12 July 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. Centre begins efforts to implement Labour Codes
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 5)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance, GS3 – Indian Economy – Changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth. |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The Union Labour Ministry is pushing to implement the four Labour Codes passed in Parliament in 2019 and 2020 after NDA’s third term began.
- Union Labour Minister Mansukh Mandaviya and Union Labour Secretary Sumita Dawra are engaging with trade unions for cooperation.
- The Labour Codes are not yet operational due to trade union objections and incomplete state-level rule framing.
- Central trade unions argue the Codes will reduce trade union rights and worker social security.
- The Citigroup employment analysis suggests the Codes could improve India’s “ease of doing business.”
- Mandaviya met with Bharatiya Mazdoor Sangh (BMS), and Dawra met with the Self-Employed Women’s Association (SEWA).
- BMS supports early implementation of the Code on Wages and the Code on Social Security but has concerns about the Industrial Relations Code and Occupational Safety and Health Code.
- SEWA opposes the four Codes, highlighting the lack of social security for unorganised and migrant workers.
- Ten central unions, including SEWA, have requested a meeting with Mandaviya to discuss worker issues.
| New Labour Codes: |
|
1. Code on Wages, 2019
2. Industrial Relations Code, 2020
3. Code on Social Security, 2020
4. Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020
|
| PYQ: Success of ‘Make in India’ programme depends on the success of ‘Skill India’ programme and radical labour reforms.” Discuss with logical arguments. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2015) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the recent labour code reforms in India, highlighting their objectives and implications for industrial relations and social security. (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. Future investments in India’s EV space
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies |
| Context |
|
Expanded Scope of EV Policy
- The government is expanding its electric vehicle (EV) policy, initially announced in March, to include retrospective benefits.
- The updated policy will extend incentives to entities that have already made investments in local production.
- Initially, entities were eligible for incentives only if they set up local facilities within three years of receiving approval.
- The revised policy is expected to be formally announced in August.
Policy Focus on Investment and Localisation
- Objective: To provide Indian consumers with access to the latest technology and strengthen the EV ecosystem.
- Encouragement of Competition: By encouraging higher production volumes, achieving economies of scale, and reducing production costs, the policy aimed to foster healthy competition among EV players.
- Domestic Manufacturing Mandate: The policy required that half of the value addition in overall manufacturing be done domestically within five years.
- Import Duty Reduction: To maintain commercial viability, the import duty on EVs as completely built units (CBUs) with a minimum cost, insurance, and freight (CIF) value of $35,000 was reduced from 70%-100% to 15%.
- Global Leadership Vision: The policy positioned India, the world’s third-largest automotive market, to potentially lead the global transition from internal combustion engines (ICE) to decarbonized electric vehicles (EVs).
Need for Investment and Intervention in the EV Ecosystem
- Consumer Investment Decisions: According to a 2022 Niti Aayog report, purchasing a vehicle is a major investment for most Indian consumers. Thus, ensuring viable economics for owning, maintaining, and running EVs is essential.
- Cost Decline and Adoption Timeline: The report suggested that a sharper decline in costs would accelerate EV adoption.
- Production Cost Disadvantages: India faces structural unit cost disadvantages in producing select cell components such as CAM NMC (8-10%) and electrolyte (2-3%).
- Capital Investment Requirements: Certain cell components like separators, copper foil, and anode active material (AAM) require significant capital investment—about $200-500 million for a 20-30 GWh plant.
- Attracting Large-Scale Investment: The Niti Aayog report emphasised the need to create an enabling ecosystem to attract large-scale capital expenditure (capex) investment compared to other geographies.
After-Sales Service and Investor Support
- After-Sales Service Issues: Bain & Company’s India EV Report (2023) highlighted after-sales service as a significant pain point for EV customers, particularly in the two-wheeler segment.
- Business Model Scalability Concerns: The report expressed doubts about the scalability of business models where original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) partner with standalone breakdown service providers.
- Investor Support: The report indicated that India would need significant investor support to realise the $100 billion-plus EV opportunity.
- Evaluation Criteria for Investors: Investors should evaluate potential assets based on sustainable competitive advantages, go-to-market and distribution capabilities, customer feedback and brand perception, talent and culture, and manufacturing and supply chain strategy.
Addressing the Paradigm Shift
- Policy Priorities: The EV policy shares priorities with policies in the U.S., China, and Europe, which offer incentives for setting up EV value chain manufacturing capacity.
