Union Budget 2024 Summary || Highlights of Budget 2024 UPSC
Union Budget 2024 Summary
Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Government Budgeting.
|
Importance of This Topic from UPSC Perspective: |
| In UPSC’s General Studies Paper 3, the topic of Government Budgeting in the Indian Economy is crucial. It assesses candidates’ understanding of fiscal policies, resource allocation, and economic priorities.
A sound grasp of this topic is essential for comprehending the country’s economic governance, policy-making, and overall financial health of the nation. |
Content in this article:
Interim Budget:
Since it is an election year, the government has not produced full budget but has produced an Interim Budget. In such a situation, generally, the budget is passed by Vote on account under the provisions of Article 116.
In order to understand the constitutional provisions regarding the passing of the budget, you can click here.
Keywords Used in the Budget 2024 & Important Highlights
“INDIA UNION BUDGET 2024 – FY25 FISCAL DEFICIT TARGETTED @ 5.1% | FY25 NET BORROWING @ ₹11.75 LAKH CRORE | REFORMS | SPENDING | NO CHANGES TO TAXATION”
PART 1 – REFORMS & SPENDING
- India’s economy witnessed a profound transformation over the last ten years.
- India govt working on all-round, all-inclusive development
- India needs to focus on the poor, women, youth and farmers
- India-middle east-Europe corridor a game changer
- India to pay attention to making the Eastern region a driver of growth.
- India to prepare financial sector to meet investment needs
- India to take up next-gen reforms, build consensus with states
- India to have policies to foster growth
- India plans housing scheme for middle-income people
- India approves bilateral investment treaty between India and UAE.
- DBT: 2.7L Cr savings for government – stopped leakage.
- SwaNIDHI – 78Lakh street vendors benefitted.
- Agriculture:
- PM Kisan – 11.8 Cr farmers benefitted
- PM Fasal Bima – 4Cr farmers were ensured
- eNAM – 1361 mandis integrated – served to 1.8Cr farmers; It has a trading volume of 3Lakh Crore.
25Cr people assisted out of Multi-dimensional poverty;
VISION FOR VIKSIT BHARAT – 5 elements
- Developed India by 2047 – Amrit Kaal
- Trinity of Demography, Democracy and Diversity
- Reform – Perform – Transform.
- Panchamrit Goals: Energy Security
- Aspirational District Program
HEALTHCARE
- India to increase the number of medical colleges on existing infra
- India plans to set up a committee to recommend more medical colleges on existing infra
- India to encourage cervical cancer vaccination for girls aged 9 to 14
- India to extent ayushman bharat to all Aasha & Anganwadi workers & helpers
- India to launch U-win platform for managing immunisation
Skilled India:
- 4Cr youth upskilled & 54Lakh reskilled.
- Established 3000 new it is, 7 IITs, 16 IIITs, 7 IIMs, 15 AIIMS and 390 new universities.
AGRI
- India will further promote investments in post-harvestimate activities.
- India will expand Nano-DAP use on crops.
- India plans a strategy for self-reliance on oil seeds.
- India will formulate a scheme for dairy development.
- India to step up fisheries program to increase productivity
- India aims to double seafood exports to ₹1 lakh crore – shrimp exporters like Avanti feeds and water base impacted positively.
- India approves scheme of sugar subsidy under PDS for AAY families
- India’s PM Kisan Sampada benefitted 38 lakh farmers & generated 10 lakh employment
- India’s pm formalisation of micro-food processing enterprises has assisted 2.4 lakh SHGs & 60,000 individuals.
INNOVATION / TECH
- INDIA TO SET UP ₹1 LAKH CRORE CORPUS WITH 50 YEARS INTERESTIMATE FREE LOAN FOR INNOVATION – one trillion rupees ($12 billion) for scaling research in sunrise sectors
- INDIA PLANS SCHEME FOR DEEP TECH FOR DEFENSE.
