Science Reporter June 2023 : Computational Gastronomy Food Science Taking Leaps
Article 1: National Quantum Mission: A Boost to India’s Quantum Endeavours
Recently, National Quantum Mission (NQM) received the union cabinet chaired by the Prime Minister approval at a total cost of Rs. 6000 crores, a significant step towards positioning India as a leading player in the field of quantum technologies.
About National Quantum Mission (NQM):
- Aim: It will mainly work towards strengthening India’s research and development in the quantum arena alongside indigenously building quantum-based (physical qubit) computers which are far more powerful to perform the most complex problems in a highly secure
- Implementing Agency: Department of Science and Technology (DST) will lead this national Mission, supported by other
- Mission period: It is planned for 2023-24 to 2030-31.
- Targets:
- Developing intermediate–scale quantum computers with 50- 1000 physical qubits in 8
- Satellite-based secure quantum communications between ground stations over a range of 2000 km within India and with other Also, Inter-city quantum key distribution over 2000 km.
- Applications areas:
- Magnetometers with high sensitivity in atomic
- Atomic clocks for precision timing, communications, and
- Design and synthesise quantum materials such as superconductors, novel semiconductor structures, and topological materials to fabricate quantum
- Single photon sources/detectors and entangled photon sources for quantum communication, sensing, and metrological
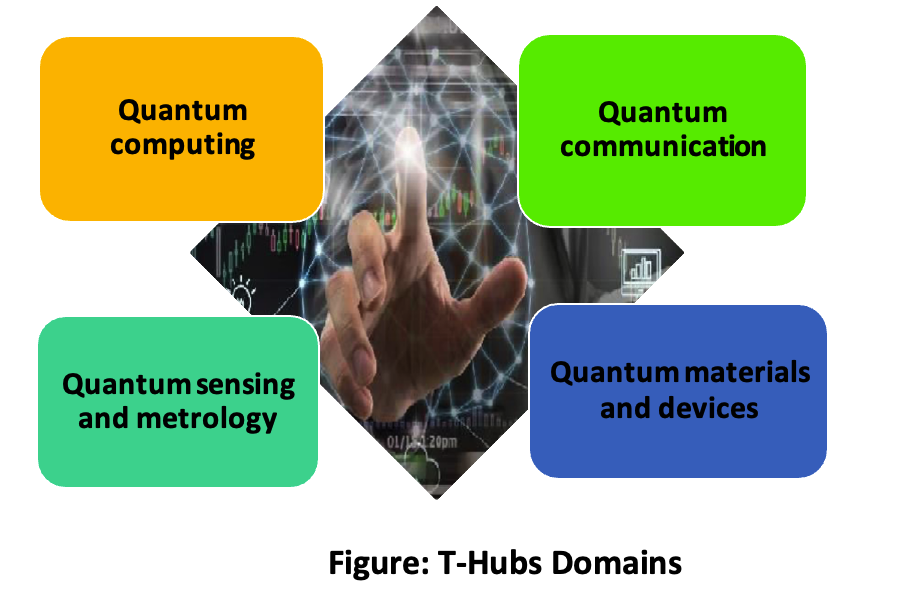
The Themes- Four thematic hubs (T-Hubs)
- T-Hubs will be established at leading academic and national research and development institutes. These T-hubs will be in the following four domains, as shown in the diagram below-

What are the Advantages of Quantum Technology?
- Increased Computing Power: Quantum computers are much faster than the computers we have today. They also can solve complex problems that are currently beyond our
- Improved Security: Because they rely on principles of quantum mechanics, quantum encryption techniques are much more secure than traditional encryption
- Faster Communication: Quantum communication networks can transmit information faster and more securely than traditional networks, with the potential for entirely unhackable
- Enhanced Artificial Intelligence (AI): Quantum machine learning algorithms can potentially enable more efficient and accurate training of AI
- Better Sensing and Measurement: Quantum sensors can detect tiny environmental changes, making them useful in medical diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and geological
- Enables large-scale simulations: In a nation such as India, where the government utilises technology to address problems on a massive scale, integrating quantum computing could prove highly advantageous, as it enables the execution of extensive
- Value addition in the economy: The adoption of quantum technologies by different industries in India can contribute $280-310 billion to the economy by
- Boost to R&D initiatives: It will provide the necessary push to the institutions involved in the research and development of quantum
- Benefits to government schemes: It will provide a considerable boost to National priorities like digital India, Make in India, Skill India and Stand-up India, Start-up India, Self-reliant India, and Sustainable Development Goals (SDG).