- Cost Comparison: The International Energy Agency (IEA)’s Global EV Outlook for 2024 noted that electric cars remain 10% to 50% more expensive than combustion engine equivalents in Europe and the U.S.
- EV Battery Import Dependence: Europe and the U.S. meet 20% and 30% of their EV battery demands through imports, highlighting the need for integrated production lines.
Conclusion
- The expanded EV policy seeks to enhance India’s EV ecosystem by encouraging local production and attracting global investments.
- This strategic move aims to position India as a key player in the global EV market while addressing cost and service challenges.
| PYQ: The adoption of electric vehicles is rapidly growing worldwide. How do electric vehicles contribute to reducing carbon emissions and what are the key benefits they offer compared to traditional combustion engine vehicles? (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2023) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of the Indian government’s expanded EV policy with retrospective benefits on local manufacturing and the EV ecosystem. (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s Historic Visit to Vienna: Strengthening India-Austria Ties Amid Global Geopolitical Shifts
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral Relations |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Historical Ties
- India played a significant role in Austria’s quest for sovereignty post-World War II, with Jawaharlal Nehru supporting Austria’s appeal for independence at the United Nations.
- This historical connection was highlighted during Modi’s visit, with Austrian Chancellor Karl Nehammer recalling Nehru’s crucial support in securing the Austrian State Treaty.
Evolving Bilateral Relations
- Diplomatic relations between India and Austria, established in 1949, have seen significant milestones, including state visits and reciprocal engagements.
- Modi’s visit aims to further elevate this relationship, focusing on economic and technological partnerships.
- The bilateral collaboration encompasses infrastructure, renewable energy, e-commerce, fintech, enterprise tech, consumer services, and media and entertainment.
Balanced Stance on Russia-Ukraine War
- Both India and Austria have adopted balanced positions regarding the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- Austria, despite supporting EU sanctions against Russia, maintains commercial ties and continues to import gas from Russia.
- Modi’s visit reinforces this balanced approach, emphasizing dialogue and economic cooperation over conflict.
Future Prospects
- The visit underscores the potential for India and Austria to navigate global tensions collaboratively.
- The focus on future-oriented economic and technological partnerships aligns with both nations’ goals of fostering sustainable development and political dialogue.
- As global partners, India and Austria aim to contribute to international stability and economic growth amidst geopolitical challenges.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Austria, considering the historical context and the current geopolitical landscape. How can India and Austria’s shared history and balanced positions on global conflicts enhance their bilateral relationship and contribute to global stability? (250 words/15 m) |
4. ISRO Eyes Historic Mission to Study Asteroid Apophis During 2029 Flyby
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology – Space |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Historical Context of Apophis
- Discovered in 2004, Apophis initially posed a 2.7% chance of colliding with Earth, the highest probability for a large asteroid in recent history.
- At approximately 450 meters wide, such an impact could cause significant damage, drawing comparisons to the event that caused the dinosaur extinction.
- However, subsequent observations ruled out any collision risks for 2029, 2036, or 2068.
- Despite this, its close approach in 2029 remains a crucial opportunity for scientific study and preparation for potential future threats.
Threats Posed by Asteroids
- Although Apophis itself poses no imminent threat, Earth constantly faces potential impacts from other asteroids.
- Thousands enter the Earth’s atmosphere daily, most burning up due to friction.
- Occasionally, larger ones cause damage, like the 2013 Chelyabinsk event in Russia, where a 20-meter-wide asteroid exploded in the atmosphere, injuring nearly 1,500 people.
- This incident highlighted the need for a planetary defense program to detect and neutralize such threats before they cause harm.
Planetary Defense and Scientific Endeavors
- NASA’s 2022 mission demonstrated the feasibility of altering an asteroid’s trajectory by crashing a spacecraft into it.
- This successful test on asteroid Dimorphos underscored the potential for a planetary defense program.
- With the upcoming approach of Apophis, numerous space agencies are planning missions to study the asteroid closely.
- NASA has already redirected a spacecraft that previously studied asteroid Bennu to track Apophis, aiming to collect data and analyze its surface during its 2029 flyby.
ISRO’s Growing Capabilities and Global Contributions
- ISRO’s intention to join the Apophis exploration effort reflects its growing confidence and capability in addressing new challenges.
- Participating in such missions highlights ISRO’s proactive role in global space objectives and reaffirms its evolution into a well-rounded space agency.
- This endeavor not only enhances ISRO’s technical expertise but also contributes to the broader scientific understanding of asteroids and planetary defense strategies.