- A detailed plan to achieve the Indian government’s 2070 Net Zero goal, which includes viability gap funding for harnessing wind energy, coal gasification plant, biofuel expansion and creating an ecosystem for EVs like payment security for procuring electric buses for public transport.
INFRA
- India to spend 11.1% more on infra in FY25 at 11.1 lakh crore rupees
- India cabinet approves extension of animal husbandry infra fund
- Air connectivity:
- Proof of booming sector: Indian airline companies placed orders for more than 1,000 new aircraft.
- India to add airport capacity. 149 Airports are already functional.
- India to provide viability gap fund for 1gw offshore wind energy
- India under PM Gati Shakti to launch three major railway economic corridors –
- Energy, mineral & cement corridor,
- Port connectivity corridor,
- High-traffic density corridor
- PM Awas Yojana: India will build 20m more houses for the poor in the next five years. Till now, three crore houses have been constructed under PMAY.
EV
- India to expand EV ecosystem.
- India will form a payment security mechanism for EV buses. It’s worth noting that EV sales made up only 1.3% of total passenger vehicles sold last year
BIOGAS
- India to give financial assistance to the biogas sector
- India to have bio-manufacturing, bio-foundry plan
- New scheme to provide environment-friendly products- bioplastics, biopharma, biodegradable polymers, bio Agri inputs.
- The phased mandatory blending of compressed biogas in CNG for transport & piped natural gas for domestic purposes.
TOURISM
- Encourage states to develop tourist centres. India plans long-term interest-free loans to states for Tourism.
- TO promote island tourism infrastructure, business and conference tourism infrastructure (similar to Bharat Mandapam as utilised in the G20 meeting).
FOR STATES
- India will have viability gap funding for offshore wind of 1GW.
- India will form a panel to address demographic change issues.
- India is negotiating bilateral investment treaties to boost FDI.
- States’ fiscal consolidation goal: India ₹75 thousand crore of 50-year interest-free loan to support states that meet milestones provision for milestone-linked reforms in states
The government will continue on the path of fiscal consolidation
- India’s FY24 total expenditure revised estimate is ₹44.90 lakh crore
- The revised estimate of receipts is ₹27.56 lakh crore rupees for FY24.
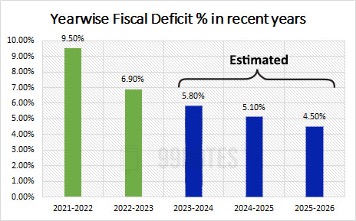
- The government has revised the FY24 budget deficit target to 5.8% of GDP
- (against the 5.9% goal).
- India aims to reach a fiscal gap of 4.5% by FY26.
- India sets FY25 budget-gap target at 5.1% of GDP.
- India’s FY25 gross market borrowing is seen as 14.1 ₹lakh crore
- India budgets FY25 net market borrowing at 11.75 lakh crore
| FISCAL DEFICIT % | 9.5 % | 6.9% | 5.8% | 5.1% | 4.5 % |
| FY | 2021-2022 | 2022-2023 | 2023-2024 | 2024-2025 | 2025-2026 |
PART 2 – TAXATION — “In keeping with the tradition.”
- India does not propose any changes in taxation.
- The same tax rates for direct and indirect retained.
- India will extend tax benefits for startups to March 31, 2025.
- India to improve taxpayer services.
- India will withdraw some outstanding direct tax demands.
- The cabinet approves the continuation of the garment tax rebate scheme.
Union Budget 2024 News
1. Net zero gain for job guarantee scheme.
News in Brief:
- The interim Budget allocates ₹86,000 crore for MGNREGS, a 43.33% increase, but a concern arises with total expenditure at ₹88,309 crore.
- Critics argue it falls short, providing only 25-30 days of work for registered households.
- Activists emphasise a need for ₹3 lakh crore.
News in Detail:
Interim Budget Allocation for MGNREGS (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme)
- Allocation Increase:
-
- ₹86,000 crore is allocated, marking a 43.33% rise from the last Budget.
