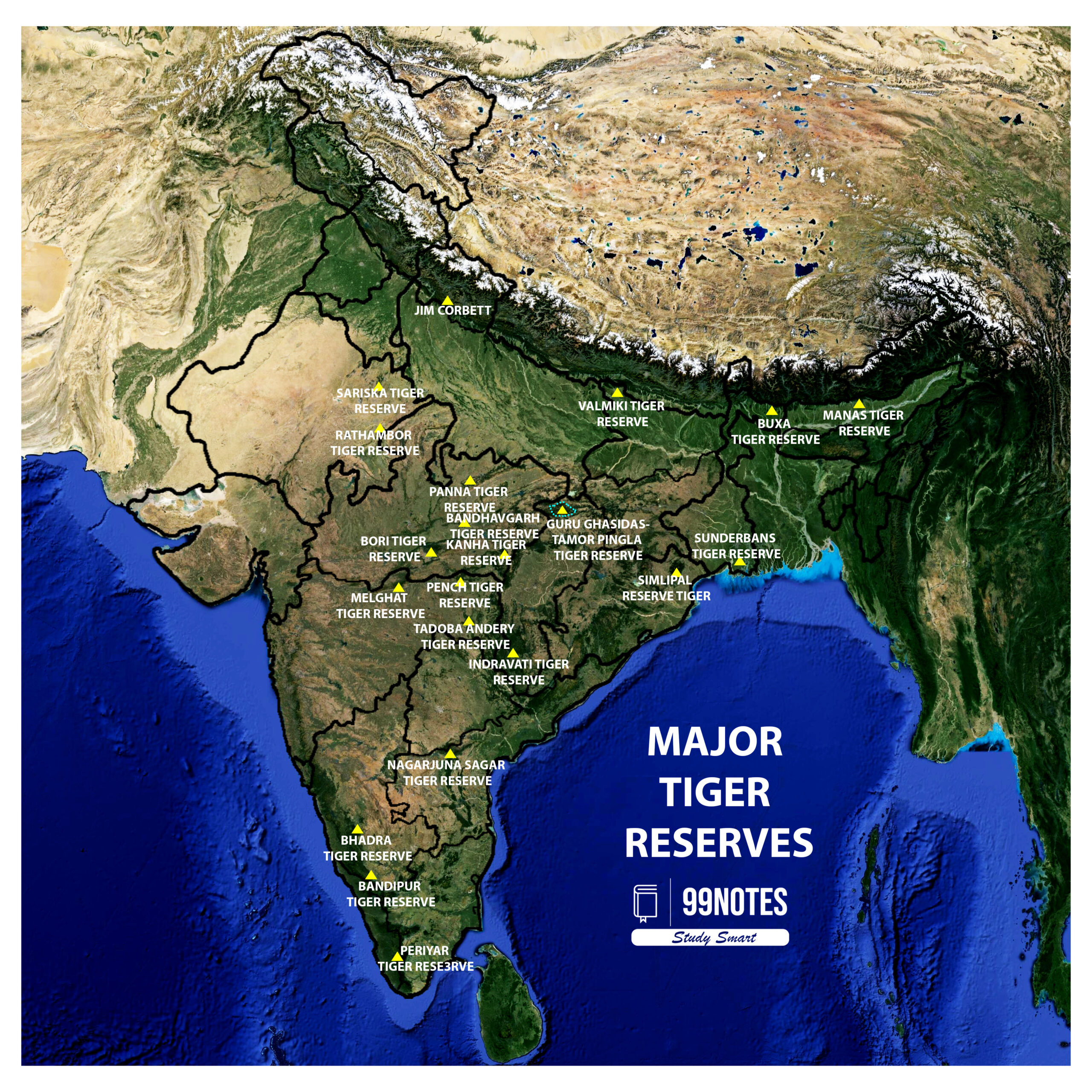
Guru Ghasidas National Park:
- Named after the Satnami reformist hero of the place, Guru Ghasidas, is the result of the carving of Chhattisgarh from Madhya Pradesh in the year of 2000. It is located in the Koriya district of Chhattisgarh.
- The park has undulating topography and it falls under the Tropical climate zone.
- Flora: The vegetation consists mainly of mixed deciduous forest with teak, sal and bamboo trees.
