10 October 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. RBI holds rate at 6.5%, shifts stance to ‘neutral’
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context |
|
RBI Shift to Neutral Stance:
- Neutral stance means RBI is neither inclined to hike nor cut interest rates in the near term.
- This shift from “withdrawal of accommodation” indicates flexibility to adjust rates depending on economic conditions.
- It reflects a balanced approach, where inflation is controlled, but growth support is also considered.
- A neutral stance allows the RBI to respond swiftly to changing inflation and growth dynamics without pre-commitment to a particular policy direction.
Reasons for the Shift:
- Moderating inflation: Headline inflation has decreased from its heightened levels in the past two years, providing room for policy adjustment.
- Balanced macroeconomic outlook: Both inflation and growth are currently stable, allowing flexibility in monetary policy.
- Resilient domestic growth: Sustained momentum in private consumption and investment supports the focus on inflation.
- Uncertainty in inflation trends: External factors like adverse weather events and geopolitical tensions may lead to volatility in inflation, requiring a cautious policy stance.
Potential Implications:
- Possible rate cut: A neutral stance opens the door for an interest rate cut if inflation remains under control and growth is stable.
- Focus on inflation management: The RBI will continue to monitor inflation closely and may intervene if inflationary pressures resurface.
- Growth support: By shifting to neutral, the RBI signals it is prepared to stimulate growth if needed while keeping inflation within the target.
- Market stability: A neutral stance can provide reassurance to markets, balancing expectations on interest rates and reducing volatility.
| Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) |
|
|
PYQ: Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)? (UPSC CSE 2017) It decides the RBI’s benchmark interest rates.It is a 12-member body including the Governor of RBI and is reconstituted every year. It functions under the chairmanship of the Union Finance Minister. Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only Ans: Option A |
| Practice Question: What does the Reserve Bank of India’s “neutral” monetary policy stance signify, and what implications does it have for the economy? (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Union Cabinet Extends Universal Fortified Rice Supply in Government Schemes Until 2028 to Combat Malnutrition
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 11)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance GS3– Science and Technology |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
What is Rice Fortification?

- Rice fortification is the process of enhancing rice with essential micronutrients such as iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12 to improve nutritional quality.
- With high malnutrition levels in India, particularly among women and children, fortifying rice, a staple food, is a key measure to address widespread anemia and nutritional deficiencies.
Process of Rice Fortification
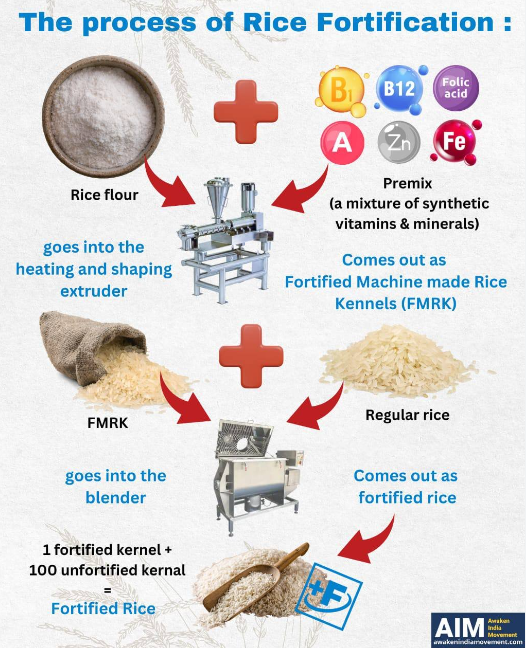
- Rice fortification involves technologies like coating, dusting, and extrusion. Extrusion is the preferred method in India, where rice flour is mixed with micronutrients and passed through an extruder to create fortified rice kernels (FRKs).
- These kernels are then blended with regular rice in a 1:100 ratio.
Consumption and Cooking of Fortified Rice
- Fortified rice is cooked and eaten like regular rice, retaining its physical properties and nutrient content after cooking.
- It is packaged with the logo ‘+F’ to indicate the addition of iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12.
Progress of the Rice Fortification Initiative
- Launched in 2015 and implemented in phases, the initiative has expanded across all districts, including high-stunting burden areas.
- As of March 2024, 406 lakh metric tonnes of fortified rice have been distributed.