- Net gain may be zero or negative considering total expenditure of ₹88,309 crore.
- Budget Trends:
-
- Breaks the trend of reducing the Budget; the 2023 Budget had a 33% lower allocation.
- Matches the revised estimates for the ongoing financial year.
- Outstanding Dues:
-
- Centre owes ₹16,000 crore in wages to State governments and ₹7,000 crore to Westimate Bengal.
- Activists’ Perspective:
-
- Critics argue allocation falls short of efficient implementation, only providing 25 to 30 days of work for 5.6 crore registered households.
- Activists emphasise the need for ₹3 lakh crore to meet employment requirements, highlighting a substantial shortfall.
2. Marginal rise in allocations for farming, fisheries
News in Brief:
- In the Budget, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman emphasises farmers’ welfare with a ₹1,997 crore increase for the Agriculture Ministry.
- While Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana sees a boost, the PM Kisan Samman Nidhi remains at ₹60,000 crore.
News in Detail:
Agricultural Allocation:
- The Finance Minister prioritises farmers’ welfare in the Budget.
- Agriculture Ministry receives ₹1,17,528.79 crore, a ₹1,997 crore increase from the previous Budget.
Schemes and Allocations:
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana sees increased allocation.
- PM Kisan Samman Nidhi remains at ₹60,000 crore, while PM Kisan Man Dhan Yojana faces a decreased allocation.
Agricultural Research:
- ₹9,941.09 crore was allocated for agricultural research.
- Direct financial assistance to 11.8 crore farmers under PM Kisan Samman Nidhi.
Dairy Farming:
- Comprehensive programme planned for supporting dairy farmers.
- Focus on controlling foot and mouth disease, building on existing schemes like the Rashtriya Gokul Mission.
Fisheries Department:
- Separate Department for Fisheries results in increased allocation of ₹4,521.24 crore.
- Significant growth in both inland and aquaculture production.
Missing Component:
- The Budget remains silent on a guaranteed minimum support price based on the M. S. Swaminathan Committee’s formula.
3. Schools and higher education departments get more money in the interim Budget.
News In Brief:
- The Interim Budget reveals a boost in allocations for both Higher Education and School Education
- The School Education Department received ₹73,008.10 crores, and the Higher Education Department allocated ₹47,619.77 crores.
- PM SHRI sees a substantial 50% increase in allocation at ₹6,050 crore.
News In Detail:
- Interim Budget presented by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman increases budgetary allocations for both Higher Education and School Education departments under the Union Ministry of Education.
- The School Education Department receives a total allocation of ₹73,008.10 crore, compared to ₹68,804.85 crore in the last Budget.
- The revised estimates for the School Education Department in the last fiscal were ₹72,473.80 crore, with the actual expenditure of 2022-23 amounting to ₹58,639.56 crore.
- PM POSHAN (Pradhan Mantri Poshan Shakti Nirman), previously known as the mid-day meal scheme, receives an allocation of ₹12,467.39 crore.
- PM SHRI (PM Schools for Rising India) sees an almost 50% increase in allocation compared to the last Budget, with a total allocation of ₹6,050 crore.
- The Higher Education Department is allocated a total of ₹47,619.77 crore, up from ₹44,094.62 crore in the last Budget.
- In the revised estimates, the allocation for Higher Education rose to ₹57,244.48 crore, while the actual expenditure for 2022-23 was ₹38,556.80 crore.
4. Fertiliser subsidy is set to decline, and food subsidy sees an increase.
News In Brief:
- The Centre reduces fertiliser subsidies, citing improved conditions in Ukraine and increased domestic production.
- Food subsidy increases to ₹2,05,250 crore, emphasising free ration distribution for 80 crore people during the pandemic.
News In Detail:
Fertiliser subsidy:
- Centre reduces fertiliser subsidies, citing an improved situation in Ukraine and increased domestic production as potential management solutions.