- Fauna: Tiger, Leopard, Chital, Nilgai, Chinkara, Jackal, Sambar, Four-horned Antelope etc.
Tamor Pingla Wildlife Sanctuary:
- It is located in the Surajpur district of Chhattisgarh bordering Uttar Pradesh. It is named after Tamor hill and Pingla Nalla.
- Tamor hill and Pingla Nalla are considered to be the old and prominent features of the sanctuary area.
- Flora: Mixed deciduous forests dominate the sanctuary. Sal and bamboo forests are seen all through.
- Fauna: Tigers, Elephants, leopards, bears, sambar deer, blue bulls, chital, bison and many such animals are found here.
Catalyst for Decision
- The decision follows a Chhattisgarh High Court directive, which gave the state government four weeks to declare the area a tiger reserve after a PIL flagged the declining tiger population.
Decline in Tiger Population
- Chhattisgarh’s tiger population has dropped from 46 in 2014 to 17 in 2022, as per a National Tiger Conservation Authority report.
- The Union Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change had highlighted this decline in a 2023 statement, noting concerning trends in states with small tiger populations, including Chhattisgarh.
Benefits and Government Action
- The new reserve is expected to boost eco-tourism and create employment opportunities for locals as guides, tourist vehicle operators, and resort managers.
- The National Project Tiger Authority will provide additional budget support, facilitating new livelihood projects in surrounding villages.
- The state authorized its Department of Forest and Climate Change to proceed with the formal establishment of the reserve.
Comparisons
- The largest tiger reserve in India is Andhra Pradesh’s Nagarjunasagar Srisailam Tiger Reserve, covering 3,296.31 sq km, followed by Assam’s Manas Tiger Reserve at 2,837.1 sq km. Both reserves have 58 tigers.
| National Parks and Sanctuaries in Chattisgarh |
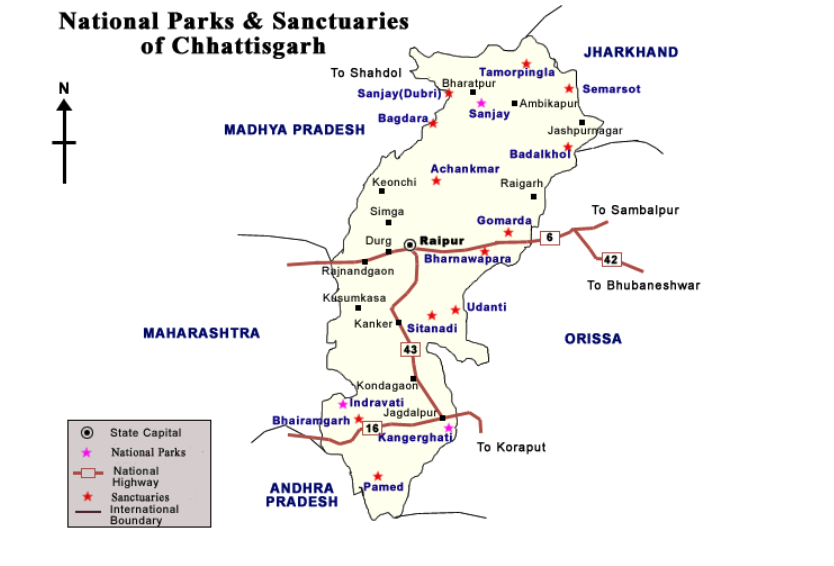 |
|
PYQ. Among the following Tiger Reserves, which one has the largest area under “Critical Tiger Habitat”? (2020) (a) Corbett (b) Ranthambore (c) Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam (d) Sundarbans Ans: (c) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of establishing new tiger reserves in India with reference to Chhattisgarh’s recent approval of the Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve. How can such initiatives contribute to wildlife conservation and local community development?. (250 words/15 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. Extra 100 gm crushes Vinesh’s Olympic dreams
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
What are the rules regarding weight limits?
- In wrestling competitions, weight limits are strictly enforced to ensure fairness among athletes.
- According to the United World Wrestling (UWW) regulations, weigh-ins are conducted each morning of the concerned weight category.
- Wrestlers must meet the weight limit during these weigh-ins to compete in their designated category.
