23 November 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis
1. Zone of Containment
(Source: Indian Express; Section: The Editorial Page; Page: 12)
| Context: |
| The article highlights the growing threat of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), global and national efforts to combat it, and the need for sustained actions, governance, and investments to address the crisis effectively. |
What is Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)?
- Antimicrobial resistance is the resistance acquired by any microorganism (bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, etc.) against antimicrobial drugs (such as antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, antimalarials, and anthelmintics) that are used to treat infections.
- As a result, standard treatments become ineffective, infections persist, and may spread to others.
- It is a natural phenomenon as bacteria evolve, making drugs used to treat infections less effective.
- Microorganisms that develop antimicrobial resistance are sometimes referred to as “superbugs”.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified AMR as one of the top ten threats to global health.
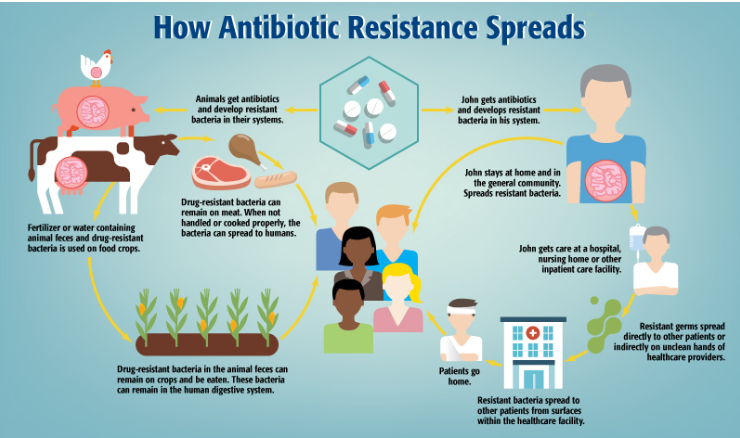
The Growing Threat of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a significant threat to modern medicine by rendering once-effective drugs powerless against microbes.
- Drug-resistant infections are increasingly difficult to treat and contribute to rising mortality rates globally.
- The absence of comprehensive surveillance systems, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, initially hindered effective responses to this crisis.
- The stark projections by economist Jim O’Neill in 2014, which estimated 10 million AMR-related deaths annually by 2050, catalyzed global action.
- This led to the creation of the Global Action Plan in 2015 and the adoption of the UN Resolution on AMR in 2016.
Progress in Understanding and Surveillance of AMR
- Over the past decade, significant strides have been made in AMR surveillance. In 2015, the World Health Organization (WHO) launched the Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS), enabling standardized sharing of AMR data among participating nations.
- As of 2023, 137 countries are part of this initiative. Despite these advancements, AMR continues to cause severe health impacts, as evidenced by a 2021 Lancet report attributing 1.14 million deaths directly to AMR, with South Asia and Africa bearing the highest burden.
- Older adults, particularly those above 70, are disproportionately affected, making AMR a pressing issue for countries with aging populations.
India’s Role and Efforts in AMR Containment
- India mirrors global trends in AMR disease burden and has demonstrated a proactive approach to containment. The nation has implemented surveillance networks in secondary hospitals and expanded its focus to livestock, poultry, and fisheries.
- The National Essential Diagnostics List mandates microbiology labs in all district hospitals, promising better data from grassroots levels in the near future.
- However, these efforts are yet to achieve national uniformity, necessitating sustained expansion and funding.
Global Commitments and India’s Strategic Roadmap
- The 79th UN General Assembly High-Level Meeting on AMR in 2023 marked a critical juncture in global efforts. Leaders, including India, committed to reducing bacterial AMR-related deaths by 10% by 2030 and achieving sustainable national financing for AMR action plans.
- India was among the first nations to launch a National Action Plan (NAP) on AMR in 2017. Moving forward, India must prioritize improved governance, accountability, and funding to achieve its targets.
- Strengthening diagnostic systems, infection control, vaccine uptake, and antimicrobial stewardship can significantly reduce AMR transmission. Moreover, investments in healthcare infrastructure and the development of new drugs, diagnostics, and vaccines are imperative.
Conclusion: Sustaining and Escalating AMR Efforts
- While India has shown commendable commitment to combating AMR, it needs to sustain ongoing efforts and accelerate ambitious initiatives.
- Strengthened governance, robust healthcare investments, and effective translation of research into practice will be pivotal in the fight against AMR.
- By addressing these priorities, India can better respond to the AMR crisis and safeguard public health against its escalating threat.
| What are the Implications of the Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance? |
| Healthcare Impact: AMR can render previously effective antibiotics ineffective against bacterial infections. This complicates the treatment of common illnesses like pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and skin infections, leading to prolonged illnesses, more severe symptoms, and increased mortality rates. Increased Healthcare Costs: Treating resistant infections often requires more expensive and prolonged therapies, increased hospital stays, and sometimes more invasive procedures. This leads to higher healthcare costs for individuals, healthcare systems, and governments. Challenges in Medical Procedures: AMR makes certain medical procedures riskier. Surgeries, cancer chemotherapy, and organ transplants become more hazardous due to the increased risk of infections that are resistant to standard antibiotics. Limitations in Treatment Options: As resistance grows, the available arsenal of effective antibiotics diminishes. This limitation in treatment options may lead to a scenario where previously manageable infections become untreatable, reverting medicine to a pre-antibiotic era where common infections could be fatal. |
| PYQ: Can overuse and the availability of antibiotics without doctor’s prescription, the contributors to the emergence of drug-resistant diseases in India? What are the available mechanisms for monitoring and control? Critically discuss the various issues involved. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2014) |
| Practice Question: Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) poses a serious threat to global health and modern medicine. Discuss the steps taken at the global and national levels to combat AMR, with a focus on India’s initiatives and challenges. Suggest measures to strengthen the fight against AMR. (250 words/15 m) |