- With a cost of Rs 2,700 crore per annum, it represents less than 2% of India’s annual food subsidy bill.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of rice fortification as a government initiative in addressing malnutrition in India. Evaluate the challenges and progress of the program since its inception. (150 words/10 m) |
3. Revolutionary AI Breakthrough in Protein Research Wins Nobel Prize in Chemistry
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 11)
| Topic: GS3– Science and Technology |
| Context: |
| The article discusses the 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry awarded for breakthroughs in using AI tools like AlphaFold to predict protein structures and create new synthetic proteins, advancing biological and medical research. |
Analysis of News:
Importance of Proteins in Life
- Proteins are fundamental to all living organisms, playing a crucial role in nearly every biological process.
- They are large and complex molecules composed of long chains of amino acids, responsible for functions such as speeding up biochemical reactions (enzymes), providing structural support, storing energy, and aiding immune responses. Life itself would be impossible without proteins.
Breakthrough in Protein Research
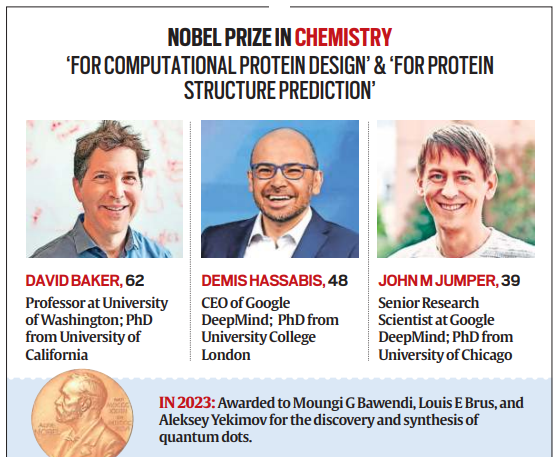
- This year’s Nobel Prize in Chemistry recognized David Baker, Demis Hassabis, and John Jumper for their revolutionary advancements in protein research.
- Their contribution differs from traditional discoveries, as they developed tools that significantly accelerate the process of determining protein structures and creating new proteins.
- These breakthroughs were achieved using artificial intelligence (AI) and computational tools, making structural prediction and protein synthesis far easier and more precise.
AlphaFold: AI-Powered Protein Prediction
- Hassabis and Jumper developed AlphaFold, an AI-based tool that predicts the three-dimensional structure of proteins using amino acid sequences.
- Previously, determining protein structures was a time-consuming process involving methods like x-ray crystallography.
- AlphaFold transformed this by using databases of known sequences and structures, achieving high accuracy in predictions and revolutionizing protein studies.
- This tool has gained widespread usage and undergone multiple upgrades since its inception.
Creating New Proteins
- David Baker utilized computational methods to design synthetic proteins not found in nature.
- These new proteins can perform functions that natural proteins cannot, such as breaking down non-biodegradable plastics.
- Baker’s method offers an efficient alternative to evolutionary approaches, which are time-consuming and require numerous mutations.
- This opens up exciting possibilities in areas like environmental protection and medical research.
Implications and Future Prospects
- The work of these scientists has far-reaching implications, particularly in drug discovery and treating diseases caused by protein malfunctions.
- The application of AI in chemistry and biology is becoming a critical area of research, and the Nobel Prize recognition highlights the transformative potential of such technological advancements.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of AI-based tools like AlphaFold in predicting protein structures and designing synthetic proteins. How can such breakthroughs contribute to advancements in biotechnology, healthcare, and environmental sustainability? (150 words/10 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. Ratan Tata, a titan of Indian industry, takes his final bow
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
About Ratan Tata:
- Ratan Tata led Tata Group from 1990 to 2012 and briefly returned as interim chairman in 2016.
- Under his leadership, Tata Group expanded globally with significant acquisitions such as Tetley, Jaguar Land Rover, and Corus Steel.
- He was known for reshaping the Tata Group into a global powerhouse while maintaining a focus on philanthropy.
- Post-retirement, Tata invested in multiple start-ups through RNT Associates.
- Philanthropy: He is known for championing causes like education, healthcare, and rural development through Tata Trusts
- He is recipient of India’s highest civilian honours, including the Padma Bhushan (2000) and Padma Vibhushan (2008)
- His influence extended beyond business, leaving an indelible mark on Indian industry and philanthropy.
2. CCS clears deals for 31 MQ-9B drones and submarines
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 8)
| Context |
| The Cabinet Committee on Security has approved the acquisition of 31 MQ-9B UAVs and the indigenous construction of two nuclear attack submarines (SSNs). This decision underscores India’s commitment to enhancing its defence capabilities across the three armed services. |


MQ-9B High Altitude Long Endurance (HALE) Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
- Altitude: Operate at altitudes above 18,000 feet.
- Endurance: Capable of flying for over 24 hours, allowing continuous surveillance and data collection.
