8 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
Daily Current Affairs
8-March -2024- Top News of the Day
1. India to Restart Penicillin G Manufacturing After Three Decades: A Milestone in Pharmaceutical Self-Reliance
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies – Interventions for development in various sectors This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of knowing facts about government’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme and its impact on reviving Penicillin G manufacturing. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Reasons for the Decline in Penicillin Manufacturing:
- Penicillin G production in India ceased primarily due to the influx of cheaper Chinese products flooding the market.
- The pricing dynamics rendered Indian manufacturing unviable, leading to the closure of production plants, including Torrent Pharma’s facility in Ahmedabad.
- The relaxation of customs rules and the Drug Prices Control Order further exacerbated the situation, prompting Indian manufacturers to opt for cost-effective imported alternatives.
Challenges in Restarting Production:
- Several factors contributed to the delay in restarting Penicillin G manufacturing.
- Firstly, the lack of perceived necessity hindered initiatives to revive production domestically.
- Additionally, the capital-intensive nature of API manufacturing, particularly for fermented products like Penicillin G, posed significant financial hurdles for companies.
- Moreover, competition from well-established Chinese suppliers and the associated investments required to match their pricing presented formidable challenges.
Impact of the PLI Scheme:
- The PLI scheme, launched during the pandemic to promote domestic manufacturing, has yielded positive outcomes in reducing API imports.
- While there has been a noticeable decline in imports, especially for essential drugs like paracetamol, the pharmaceutical industry still heavily relies on imports for antibiotics and other APIs.
- Nonetheless, the scheme’s incentivization structure has encouraged investment in fermentation-based bulk drugs and chemically synthesized drugs, aiming to build self-reliance in critical pharmaceutical ingredients.
Future Prospects and Government Initiatives:
- Despite the progress made under the PLI scheme, achieving self-sufficiency in API manufacturing remains a gradual process.
- The scheme’s support mechanisms, including incentives for eligible sales and prescribed investment commitments, aim to stimulate growth and capacity-building in the pharmaceutical sector.
- However, sustained efforts are required to overcome existing challenges and ensure a robust domestic manufacturing ecosystem.
Conclusion:
- The revival of Penicillin G manufacturing symbolizes India’s endeavor to strengthen its pharmaceutical industry and reduce dependence on imports.
- While challenges persist, initiatives like the PLI scheme offer a promising pathway towards self-reliance.
- By addressing barriers to production and fostering a conducive environment for investment, India can emerge as a leading global hub for pharmaceutical manufacturing, ensuring accessibility and affordability of essential medicines for its population.
| What is the Production Linked Incentive Scheme (PLI)? |
About:
|
| PYQ: Consider, the following statements: (2023) Statement-I: India accounts for 3.2% of global export of goods. Statement-II: Many local companies and some foreign companies operating in India have taken advantage of India’s ‘Production-linked Incentive’ scheme. Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
Ans: (d) |
| Practice Question: Examine the challenges faced by the Indian pharmaceutical industry in the production of Penicillin G and the factors contributing to its revival after a three-decade hiatus. Evaluate the role of government initiatives in promoting domestic manufacturing and reducing dependency on imports in the pharmaceutical sector. (250 words/15 m) |
2. India Braces for Hot Summer as El Niño Weakens, Southwest Monsoon Outlook Remains Optimistic
| Topic: GS1 – Geography – World’s physical geography This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of knowing facts about El Niño, its impact on global weather patterns, and its correlation with the Indian southwest monsoon. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
El Niño Phenomenon: Overview and Impact:
- El Niño, characterized by abnormal warming of sea surface waters in the equatorial Pacific Ocean, has significant implications for global weather patterns.
- The recent El Niño event, one of the strongest on record, peaked between November 2023 and January 2024, contributing to rising temperatures and disrupted rainfall patterns worldwide.
- The phenomenon typically lasts for 9 to 12 months, influencing temperatures, dryness, and droughts globally.
Peaking and Weakening of El Niño: Significance:
- The peaking and subsequent weakening of the El Niño event, as indicated by declining Oceanic Niño Indices (ONI) values, suggest a gradual transition towards neutral conditions.
- This transition is crucial as it signifies the conclusion of the current El Niño episode, alleviating concerns about its potential prolongation and impact on global climate patterns.
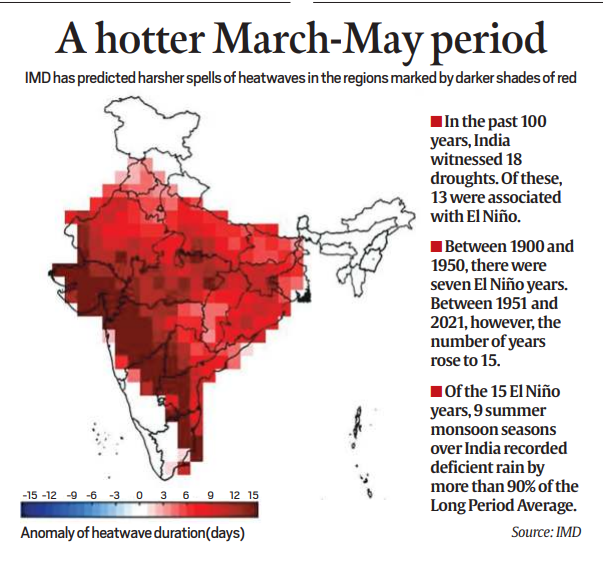
Heat Forecast for India: Implications:
- The IMD’s forecast for above-normal temperatures across India during March, April, and May underscores the influence of El Niño conditions on the country’s climate.