- Fertiliser and Chemicals Ministry claims rising domestic production, particularly of urea, will lead to a decrease in fertiliser subsidies.
- The Budget allocates ₹1,64,150.81 crore for the Fertilizer Department, down from ₹1,75,148.48 crore in the last Budget.
- Actual expenditure in 2022-23 for fertiliser subsidies was ₹2,51,369.18 crore, with a focus on indigenous and imported urea payments.
- Finance Minister announces expansion of Nano DAP application on crops across agro-climatic zones after the successful adoption of Nano Urea.
Food subsidy:
- Food subsidy increases, with a total allocation of ₹2,05,250 crore for PM-GKAY and ₹1 lakh crore for Sugar Subsidy under the Public Distribution System.
- Last year’s food subsidy allocation was ₹1,97,350 crore, and the actual expenditure in 2022-23 was ₹2,72,802.38 crore.
Nirmala Sitharaman highlights the elimination of food worries through free ration distribution for 80 crore people during the pandemic.
5. Prudent, promises bigger things
News In Brief:
- FM Nirmala Sitharaman presents an interim budget with an 11% increase in capex to ₹11.11 lakh crore, focusing on inclusive growth and a detailed roadmap for a developed India by 2047.
- Housing initiatives, infrastructure boost, fiscal prudence, and support for tech entrepreneurs are also some of the highlights of the interim Budget.
News In Detail:
- Capex Outlay Increase:
-
- The government raises the capex outlay for the next financial year by 11% to ₹11.11 lakh crore.
- Emphasis on inclusive growth with policies targeting women, youth, farmers, and the poor.
- Housing Initiatives:
-
- Two crore more houses were promised under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana in addition to the existing three crore.
- Commitment to ensuring affordable housing for the middle class, potentially boosting the real estate sector.
- Infrastructure Focus:
-
- The government’s core philosophy is pushing capital expenditure, particularly in the infrastructure sector.
- Capex on infrastructure increased, which is expected to have a multiplier effect on the economy.
- Fiscal Prudence:
-
- Despite economic upheavals, the government remains fiscally prudent.
- The fiscal deficit is projected at 5.8% for FY24, showing improvement over the initial estimate of 5.9%.
- Market Borrowing Reduction:
-
- Reduced market borrowing plan for 2024-25, with gross and net market borrowing at ₹14.13 lakh crore and ₹11.75 lakh crore, respectively.
- The government seeks private-sector collaboration to fund massive infrastructure development.
- Long-Term Vision:
-
- The government outlines a detailed roadmap for a developed India by 2047, emphasising long-term vision and planning.
- Fiscal deficit target of 4.5% by 2025-26 aligns with the commitment to fiscal responsibility.
- Support for Tech Entrepreneurs:
-
- Pledge to establish a ₹1 lakh crore fund for research and development in the tech space.
Aim to power the entrepreneurial spirit of India’s young tech innovators.
6. Solar panels to give free power to 1 cr. homes
News In Brief:
- Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announces a rooftop solar initiative
- It aims to electriFY one crore households, providing up to 300 free units monthly, translating to ₹15,000-18,000 annual benefits.
- Last year’s expenditure on the program was ₹2,167 crore, with a budget allocation of ₹4,555 crore for 2024-25.
News In Detail:
Rooftop Solar Initiative:
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced the rooftop solarisation initiative to electrify one crore households, providing up to 300 free units monthly.
- Estimated benefits for households range from ₹15,000 to ₹18,000 annually through free solar electricity and surplus sales to distribution companies.
Current Rooftop Solar Scenario:
- India has 11 GW of installed rooftop solar capacity, with only 2.7 GW in residential units and the rest in commercial or industrial spaces.
- No centralised estimate on the number of households with rooftop solar units; estimated to be below 10 lakh.
Potential Impact and Savings:
- Rooftop solarisation of one crore households could support 20-25 GW of rooftop solar capacity.
