26 April 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis
Indian Express Editorial Analysis
26-April-2024
1. Health on a hot planet
|
Topic: GS1 – Geography – Climate Change GS3 – Environment – Environmental pollution and degradation This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains as the article delves into the scientific consensus on climate change, urbanization’s impact on heat islands, and the multifaceted consequences of global warming. |
| Context: |
|
Urbanization and Heat Islands:
- As urbanization intensifies, cities expand at the expense of forests, transforming into heat islands characterized by elevated temperatures and humidity levels.
- This phenomenon exacerbates the heat-related challenges faced by densely populated areas.
Multifaceted Consequences of Climate Change:
- The consequences of climate change, primarily driven by global warming, manifest across various domains, significantly impacting human, animal, and plant health.
- These repercussions include direct heat exposure effects on the body, extreme weather events, water scarcity, and the proliferation of vector-borne and water-borne infections.
- Moreover, non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as strokes, heart attacks, diabetes, respiratory diseases, and cancers are on the rise.
- Climate change also strains healthcare systems, exacerbating demand and disrupting infrastructure due to the influx of displaced climate refugees and the adverse effects of extreme weather events.
Immediate Concern: Heatwaves on the Indian Subcontinent:
- The Indian Subcontinent faces immediate concerns as heatwaves intensify, posing significant health risks.
- Heatwaves, characterized by a combination of high temperatures and humidity, have become more prevalent, amplifying their impact on human health.
- Vulnerable populations, including infants, young children, the elderly, and individuals with disabilities or comorbidities, face heightened risks.
Health Impacts of Heat Exposure:
- Prolonged or severe heat exposure poses severe health risks beyond immediate consequences like heat exhaustion and heatstroke.
- Notably, heat exacerbates the prevalence and severity of non-communicable diseases (NCDs), including cardiovascular events such as strokes and heart attacks.
- Moreover, excessive heat contributes to respiratory issues, kidney damage, cataracts, delayed wound healing, and increased mortality rates.
Long-term Health Effects and Mortality Risks:
- Studies indicate a substantial increase in mortality rates associated with heatwaves, particularly due to stroke, coronary heart disease, and cardiac arrhythmias.
- With an aging population and rising cardiovascular risk factors, every degree rise in ambient temperature compounds the risk of serious cardiovascular events, underscoring the critical need for proactive adaptation strategies.
Environmental Impact on Food Systems:
- Climate change poses a significant threat to food systems, compromising nutrition security and exacerbating deficiencies in essential nutrients such as zinc, protein, and iron.
- Staple crops grown in regions with high heat tolerance levels are projected to experience yield reductions, further exacerbating malnutrition.
- Rising ocean temperatures threaten coastal agriculture and fish yields, while biodiversity loss limits access to nutritious foods.
Adaptation Strategies and Preparedness
- In light of these challenges, proactive adaptation plans are imperative. These plans should encompass heat action strategies tailored for both urban and rural areas, climate-smart food and healthcare systems, public education initiatives, and infrastructure improvements.
- Measures such as heat shelters, water stations, heat-reflective surfaces, and increased green spaces should be integrated into urban planning.
- Personal protective measures, including appropriate clothing and hydration practices, are essential for mitigating the adverse effects of heat exposure.
Conclusion:
- Addressing the multifaceted challenges posed by climate change and global warming demands a comprehensive approach encompassing mitigation efforts and proactive adaptation strategies to safeguard human health and well-being.
| Impact of climate change on Health |
|
Many of these health problems are not new but are existing challenges and inequalities made worse by climate change.
|
| PYQ: ‘Climate Change’ is a global problem. How India will be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India will be affected by climate change? (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2017) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the health impacts of climate change, focusing on the risks posed by heatwaves and the importance of adaptation strategies. (150 words/10 m) |
2. A WARMING ASIA
|
Topic: GS1 – Geography – Climate Change GS3 – Environment – Environmental pollution and degradation This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains as the article provides detailed insights into the impact of climate change on Asia, focusing on extreme weather events and water-related hazards. |
| Context: |
|
Specific Impacts in India:
- India, in particular, bore a heavy burden from heatwaves, floods, and landslides, underscoring the sobering reality of climate vulnerabilities.
- The warnings issued by scientific studies resonate as various regions, including coastal areas, mountainous regions, and even plains, experience the adverse impacts of climate variability.
Political Response and Awareness:
- While manifestos of major political parties in India include sections dedicated to sustainability and the green economy, the devastating effects of climate-related disasters have yet to become prominent campaign issues.
- This highlights a gap between political discourse and the urgent need for climate action.
Urgency for Climate Action:
- The report emphasizes the imperative of limiting temperature rise to prevent catastrophic consequences while also urging preparedness for receding glaciers, rising sea levels, and droughts.
- Collaboration at both national and regional levels is essential to build resilience against climate change, as natural phenomena often transcend national boundaries.
- Joint efforts in Asia, especially in South Asia, are crucial due to shared ecological continuities.
Need for Collaboration and Cooperation:
- The Climate Asia report underscores the necessity for mechanisms of cooperation among Asian countries to address energy security concerns and tackle the challenges posed by climate change.
- While India and China have made progress in renewable energy, factors like historical conflict and energy diplomacy complexities pose challenges.
- The absence of collaboration mechanisms similar to ASEAN in the Subcontinent further complicates regional efforts to address the climate crisis.
Conclusion:
- The State of the Climate Asia report highlights the urgent need for concerted action to mitigate the impacts of climate change and build resilience in the face of increasing disasters.
- Collaboration among countries in the region is crucial to address shared challenges and ensure a sustainable future.
| ‘State of the Climate in Asia 2023’ Report |
|
|
PYQ: The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has predicted a global sea level rise of about one metre by AD 2100. What would be its impact in India and the other countries in the Indian Ocean region? (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2023) |
| Practice Question: What are the key challenges posed by climate change in Asia, and how can regional cooperation help address them? (250 words/15 m) |
For Enquiry