What are the Challenges of Quantum Technology?
- Expensive: The technology requires specialised equipment and materials, which makes it more costly than traditional
- Limited Applications: Currently, quantum technology is only valid for specific applications such as cryptography, quantum computing, and quantum
- The skilled workforce required: Organisations need to upskill current workers and create pathways for new talent to ensure they have enough quantum computing expertise, as they have done for
- Sensitivity to Environment: Quantum technology is susceptible to environmental interference, such as temperature changes, magnetic fields, and
- Limited Control: It is difficult to control and manipulate quantum Quantum-powered AI could create unintended consequences.
Conclusion:
The recent decision approving the National Quantum Mission has boosted India’s Quantum efforts. However, Quantum technologies can be challenging for the general public; there is also a need to raise awareness about the potential impact of quantum technologies, address misconceptions, and foster public acceptance by communicating the benefits and societal implications of quantum advancements.
Article 2: Previously unknown isotope of Uranium discovered
Nuclear physicists from Japan and Korea have recently achieved a significant breakthrough in their search for a “magic number.” They have successfully identified a new isotope of Uranium, having an atomic number of 92 and a mass of 241. It is Uranium-241.

What is a “Magic Number”?
In nuclear physics, “magic numbers” are specific numbers of protons or neutrons in atomic nuclei that correspond to Stable configurations. The heaviest known ‘magic’ nucleus is lead (82 protons) after this nucleus becomes unstable.
What are Isotopes?
Isotopes refer to atoms of a particular element with varying numbers of neutrons. They have similar chemical properties but may differ in physical properties like density and radioactivity.
- Atomic number = of Protons = No. of Electrons
- of Neutrons = Atomic mass- Atomic No.
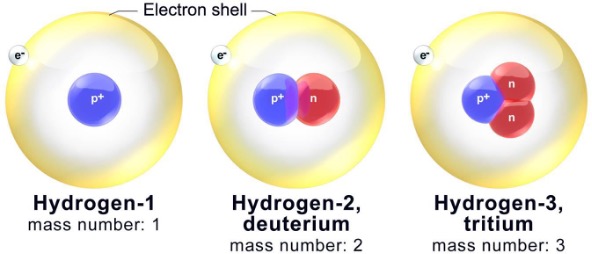
Fig: Hydrogen and its two naturally occurring isotopes, deuterium and tritium. All three have the same number of protons (labelled p+) but different numbers of neutrons (labelled n).
What is Uranium?
- Uranium is a silvery-grey metal with the symbol U and atomic number 92.
- It belongs to the actinide series of the periodic table and has isotopes like U-235 and U-238 with different numbers of
- It is a radioactive heavy metal that occurs naturally in low concentrations in soil, rock and water and is commercially extracted from uranium-bearing minerals.
Note: In its natural state, Uranium consists of three isotopes (U-234 (0.0057%), U-235 (0.72%) and U-238 (99.28%). Other isotopes that cannot be found in natural Uranium are U-232, U-233, U-236 and U-237.
What is the significance of a new isotope?
- Physicists rely on it to enhance the accuracy of models for nuclear power plants and exploding stars, pushing the boundaries of existing models to new
- Furthermore, it provides crucial insights into the formation of heavy elements in astronomical
Details of the Finding:
- In this new effort, the research team tried a new approach—they fired a sample of uranium-238 nuclei at a sample of platinum-198 nuclei using an isotope separation
- Such interactions result in multi-nucleon transfer, in which isotopes swap neutrons and protons. The collision resulted in the creation of many fragments, which the researchers studied to determine their
- They found evidence of 19 heavy isotopes holding from 143 to 150 Each was measured using time-of-flight mass spectrometry, a technique that involves determining the mass of a travelling ion by tracking the time it takes to travel a given distance when its initial acceleration is known.
