12 December 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Opposition plans motion to impeach Uttar Pradesh judge
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
Removal of High Court Judges in India
Grounds for Removal:
- Proved misbehavior or incapacity.
- Misuse of office, grave offenses undermining a judge’s integrity.
- Contravention of the Constitution’s provisions.
Procedure:
- Motion: 100 members of Lok Sabha or 50 members of Rajya Sabha can raise a motion for removal.
- Admission: The Speaker/Chairman decides whether to admit the motion.
- Inquiry Committee: If admitted, an Inquiry Committee is formed, comprising:
- A Supreme Court Judge
- A High Court Chief Justice
- A distinguished jurist
- Investigation: The committee investigates the charges against the judge.
- Report: The committee submits its report to the Speaker/Chairman.
- Parliamentary Consideration: If the committee finds the judge guilty, the motion is considered by each House of Parliament.
- Special Majority: Removal requires a special majority:
- Majority of the total membership of that House.
- Majority of not less than two-thirds of members present and voting.
- Presidential Order: After the address is passed by both Houses, the President issues an order for the judge’s removal.
| Practice Question: The process for removal of High Court judges in India, though enshrined in the Constitution, is often perceived as complex and challenging. Critically analyze this statement, highlighting the key procedural hurdles and their implications for judicial accountability. (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. Climate impact of exploring space passing below the radar
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
The Environmental Cost of Space Exploration
- The increasing reliance on space technology for vital functions like climate monitoring necessitates urgent action to address the environmental impact of space activities.
- The growing number of satellites in orbit and the frequency of rocket launches contribute to atmospheric pollution and the accumulation of orbital debris, posing risks to the sustainability of space activities and our ability to monitor Earth’s climate.

| How Rockets Affect the Environment |
|
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Rockets release CO2, black carbon, and other greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change. Black carbon is particularly harmful due to its high sunlight absorption. Ozone Layer Depletion: Some rocket propellants contain chlorine-based chemicals that damage the ozone layer, increasing our exposure to harmful UV radiation. Atmospheric Pollution: Solid rocket boosters release chlorine and aluminum oxide, which can linger in the atmosphere and potentially contribute to ozone depletion. Space Debris: Inactive satellites, spent rocket stages, and fragments from collisions pose a risk of collision with active satellites and spacecraft. Resource Depletion: Manufacturing rockets and satellites requires significant resources and energy, contributing to environmental strain on Earth. Light and Noise Pollution: Rocket launches generate significant light and noise pollution, affecting local communities and wildlife. Impact on Upper Atmosphere: Rocket exhaust plumes can create artificial clouds and alter the chemical composition of the upper atmosphere. |
| Dangers of Orbital Debris |
|
Collision Risks: Space junk, including defunct satellites and fragments from collisions, poses a significant collision risk to operational satellites. Magnitude: Over 36,860 objects are in orbit, including debris from over 650 fragmentation events. The total mass exceeds 13,000 tonnes. Impact on Data Collection: Debris can interfere with instruments used to collect data about Earth, hindering weather monitoring and scientific research. Increased Mission Costs: Avoiding collisions requires costly maneuvers and shielding, increasing the expense of space missions. Risk to Human-crewed Missions: Debris poses a risk to the International Space Station, which frequently adjusts its orbit to avoid collisions. |
Barriers to Space Sustainability
- Lack of International Regulations: The absence of specific international regulations addressing the environmental impact of space activities hinders efforts to mitigate emissions, manage debris, and ensure responsible use of space. This regulatory gap needs to be addressed to promote sustainable practices.
- Technological Challenges: Solutions like reusable rockets, cleaner fuels, biodegradable materials, and debris removal technologies hold promise but face challenges related to cost, efficiency, and technological maturity. Overcoming these challenges requires further research and development.
Achieving Sustainability
- Global Cooperation: International cooperation is crucial to establish enforceable standards for emissions, debris mitigation, and data sharing. Organizations like the Committee on the Peaceful Use of Outer Space (COPUOS) can play a vital role in developing and implementing these standards.
- Investment in Green Technologies: Governments and private companies must prioritize funding for research and development of sustainable technologies, including green propellants, debris removal systems, and biodegradable materials for satellites.