- Applications: Used for intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance (ISR), and targeted strikes in military operations.
- Examples: The MQ-9B, also known as the Reaper, is a prominent HALE UAV.
- Features: Equipped with advanced sensors, cameras, and communication systems for real-time data transmission.
- Strategic Importance: Enhance situational awareness and operational capabilities without risking human life in combat zones.
Nuclear Attack Submarines (SSNs)
- Operational Role: They serve as a second-strike capability, ensuring a nation can retaliate after a nuclear attack.
- Indigenous Development: India has developed its SSBN fleet under the Advanced Technology Vessel (ATV) program, enhancing its nuclear triad.
- Current Fleet: The first operational SSBN, INS Arihant, was commissioned in 2016, followed by INS Arighaat in August 2023.
- Displacement: SSBNs typically displace around 6,000 to 7,000 tons, allowing for stealth and substantial weapon capacity.
- Range: Equipped with intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), they can strike targets over 5,000 kilometres away.
- Significance: SSBNs bolster India’s national security and strategic autonomy, deterring potential adversaries and ensuring regional stability.
3. HOW EVM BATTERIES WORK, HOW THEY ARE CHANGED
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 11)
| Context: |
| A delegation of Congress leaders approached the Election Commission of India (ECI), alleging discrepancies in the functioning of Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) during Haryana elections, particularly concerning battery levels in the devices. |
Analysis of News:

What is an Electronic Voting Machine?
- EVM is a device used to record votes electronically. They were first used in the Paravur Assembly Constituency of Kerala in the year 1982.
- Since 1998, the Election Commission has increasingly used EMVs instead of ballot boxes.
- In 2003, all state elections and by-elections were held using EVMs.
- Encouraged by this, in 2004, the Commission took a historic decision to use only EVMs for the Lok Sabha elections.
How EVM Batteries Function:
- Power Source: EVMs use battery power to operate, especially in remote areas without electricity. The Control Unit (CU) runs on 7.5-8 volts, while the Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT) has a 22.5-volt power pack.
- Battery Monitoring: The ECI system monitors battery levels, displaying statuses like “High,” “Medium,” “Low,” and “Change Battery,” based on voltage. A battery is replaced if it drops to “Change Battery” status, i.e., below 5.8 volts.
- Lifespan: Battery life varies based on the number of votes cast, mock polls, and vote tallying during the election process.
Battery Change Protocol:
- First-Level Checks: EVMs are equipped with new batteries before elections during the first-level check, in the presence of political party representatives.
- Mock Poll Replacement: If battery issues arise during the mock poll on election day, the power pack is changed under the supervision of polling agents.
- Documentation: A report detailing any battery change, including the control unit’s unique ID and signatures of polling agents, is submitted by the presiding officer to the ECI.
4. Global Wildlife Populations Plummet by 73% in 50 Years Due to Habitat Loss, Climate Change, and Invasive Species: WWF Report
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 10)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Ecosystem-Specific Declines
- The report highlights that freshwater ecosystems experienced the highest decline, with an 85% reduction in populations.
- Terrestrial populations fell by 69%, and marine populations by 56%.
- The major drivers behind this decline include habitat loss due to unsustainable agriculture, deforestation, mining, and other human activities, as well as overexploitation, climate change, pollution, and diseases.
Impacts on Ecosystem Functions
- As populations dwindle, species are unable to fulfill their roles within ecosystems, such as seed dispersal, pollination, and nutrient cycling.
- The report warns that the continued decline of wildlife could push ecosystems to tipping points, with potentially irreversible consequences.
India’s Vulture Crisis
- In India, WWF draws attention to the sharp decline of three vulture species—the white-rumped vulture, Indian vulture, and slender-billed vulture.
- These species are facing severe population declines, which could further disrupt local ecosystems and biodiversity.
| World Wildlife Fund for Nature |
|
5. Over 95% of Indian Households Own Mobile Phones, But Only 9.9% Have Computers: MoSPI Survey
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Economy; Page: 17)
| Context: |
| The article highlights the widespread mobile phone ownership in India contrasted with low computer penetration and regional disparities in education levels, based on the 2022-23 MoSPI survey. |
Analysis of News:
Digital Access in Indian Households
- The Comprehensive Annual Modular Survey 2022-23, released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI), shows that over 95% of households in India possess a telephone or mobile phone.
- However, only 9.9% of households have a computer, including desktops and laptops.
- The urban-rural divide is evident, with 21.6% of urban households owning computers compared to just 4.2% in rural areas.
- Among states and union territories, Delhi leads in computer ownership (27.8%), followed by Sikkim, Mizoram, Kerala, and Nagaland.