- The research team noted that most of the isotopes they measured had never been measured
- They also noted that one of them, uranium-241, had never been observed before and that it marks the first time since 1979 that a neutron-rich uranium isotope has been discovered. The researchers also calculated that uranium-241 likely has a half-life of just 40
Future Implications:
Implementing a multi-nucleon transfer reaction in conjunction with the KEK Isotope Separation System (KISS) is poised to revolutionise the identification of neutron-rich actinide nuclides. This advancement will significantly increase our knowledge of their stability and the intricacies of astronomical nucleosynthesis.
Article 3: The Abel Prize -2023: For Equations that Predict the Physical World
Argentine-American Luis Caffarelli has won the 2023 Abel Prize for his contributions to regularity theory for nonlinear partial differential equations, including free-boundary problems and the Monge-Ampère equation.

About the Abel Prize:
- It is named after the Norwegian mathematician Niels Henrik Abel (1802-1829) and is one of the most coveted awards in
- The Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters presents a prize bestowed by King
- The choice of the Abel laureate is based on the recommendation of the Abel Committee, composed of five internationally recognised
About Partial Differential Equations:
- Differential equations are tools scientists use to predict the behaviour of the physical world. These equations are prominent in many disciplines, including engineering, physics, economics, and
- Partial differential equations arise naturally as laws of nature to describe phenomena as different as the flow of water or the growth of
- For centuries, mathematicians have dedicated their efforts to studying these equations. However, the solutions to some of these equations still remain
Luis Caffarelli & his contributions:
- Luis Caffarelli is a professor at the University of Texas and was honoured for his seminal contributions to regularity theory for nonlinear partial differential equations. He is the first person born in South America to win the
- Cafarelli studied partial differential equations for 50+ years, which explain natural phenomena like water flow and population growth. Scholars have researched them since Newton and Leibniz’s
- His contributions have significantly improved our comprehension of several nonlinear equations that have multiple applications.
- It’s worth recognising that Helge Holden recognises the significant impact an individual can have on their profession through their skilful use of geometric intuition and analytical
- Luis A. Caffarelli is a renowned mathematician with many prestigious awards, including the Guido Stampacchia Prize (1982), Bocher Prize (1984), Rolf Schock Prize (2005), Steele Prize (2009), Wolf Prize (2012), and Shaw Prizes (2018).
Article 4: Eco-tourism on the Coral Island of Lakshadweep
Niti Aayog is exploring eco-tourism in Lakshadweep to attract tourists seeking a Maldives-like experience.
About Lakshadweep:
- Lakshadweep is a union territory of India with 12 atolls, three reefs, five submerged banks, and ten inhabited islands. The capital is Kavaratti.
- The area has beautiful islands, coral reefs, atolls, lagoons, seawater, and sandy
- Lakshadweep’s soil is mainly limestone from coral and sedimentary rocks. Beaches have silvery-white shimmer due to coral dust, while inland soil is ash-coloured.
- The entire Lakshadweep group of islands has recently been declared as an organic agricultural area under India’s Participatory Guarantee System (PGS).
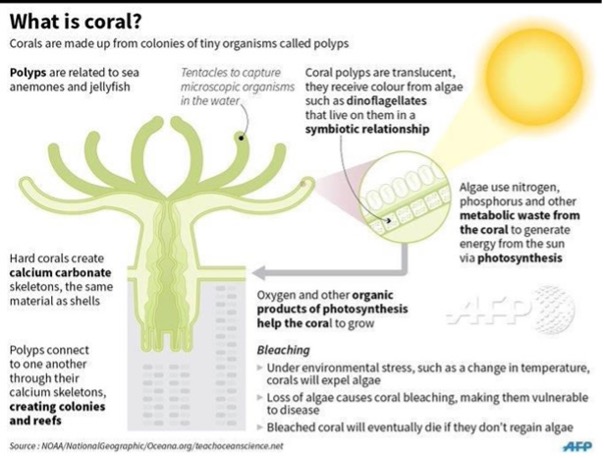
Coral Islands:
- Lakshadweep is a popular tourist spot known for its beautiful coral islands formed on submerged volcanoes.
