23 July 2024 : PIB Summary For UPSC
1. INDIA’S REAL GDP PROJECTED TO GROW BETWEEN 6.5–7 PER CENT IN 2024-25
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2034973 )
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
Economic Performance

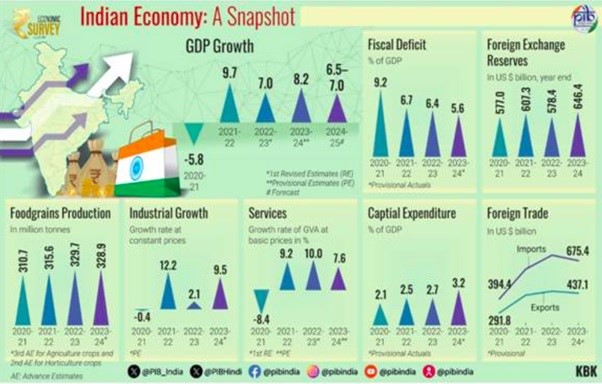
- GDP Growth: India’s real GDP grew by 8.2% in FY24, surpassing 8% in three out of four quarters.
- Sector Contributions: Shares in GVA at current prices: Agriculture (17.7%), Industry (27.6%), Services (54.7%).
- Manufacturing & Construction: Both sectors grew by 9.9% in FY24.
Inflation and Investment
- Retail Inflation: Declined to 5.4% in FY24 from 6.7% in FY23.
- Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF): Increased by 19.8% in FY23, driven by private non-financial corporations.
- Real Estate: Residential units sold in top eight cities grew by 33% YoY in 2023.
Fiscal Performance
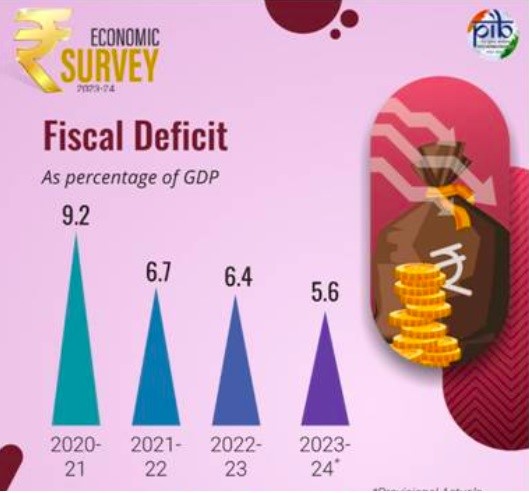
- Fiscal Deficit: Reduced from 6.4% of GDP in FY23 to 5.6% in FY24.
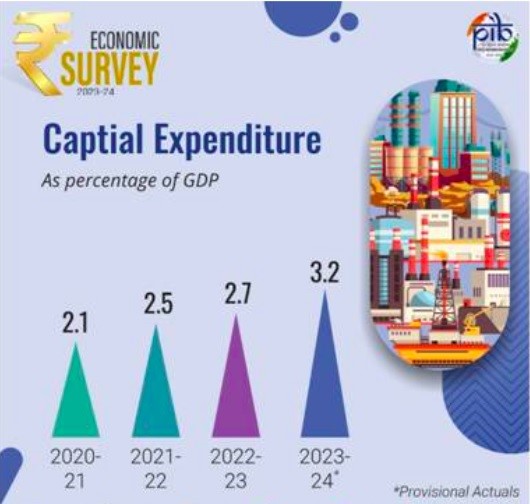
- Capital Expenditure: Stood at ₹9.5 lakh crore, a 28.2% YoY increase.
- State Government Spending: Gross fiscal deficit was 8.6% lower than budgeted.
Banking and Finance
- GNPA Ratio: Declined to 2.8% in March 2024, a 12-year low.
- Credit Disbursal: Continued double-digit growth for MSMEs and personal housing loans.
External Sector
- Service Exports: Reached USD 341.1 billion in FY24.