- Elevated temperatures and extended heatwave spells are anticipated, particularly in central and northern peninsular India.
- The IMD warns of harsher heatwave conditions, posing challenges for regions already vulnerable to extreme temperatures.
Southwest Monsoon Outlook: Potential Impact:
- The southwest monsoon, critical for India’s agrarian economy and water reservoir replenishment, is closely linked to El Niño events.
- While past episodes have coincided with below-average rainfall, the emergence of ENSO-neutral conditions post-El Niño suggests a potential deviation from this trend.
- Models indicate a transition to neutral conditions by May, offering optimism for a normal monsoon season.
Conclusion:
- As India awaits the Long Range Forecast (LRF) for the upcoming southwest monsoon, the prediction of ENSO-neutral conditions offers hope for normal rainfall patterns.
- While the ongoing El Niño episode poses challenges such as above-normal temperatures and prolonged heatwaves, the anticipated transition to neutral conditions suggests a favorable outlook for the southwest monsoon.
- Continued monitoring of ocean-atmosphere parameters and weather patterns remains essential for accurate predictions and effective climate resilience measures.
| PYQ: Most of the unusual climatic happenings are explained as an outcome of the El-Nino effect. Do you agree? (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2014) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of the recent predictions by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) and the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) on India’s climate, particularly focusing on the forecasted hot summer and the weakening El Niño event. Evaluate the potential impact of these forecasts on the Indian southwest monsoon and agricultural productivity. (250 words/15 m) |
3. Kerala Declares Man-Animal Conflict as State-Specific Disaster: A Paradigm Shift in Crisis Management
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Conservations, Disaster and disaster management. This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of knowing facts about the issue of man-animal conflict which intersects with environmental conservation and wildlife protection. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Shift in Responsibility: From Forest Department to Disaster Management Authority:
- Currently, the responsibility for managing man-animal conflict lies with the forest department, operating under the Wildlife Protection Act.
- However, with the declaration of this issue as a state-specific disaster, the onus shifts to the state disaster management authority.
- Empowered by the Disaster Management Act, this authority gains the ability to take swifter and more decisive action in addressing the crisis.
Changes at the Administrative Level: Roles and Authorities:
- At the state level, the Chief Minister assumes the role of ex officio chairman of the disaster management authority, with various departments, including the forest department, becoming stakeholders.
- In the districts, the district collectors, who also serve as executive magistrates, lead the district disaster management authorities.
- This shift in administrative structure enables quicker interventions and decision-making processes, with district collectors having the authority to intervene directly in their capacity as the chairman of the district disaster body.
Justification for the Change: Public Outcry and Legal Challenges:
- The decision to declare man-animal conflict as a state-specific disaster comes in response to mounting public pressure following repeated fatalities.
- Each loss of life has sparked demands for action, including calls for tranquilizing, capturing, or killing the animals responsible.
- Currently, the chief wildlife warden holds sole authority to decide on actions concerning wild animals posing threats to human settlements.
- However, past decisions, such as tranquilizing wild elephants, have faced legal challenges, prompting the need for a more decisive approach.
Legal Implications and Overrides:
- Under the Disaster Management Act, the disaster management authority gains the power to take actions that override other norms, including those established under the Wildlife Protection Act.
- Sections 71 and 72 of the Act grant the authority immunity from legal challenges, except in cases brought before the Supreme Court or a High Court.
- This legal framework ensures that decisions made in response to declared disasters have overriding effects on other laws during the specified period.
Comparison with Other State-Specific Disasters:
- Kerala’s declaration of man-animal conflict as a state-specific disaster joins a list of other such declarations in India.
- Examples include Odisha’s declaration of snakebites as a state-specific disaster in 2015 and Kerala’s declaration of Covid-19 as a state-specific disaster in 2020.
- These declarations highlight the diverse range of crises that states face and the flexibility provided by the Disaster Management Act in addressing them effectively.
Conclusion:
- Kerala’s decision to declare man-animal conflict as a state-specific disaster represents a strategic response to a pressing crisis.
- By shifting responsibilities to the disaster management authority and streamlining decision-making processes, the state aims to address the issue more effectively while navigating legal challenges and public demands for action.
- This move underscores the importance of adapting governmental structures and policies to address evolving challenges and protect public safety effectively.