- Corals are marine animals that form polyp-like formations and live in colonies. They secrete calcium carbonate to form skeleton-like structures, and when they die, they create coral
- Reefs need water, plankton, sunlight, 20°C temperature, and air to There are three coral reefs: Atolls, Fringing reefs, and Barrier reefs.
- The coral reefs are one of India’s most ancient and dynamic They provide a sanctuary to countless marine life and play a crucial role in protecting the coastline from erosion. The Lakshadweep have both fringing reefs and atolls.
- The atolls have been formed because of the coral gathering on the volcanic crests in the Indian Ocean that were submerged long ago.
Tourism and economic potential:
- The most outstanding strength of the islands is that it offers a precious heritage of ecology and culture. (The blue water lagoon, corals, coral reefs).
- Lakshadweep’s underwater view is diverse and mesmerising, with perfect water sports opportunities. It’s a popular destination for nature tourism in India. Beautiful beaches attract many international tourists.
Lakshadweep won the National Eco-Tourism Award in 1997.
- These attractions and the possibilities of sea-based aqua sports should be adequately publicised in the international
- Islands rely on fishing and coconut cultivation but need more value-added activities.
- There is a lot of scope to tap solar energy in Issues related to the proposal of building tourism:
- Ecological impact: The environmental impact of such a project on the lagoons and coral reefs is likely to be far more complex and
- Endangered marine life: These waters are home to various threatened and endangered marine life. Any development project will impact this marine
- Waste generation: Tourism in the area would lead to waste generation, harming local ecology. For instance, plastic waste is dangerous if it enters the marine food
- Coral bleaching: Human concentration and tourism in the area would disturb local coral species and destroy their
- Destroy the island’s beauty: Tourism often destroys the serenity and beauty of islands through congestion, traffic, and unpleasant
Conclusion:
The Indian government aims to develop the Lakshadweep Islands while preserving their natural ecosystems and species.
Article 5: Computational Gastronomy (Food Science Taking Leaps)
We study traditional recipes and their impact on health with data and AI. This is “computational gastronomy,” using science to revolutionise the food industry.
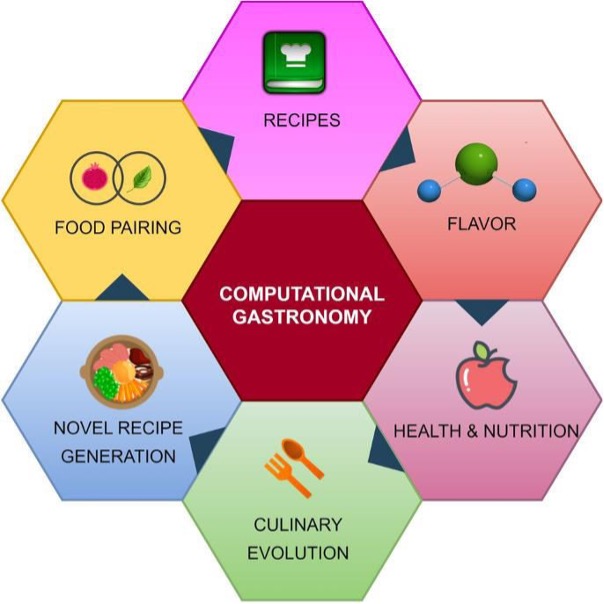
FIGURE: Science that blends food with data and the power of computation for achieving data-driven food innovations.
What is Computational gastronomy?