- Policy Incentives: Financial incentives, such as subsidies and tax breaks, can encourage private companies to adopt sustainable practices. Conversely, penalties can discourage unsustainable behavior.
Conclusion
- The future of space exploration depends on our ability to balance technological advancement with environmental responsibility.
- By promoting international cooperation, investing in green technologies, and implementing effective regulations, we can ensure that space activities remain sustainable.
| PYQ: What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2019) |
| Practice Question: Analyze the environmental challenges posed by the growing reliance on space technology. Discuss the role of international cooperation and technological advancements in ensuring the sustainable exploration and utilization of outer space. (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. Stagnant Wages and Slowing Growth: Addressing India’s Economic Imbalance
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page: 01)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
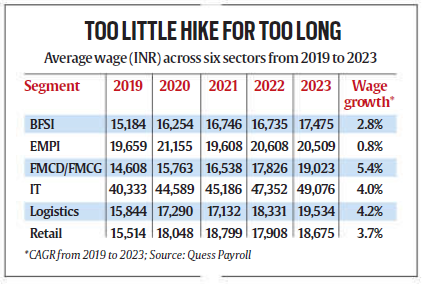
Real Wage Decline and Inflationary Pressures
- Real wage growth, when adjusted for inflation, has been stagnant or negative, exacerbating workers’ financial struggles.
- With retail inflation consistently high over five years, wage stagnation has led to reduced purchasing power, impacting consumption levels and slowing recovery to pre-pandemic economic activity.
Wage Growth Across Sectors
- The FICCI-Quess report highlights wage disparities among sectors. IT wages averaged the highest at ₹49,076 in 2023, while FMCG wages were the lowest at ₹19,023.
- Growth rates varied, with logistics and IT sectors seeing moderate increases (4.2% and 4%, respectively), but these gains remain insufficient to counter inflation.
Corporate Profitability vs. Wage Allocations
- Corporate profitability reached a 15-year high at 4.8% of GDP in 2024, yet staff costs have declined, with non-managerial compensation dropping sharply.
- Experts warn that this imbalance between capital and labor income weakens demand, creating a self-destructive cycle for businesses reliant on consumer spending.
Broader Challenges: Productivity and Job Quality
- Economists attribute slow wage growth to low labor productivity, surplus labor, and underemployment.
- India’s workforce faces a lack of quality jobs, with nominal wages declining as bargaining power diminishes.
- Raising productivity is seen as the key to sustainable wage growth and economic expansion.
Informal Sector Vulnerabilities
- Experts argue that wage stagnation disproportionately affects the informal sector, where job creation remains inadequate.
- While formal sector companies maintain consistent salary increments, the informal sector struggles with low wages and employment instability, highlighting the need for workforce formalization and targeted policy interventions.
Path Forward: Enhancing Productivity and Job Creation
- Raising labor productivity and promoting employment-generating sectors such as textiles and tourism are critical.
- Policymakers must focus on creating quality jobs, balancing wage and profit growth, and formalizing the workforce to ensure broad-based economic recovery and sustainable consumption growth.
| Practice Question: The sharp slowdown in wage growth despite rising corporate profits has raised concerns about subdued demand and inequality in India’s economic recovery. Discuss the factors contributing to stagnant wages and suggest measures to balance wage growth, labor productivity, and economic expansion. (250 words/15 m) |
4. Maternal Challenges and Infanticide in Captive Big Cats: Understanding Behavioral Complexities
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Topic: GS3 – Environment |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Infanticide in Mythology
- Infanticide has long been a theme in human history and mythology.
- Examples include the ancient Spartans abandoning weak infants and Greek myths like Cronus devouring his children, showcasing parallels between human narratives and animal behavior driven by survival instincts.
Infanticide in the Animal Kingdom
- Infanticide among animals often stems from resource management or territorial dynamics.
- Male cats kill rival offspring to secure their lineage, while mothers may selectively kill weak cubs to allocate resources more effectively.
- These behaviors reflect survival strategies rather than emotional decisions.