- Specifically, UWW Article 11 states that if an athlete fails to meet the weight limit in either the first or second weigh-in, they are disqualified and ranked last without a position in the competition.
- This rule is upheld to maintain the integrity of the sport and ensure a level playing field.
- For women’s wrestling, the weight categories are: 50kg, 53kg, 57kg, 62kg, 68kg, 76kg, and 76+kg. The 50kg category, in which Vinesh Phogat competed, requires athletes to weigh no more than 50kg.
- In cases where athletes are overweight, even by a small margin, they are ineligible to participate, as demonstrated by Vinesh Phogat’s disqualification in the 2024 Olympics for being 100 grams over the limit.
2. Tiny bones shed light on mystery ‘hobbits’
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
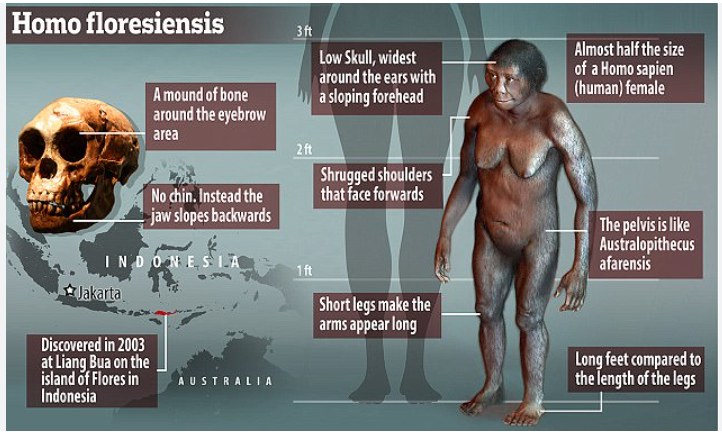
- Discovery: A tiny upper arm bone and some teeth from Homo floresiensis were found on Flores Island, Indonesia, providing new insights into their size evolution.
- Significance: The arm bone is identified as the smallest humerus fossil of an adult hominin ever discovered.
- New Findings: The fossils suggest that Homo floresiensis stood about one metre tall around 700,000 years ago, which is smaller than previous estimates of around 1.06 metres.
- Previous Estimates: Earlier findings, including teeth and jawbones from around 60,000 years ago, had indicated a height of approximately 1.06 metres.
- Evolutionary Debate: Two main theories exist:
- Theory 1: Homo floresiensis evolved from a small hominin that arrived on Flores about a million years ago.
- Theory 2: Homo erectus, a larger hominin, arrived on the island, and through island dwarfism, evolved into the smaller Homo floresiensis over the next 300,000 years.
- Island Dwarfism: The phenomenon where larger animals reduce in size due to limited resources and space on isolated islands.
- About other animals: Other small mammals, including a cow-sized relative of the elephant, were also present on the island.
- Migration Hypothesis: It is suggested that Homo erectus may have reached Flores by crossing deep-sea barriers, potentially using natural debris for rafting.
- Survival: Once isolated, these hominins adapted and evolved into distinct forms, surviving on the island for hundreds of thousands of years.
3. ‘BIMSTEC FTA talks needs revival with realistic possibilities’
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 12)
| Context |
|
BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation):
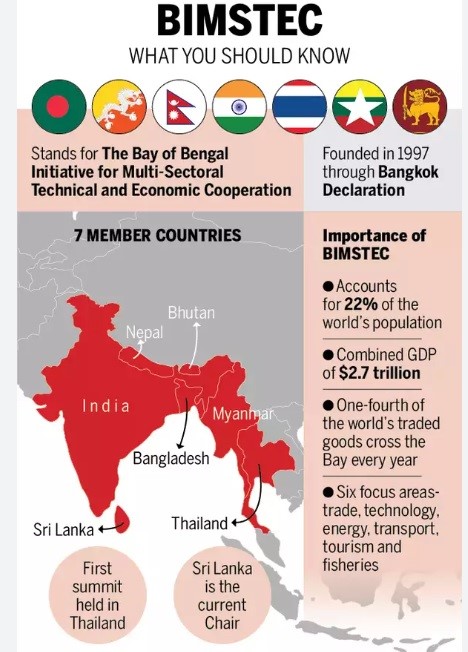
- BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) is a regional organization established in 1997, aimed at fostering cooperation among countries in the Bay of Bengal region.
