9 December 2024 : PIB Summary For UPSC
1. India’s Digital Revolution: Transforming Infrastructure, Governance, and Public Services
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2082144®=3&lang=1 )
| Topic: GS2 – Governance, GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
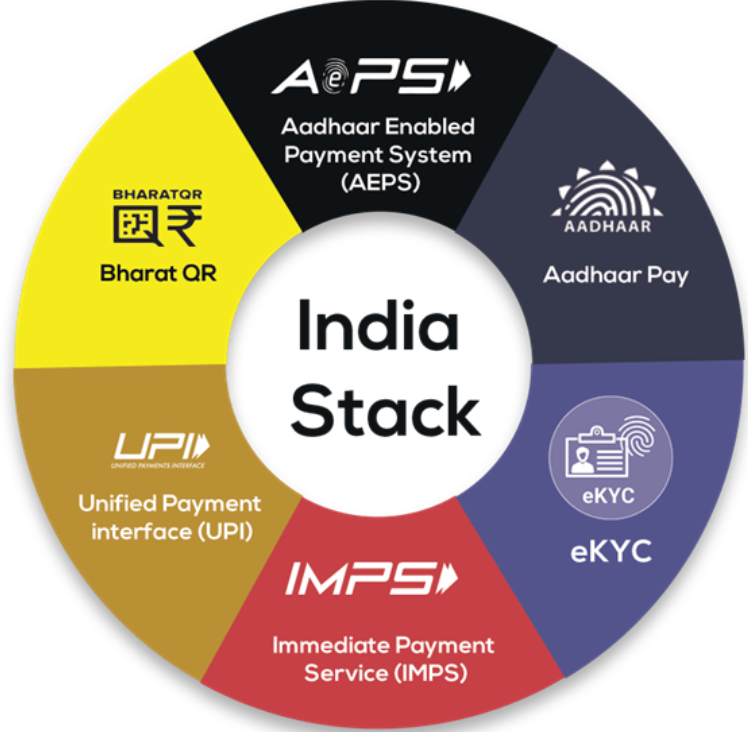
India’s Digital Public Infrastructure
India’s Digital Infrastructure Landscape
- India has rapidly evolved as a global leader in digital adoption, driven by innovations in cloud computing, AI, machine learning, and digital governance.
- The country’s digital infrastructure aims to ensure accessibility, scalability, and security in delivering government services and fostering economic growth.
Expansion of Data Centres
- Data centres are essential for supporting India’s increasing demand for cloud computing and data storage.
- The National Informatics Centre (NIC) has set up National Data Centres (NDC) in cities like Delhi, Pune, Bhubaneswar, and Hyderabad, offering cloud services to various government entities.
- These data centres provide disaster recovery and hosting services, with storage capacities expanding to approximately 100PB.
- The NDC-North East Region (NDC-NER), launched in 2020, aims to bridge the digital divide in Northeast India.
Enhancing Cloud Services: NIC and MeghRaj
- The NIC National Cloud Services project, launched in 2022, upgrades cloud infrastructure to support over 300 government departments.
- The GI Cloud (MeghRaj) initiative ensures the optimal use of IT infrastructure and accelerates the development of e-Gov applications, including digital payments and data sharing.
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
- DPI plays a critical role in transforming India’s digital economy, with key initiatives like Aadhaar, UPI, DigiLocker, and DIKSHA.
- Aadhaar, with over 138 crore registrations, provides a digital identity to citizens.
- UPI has facilitated 24,100 crore transactions, enhancing financial inclusion.
- DigiLocker has served 37 crore users for digital document verification.
- DIKSHA is the world’s largest education platform, with over 556 crore learning sessions.
National Knowledge Network (NKN)
- NKN connects national and state data centres, promoting resource sharing and collaborative research, with 1,803 institutional links and 637 district centre links.
Common Services Centres (CSCs)
- With over 5.84 lakh CSCs operational – this initiative brings essential e-services to rural India, including government schemes, education, telemedicine, and financial services.
Citizen-Centric Digital Services
- UMANG, with over 7.12 crore users, simplifies access to government services across various sectors.
- Platforms like MyGov and API Setu encourage citizen engagement and open data exchange, facilitating over 312 crore transactions.
Revolutionizing Government Operations
- Platforms like DigiLocker and GovDrive have transformed document management, enabling paperless governance.
- The Gov Intranet Platform streamlines workflow management for government officials, ensuring efficient communication and coordination.
Conclusion
- India’s digital infrastructure is revolutionizing governance and public service delivery, positioning the nation as a global leader in digital innovation.
- Through initiatives like Aadhaar, UPI, and DigiLocker, India is creating scalable digital solutions that empower citizens and promote socio-economic growth.
| PYQ: How have digital initiatives in India contributed to the functioning of the educational system in the country? Elaborate your answer. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2020) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the role of Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in enhancing governance and socio-economic development in India. Highlight key initiatives like Aadhaar, UPI, and MeghRaj in this context.(250 Words /15 marks) |