- By aligning with international efforts, ISRO can further solidify its position as a leading space agency and ensure its readiness to protect Earth from potential asteroid threats in the future.
| Practice Question: Examine ISRO’s strategic decision to explore asteroid Apophis in 2029, highlighting its implications for India’s space ambitions and global scientific collaboration. (250 words/15 m) |
5. Maharashtra Government Introduces Controversial Bill to Combat Urban Naxalism
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page: 01)
| Topic: GS3 – Internal Security GS2 – Governance |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:

Provisions of the Bill
The Maharashtra Special Public Security Bill, 2024, outlines several key provisions aimed at curbing Naxal activities:
Criminalization of Support Activities
The Bill criminalizes not only membership in unlawful organizations but also various forms of support:
- Contributing or Soliciting Contributions: Individuals who contribute, solicit, or receive contributions for such organizations face imprisonment up to three years and fines up to Rs 3 lakh.
- Harboring Members: Those who harbor members of unlawful organizations can be imprisoned for up to two years and fined up to Rs 2 lakh.
- Management and Promotion: Managing or promoting activities of unlawful organizations is punishable with imprisonment up to three years and fines up to Rs 3 lakh.
- Unlawful Activities: Committing, abetting, or planning unlawful activities can lead to imprisonment up to seven years and fines up to Rs 5 lakh.
Authority to Declare Organizations Unlawful
- The Bill empowers the state to declare any organization as unlawful. This decision can be reviewed by an advisory board comprising individuals qualified to be high court judges.
- If the board does not find sufficient cause, the government must revoke the notification.
Seizure of Assets
- Upon declaring an organization unlawful, authorities can seize properties used for its activities, including movable assets like money and securities. The government can also forfeit assets if they are found to be used for unlawful purposes.
Rationale Behind the Bill
Addressing Urban Naxalism
- The Bill’s “statement of objects and reasons” highlights the increasing presence of Naxalism in urban areas through frontal organizations.
- It notes that these groups provide logistical support and safe refuge for armed cadres, creating unrest and propagating armed rebellion against the constitutional mandate.
Legal Framework and Enforcement
- Existing laws are deemed ineffective in tackling urban Naxalism, necessitating this new legislation.
- The Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has advised states to enact laws to combat unlawful activities of such organizations.
- The Bill follows the example of other states like Chhattisgarh, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Odisha, which have enacted similar laws and banned multiple frontal organizations.
Opposition and Criticism
Concerns Over Civil Liberties
- The Opposition has labeled the Bill as “draconian,” arguing that it aims to suppress protests and dissent.
Conclusion
- The Maharashtra Special Public Security Bill, 2024, represents a significant legislative effort to counter the growing threat of urban Naxalism.
- By criminalizing various forms of support for unlawful organizations and granting the state broad powers to declare organizations unlawful and seize assets, the Bill aims to disrupt the infrastructure of Naxal networks.
- However, the legislation has sparked controversy, with critics warning that it could be used to stifle legitimate dissent and civil liberties.
- As the Bill progresses through the legislative process, these concerns will likely continue to be a point of significant debate.
| PYQ: Naxalism is a social, economic and developmental issue manifesting as a violent internal security threat. In this context, discuss the emerging issues and suggest a multilayered strategy to tackle the menace of Naxalism. (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2022) |
| Practice Question: The Maharashtra Special Public Security Bill, 2024, seeks to address the menace of Naxalism, particularly in urban areas. Critically analyze the key provisions of this bill and discuss its potential impact on internal security and civil liberties. (250 words/15 m) |
6. Drop in Informal Sector Employment by 16.45 Lakh in 2022-23: ASUSE Report
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Cover Page; Page: 01)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian economy – Issues relating to development and employment. |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Impact of Major Exogenous Shocks
- The informal sector bore the brunt of three significant shocks: demonetization in November 2016, which led to a sudden withdrawal of cash from the system; the introduction of GST in July 2017, which brought new regulatory compliances and tax inclusion; and the Covid-19 pandemic in March 2020, which prompted a national lockdown.
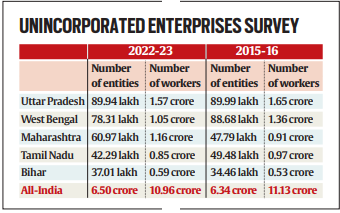
- These events collectively contributed to the decline in informal sector employment, despite an increase in the number of unincorporated enterprises from 6.33 crore in 2015-16 to 6.50 crore in 2022-23.