It is a science that blends food with data and the power of computation to achieve data-driven food innovations. It involves data to understand the various ingredients and flavours and then uses algorithms to create new combinations and recipes.
How does computational Gastronomy work?
Computational gastronomy combines food with data and computation.
While there are existing databases like RecipeDB and FlavorDB, there is still room for improvement in the granularity of recipe data and information on flavour compound concentrations. Predicting taste using data alone is difficult, but tools like BitterSweet, SpiceRx, and DietRx provide useful insights. Food pairing analysis and language modelling can generate novel recipes, but better training strategies and high-resolution food images are needed for accuracy. Nutritional profiles and servings can also be included in recipe generation.
Benefits of Computational Gastronomy:
The field of computational gastronomy is brimming with practical applications that can significantly enhance our food and eating habits. With its growth, we can expect an influx of technological advancements that will pave the way towards the following:
- Recipe optimisation
- Better food safety and quality control
- Personalised Nutrition
- Reduced food waste and
- Comprehensive flavour profiling.
FUTURE IMPLICATIONS:
Computational gastronomy using data science and AI can revolutionise food pairing, recipe development, and personalised nutrition plans. It can also create innovative food products to mitigate health issues related to lifestyle choices. India is poised to benefit from this technology with its bright future.
Article 6: Emerging Threat of Nanoplastics Pollution to terrestrial ecosystems
World Environment Day 2023 theme: “Beat Plastic Pollution” due to the rise of nano plastic pollution on land. It severely affects soil fertility, crop productivity, and human well-being.
https://sciencereporter.niscpr.res.in/home/article/959
How are Nanoplastics (NPs) created?
The problem of plastic pollution is a serious concern. 85% of ΩΩthe 400 million tons of plastic waste generated each year ends up in landfills or is disposed of improperly. Developing countries are particularly affected due to a need for proper garbage disposal and recycling systems. The degradation and disintegration of plastic in the environment create harmful microplastics and nanoplastics.
Why is Plastic pollution on land more prevalent than in the ocean?
- Plastic waste is a serious issue that harms both humans and the Land pollution from plastic is worse than ocean pollution, with agricultural lands having more plastic particles than sea basins. Unfortunately, the impact on agriculture has not received enough attention.
- Nanoparticles can enter soil through various human activities like water pipes, agriculture, sewage, and industrial waste. They can also come from rainfall and airborne sources.
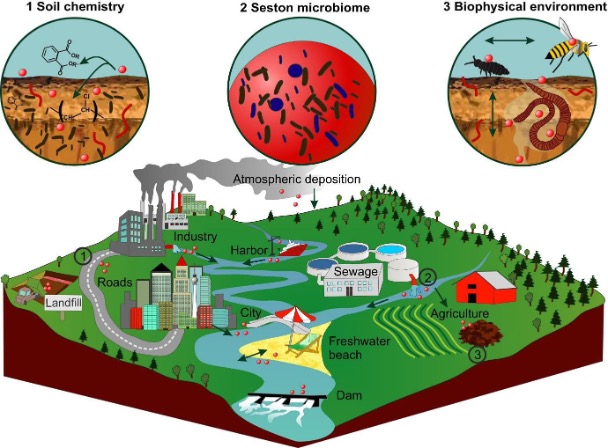
Impact of NPs on ecosystems:
- Scientists are studying the long-term impact of NPs on the environment and ways to reduce any risks they may
- Studies show that NP particles directly impact soil microbes, animals, and plants in the rhizosphere. NPs can harm earthworms and filter feeders by getting absorbed into their digestive
- NPs or fine particles can attach themselves to harmful chemicals and transport them, negatively impacting the environment and hindering seedling growth.
- Nanoparticles (NPs) in soil affect plant growth and can accumulate in plant tissue, harming food yield and safety. Lettuce has the ability to take in NPs and transfer them to other organisms in the food chain, which can be harmful to the health of both herbivores and humans.
- Nanoparticles can hinder plant growth by disrupting mineral transporters, leading to decreased photosynthesis and respiration and resulting in stunted
- Nanoparticles can harm plants, but more research is needed to understand how they affect gene regulation and signalling.