| Reasons Behind Rise in Human-Animal Conflict in Kerala |
Decline in Quality of Forest Habitats:
Changing Agri-practices:
Apart from declining quality of forests and changing agri-practices, following human activities also contribute to increasing animal-human conflict in Kerala:
|
PYQ: Consider the following statements in respect of Trade Related Analysis of Fauna and Flora in Commerce (TRAFFIC): (2017)
Which of the above statements is/are correct? |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of Kerala’s declaration of man-animal conflict as a state-specific disaster. How does this decision alter the administrative and legal landscape concerning wildlife management and disaster response in the state? (250 words/15 m) |
4. Union Cabinet Approves India AI Mission with Rs10,372 Crore Outlay to Revolutionize Artificial Intelligence Development
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies – Interventions for development in various sectors GS3 – Science & Technology – Achievements of Indian S&T; Indigenization of technology This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains as this analysis delves into the government’s policy framework and funding mechanisms for promoting AI development in India. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Subsidizing Private Companies and Supporting Startups:
- Under the India AI Mission, the government plans to allocate funds to subsidize private companies intending to set up AI compute capacity in the country.
- Additionally, seed funding will be provided to AI startups, facilitating innovation and growth in the sector.
- This initiative is expected to democratize access to compute power, benefiting innovators, startups, students, and educational institutions.
Creating a Framework for Curating Non-Personal Data:
- Part of the mission’s objectives includes establishing a framework for curating non-personal data.
- This framework aims to streamline data management processes, facilitating access to valuable datasets for AI development and research.
Establishment of Computing Infrastructure:
- The government aims to establish a significant computing capacity, including over 10,000 GPUs and foundational models with a capacity of more than 100 billion parameters.
- These resources will be trained on datasets covering major Indian languages and prioritized for sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, and governance.
Public-Private Partnership Model and Viability Gap Funding:
- The implementation of the AI compute infrastructure will be carried out through a public-private partnership model, with 50% viability gap funding.
- This approach encourages private investment in building compute infrastructure while ensuring government support to bridge financial gaps..
Challenges and Considerations:
- Despite the ambitious goals of the India AI Mission, challenges such as the high cost of cutting-edge GPUs and the complexity of procuring computing capacity remain significant.
- The government’s focus on financing deeptech startups at various stages of growth reflects a commitment to overcoming these challenges and fostering AI innovation in the country.
Conclusion:
- The approval of the India AI Mission marks a significant milestone in India’s journey towards becoming a global leader in AI innovation.
- By allocating substantial funds, supporting startups, and establishing robust computing infrastructure, the government aims to unleash the potential of AI across various sectors, driving economic growth and technological advancement.
| Recent Global Efforts to Regulate AI |
|
| PYQ: “The emergence of Fourth Industrial Revolution (Digital Revolution) has initiated e-Governance as an integral part of government”. Discuss. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2020) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the Union Cabinet’s approval of the India AI Mission and its implications for India’s technological advancement, economic growth, and governance. (150 words/10 m) |
5. State benefits doled out on caste lines also leading to ‘caste ferocity’: HC judge
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice GS2 – Governance – Government policies – Issues arising out of their design & implementation. Madras High Court’s analysis on caste conflicts and historical context is crucial for understanding social issues, relevant for UPSC aspirants. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- Justice Anita Sumanth of the Madras High Court notes that caste-based conflicts are fueled not solely by ancient Varna Dharma but also by state-accorded benefits to different caste groups.
- The judge, while addressing quo warranto pleas against political figures, emphasises that divisions based on caste are deeply rooted in the state, despite the present-day caste system being less than a century old.
- She laments the tendency of individuals to fan casteist passions, which she deems detrimental to the state and its people.
- Justice Sumanth clarifies that attacking Sanatana Dharma by equating it with Varna Dharma is a misrepresentation, emphasizing that the latter historically divided people based on avocation, not birth.
- While acknowledging present-day caste inequities, the judge urges the state to eliminate them, emphasizing that the origins of the contemporary caste system are less than a century old in Tamil Nadu.
| Perpetuation of Caste Identity In India |
Reasons for Perpetuation:
Way Forward:
