6 November 2024 : PIB Summary For UPSC
1. Towards a TB-Free India: Achievements, Challenges and the Way Forward
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2070942®=3&lang=1 )
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health |
| Context |
|
India’s Journey Towards Tuberculosis (TB) Elimination
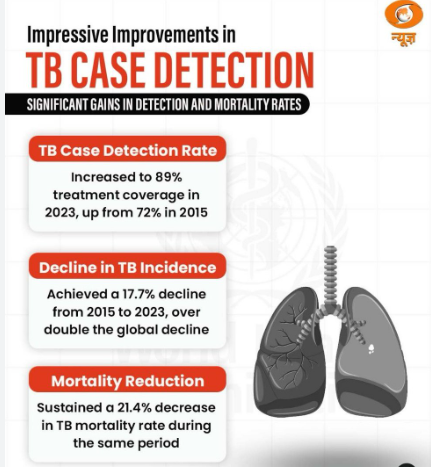
- India achieved a 17.7% decline in TB incidence from 2015 to 2023, which is more than twice the global average decline of 8.3%, according to the WHO Global Tuberculosis Report 2024.
- This success is attributed to the National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP), aimed at eliminating TB by 2025.
Strategies and Goals for Ending Tuberculosis in India
- SDG Target 3.3:
- Aims to end epidemics of tuberculosis by 2030.
- India targets to meet the End TB goal by 2025, five years ahead of the SDG deadline.
- Key Indicators for India’s TB elimination target:
- 80% reduction in TB incidence (compared to 2015 levels).
- 90% reduction in TB mortality (compared to 2015 levels).
- Zero TB-affected households experiencing catastrophic expenses due to TB.
- Political Commitment:
- The Indian government first announced the commitment to end TB at the End TB Summit in 2018.
- Reaffirmed at the One World TB Summit in Varanasi on World TB Day 2023.
- India is a signatory to the Gandhinagar Declaration to accelerate TB elimination by 2030 in the South-East Asia region.
India’s Approach: National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP)
- Post-COVID-19 Efforts:
- Intensified focus on TB elimination under NTEP, aligned with the National Strategic Plan (NSP) 2017-2025.
- In 2023, around 1.89 crore sputum smear tests and 68.3 lakh nucleic acid amplification tests were conducted.
- Comprehensive Care:
- Introduced shorter oral regimens for drug-resistant TB (DR-TB).
- Decentralised services to reduce treatment delays.
- Focused on addressing coexisting health conditions like malnutrition, diabetes, HIV, and substance abuse.
Strengthening Patient Care Through Supportive Services
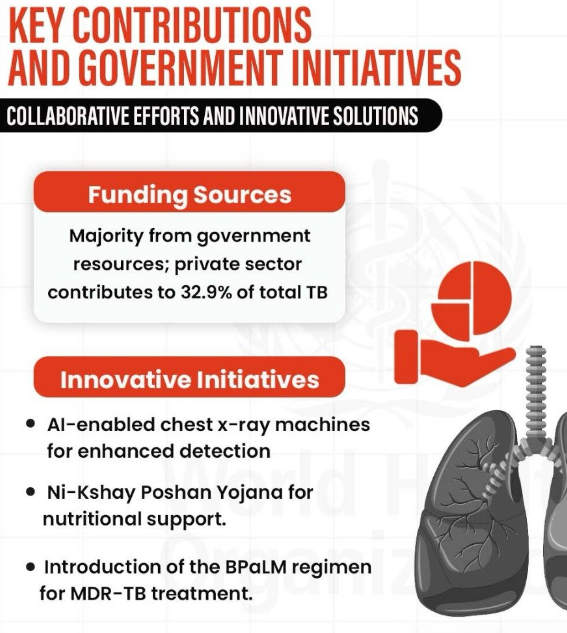
- Financial Support:
- Under Ni-kshay Poshan Yojana, Rs. 2,781 crores were disbursed to nearly 1 crore beneficiaries for nutritional support to TB patients.
- Community Engagement:
- Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan (PMTBMBA) launched in 2022, strengthening community participation.
- Over 1.5 lakh Ni-kshay Mitras committed to supporting TB patients through awareness and advocacy.
- Incentives for Treatment Supporters:
- Initiatives like TB Vijeta (TB champions) and ASHA workers were incentivized to support patients.
The Way Forward
- Future Interventions:
- Conduct studies on adult BCG vaccination.
- Rapidly scale up Tuberculosis Preventive Therapy (TPT), including shorter regimens.
- Increase access to molecular diagnostic testing for all suspected TB cases.
- Decentralise TB service delivery through “Ayushman Arogya Mandirs”.
- Strengthen community-based patient support systems through PMTBMBA.
Conclusion
- India’s approach to TB elimination is showing positive results with a decline in TB incidence and a strengthened healthcare response.
- By emphasising cross-sector partnerships, innovative care solutions, and community engagement, India is well-positioned to meet its TB-free nation goal by 2025.
| Practice Question: Discuss the strategies adopted under the National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP) in India to achieve the goal of TB elimination by 2025. (150 Words /10 marks) |