- Estimated savings for distribution companies could reach ₹2 lakh crore over 25 years.
Offshore Wind Support:
- ‘Viability gap funding’ announced for the capital-intensive offshore wind sector, supporting up to 1 GW capacity.
- Details and budgetary allocations for the offshore wind initiative are not specified.
Global Context:
- Rooftop Solar aims to address the intermittent nature of solar power and reduce reliance on the grid.
- The initiative aligns with the government’s commitment to electriFY one crore households.
7. Fiscal consolidation surprised everyone.
News In Brief:
- The 2024 Budget, a vote-on-account, prioritises fiscal consolidation despite lower-than-expected GDP growth.
- The government aims to end FY24 with a reduced fiscal deficit of 5.8%, consolidating to 5.1% in FY25.
- Capital expenditure appears to improve, but rural scheme allocations remain flat.
News In Detail:
Budget Type:
- The 2024 Budget is a vote-on-account, limiting parliamentary discussion and avoiding significant tax modifications.
- Its purpose is to seek permission for spending and collecting receipts until the new government forms.
Fiscal Consolidation:
- Despite being a pre-election year and lower-than-budgeted nominal GDP growth in FY24 (10.5% y-o-y vs. 8.9%), the government aims for a lower fiscal deficit (5.8% vs. 5.9% of GDP) and plans to consolidate it further to 5.1% in FY25, aligning with the FY26 target of 4.5%.
Expenditure Overview:
- The central government’s total expenditure, budgeted to grow at 6.1% in FY25, is lower than India’s nominal growth.
- Fiscal impulse reduces further when adjusting for interest outgo. Capital expenditure appears to improve, but key infrastructure sectors show low single-digit growth.
Rural Allocations:
- Except for rural housing (FY25 budget at ₹545 billion vs. ₹320 billion in FY24), allocations for key rural schemes remain largely flat.
Borrowing and Market Trends:
- Gross borrowing is lower in FY25 at ₹14.1 trillion compared to ₹15.4 trillion in FY24.
- Actual net market borrowing in FY25 falls to ₹10.5 trillion from ₹11 trillion in FY24.
8. Focus firmly on jobs and reforms.
News In Brief:
- The 2024 interim Budget focuses on technology, youth, and innovation, aiming to empower the poor, youth, farmers, and women.
- With a continued emphasis on capital investments, it recognises 1.14 lakh startups, supporting high-growth and resource-efficient economic development.
- Sustainable growth is prioritised through eco-friendly alternatives and a commitment to ‘net zero’ by 2070.
News in Detail:
Budget Focus:
- The 2024 interim Budget emphasises technology, youth, and innovation as the cornerstones of the government’s strategy.
- Aims to empower people with low incomes, youth, farmers, and women to unlock India’s potential.
Economic Growth and Employment:
- Continued focus on increased capital investments to generate employment opportunities and drive economic growth.
- Recognition of 1.14 lakh startups under the ‘Startup India’ initiative, creating over 12 lakh jobs.
MSMEs and Next-Generation Reforms:
- MSMEs are integral to the economy; next-gen reforms focus on timely finances, relevant technologies, and training for global competitiveness.
- Aims to sustain high and resource-efficient economic growth, creating opportunities for all.
Youth and Innovation:
- India’s young workforce offers a massive opportunity: a 43% increase in women’s enrollment in STEM courses.
- Technology, youth, and innovation remain central to the government’s strategy.
Innovation Funding:
- Creation of a ₹1 lakh crore corpus with a 50-year interest-free loan to harness the power of youth and technology for driving innovation.
Sustainable Growth:
- Promoting sustainable growth is a top priority, aligning with the commitment to achieve ‘net zero’ by 2070.
- Focus on environment-friendly alternatives, including rooftop solar, offshore wind power, and bio-fuel blending with CNG.
Women-Led Initiatives:
- Urgency in having more women in the workforce; women-led initiatives are imperative.
