21 November 2024 : PIB Summary For UPSC
1. Centre committed to efficient and transparent Public Distribution System
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2074977®=3&lang=1 )
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
Overview
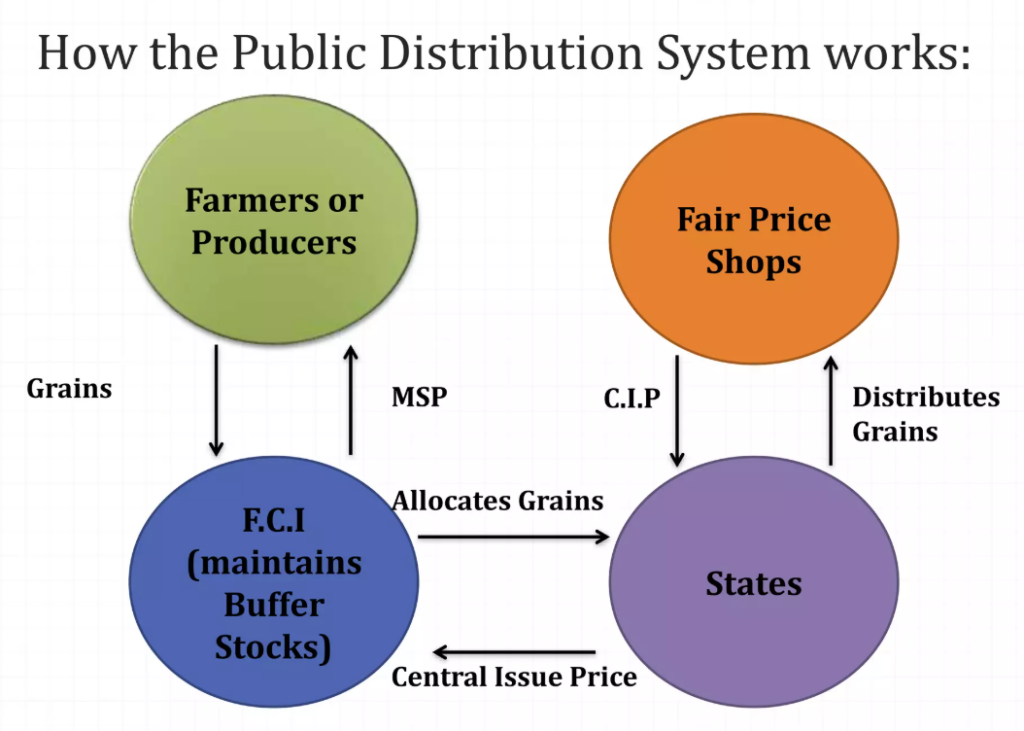
- The Public Distribution System (PDS) ensures food security by distributing subsidized food grains to beneficiaries under the National Food Security Act (NFSA) and Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY).
- The system currently covers 80.6 crore beneficiaries, with 20.4 crore household ration cards digitised.
Digitization and Aadhaar Integration
- 99.8% of ration cards and 98.7% of individual beneficiaries have been Aadhaar-seeded.
- Approximately 5.8 crore ineligible ration cards have been removed, ensuring rightful targeting.
- 64% of PDS beneficiaries have completed eKYC, with Aadhaar-linked eKYC in progress for others.
Distribution Mechanism
- Foodgrain distribution operational through 5.33 lakh e-PoS devices at nearly all Fair Price Shops (FPS) nationwide.
- Aadhaar authentication is used for 98% of total foodgrain distribution, reducing leakages and pilferage.
Supply Chain Reforms
- Implementation of the Supply Chain Management System for end-to-end tracking.
- Development of the Central Food Procurement Portal (CFPP) for streamlined procurement and MSP operations.
- Introduction of Warehouse Inventory Network and Governing System (WINGS) and Vehicle Location Tracking System (VLTS) for real-time tracking of consignments.
One Nation One Ration Card (ONORC)
- Objective: Ensures foodgrain access for NFSA beneficiaries nationwide using a single ration card.
- Portability: Allows ration access from any Fair Price Shop, irrespective of the origin state.
- Impact: Enhances food security for migrant workers.
- Technology: Operates through Aadhaar-enabled e-PoS devices, ensuring rightful targeting and reducing pilferage.
Through these reforms, India has established a transparent and efficient PDS, minimising leakages and improving food security.
| Practice Question: The integration of digitization and Aadhaar in India’s Public Distribution System (PDS) has enhanced transparency and minimised inefficiencies. Discuss the impact of these reforms on food security and equitable distribution while addressing the challenges in implementing such measures. (250 Words /15 marks) |