Resource Allocation and Maternal Challenges
- Mothers in both the wild and captivity may reject or kill weaker cubs to focus on stronger offspring.
- Hormonal imbalances, inexperience, or stress can exacerbate this behavior. Instances across Indian and international zoos reveal patterns of abandonment, accidental injuries, and outright infanticide driven by maternal anxiety or environmental factors.
Stress and Environmental Factors
- Captivity introduces stressors that amplify maternal insecurity. Changes in familiar routines or sudden environmental shifts can provoke extreme protective instincts, often leading to fatal consequences for cubs.
- Examples from Hyderabad and Antwerp zoos underscore how stress impacts maternal decisions.
Misinterpretations of Animal Behavior
- Humans often misjudge animal behavior through emotional or anthropomorphic lenses.
- Infanticide in the wild or captivity is sometimes a survival tactic, such as consuming dead cubs to regain energy or removing carcasses to protect living cubs from predators.
- Understanding these actions requires a shift away from human-centric interpretations.
Conclusion
- Infanticide among animals, particularly in captivity, reflects complex biological and environmental factors rather than cruelty.
- Addressing such incidents calls for improved management practices in zoos, better understanding of animal behavior, and the creation of stress-free environments to mitigate risks to offspring.

| What are the Conservation Efforts of Big Cats in India? |
|
| Practice Question: Infanticide among captive animals, especially in zoos, is often driven by resource management, hormonal imbalances, and environmental stress. Discuss the factors contributing to such behavior in animals and the implications for zoo management and conservation efforts. (250 words/15 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. Indian scientists develop novel gene therapy for haemophilia
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 1)
| Context |
|
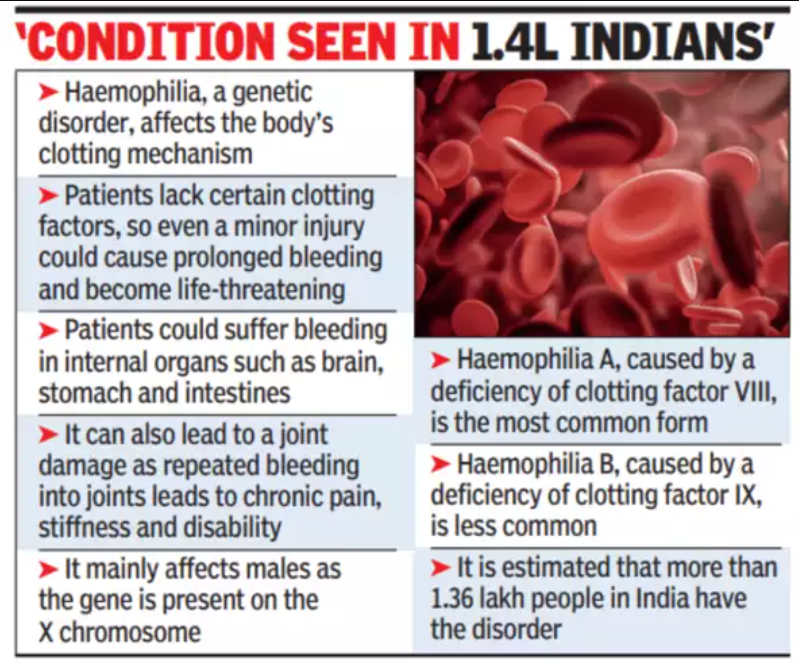
Analysis of the news:
- Gene therapy trial in India successfully treats severe hemophilia A, a bleeding disorder.
- Five patients treated in Tamil Nadu have remained free of bleeding episodes for over a year. Typically, these patients experienced frequent, potentially fatal bleeds.
- This gene therapy could be a one-time solution for hemophilia A, unlike current treatments requiring frequent injections.
- The new approach is safer than traditional methods and may be suitable for children.
- It could lead to more affordable treatment in India, where conventional hemophilia care is very expensive.