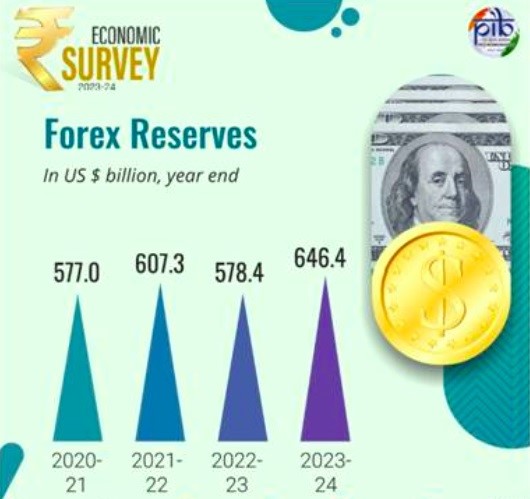
- Forex Reserves: Sufficient to cover 11 months of projected imports.
- Current Account Deficit: Improved to 0.7% of GDP from 2.0% in FY23.
Social Welfare and Employment
- Direct Benefit Transfer: ₹36.9 lakh crore transferred since 2013.
- Female Labour Force Participation: Increased from 23.3% in 2017-18 to 37% in 2022-23.
- Unemployment: Declined with an increase in labour force participation and worker-to-population ratio.
Global Economic Context
- Global Growth: According to IMF, the global economy grew by 3.2% in 2023.
- Geopolitical Risks: Potential escalation could impact supply chains, inflation, and monetary policy.
Economic Outlook
- Projected Growth: India’s real GDP projected to grow between 6.5–7% in 2024-25.
- Investment Drivers: Domestic growth supported by stable consumption and investment demand.
- Policy Implications: Continued focus on capital expenditure and private sector participation needed for sustainable growth.
2. INDIAN ECONOMY NEEDS TO GENERATE NEARLY 78.5 LAKH JOBS ANNUALLY IN THE NON-FARM SECTOR UNTIL 2030 TO CATER TO THE RISING WORKFORCE
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2034952 )
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
Technological and Economic Landscape:
- AI’s Role: AI’s growth, especially in sectors like BPO, poses risks and opportunities for India’s young population. Government initiatives aim to harness AI for productivity.
- Job Creation: India needs to create 78.5 lakh non-farm jobs annually until 2030. Schemes like PLI, MITRA Textile, and MUDRA are key to this goal.
- Corporate Sector: Profitability at a 15-year high in FY24, with profits quadrupling between FY20 and FY23.
- Agro-Processing and Care Economy: Promising sectors for generating quality employment, especially for women and youth.
Gig and Platform Workers:
- Social Security: Code on Social Security (2020) includes gig and platform workers, enhancing their social security measures.
- Gig Economy Growth: Gig workforce expected to grow to 2.35 crore (23.5 million) by 2029–30, forming 6.7% of the non-agricultural workforce.
Economic Metrics and Projections:
- GDP Growth: India’s real GDP grew by 8.2% in FY24, with an expected growth of 6.5-7% in FY25.
- Sectoral Contributions: Agriculture (17.7%), Industry (27.6%), and Services (54.7%) sectors in overall GVA at current prices in FY24.
- Manufacturing and Construction: Both sectors grew by 9.9% in FY24.
- Inflation: Retail inflation declined to 5.4% in FY24 from 6.7% in FY23.
- Fiscal Deficit: Reduced from 6.4% of GDP in FY23 to 5.6% in FY24.
- Capital Expenditure: Increased by 28.2% YoY, reaching ₹9.5 lakh crore in FY24.
Financial Sector:
- Banking Stability: Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPA) ratio at a 12-year low of 2.8% in March 2024.
- Forex Reserves: Sufficient to cover 11 months of projected imports as of March 2024.
- Service Exports: Reached a new high of USD 341.1 billion in FY24.
Social Welfare and Labour Force:
- Female Labour Force Participation: Increased from 23.3% in 2017-18 to 37% in 2022-23, mainly driven by rural women.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT): ₹36.9 lakh crore transferred since 2013, enhancing fiscal efficiency and minimising leakages.
- Employment Needs: Emphasis on shifting MGNREGS labour to more productive ventures and boosting employment in agro-processing and care sectors.
Climate Change and Green Transition:
- Impact on Jobs: Climate change may lead to job losses and productivity declines. Transition to green technologies and ESG standards can drive job creation.