Mobile Phone Ownership
- Chandigarh stands out, with 100% of households possessing a mobile phone or telephone. Other regions with over 99% phone ownership include Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Kerala, and Ladakh, reflecting the near-universal penetration of mobile technology across the country.
Educational Attainment
- In terms of formal education, Goa, Manipur, Delhi, Puducherry, Lakshadweep, Sikkim, and Kerala have the highest mean years of schooling.
- Nationally, individuals aged 15 years and above have an average of 8.4 years of formal schooling.
- Goa leads with 12.1 mean years of schooling, with males averaging 13 years and females 11.1 years. Manipur, Delhi, and Puducherry follow closely behind.
Gender Gap in Education
- The survey highlights a significant gender gap in educational attainment, particularly in Goa, where males have two more years of formal schooling than females.
- Other states such as Manipur and Kerala show similar trends, though the gap varies across regions.
6. EXERCISE MALABAR 2024 – OPENING CEREMONY
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2063584®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
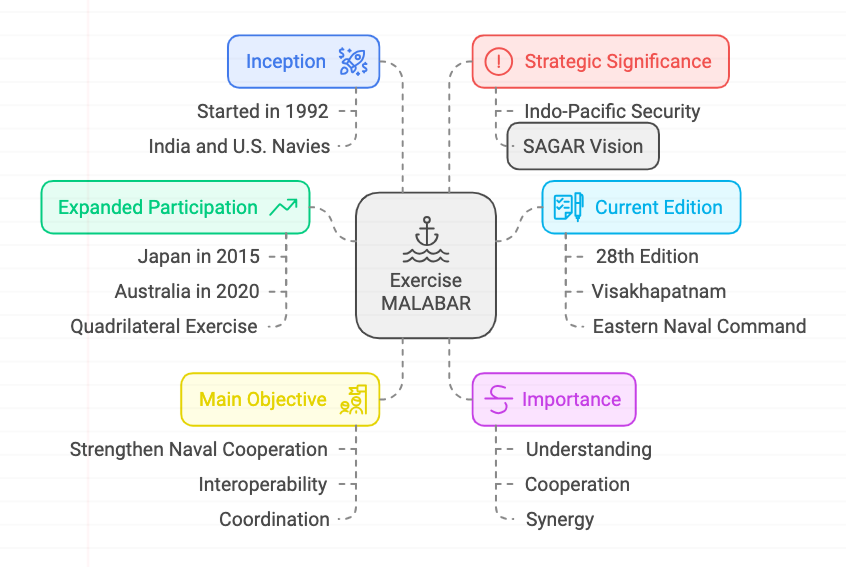
Exercise MALABAR:
- Inception: Started in 1992 as a bilateral exercise between the Indian and U.S. navies.
- Expanded Participation: Japan became a permanent member in 2015, and Australia joined in 2020, making it a quadrilateral maritime exercise involving India, the USA, Japan, and Australia.
- Current Edition: The 28th edition, hosted by India’s Eastern Naval Command at Visakhapatnam.
- Main Objective: Strengthen naval cooperation, interoperability, and coordination among participating nations to address common maritime challenges.
- Strategic Significance: Promotes regional security in the Indo-Pacific, aligned with India’s vision of Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR).
- Importance: Enhances understanding, cooperation, and synergy between participating navies, improving their ability to operate jointly for maintaining regional maritime security.
- Multilateral Focus: Reflects the growing defence cooperation among Quad nations, addressing evolving geopolitical and security dynamics in the Indo-Pacific.
7. PM E-DRIVE Scheme: Driving Towards a Greener Future
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2063515®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
PM E-DRIVE Scheme Overview
| Feature | Details |
| Duration | October 1, 2024 – March 31, 2026 |
| Objective | Accelerate EV adoption, establish charging infrastructure, boost EV manufacturing |
| Financial Outlay | Rs. 10,900 crore |
| Target Vehicles | E-2 wheelers (24.79 lakh), e-3 wheelers (3.2 lakh), e-ambulances, e-trucks, e-buses |
| Subsidies | Demand incentives for EVs with advanced batteries; excludes government-owned EVs |
| Charging Infrastructure | Rs. 2,000 crore allocated for 72,300 charging stations, including fast chargers |
| Impact | Reduces pollution, promotes green mobility, enhances EV manufacturing, creates employment opportunities |
| PYQ: The adoption of electric vehicles is rapidly growing worldwide. How do electric vehicles contribute to reducing carbon emissions and what are the key benefits they offer compared to traditional combustion engine vehicles? (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2023) |