Regional Variations in Informal Employment
- The survey highlights regional variations in informal sector employment among the top ten states, which account for nearly three-quarters of informal sector workers in India.
- States like Maharashtra, Bihar, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Odisha saw an increase in informal employment between 2015-16 and 2022-23.
- Conversely, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh experienced a decline in the same period.
- Notably, Uttar Pradesh recorded a decline in informal sector workers from 1.65 crore in 2015-16 to 1.57 crore in 2022-23, despite an increase from the 2021-22 level of 1.30 crore.
Post-Pandemic Employment Trends
- The immediate aftermath of the Covid-19 pandemic saw an increase in the share of informal sector workers in most states, indicating economic distress and a possible shift from the formal to the informal sector.
- For instance, Maharashtra consistently recorded an increase in informal sector workers throughout the seven-year period, rising to 1.15 crore in 2022-23 from 91.23 lakh in 2015-16.
- Similarly, Bihar, a major source of migrant workers, reversed its declining trend to record a sharp increase in informal sector workers to 58.95 lakh in 2022-23, surpassing pre-pandemic levels.
Gross Value Added in the Informal Sector
- In terms of output, the real Gross Value Added (GVA) of unincorporated sector enterprises (USE) grew by 6.9 percent in 2022-23 but remained lower than pre-pandemic levels.
- According to India Ratings, the real GVA of USE in 2022-23 was still 1.6 percent lower than in 2015-16. The compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of real GVA for USE contracted by 0.2 percent between 2015-16 and 2022-23, contrasting with a 7.4 percent CAGR between 2010-11 and 2015-16.
Distribution of Unincorporated Enterprises
- The survey indicates that Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Maharashtra accounted for the highest share of informal sector enterprises in both rural and urban areas in 2022-23.
- The State Bank of India’s research report corroborates these findings, showing around 8.9 crore employment in industry and services for the nine-year period during FY14-FY23, aligning broadly with the ASUSE employment numbers.
Importance of Informal Sector Data
- The unorganized sector is crucial for India’s economy, contributing over 44 percent to the country’s GVA and employing nearly 75 percent of the workforce in non-agricultural enterprises.
- Given the sector’s significant role in employment generation, especially during formal sector slowdowns, the release of ASUSE data after a long gap is critical for understanding employment trends and policy-making.
| PYQ: Most of the unemployment in India is structural in nature. Examine the methodology adopted to compute unemployment in the country and suggest improvements. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2023) |
| Practice Question: The latest Annual Survey of Unincorporated Enterprises (ASUSE) for 2021-22 and 2022-23 reveals a decline in informal sector employment by 16.45 lakh workers compared to 2015-16. Discuss the factors contributing to this decline and analyze the regional variations in informal employment. (250 words/15 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. Carrying 1,930 containers, San Fernando becomes first mothership to dock at Kerala’s Vizhinjam port
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Context |
|
What is a mothership?
- A mothership is a large vessel or aircraft that carries, launches, or supports smaller vehicles or vessels.
- In maritime contexts, it typically refers to a large ship that provides logistical support, housing, and transportation for smaller boats or submarines.
- Motherships are crucial in various operations, including military, exploration, and commercial activities.
- They offer facilities like maintenance, supplies, and crew quarters for the smaller crafts they support.
2. India hosts BIMSTEC Foreign Ministers amid raging Myanmar crisis
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Context |
|
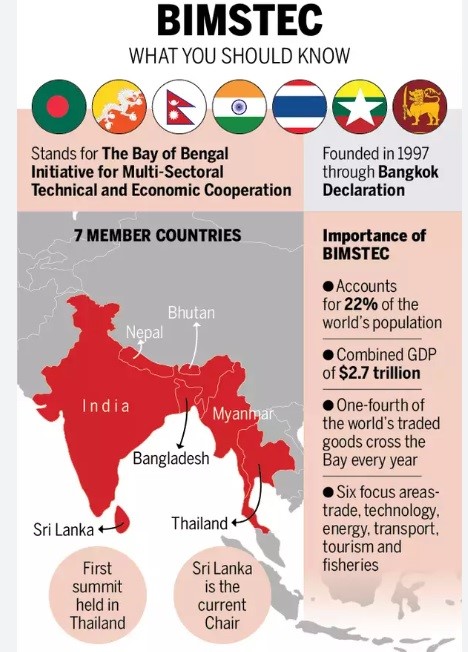
BIMSTEC:
- Full Name: Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation.
- Established: 1997.
