25 October 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Union Cabinet Approves Rs 1,000-Crore Venture Fund to Propel India’s Space Start-up Ecosystem
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 12)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context: |
| The Union Cabinet has sanctioned a Rs 1,000-crore venture capital fund aimed at supporting 30-35 space start-ups over the next five years, intending to stimulate private investment and innovation within India’s space sector. |
Analysis of News:

What is Venture Capital Fund?
- Venture capital is a type of funding that provides funds to start-ups or, emerging companies in exchange for equity. Read here to learn about venture capital and venture debt.
- Venture capital (VC) refers to a type of private equity financing that venture capital firms or funds offer to startups, early-stage, and emerging businesses that have shown a high growth trajectory (either in terms of annual revenue or staff count) or are deemed to have high growth potential.
- These businesses are funded by venture capital firms or funds in return for equity, or a share of the business.
- Large organizations like pension funds, university endowments, and affluent individuals are usually the investors in venture capital firms.
Focus on Commercialisation and Early-Stage Support
- The fund will target start-ups that have developed a proof of concept but need support for commercialisation.
- Early-stage backing is critical for these companies, as timely funding can significantly enhance their chances of success.
- Funding levels will vary from Rs 10 to Rs 60 crore based on the start-up’s growth, stage, and potential to contribute to national space capabilities.
Driving India’s Global Space Market Presence
- Aligned with India’s ambition to capture a larger portion of the global space market, this initiative could help the domestic space industry grow from its current USD 8.4 billion valuation to USD 44 billion.
- Since 2020’s space sector liberalisation, 250 space start-ups have emerged, a number expected to rise with this venture fund.
- The initiative will also generate thousands of jobs, create supply chains, and develop manufacturing and technical capabilities.
Scope for Innovation and Economic Impact
- The fund will promote advancements in satellite and launch vehicle technology, expand space applications, and further space sector reforms, positioning India’s ecosystem on par with other major space-faring nations.
Structured and Professionally Managed Funding Approach
- Following an alternative investment fund structure regulated by SEBI, the fund will be professionally managed, deploying Rs 150 crore in the first year and progressively increasing over time.
- According to the Indian Space Association, this funding will not only aid start-up growth but also attract investors, marking a significant step toward bolstering India’s space start-up ecosystem.
| Practice Question: Examine the role of government-backed venture capital in fostering innovation within India’s space start-up ecosystem. Discuss how such funding initiatives could help India capture a larger share of the global space market and enhance national space capabilities. (250 words/15 m) |
2. India Achieves Milestone in Great Indian Bustard Conservation with First Chick Born through Artificial Insemination
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 12)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Conservation |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
What is the Great Indian Bustard?
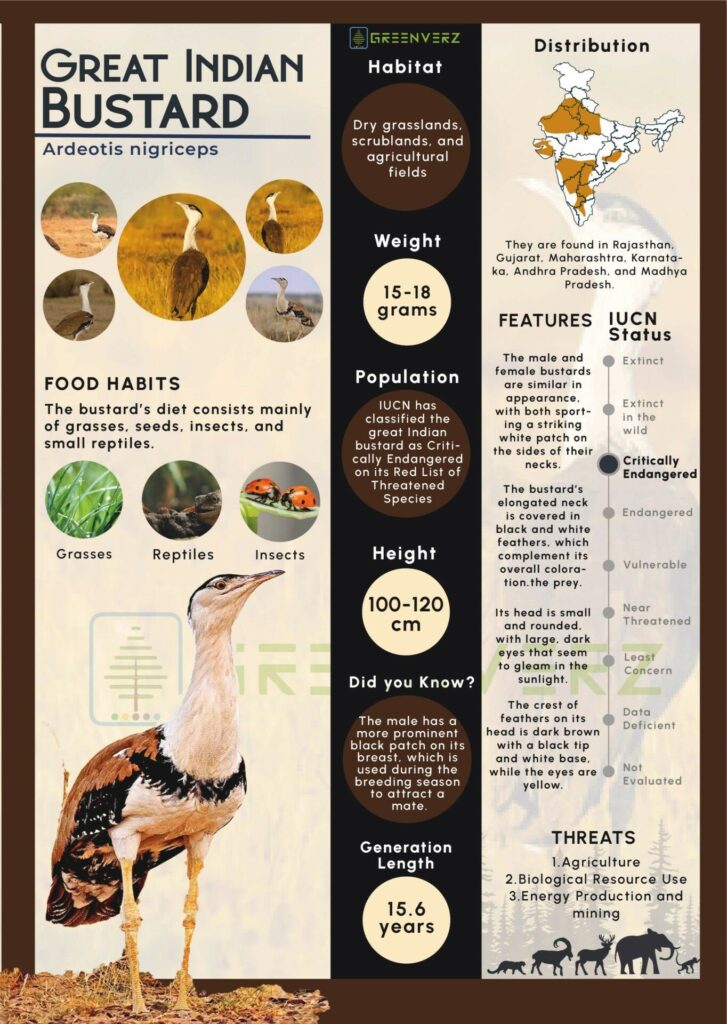
- The Great Indian Bustard (Ardeotis nigriceps), the State bird of Rajasthan, is considered India’s most critically endangered bird.