- Headquarters: Dhaka, Bangladesh.
- Member States: Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Nepal, and Bhutan.
- The organisation focuses on enhancing economic and technical cooperation in sectors such as trade, investment, technology, and infrastructure.
- BIMSTEC operates through various sectors, including trade, energy, environment, and people-to-people contacts, with the goal of promoting regional integration and development.
- The grouping seeks to leverage its members’ shared geographical and cultural ties to boost economic growth and stability in the region.
- The organization also addresses regional challenges like climate change and security issues through collaborative initiatives.
4. Raging Wildfires in US and Canada Create Dangerous Pyrocumulonimbus Clouds, Increasing Fire Risks
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 14)
| Context |
| The article discusses the intense wildfires in the United States and Canada that are creating pyrocumulonimbus clouds. |
Analysis of News:
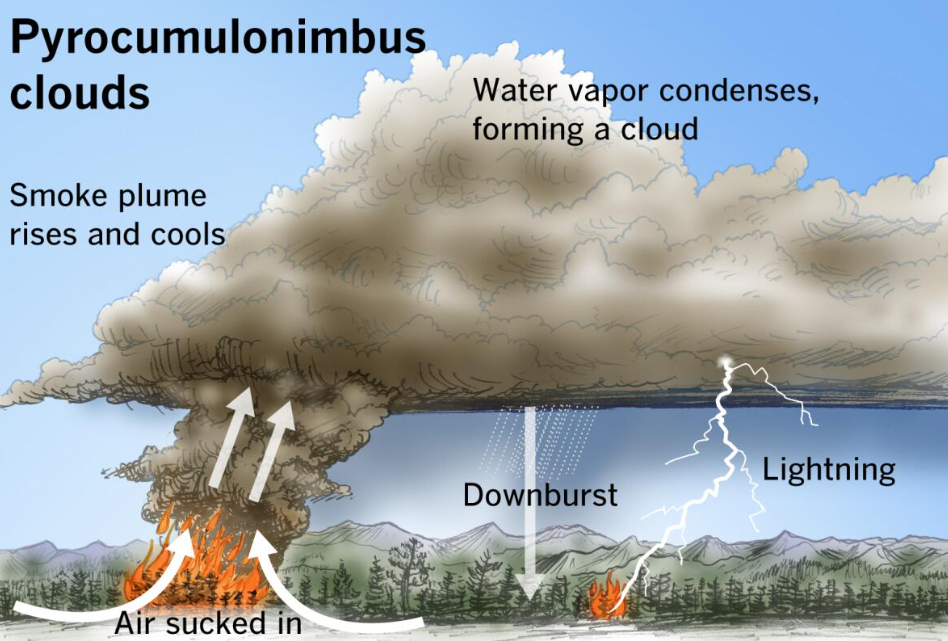
Formation of Pyrocumulonimbus Clouds
- The wildfires currently devastating the United States and Canada are creating ‘pyrocumulonimbus’ clouds, which can generate thunderstorms and spark additional fires.
- These clouds form when extremely hot wildfires, or volcanic eruptions, cause air to rise, cool, and condense water vapor on ash.
- If conditions are right, pyrocumulus clouds evolve into pyrocumulonimbus clouds, reaching up to 50,000 feet and producing lightning but little rain, thus igniting new fires.
Increasing Frequency
- The occurrence of pyrocumulonimbus clouds has surged recently.
- Before 2023, the average annual global count was 102, with 50 in Canada. In contrast, 2023 saw 140 such clouds in Canada alone, indicating a significant rise.
Factors Contributing to Increased Occurrence
- The exact reasons for the increased frequency of pyrocumulonimbus clouds are not fully understood, but climate change is suspected to play a role.
- Higher global temperatures lead to more frequent and intense wildfires, thereby increasing the likelihood of these cloud formations.
- Atmospheric conditions also influence their development, with intense wildfires enhancing the probability of their occurrence.