- Member Countries: Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
- Objective: Promote regional cooperation, economic growth, and development.
- Headquarters: Dhaka, Bangladesh.
- Key Sectors of Cooperation: Trade and investment, technology, energy, transport and communication, tourism, fisheries, agriculture, public health, poverty alleviation, counter-terrorism, environment, culture, and people-to-people contact.
- Significance:
- Bridges South and Southeast Asia.
- Enhances regional connectivity.
- Facilitates economic integration and cooperation.
- Recent Focus:
- Combating terrorism and transnational crime.
- Enhancing connectivity and trade.
- Addressing climate change and disaster management.
- Strategic Importance: Enhances India’s Act East Policy and strengthens ties with Southeast Asian nations.
3. Why are dengue cases on the rise worldwide?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Context |
|
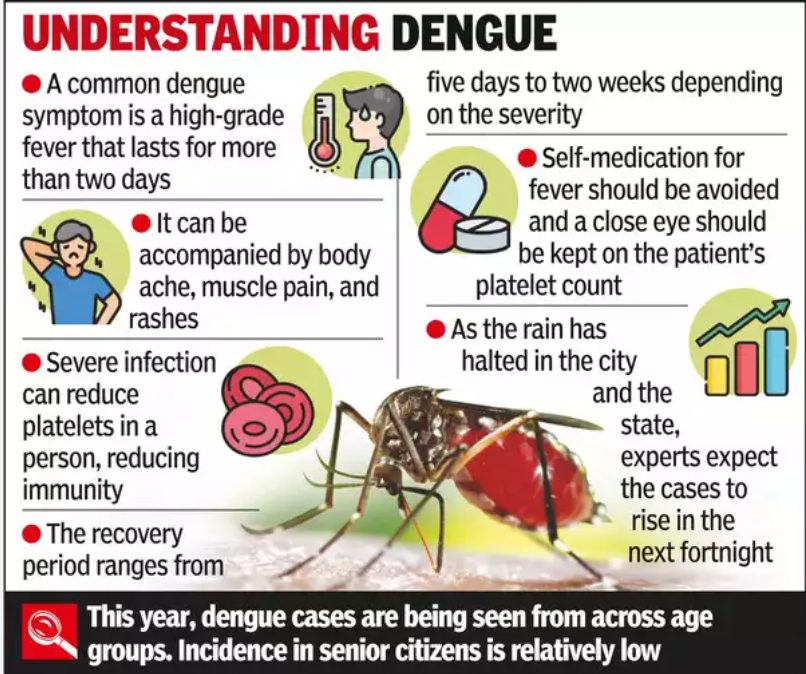
Dengue Cases in India:
- Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu have seen significant increases in dengue cases.
- Karnataka reported 7,840 cases and seven deaths by July 10.
- India recorded 19,447 cases and 16 deaths as of April 30.
Global Dengue Situation:
- Over 7.6 million cases reported globally in 2024.
- Southeast Asia, the Americas, and Western Pacific regions are most affected.
- Dengue spreading to new areas in Europe, Eastern Mediterranean, and South America.
Transmission and Treatment:
- Spread through Aedes mosquito bites.
- Symptoms include fever, headache, severe bleeding, and organ impairment.
- Managed with symptomatic and supportive treatment.
Emerging Patterns:
- Factors contributing to epidemics include urbanisation and climate change.
- Dengue is endemic in over 100 countries worldwide.
India’s Historical Context:
- First reported dengue fever in India in 1956.
- Periodic outbreaks influenced by urbanisation and climatic changes.
- Surveillance, immediate response, and community education critical for control.
4. Manufacturing entities in informal sector slid by 24 lakh between 2016-21
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 12)
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
- The Indian economy’s manufacturing sector has faced slow growth, exacerbated for small informal enterprises due to events like demonetisation, GST implementation, and the pandemic.
- According to NSSO’s surveys, unincorporated non-agricultural enterprises numbered 6.34 crore in 2015-16, dropping to 5.97 crore in 2021-22 before slightly recovering to 6.5 crore in 2022-23.
- In manufacturing, there was a notable decline of 24 lakh enterprises, reducing the sector’s share from 31% to 27.4%.
- Workforce numbers in the informal sector decreased by 1.3 crore between 2016 and 2021, with significant losses in manufacturing.
- Nominal GVA per small enterprise increased, but real GVA remained below pre-shock levels, showing a 4.12% dip in 2022-23 compared to 2015-16.
- Emoluments per worker rose nominally but only marginally in real terms, indicating incomplete recovery for the informal sector.