26 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

26 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

26 April 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

26 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC

26 April 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis

26 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

25 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

25 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

25 April 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

25 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC
Daily Quiz 26 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 26- April 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 26 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
26-April-2024
Q1) Discuss the multifaceted significance of the fisheries sector…
April 2024 The Hindu Editorial 26 April 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu EDITORIAL
26-April-2024
1. Questioning the polls ‘rain washes out play’ moments
Topic:…
April 2024 PIB 26 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
26-April-2024
1. Council of Scienific & Industrial Research (CSIR)- National…
April 2024 Indian Express 26 April 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
26-April-2024
1. Health on a hot planet
Topic: GS1 – Geography –…
April 2024 Daily Current Affairs 26 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
26-April -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Ocean floor holds vital clues on weather…
Daily Quiz 25 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 25- April 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 25 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
25-April-2024
Q1) What is regenerative agriculture? How is it helpful in addressing…
April 2024 The Hindu Editorial 25 April 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu EDITORIAL
25-April-2024
1. The Indian seafarer deserves better in choppy high seas
Topic:…
April 2024 PIB 25 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
25-April-2024
1. PM addresses 6th edition of International Conference on Disaster…


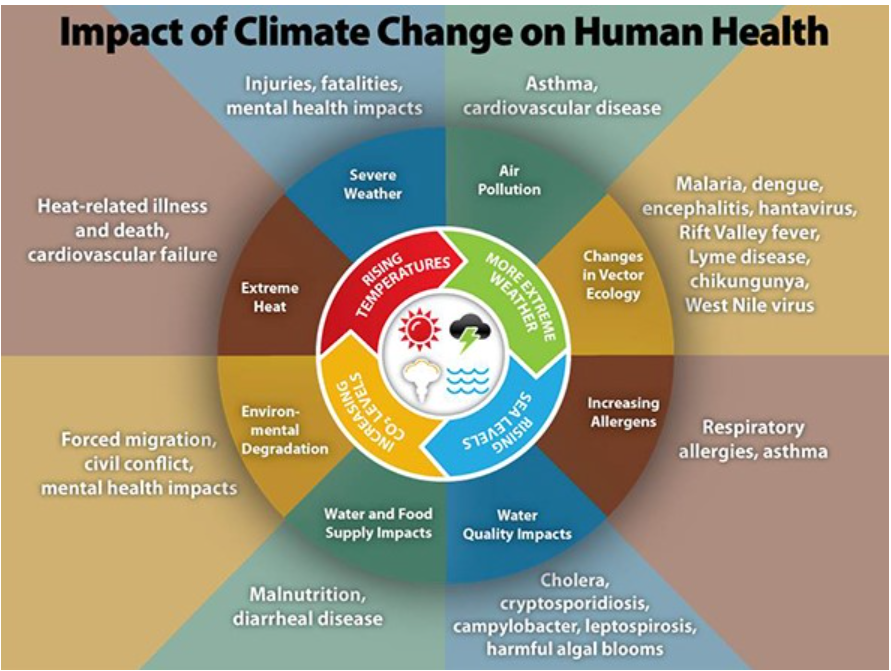 What increases the risk of Climate-Sensitive Health Threats?
What increases the risk of Climate-Sensitive Health Threats?