- Green Investments: Facilitating green transition in businesses can create jobs and support sustainable economic growth.
Care Economy:
- Future Needs: Expanding care requirements for an ageing population by 2050. Developing the care sector can increase female labour participation and create jobs.
- Elderly Care: Formulating a comprehensive policy for senior care is crucial for leveraging the ‘silver dividend’ and boosting GDP growth.
3. INDIAN AGRICULTURE SECTOR IS A SUCCESS STORY: ECONOMIC SURVEY 2023-24
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2034946)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Agriculture |
| Context |
|

Overview:
- Agricultural Success: India has evolved from a food-deficit nation in the 1960s to a net exporter of agricultural products.
- Shift in Focus: The survey emphasises the transition from basic food security to nutritional security, highlighting the need for diverse and nutritious food options like pulses, millets, fruits, vegetables, milk, and meat.
- Challenges: The sector faces three major challenges: ensuring food and nutritional security, addressing climate change, and sustainable resource use (water, energy, land).
Five Policy Recommendations:
- Regulate Futures Markets:
- Avoid banning futures or options during price spikes.
- Implement intelligent regulatory designs to minimize bureaucratic interference.
- Export Policies:
- Invoke export bans only in exceptional circumstances.
- Allow farmers to benefit from higher international prices.
- Ensure domestic consumers can substitute non-essential agricultural commodities if needed.
- Inflation-Targeting Framework:
- Re-examine the current framework to possibly exclude food prices from inflation targeting.
- Higher food prices are often supply-induced, not demand-induced.
- Mitigate hardships from higher food prices for low-income consumers through direct benefit transfers or purchase coupons.
- Increase Net Irrigated Area:
- Address the disparity in irrigation efficiency across states.
- Improve water utilization farming practices and technologies such as drip irrigation and fertigation.
- Current irrigation efficiency is 30-40% for surface water and 50-60% for groundwater.
- Climate-Consistent Farming:
- Promote crop-neutral incentive structures.
- Address environmental impacts of water-intensive crops like rice and sugarcane.
- Focus on reducing methane emissions from paddy cultivation.
Sectoral Challenges and Transformation:
- Employment Potential: Agriculture and allied sectors hold potential for significant employment, but this potential is not fully tapped.
- Structural Transformation: A structural overhaul is necessary to address water scarcity and climate change impacts.
- COVID-19 Impact: The pandemic led to a surge in agricultural employment due to reverse migration.
- Value Addition: There has been a decline in the growth rate of value addition in agriculture in FY24.
- Environmental Stress: The summer of 2024 saw extreme heat and rising water stress, necessitating a reassessment of agricultural policies.
Conclusion:
- The Economic Survey calls for a serious and honest evaluation of India’s farm sector policies to address ongoing and future challenges, ensuring sustainability and resilience in the agricultural sector.
4. HEALTH SECTOR VITAL FOR RESILIENT ECONOMY, STATES ECONOMIC SURVEY 2024
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2034933 )
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health |
| Context |
| The Economic Survey 2023-24 highlights significant achievements in India’s healthcare sector, focusing on initiatives like AB-PMJAY, Jan Aushadhi Kendras, and the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission.Key milestones include 49% female beneficiaries, 10,000 Jan Aushadhi Kendras, and the creation of 64.86 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts. |
Overview:
- Healthcare System Importance: A resilient economy requires a robust healthcare system interconnected with factors driving inclusive growth.
- Government Commitment: Emphasis on preventive and promotive healthcare, ensuring universal access to quality healthcare services.
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY):
- Objective: Provides health insurance cover of ₹5 lakh/year for underprivileged families for secondary and tertiary hospitalisation.
- Achievements (as of 8th July 2024):
- 34.73 crore Ayushman Bharat cards generated.
- 7.37 crore hospital admissions covered.
- 49% of beneficiaries are women.
PM Jan Aushadhi Kendras:
- Objective: Provides quality medicines at 50-90% cheaper than market rates.
- Milestone: 10,000th Jan Aushadhi Kendra inaugurated in AIIMS Deoghar.
- Availability: 1965 medicines and 293 surgical equipment.