- It is considered the flagship grassland species, representing the health of the grassland ecology.
- Its population is confined mostly to Rajasthan and Gujarat. Small populations occur in Maharashtra, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES): Appendix 1
- Convention on Migratory Species (CMS): Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
Learning from Global Efforts
- The artificial insemination method was adapted from the International Fund for Houbara Conservation in Abu Dhabi, where similar techniques have been successfully applied.
- Indian researchers from the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) trained in these methods to enhance GIB conservation efforts.
Threats to GIB Population and Habitat
- The GIB population faces multiple threats, including predation of eggs, habitat destruction due to human encroachment, and fatal collisions with power lines.
- A 2020 WII study indicated that around 84,000 birds, including GIBs, die annually in GIB habitats due to power lines, primarily because GIBs have narrow frontal vision.
- The Supreme Court mandated underground power lines in the GIB habitat in 2021, although the feasibility of this measure remains under review.
Conservation Initiatives and Future Challenges
- The GIB breeding programme initiated in 2019 aims to release captively bred birds into the wild. However, experts highlight the long-term nature of this effort, estimating it may take 25 years to develop a self-sustaining population.
- Wildlife biologist experts underscores that habitat protection remains critical, as GIB nesting practices make them vulnerable.
- Without preserving and rehabilitating wild habitats, artificial insemination efforts alone may be insufficient to prevent the species’ decline.
| What Steps are Being Taken to Conserve the GIB? |
|
Species Recovery Programme:
Firefly Bird Diverters:
Artificial Hatching:
National Bustard Recovery Plans:
Conservation Breeding Facility:
Project Great Indian Bustard:
|
|
PYQ: Which one of the following groups of animals belongs to the category of endangered species? (2012) (a) Great Indian Bustard, Musk Deer, Red Panda and Asiatic Wild Ass (b) Kashmir Stag, Cheetal, Blue Bull and Great Indian Bustard (c) Snow Leopard, Swamp Deer, Rhesus Monkey and Saras (Crane) (d) Lion-tailed Macaque, Blue Bull, Hanuman Langur and Cheetal Ans: (a) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the successful artificial insemination of the great Indian bustard in conservation efforts. What are the key challenges that still need to be addressed to ensure the long-term survival of this critically endangered species? (250 words/15 m) |
3. India, Germany discussing military logistics support agreement: official
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral Relations |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- India and Germany are close to finalising a memorandum of arrangement for logistics cooperation between their armed forces.
- The arrangement aims to enhance maritime security cooperation, including posting a liaison officer at the Indian Navy’s Information Fusion Centre in Gurugram.
- The agreement will facilitate joint exercises and may support co-development and co-production initiatives in defence.
- Key focus areas include underwater technology, cruise missiles, and drones.
- Germany seeks to establish repair and maintenance capabilities for its ships in India.
- A significant number of export licences have been granted to deepen defence collaboration since June 2023.
- Both countries plan to sign a peacekeeping training agreement and explore further cooperation.