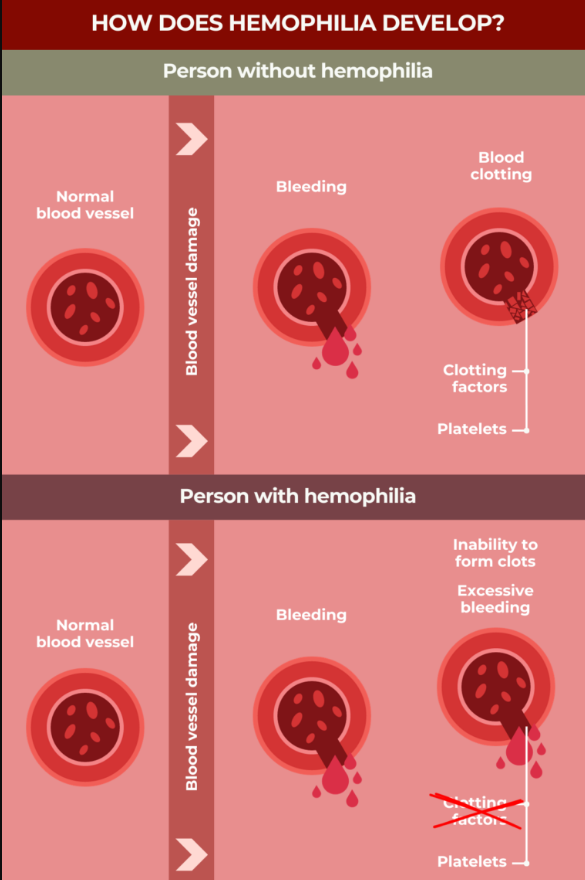
What is the new therapy?
- Target: Addresses the root cause of severe hemophilia A by providing a functional copy of the faulty gene that prevents the body from producing a crucial blood clotting factor (Factor VIII).
- Delivery: Uses a harmless carrier, or vector, to deliver the therapeutic gene into the patient’s body. This vector is likely a modified virus that cannot cause disease.
- Production: Once inside the body, the gene instructs the patient’s cells to produce Factor VIII, enabling normal blood clotting.
- One-time treatment: This approach aims to be a one-time solution, unlike current treatments that require regular injections of clotting factors.
- Safer alternative: The specific vector used in this trial is believed to be safer than traditional adenovirus-based vectors, potentially making it suitable for children as well.
| Hemophilia A |
|
Genetic disorder: Hemophilia A is typically inherited, caused by a faulty gene on the X chromosome. Blood clotting deficiency: Leads to a deficiency in Factor VIII, a protein essential for blood clotting. Bleeding episodes: People with hemophilia A experience prolonged or excessive bleeding, even from minor injuries. Severity: Ranges from mild to severe, depending on the level of Factor VIII in the blood. Treatment: Traditionally managed with frequent injections of Factor VIII to prevent or stop bleeding. Prevalence: A rare disorder, but India has a significant number of patients. Complications: Can include joint damage, internal bleeding, and life-threatening hemorrhages. |
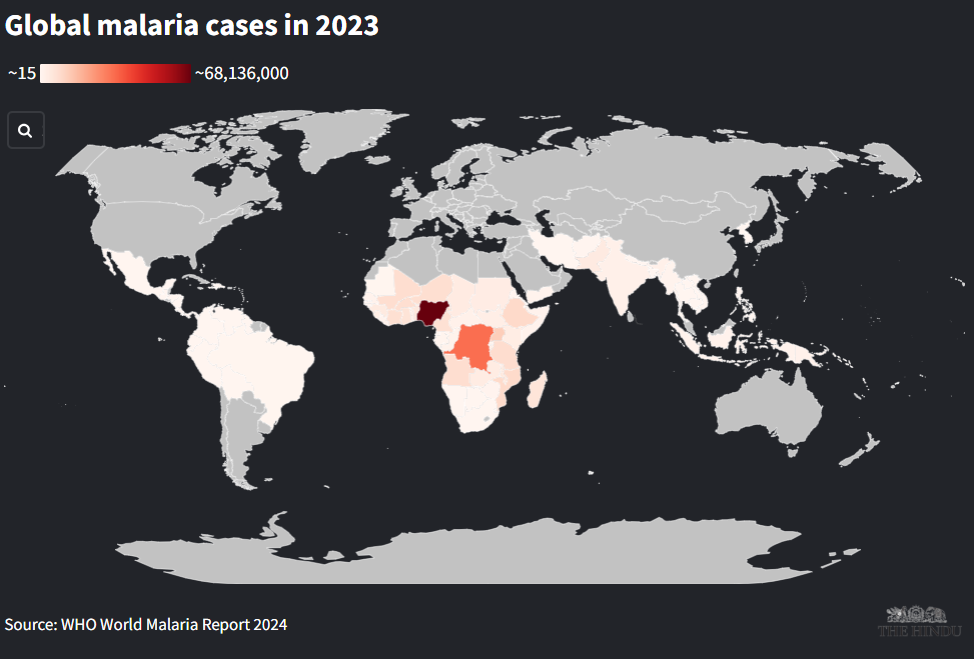
2. India accounts for half of malaria cases in Southeast Asia in 2023
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 6)
| Context |
|

World Malaria Report for 2024:
- Global malaria cases and deaths plateaued in 2023 after years of decline.