- Emphasis on health and nutrition programs, ensuring sustainable and inclusive livelihood options.
Pragmatic Approach:
- The Budget avoids unnecessary populist measures, concentrating on maintaining India’s high-growth trajectory and addressing key economic and social challenges.
9. Centre moots ₹1 lakh-crore corpus for R&D.
News In Brief:
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announces a ₹1 lakh crore corpus at minimal or nil interest rates to encourage private sector investment in research and development for ‘sunrise sectors.’
- The National Research Foundation Bill, cleared in 2023, expects ₹36,000 crore from the private sector.
- The National Quantum Mission receives ₹2,819 crores, and a new scheme for deep-tech technologies in defence is introduced.
News In Detail:
Innovation Fund for Research:
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announces a ₹1 lakh crore corpus, available at minimal or nil interestimate rates, to encourage private sector investment in research and development in ‘sunrise sectors.’
- The specific ministry or beneficiaries are not clarified.
Implementation Challenges:
- Experts welcome the initiative but express uncertainty about implementation details.
- The Budget emphasises the positive aspect of involving both public and private sectors in research and development.
National Research Foundation Bill:
- In 2023, the Science Ministry cleared the National Research Foundation Bill, piloted by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), with a ₹50,000 crore corpus.
- Nearly ₹36,000 crore is expected from the private sector and non-governmental sources.
Private Sector Participation in R&D:
- The government seeks increased private sector investment in core research and development, addressing a long-standing concern.
- DST allocates ₹2,000 crore in 2024-25 towards the National Research Foundation (NRF).
National Quantum Mission:
- Provision of ₹2,819 crore for the National Quantum Mission, a significant scheme of the DST, in the interim Budget.
Deep-Tech Technologies for Defence:
- A new scheme is to be launched to strengthen deep-tech technologies for defence purposes and expedite ‘Atmanirbharta.’
Specific details about the scheme are not provided.
10. New scheme for bio-manufacturing, bio-foundry on the cards
News in Brief:
- In the interim budget, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman unveiled a bio-manufacturing and bio-foundry scheme.
- The scheme targets eco-friendly alternatives like biodegradable polymers, bio-plastics, and bio-pharmaceuticals.
- The initiative aims to boost India’s bio-economy, targeting a $300 billion contribution by 2030 and $1 trillion by 2047.
- The Department of Biotechnology sees a 16% budget cut to ₹2,251.52 crore.
News in Detail:
Bio-Manufacturing Scheme:
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman introduced a new scheme for bio-manufacturing and bio-foundry in the interim budget.
- Aims to provide environment-friendly alternatives such as biodegradable polymers, bio-plastics, bio-pharmaceuticals, and bio-agri-inputs.
Bio-Economy Targets:
- Seeks to have the bio-economy contribute $300 billion to the Indian economy by 2030, with a further target of $1 trillion by 2047.
- These products play a crucial role in achieving sustainability and ‘green’ economy targets.
Upskilling Bio-Science Sector:
- Focuses on upskilling India’s bio-science sector through investments in bio-manufacturing, prioritising practical applications over research.
- The step has been taken with an understanding of the need for monetary support in bio-manufacturing.
Budget Allocations :
- The 2024-2025 Budget reduces the total allocation for the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) by 16%, amounting to ₹2,251.52 crore.
- Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) receives ₹40 crore, unchanged from the previous year, potentially impacting post-pandemic recovery efforts.
Regenerative Manufacturing:
- The bio-manufacturing scheme aims to transform the current consumptive manufacturing paradigm into one based on regenerative principles.
The initiative is seen as necessary for changing consumption patterns and addressing environmental concerns.
11. Three economic rail corridors on the anvil.
News in Brief:
- The Union Ministry of Railways receives ₹2.55 lakh crore for FY 2024-25, a 5.8% increase, focusing on economic corridor programs with 434 projects worth ₹11 lakh crore.
- Plans include revamping 40,000 coaches over five years for an enhanced passenger experience. Budget allocation for public sector units decreases, signalling an intent to involve private players.