| What is a Logistics Support Agreement? |
India’s LSAs:
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the logistics support agreement between India and Germany in enhancing defence cooperation. How can such agreements help in co-development of defence technologies? (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. Trachoma eliminated as a public health problem in India; what next?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health |
| Context |
|
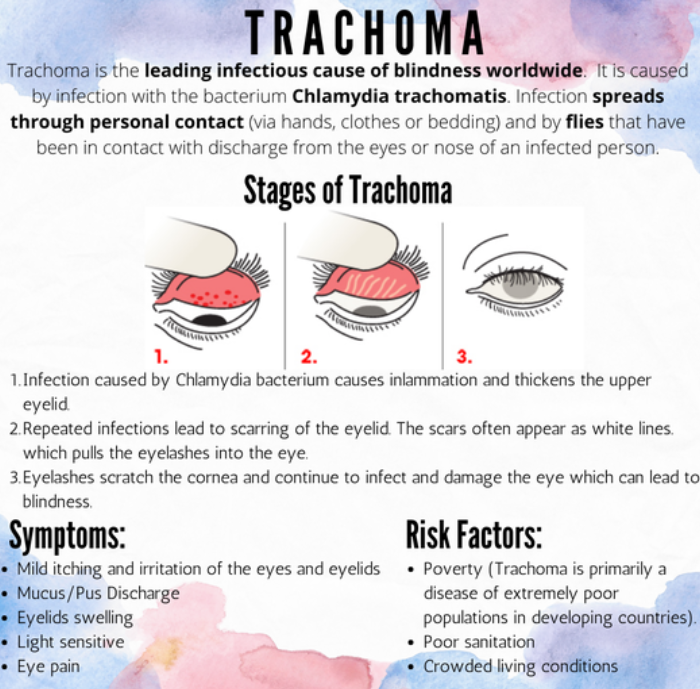
What is Trachoma?
- Trachoma is a chronic infectious eye disease caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis.
- It primarily affects young children and women in areas with poor hygiene, sanitation, and limited access to clean water.
- The disease leads to symptoms like eye irritation, discharge, swollen eyelids, and, in severe cases, blindness due to scarring of the inner eyelid.
Impact of Trachoma in India
- Trachoma was responsible for about 4% of all blindness cases in India in 2005.
- It imposes an estimated economic loss of $2.9 to $5.3 billion annually due to reduced productivity associated with blindness and visual impairment.
- Trachoma’s transmission is exacerbated by poor living conditions and hygiene practices, particularly in northern states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh.
Elimination of Trachoma in India
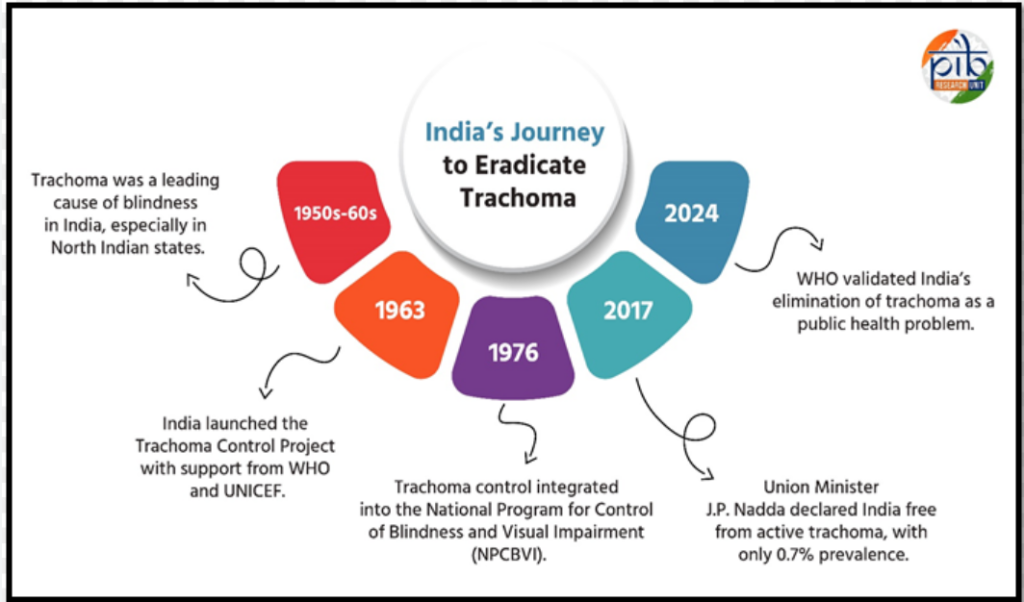
- India has achieved the elimination of trachoma as a public health problem, with a prevalence of 0.7%.
- The WHO’s SAFE strategy (Surgery, Antibiotics, Facial cleanliness, and Environmental improvements) has been instrumental in this success.
- Despite this achievement, sporadic cases may still exist, necessitating ongoing surveillance and health education to maintain the elimination status and prevent resurgence.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of eliminating trachoma as a public health problem in India. What strategies have been employed to achieve this? (150 Words /10 marks) |
PRELIMS FACTS
1. UN Report Warns of Rising Emissions: China and India Contribute to Growing Climate Crisis
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 12)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Threats to Global Temperature Targets
- The Emissions Gap Report, an annual publication from the UN Environment Programme, warns that the goal of keeping global temperature rise within 1.5 degrees Celsius is at risk of being unattainable within a few years.