- The WHO South-East Asia Region has significantly reduced its malaria burden since 2000.
- India and Indonesia account for most malaria cases and deaths in the region.
- Four countries in the region successfully reduced malaria cases in 2022-2023.
- Three countries saw increases in malaria cases during the same period: Democratic People’s Republic of Korea, Thailand, Myanmar.
- Timor-Leste and Bhutan reported zero indigenous malaria cases in 2023.
- India’s progress has significantly contributed to the region’s achievements.
- Despite global progress, malaria remains a major health concern, especially in Africa.
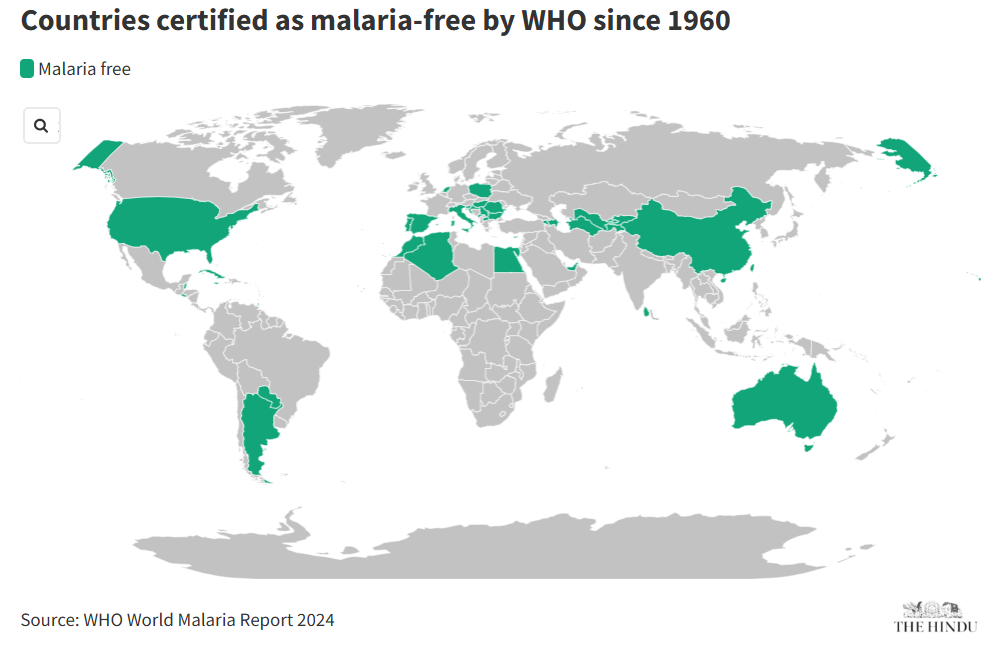
- 44 countries and one territory are now certified malaria-free.
3. Webb confirms the cosmos is expanding at unexpected rate
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has confirmed previous Hubble observations showing the universe is expanding faster than expected. This discrepancy is called the Hubble Tension.
- JWST’s findings, based on two years of data, rule out the possibility of Hubble’s measurements being flawed.
- The expansion rate is about 8% faster than predicted by current cosmological models.