5. Zika virus: the need to improve surveillance and vector control
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health |
| Context |
|

Zika Virus:
- The Zika virus is a mosquito-borne illness primarily transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes, notably Aedes aegypti, which also spreads dengue and chikungunya.
- Discovered in Uganda in 1947, Zika can also be transmitted through sexual contact, from mother to foetus, and via blood transfusions.
- While many infected individuals are asymptomatic, those who develop symptoms may experience mild fever, rash, conjunctivitis, muscle and joint pain, and headache, typically lasting 2-7 days.
- Zika is particularly dangerous for pregnant women, as it can cause severe birth defects such as microcephaly and other congenital malformations.
- It is also linked to neurological disorders like Guillain-Barré syndrome.
- Diagnosis is challenging due to symptom overlap with other diseases and limited diagnostic testing capabilities.
- Currently, no vaccine exists, although research is ongoing. Preventive measures focus on controlling mosquito populations and avoiding bites.
- Indian companies like Bharat Biotech and Indian Immunologicals Limited are working on potential vaccines. Bharat Biotech’s vaccine showed 100% efficacy in animal studies.
- Increased vigilance and public health efforts are essential to manage outbreaks and protect vulnerable populations.
| Practice Question: Discuss the public health challenges posed by the Zika virus in India and evaluate the measures that need to be taken by the government and public to manage and control its spread. (150 Words /10 marks) |
6. Late sleepers are cognitively sharper than early risers: Study Reveals
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Impact of Sleep Duration on Cognitive Performance
- The study analyzed cognitive test results from over 26,000 individuals, focusing on intelligence, reasoning, reaction time, and memory.
- It found a positive association between normal sleep duration (7-9 hours) and cognitive scores.
- Sleep duration emerged as the most significant determinant of cognitive performance.
Chronotype and Cognitive Function
- Interestingly, the study discovered an inverse relationship between “morningness” (a preference for being active in the morning) and cognitive function among adults.
- Those who stayed up late and were most productive in the evenings performed better cognitively than early risers.
- This finding challenges conventional wisdom, which often promotes early rising as a hallmark of productivity and mental sharpness.
Circadian Rhythms and Age
- The study’s findings also contrast with previous research conducted on adolescents, which suggested that early risers tend to perform better cognitively.
- This discrepancy points to the possibility that circadian rhythms evolve with age, and the optimal time for cognitive activities might shift from morning to evening as people grow older.
7. Western US Sizzles Under Record-Breaking Heatwave, California Cities Hit Hardest
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
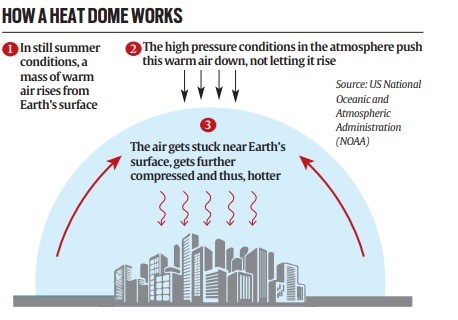
What is a Heat Dome?
- A heat dome is a weather phenomenon where a high-pressure system in the atmosphere traps warm air like a lid on a pot for an extended period.
- The trapped warm air cannot rise, preventing cloud formation since clouds form when warm, moist air rises, cools down, and the water vapor in it condenses.
- The clear skies resulting from the lack of clouds allow more sunlight to reach the Earth’s surface, causing further warming and drying of the soil. The longer the heat dome stays in one place, the more the temperature increases.
Formation of Heat Domes
- The formation of a heat dome is closely tied to the behavior of the jet stream, a region of fast-moving air high in the atmosphere that usually moves weather systems along the Earth’s surface.
- The jet stream typically has a wave-like pattern moving from north to south and back north. When these waves become larger and more elongated, they move more slowly and can sometimes become stationary.
- When a high-pressure system gets stuck in place, it leads to the formation of a heat dome.
Climate Change and Heat Domes
- Scientists are still investigating how climate change impacts the blocking weather events that cause heat domes.
- However, it is clear that rising global temperatures have made heat domes larger and more intense.
- A 2021 study by international climate researchers part of the World Weather Attribution team found that the temperatures recorded during a heat dome formation in Canada that June “would have been virtually impossible without the influence of human-caused climate change.”
- Additionally, a 2023 study published in the journal Nature indicated that the intensity of heat domes is outpacing the rate of global warming, suggesting that climate change is fueling their severity.