Addressing the perpetuation of caste identity in India requires a multifaceted approach, combining legal, educational, economic, and societal interventions to foster a more inclusive and equitable society. |
| PYQ: Has caste lost its relevance in understanding the multi-cultural Indian Society? Elaborate your answer with illustrations. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2020) |
| Practice Question: Examine the factors contributing to the persistence of caste identity in India and propose comprehensive strategies for fostering social harmony and dismantling caste-based inequalities. (150 Words /10 marks) |
6. ‘Political parties got 60% of funds from unknown sources’
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Important aspects of governance – Transparency and accountability Critical for UPSC as it highlights transparency issues in political funding, electoral bonds, and their impact on democratic processes. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- A report by the Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR) reveals that almost 60% of funds received by Indian political parties (between 2004-05 and 2022-23) cannot be traced and come from “unknown” sources, including electoral bonds.
- Political parties are not required to disclose names for donations below ₹20,000, contributing to the inability to trace three-fifths of the funds received.
- In the financial year 2022-23, the six national parties collected ₹19,083.08 crore from unknown sources, with ₹1,832.87 crore (over 59%) coming from such sources. Electoral bonds constituted ₹1,510.61 crore (82.42%) of this amount.
- The BJP received the majority of these funds, declaring ₹1,400.23 crore (76.39% of total income from unknown sources), while the Congress came second with ₹315.11 crore (17.19%).
- Other parties analyzed include CPI(M), BSP, Aam Aadmi Party, and the National People’s Party.
| Issues with political party funding in India |
Issues with Political Party Funding in India:
Way Forward:
|
| Practice Question: Critically analyze the challenges associated with political party funding in India and propose effective reforms to enhance transparency and accountability in the electoral process. (250 Words /15 marks) |
7. 85% of gig workers sweat it out for over 8 hours, 65% women feel unsafe: study
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Issues related to development and employment The gig workers’ survey highlights labour challenges, gender safety issues, and recommends regulatory changes, crucial for UPSC aspirants understanding socio-economic issues. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- A survey conducted by Janpahal, a Delhi-based NGO, interviewed over 5,000 gig and platform workers in 32 cities.
- Findings reveal that 85% of workers, particularly drivers and riders, exceed eight hours of work daily, with 21% working over 12 hours a day.
- 65% of surveyed women feel unsafe in their gig jobs.
- The report suggests renaming gig, platform, and e-commerce workers to “e-commerce workers” due to the sustained nature of their work.
- Recommendations include regulations for fair payment structures, stipulating regular working hours, and payment of a minimum wage to protect workers from exploitation.
- The report condemns practices such as blocking worker IDs indefinitely and calls for platforms to address income insufficiency concerns by reducing commissions and separately compensating fuel expenses amid rising fuel prices.
| PYQ: Examine the role of ‘Gig Economy’ in the process of empowerment of women in India. (150 words) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2021) |
8. Centre to rope in ISRO to provide Internet in 80 remote tribal villages
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies – Interventions for development in various sectors GS3 – Science and Technology – Development & their applications The collaboration between the Tribal Affairs Ministry and ISRO for connectivity aligns with UPSC themes on inclusive development and technological empowerment |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- The Tribal Affairs Ministry plans to collaborate with ISRO for a pilot project deploying V-SAT stations in 80 tribal villages.
- Villages in Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, and Maharashtra will benefit, overcoming geographical and connectivity challenges.
- The collaboration aims to provide internet, medical, and educational connectivity to remote tribal areas.
- ISRO Chief S. Somnath confirms the impending memorandum of understanding for the pilot project.
- The initiative seeks to enable e-governance in these underserved regions and may be expanded based on the pilot’s success.
- Other proposed collaborations include partnerships with AIIMS for tribal health research, IIT Delhi and IIM Calcutta for technology and entrepreneurship programs, and IISc Bengaluru for semiconductor courses for tribal students.
- The Tribal Affairs Ministry aims to address health issues like sickle cell anaemia and promote technological education and entrepreneurship in tribal communities.
| Deploying Technology for tribal development |
Advantages:
Challenges:
The Way Forward:
By overcoming these challenges and adopting a community-driven approach, technology can be a powerful tool for empowering tribal development. |
| Practice Question: Critically examine the role of technology in promoting tribal development in India. Discuss both the potential benefits and challenges associated with this approach. (150 Words /10 marks) |
For Enquiry