- Scientists suspect the anomaly may be due to unknown factors related to dark energy and dark matter, which make up 96% of the universe.
- Dark matter is invisible but its gravitational effects are observed on visible matter.
- Dark energy is thought to counteract gravity and drive the universe’s accelerating expansion.
- Possible explanations for the discrepancy include exotic properties of dark matter, dark energy, neutrinos, or gravity itself.
- The findings suggest a potential need to revise our understanding of the universe and its evolution.
| Telescopes |
|
James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) Launch Date: December 25, 2021Location: Orbits the Sun about 1.5 million kilometers from Earth Type: Infrared telescope Key Features: 6.5-meter segmented primary mirror, sunshield for passive cooling, high sensitivity infrared instruments Mission: Observe the first stars and galaxies formed after the Big Bang, study the formation and evolution of galaxies, stars, and planetary systems, analyze the atmospheres of exoplanets. Significance: Largest and most powerful space telescope ever built, providing unprecedented resolution and sensitivity in the infrared spectrum. Hubble Space Telescope Launch Date: April 24, 1990 Location: Low Earth orbit, about 540 kilometers above Earth Type: Optical and ultraviolet telescope Key Features: 2.4-meter primary mirror, serviced and upgraded by astronauts five times Mission: Observe distant galaxies, stars, and planets; study the expansion of the universe; investigate the birth and death of stars; analyze the composition of celestial objects. Significance: Helped astronomy with its images and groundbreaking discoveries, providing crucial data for understanding the universe’s history and evolution. |
4. Ghost Guns: The Untraceable Threat Challenging US Gun Control
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Context: |
| The article examines the growing prevalence of untraceable ghost guns in the US, their legal ambiguities, and the challenges they pose to law enforcement and public safety. |

Analysis of News:
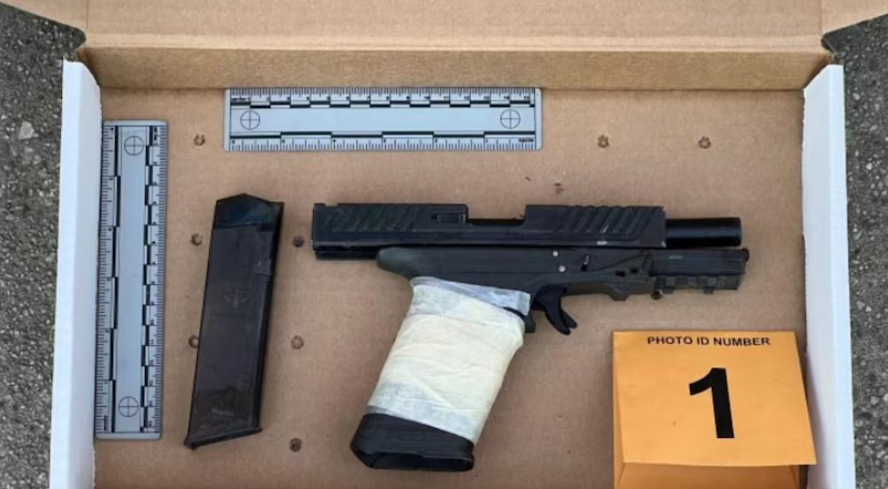
What Are Ghost Guns?
- Ghost guns, officially termed Privately Made Firearms (PMF), are untraceable weapons crafted using components that can include parts manufactured through 3D printing.
- These firearms often lack serial numbers, making them nearly impossible to trace back to individual owners.
- Ghost guns evade the regulatory scrutiny typically associated with commercial firearms, as they can be assembled at home without background checks.
- Initially a niche interest among hobbyists and libertarians, these guns have evolved into a significant issue due to advancements in 3D printing technology, enabling them to fire lethal rounds.
The Problem with Ghost Guns in the US
- Ghost guns have become a growing concern in the United States, particularly for law enforcement.
- Their untraceable nature has made them attractive to criminals. In 2022, the US Department of Justice reported the recovery of 25,785 ghost guns, a dramatic 1,300% increase from 2016.
- Between 2017 and 2021, nearly 38,000 suspected ghost guns were recovered, with numbers rising sharply each year.