5. Indian Army Constructs Crucial Bailey Bridge in Landslide-Hit Wayanad
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 14)
| Context: |
| The Indian Army’s Madras Engineer Group recently assembled a 190-foot Bailey bridge at Chooralmala to access Mundakkai village in Wayanad, heavily impacted by landslides. |
Analysis of News:
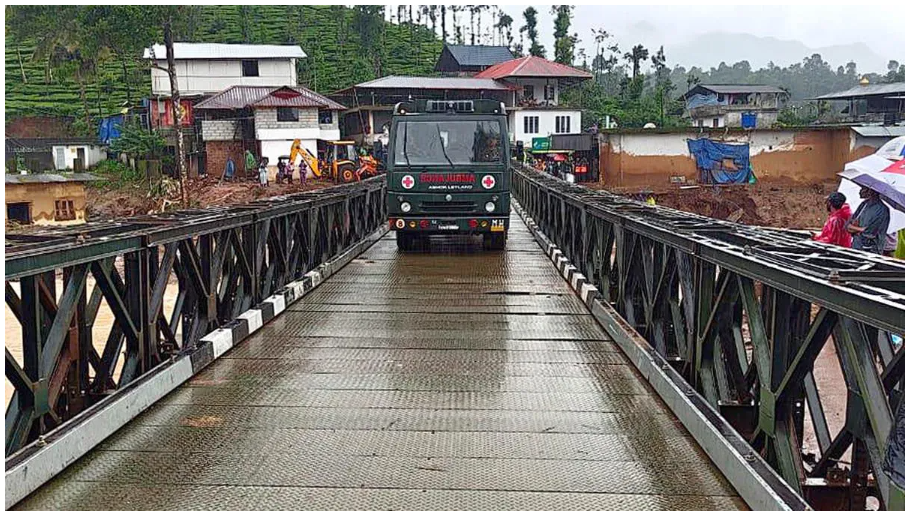

About Bailey bridge:
- It is a type of modular bridge, one whose parts are pre-built so that they need minimal construction work and can be assembled quickly when needed.
- Origin: A US Army Engineer School manual notes that the Bailey bridge originated during wartime. Donald Coleman Bailey, an English civil engineer, invented it during World War 2 (1939-45).
How does the Bailey bridge work?
- The pre-fabricated parts in a Bailey bridge include light steel panels linked through pins, which are big, screw-like objects.
- These help establish the guardrails of the bridge. Through the guardrails on either side, workers place beams to form the deck or path of the bridge.
- All beams were constructed such that they would lock in on the guardrails to ensure stability.
- After that, the bridge can be extended, and the lightness of the parts allows it to be mobile.
- No heavy installation equipment is needed. In disaster relief situations, this is ideal because parts can be transported in small trucks — something also of use during wartime.
Key facts about Madras Sappers
- The Madras Sappers is an engineering group of the Corps of Engineers of the Indian Army, which originated in the erstwhile Madras Presidency army of the British Raj.
- This regiment has its headquarters in Bengaluru.
- The Madras Sappers were the only regiment of the Madras Presidency Army to survive the reorganisations that took place between 1862 and 1928.
6. Inaugural Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar Honors Top Indian Scientists and Research Teams
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 09)
| Context: |
| The article highlights the recipients of the inaugural Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar (RVP), a new set of national science awards. |
Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar
- The RVP was established in 2023, disbanding previous awards including the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize.
- The awards aim to recognize and promote excellence in scientific research and innovation in India.
Award Categories and Recipients
Vigyan Ratna: Award for lifetime achievement.
- G. Padmanabhan: Celebrated biochemist known for work on the malaria parasite, honored with Padma Shri and Padma Bhushan.
Vigyan Team: Award for collaborative research.
- Chandrayaan-3 Team: Recognized for successfully landing India’s first spacecraft on the Moon.
Vigyan Yuva: Award for scientists under 45 years, replacing the Bhatnagar Prize.
- Vivek Polshettiwar: Chemist from Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, works on carbon capture technologies.
- Urbasi Sinha: Quantum research expert from Raman Research Institute, Bengaluru.
- Roxy Mathew Koll: Climate scientist from Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune.
Vigyan Shri: Award for scientists of all ages.
- Annapurni Subramaniam: Director of Indian Institute of Astrophysics, research on star clusters and galaxies.
- Jayant Bhalchandra Udgaonkar: Biologist and former director of IISER Pune.
- Naba Kumar Mondal: Particle physicist from Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics, Kolkata.