AMRIT (Affordable Medicines and Reliable Implants for Treatment):
- Objective: Provides subsidised medicines for critical illnesses.
- Network: Over 300 AMRIT pharmacies operating in various States/UTs.
Ayushman Bhav Campaign:
- Launch: September 2023.
- Objective: Saturates selected healthcare services in every village/town, informs citizens about flagship schemes.
- Achievements:
- 16.96 lakh wellness, yoga, and meditation sessions.
- 1.89 crore Tele consultations.
- Free drugs availed by 11.64 crore people.
- Free diagnostics services availed by 9.28 crore people.
- Ante-natal check-up and immunisation availed by 82.10 lakh mothers and 90.15 lakh children.
- Seven types of screening (TB, Hypertension, Diabetes, Oral Cancer, Breast Cancer, Cervical Cancer, Cataract) availed by 34.39 crore people.
- 2.0 crore patients consulted general OPD, 90.69 lakh patients consulted specialist OPD.
- 65,094 major surgeries and 1,96,156 minor surgeries conducted.
- 13.48 crore ABHA accounts created, 9.50 crore Ayushman cards generated, 1.20 lakh Ayushman Sabhas organised.
- Cumulative footfall of 20.66 crore in 25.25 lakh health melas (as of 31 March 2024).
Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM):
- Launch: 2021.
- Objective: Create a national digital health ecosystem.
- Achievements:
- 64.86 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA) created.
- 3.06 lakh Health Facility Registries generated.
- 4.06 lakh healthcare professionals registered.
- 39.77 crore health records linked with ABHA.
eSanjeevani:
- Launch: 2019.
- Objective: Provides telemedicine services for virtual doctor consultations in remote areas.
- Achievements (as of 9th July 2024):
- Served 26.62 crore patients across 128 specialties.
- Operates at 1.25 lakh Health & Wellness Centres (Ayushman Arogya Mandirs) through 15,857 hubs.
Conclusion:
- The Economic Survey 2023-24 underscores the significance of these healthcare initiatives in ensuring quality healthcare for all, contributing to the overall resilience and inclusive growth of the Indian economy.
5. SHARE OF MSMEs IN MANUFACTURING OUTPUT STANDS AT 35.4 PER CENT.
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2034923 )
| Context |
|
Overview:
- MSME Sector Significance: Contributes 35.4% to India’s manufacturing output.
- Increased Productivity:
- GVA per worker: Increased from ₹1,38,207 to ₹1,41,769.
- GVO per establishment: Increased from ₹3,98,304 to ₹4,63,389.

Udyam Registration Portal:
- Formalisation of MSMEs: 4.69 crore registrations as of 05 July 2024.
- Registration Process: Simple, online, and free based on self-declaration.
Credit Guarantee Fund:
- Union Budget 2023-24 Allocation: ₹9,000 crore to Credit Guarantee Fund Trust.
- Credit Facilitation: Aiming for an additional ₹2 lakh crore in credit with reduced costs.
- Growth: Significant increase in guarantees for MSMEs between FY20 to FY24.
Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme:
- Objective: Enhance manufacturing capabilities and exports for 14 key sectors.
- Outlay: ₹1.97 lakh crore.
- Investment and Impact (till May 2024):
- Reported Investment: Over ₹1.28 lakh crore.
- Production/Sales: ₹10.8 lakh crore.
- Employment Generation: Over 8.5 lakh (direct & indirect).
- Export Boost: ₹4 lakh crore.
- Key Sectors: Large-scale electronics manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and telecom & networking products.
One District One Product (ODOP) Initiative:
- Unity Mall Concept:
- Purpose: Promote and sell ODOPs.
- Locations: State capitals, prominent tourism centres, or financial capitals.
- PM-Ekta Malls:
- Objective: Link artisans with consumers.
- Marketplace Creation: Targeting domestic and foreign markets.
- ODOP Sampark Workshops:
- Collaboration Facilitation: Conducted in 15 states to foster collaboration between the Centre and local sellers.
- Indigenous Industry Revival: Aim to revive indigenous industries.
- Global Exposure: Showcased India’s unique products at G20 events during India’s G20 Presidency, providing visibility to artisans, sellers, and weavers on the global stage.