8 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

8 March 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

8 March 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC

8 March 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis

7 Mar 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

7 Mar 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

7 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

7 March 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

7 March 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC

7 March 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis
Daily Current Affairs 8 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
8-March -2024- Top News of the Day
1. India to Restart Penicillin G Manufacturing…
March – The Hindu Editorial 8 March 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu Editorial
8-March-2024
1. A bold step towards a cervical cancer-free future
Topic: GS2…
March 2024 PIB 8 March 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
8-March -2024
1. Cabinet approves Uttar Poorva Transformative Industrialization…
Indian Express 8 March 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
8-March-2024
1. The bias that must go
Topic: GS1 – Society – Role…
Daily Quiz 7 Mar 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 7 Mar 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 7 Mar 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
7-March-2024
Q1) While decriminalization of politics is crucial, it is equally…
Daily Current Affairs 7 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
7-March -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Amit Shah Offers Article 371-like Protections…
March – The Hindu Editorial 7 March 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu Editorial
7-March-2024
1. The tale of ‘have money, buy miracle drug’
Topic: GS2 – Social…
March 2024 PIB 7 March 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
7-March -2024
1. Promoting Clean Coal Technology: Coal Gasification
Topic: GS3…
Indian Express 7 March 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
7-March-2024
1. The thin-fat Indian
Topic: GS2 – Social Justice…