- Furthermore, even the 2 degrees Celsius threshold is in jeopardy unless countries significantly intensify their efforts to reduce emissions.
Current Climate Actions Fall Short
- The report indicates that existing climate initiatives, even under optimistic conditions, might only reduce global greenhouse gas emissions by 10% by 2030 compared to 2019 levels.
- However, a reduction of 42% is needed to maintain the 1.5-degree target. To remain on track, reductions must escalate to 57% by 2035.
- A drastic turnaround, with annual reductions of at least 7.5%, is critical to keep the 1.5-degree goal achievable.
Financial Investment Needed for Emission Reductions
- To bridge the emissions gap for 2030 and 2035, the report advocates for a substantial increase in investment, estimating a cost of US$ 200 per ton of CO2 equivalent.
- Such investments could potentially eliminate 31 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent annually by 2030, exceeding the nearly 28 billion tonnes required to meet the 1.5-degree target.
Upcoming Climate Conference and Call for Urgent Action
Climate activists emphasize the urgency of the findings, stating that political inaction is leading to irreversible damage, as every fraction of fossil fuel emissions pushes the planet closer to a climate catastrophe.
In three weeks, nations will convene at the annual climate conference in Baku to discuss significantly increasing financial resources for climate action.
2. Satellites tracking Cyclone Dana since October 20: ISRO
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Context |
|
EOS-06:
- Launch Date: November 26, 2022
- Type: Earth Observation Satellite (EOS) developed by ISRO
- Purpose: Designed to monitor weather patterns, including cyclones, rainfall, and ocean winds
- Key Features: Equipped with a Scatterometer sensor for assessing wind speed and direction over oceans
- Significance: Enhances disaster management and environmental monitoring capabilities in India
- Orbit: Positioned in a sun-synchronous orbit for consistent observations
INSAT-3DR:
- Launch Date: INSAT-3DR was launched on September 8, 2016.
- Type: Geostationary satellite primarily for meteorological and search-and-rescue operations.
- Purpose: Provides real-time data on weather patterns, climate monitoring, and disaster management.
- Significance: Enhances weather forecasting accuracy and supports emergency response during natural disasters.
- Orbit: Maintains a fixed position over the Indian subcontinent for continuous monitoring.
| Cyclone Dana |
|
3. Justice Sanjiv Khanna appointed next CJI, to take oath on Nov. 11
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
Appointment of Chief Justice of India
- The seniormost Judge of the Supreme Court is appointed as Chief Justice.
- The outgoing Chief Justice recommends the next Chief Justice to the Union Minister of Law.
- If fitness is in doubt, consultation with other Judges is required.
- The Union Minister presents the recommendation to the Prime Minister, who advises the President for appointment.
Appointment of Judges of the Supreme Court
- The Chief Justice initiates the proposal for filling vacancies.
- Recommendations are made in consultation with the collegium of four seniormost Judges.
- The incoming Chief Justice, if not in the collegium, joins the selection process.
- The views of the seniormost Judge from the relevant High Court are sought.
- Written opinions from the collegium and the concerned Judge are submitted to the Government.
- The Union Minister presents these recommendations to the Prime Minister, who advises the President for appointment.
4. SINGAPORE INDIA MARITIME BILATERAL EXERCISE (SIMBEX) 2024 – 23 TO 29 OCT 24
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
| The Singapore India Maritime Bilateral Exercise (SIMBEX) is set to start from October 23 to 29, 2024, in VisakhapatnamThis exercise aims to enhance interoperability and address common maritime challenges in the region. |
Singapore India Maritime Bilateral Exercise (SIMBEX):
- History: SIMBEX originated as ‘Exercise Lion King’ in 1994 and has evolved into a key maritime collaboration between the Indian Navy and Republic of Singapore Navy.
- Structure of 2024 Exercise: The exercise consists of two phases:
- Harbour Phase (October 23-25): Includes Subject Matter Expert Exchanges, cross-deck visits, sports, and pre-sail briefings.
- Sea Phase (October 28-29): Features advanced naval drills, live weapon firings, anti-submarine warfare training, and tactical maneuvers.
- Participants: Participants include the Republic of Singapore Navy Ship RSS Tenacious and the Indian Navy.