Conclusion:
- The Economic Survey 2023-24 underscores the importance of the MSME sector and highlights the significant impact of the PLI scheme on India’s manufacturing capabilities, exports, and employment.
- The initiatives such as the Udyam Registration portal and ODOP aim to formalise and promote MSMEs, driving economic growth and self-reliance (Aatmanirbhar Bharat).
6. DESPITE BEING ONE OF THE FASTEST-GROWING ECONOMIES IN THE WORLD, INDIA’S ANNUAL PER CAPITA CARBON EMISSION IS ONLY ABOUT ONE-THIRD OF THE GLOBAL AVERAGE
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2034915 )
| Context |
|

Analysis of the news:
Overview:
- India’s Per Capita Carbon Emission: About one-third of the global average despite being one of the fastest-growing economies.
- G20 Status: India is the only G20 nation on track to meet the 2-degree Celsius warming target.
Key Achievements:
- Early Achievement of NDC Targets:
- Electrical Power Capacity: Achieved 40% from non-fossil fuel sources in 2021, ahead of the 2030 target.
- Emission Intensity Reduction: Reduced GDP emission intensity by 33% from 2005 levels by 2019, nine years ahead of the 2030 target.
- Current Non-Fossil Power Share: 45.4% of installed electricity generation capacity is from non-fossil sources as of May 2024 (up from 32% in April 2014).
- Carbon Sink Creation: Created a carbon sink of 1.97 billion tonnes CO2 equivalent from 2005 to 2019; on track to create an additional 2.5 to 3.0 billion tonnes by 2030.
- Decoupling Economic Growth from Emissions:
- GDP Growth: CAGR of about 7% from 2005 to 2019.
- Emissions Growth: CAGR of about 4% during the same period.
- Result: Economic growth rate exceeds the growth rate of emissions, indicating successful decoupling.
- Adaptation Expenditure:
- Increase: Total adaptation-relevant expenditure rose from 3.7% of GDP in 2015-16 to 5.60% in 2021-2022.
Low Carbon Development and Energy Transition:
- Energy Needs Projection: Expected to grow 2 to 2.5 times by 2047.
- Energy Transition Challenges:
- Land and Water Demand: Expansion of renewable energy is land-intensive and increases demand for water.
- Battery Storage: Requires critical minerals, which are geographically concentrated.
- Energy Efficiency Initiatives:
- Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC): Applied to buildings.
- Standards and Labelling (S&L): For appliances.
- Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE) Initiative: Encourages sustainable lifestyles.
- Perform, Achieve, and Trade (PAT) Scheme: For the industrial sector.
- Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure: For the transport sector.
- Annual Savings and Emissions Reduction:
- Cost Savings: ₹1,94,320 crore.
- CO2 Emissions Reduction: Approximately 306 million tonnes.
Finance for Sustainable Development:
- Sovereign Green Bonds:
- January-February 2023: ₹16,000 crore issued.
- October-December 2023: ₹20,000 crore issued.
- RBI Initiatives:
- Green Deposits Framework: Encourages green finance.
- Priority Sector Lending (PSL) Rules: Promotes renewable energy.
Innovative Green Credit Program:
- Mission LiFE:
- Objective: Mass movement for climate change and sustainable living based on conservation and moderation.
- Green Credit Programme (GCP): Incentivizes environment-positive activities through green credits for individuals, communities, and businesses.
International Leadership:
- Key Initiatives Led by India:
- International Solar Alliance (ISA): Promotes solar energy.
- One World, One Sun, One Grid (OSOWOG): Facilitates a unified global solar grid.
- Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI): Enhances infrastructure resilience to disasters.
- Infrastructure for Resilient Island States (IRIS): Supports island nations in building resilient infrastructure.
- Leadership Group for Industry Transition (LeadIT): Encourages industrial transitions to low-carbon practices.
Conclusion:
- The Economic Survey 2023-24 highlights India’s remarkable progress in climate action, achieving key targets ahead of schedule, successfully decoupling economic growth from emissions, and leading several international climate initiatives. The emphasis on energy efficiency, sustainable finance, and innovative programs like Mission LiFE demonstrates India’s commitment to a low-carbon future and global climate leadership.