- For instance, 19,273 suspected ghost guns were traced in 2021, more than double the 2020 figure of 8,504. These statistics underscore the proliferation and significant impact of ghost guns on public safety.
Legality and Regulation of Ghost Guns
- In 2022, President Joe Biden introduced a rule mandating that ghost guns adhere to the same regulations as commercial firearms, requiring serial numbers and background checks for buyers.
- However, this measure faced legal challenges, and the Supreme Court has yet to issue a final ruling. Critics of stricter regulations argue that building guns at home falls under the Second Amendment’s right to bear arms.
- The Gun Control Act of 1968 permits citizens to build firearms for personal use without requiring registration, provided the weapons are not sold.
- This legal ambiguity continues to fuel the debate over the regulation of ghost guns.
5. NAMASTE YOJANA
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2083106®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
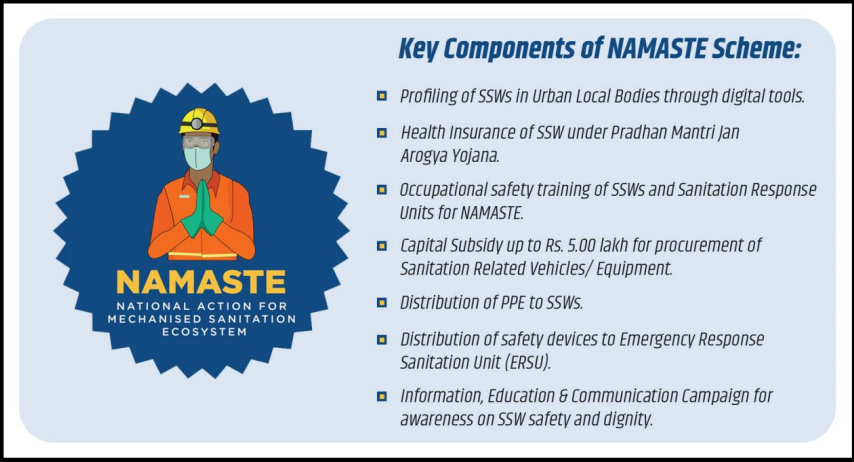
NAMASTE scheme:
- Launched in 2023-24, NAMASTE aims to improve the lives of sanitation workers in India.
- Focuses on mechanization of sewer cleaning to eliminate hazardous manual scavenging.
- Provides sanitation workers with:
- Safety gear and training
- Access to machines
- Capital subsidies to become ‘Sanipreneurs’ (sanitation entrepreneurs)
- Skilled wage employment opportunities
- Promotes behavioral change among citizens to reduce reliance on informal workers for unsafe sanitation practices.
- Implemented across all 4800+ Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) in India in convergence with the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- Aims to create a safe and dignified ecosystem for sanitation workers, recognizing their crucial role in maintaining sanitation infrastructure.
6. NATIONAL QUANTUM MISSION
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2083199®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|
National Quantum Mission (NQM)
Overview
- Aims to advance India’s capabilities in quantum technology across various domains.
- Approved with a budget of Rs. 6003.65 crores.
Objectives
- Quantum Computing:
- Develop intermediate-scale quantum computers with increasing qubit capacity (20-50, 50-100, 50-1000) using superconducting and photonic technologies.
- Quantum Communication:
- Establish satellite-based secure quantum communication within India (2000 km range) and with other countries.
- Develop inter-city quantum key distribution (2000 km) with trusted nodes.
- Create a multi-node quantum network with quantum memories and repeaters.
- Quantum Sensing & Metrology:
- Develop highly sensitive magnetometers and gravity measurement devices.
- Develop atomic clocks with exceptional stability for precision timing and navigation.
- Quantum Materials & Devices:
- Design and synthesize quantum materials (superconductors, semiconductors, topological materials) for quantum devices.
- Develop single-photon sources/detectors and entangled photon sources for various applications.
Implementation
- Pan-India initiative with four Thematic Hubs (T-Hubs) and 14 Technical Groups across 17 states and 2 Union Territories.
- Focuses on technology development, human resource development, entrepreneurship, and international collaborations.
- Encourages participation of female scientists from all over India.