- The National High-Speed Rail Corridor’s bullet train project sees a notable increase in funding.
News in Detail:
Railway Budget Highlights:
- Union Ministry of Railways receives ₹2.55 lakh crore for FY 2024-25, marking a 5.8% increase from the previous year’s ₹41 lakh crore allocation.
- Railway Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw notes that 82% of last year’s allocation had been spent by January.
Economic Corridor Programs:
Three major economic corridor programs were announced:
- Energy, Mineral, and Cement Corridor (Energy Economic Corridor),
- Port Connectivity Corridor (Rail Sagar), and
- High-Traffic Density Corridors (Amrit Chaturbhuj).
434 projects with a total investment of ₹11 lakh crore are planned under these programs.
Integrated Railway Planning:
- An integrated approach to railway planning involves consultation with 18 ministries over two years.
- Planning based on PM Gati Shakti framework, focusing on origin and destination nodes for railway development.
Coach Overhaul Project:
- Over the next five years, 40,000 coaches will be overhauled, costing ₹15,200 crore.
- Upgrades aim to provide a better passenger experience with improved toilets, safety standards, charging points, GPS, and CCTV cameras.
Budget Allocation Changes :
- Budget allocation for investment in public sector units and joint ventures decreases from ₹34,353 crore in 2023-24 to ₹31,107 crore in 2024-25.
- Experts suggested the reduction is to open up the market to private players.
Bullet Train Project:
- The National High-Speed Rail Corridor’s bullet train project receives a significant increase in allocation, rising from ₹19,592 crore to ₹25,000 crore.
12. Industry welcomes plan to augment electric vehicle ecosystem.
News in Brief:
- Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announces a focus on strengthening the electric vehicle (EV) ecosystem, emphasising charging infrastructure development for net-zero emissions.
News in Detail:
- The government aims to increase the adoption of electric public transport buses with a formal payment mechanism.
- Industry responses express support for the move, foreseeing benefits for EV manufacturing and innovation.
The Budget’s infrastructure focus aligns with developmental goals, and many private automotive manufacturers in India applaud the emphasis on advancing the EV ecosystem.
13. Space programme gets nominal hike of 4%.
News In Brief:
- The Department of Space receives a 4% budget increase in the interim Union Budget for 2024-25, with a focus on pre-launch testing milestones.
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announces a ₹1 lakh crore corpus for private sector R&D.
News In Detail:
Department of Space Budget Overview:
- Interim Union Budget for 2024-25 allocates ₹13,043 crore to the Department of Space, marking a nominal 4% increase from ₹12,545 crore.
- No major space missions are scheduled for the year, focusing on pre-launch testing milestones for lunar and human spaceflight missions.
Key Achievements in 2023:
- Successful execution of Chandrayaan-3 mission.
- Launch of Aditya-L1 to study the sun and XPoSat for neutron stars and black holes.
- Signing of Artemis Accords for participation in the U.S. moon program.
Planned Launches in 2024:
- Uncrewed Gaganyaan test flight, Small Satellite Launch Vehicle’s third developmental flight, and NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar mission.
- Ongoing research on propellants, satellite propulsion systems, new launch vehicles, and technology transfer to the industry.
Private Sector Boost:
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announces a ₹1 lakh crore corpus with five-decade interest-free loans to boost private sector investment in research and development.
- Expected benefits for India’s private spaceflight sector and around 200 startups.
IN-SPACe and Space Technologies:
- IN-SPACe’s revenue expenditure increased by 24%.
- Revenue for space technologies, covering Gaganyaan and new launch vehicles, sees a 27% increase.
Budget Discrepancies:
- 8% increase in space technologies allocation contrasts with planned work on Chandrayaan-4 and Lunar Polar Exploration mission.
- Expenditure for INSAT satellite systems halved from ₹531 crore in 2023-24 to ₹276 crore in 2024-25.