Ways to reduce the impact of NPs:
- Understanding the mechanisms of NPs in plants is crucial for reliable monitoring and risk evaluation.
- Bridging gaps in knowledge of their sources and transport pathways is necessary for effective regulation and
- Maintaining soil fertility and implementing sustainable farming practices are essential for agriculture.
- Additionally, students studying biology should also gain knowledge about the plastic cycle, which operates similarly to the natural carbon cycle, circulating through the atmosphere, oceans, and
- More research on the effects of soil NPs on organisms is We should reduce plastic usage, especially in our countries.
- Educating the public about NP contamination and soil protection is also
CONCLUSIONS:
Environmental policies can help manage plastic waste and NPs.
General regulations can discourage the use of plastic products made by primary NPs. Let’s work together for a safer future.
Article7: MICROPLASTIC in the ENVIRONMENT
Plastic production has increased to 353.3 million tonnes per year, with 80% ending up in landfills or contaminating soil, water, and food. Only 9% of plastic is recycled.
What are microplastics?
Plastics don’t decompose on their own. When exposed to natural elements like sunlight, heat, air, and water, they break down into microplastics. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration(NOAA) and the European Chemical Agency classify particles smaller than 5mm in size.
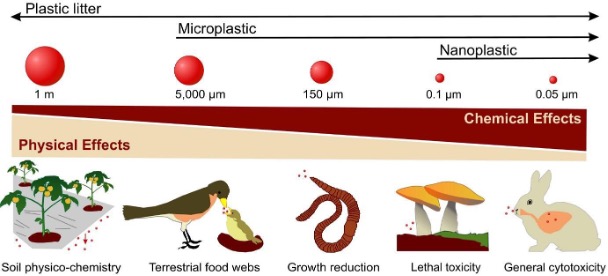
Sources of microplastics:
- Microplastics come from many sources, including household waste, wet pipes, cigarette butts, and tyres. They end up in water, air, food, soil, and drinking water, causing significant
- Microplastic particles are released when washing and drying synthetic fibres. Plastic materials also release microplastics when exposed to sunlight, heat, air, or rain.
- Commonly consumed foods and packed meat and fish may contain hazardous levels of microplastics, according to researchers from China and the
- These include salt, beer, tea, wine, sugar, apple, carrot, rice, peanut, broccoli, honey, lychee, radish, spinach, chicken, prawn, crab, and various types of
Key results:
- A recent survey found that 77% of people tested had high levels of microplastics in their bodies. The most common types were polythene terephthalate, polystyrene, and polymethyl acrylate. Another report estimated that an average of 40,000 to 50,000 microplastic particles enter the human
- Microplastics have been found in human faeces and deceased Studies show high levels of microplastics in both.
- Bottled water has 400-700 microplastic particles per litre, while tap water has 30-40. 94% of US tap water is contaminated, with 72% in Europe and 82% in New
- A study in Italy found micro-plastics in commonly consumed foods, with apples having the highest concentration. Humans consume 5-10 grams of microplastics per week based on Microplastics were also found in salt samples, requiring further research on the impact on human health.
Impact of microplastics:
- Harmful particles can accumulate in sea animals and harm larger creatures. Microplastics damage the ocean floor. Soil and organisms on land can decline and harm animals and the
- Microplastics in the ocean have caused high levels of toxins in sea fish. Avoid microwaving food in plastic to reduce exposure to harmful
- Microplastics harm all living organisms, from tiny zooplankton to large animals like whales, elephants, and even humans.
- Microplastics can contain harmful components like polystyrene, polyethene, and polyester. Animal experiments show they can cause health problems like infertility, hormonal imbalances, and cancer. They can also lead to oxidative stress, DNA damage, and improper fetal growth.
What can we do to limit the impact of microplastics?
- There is an urgent need to implement a global resolution to limit the production of single-use, throwaway
- To minimise the impact of microplastics, we can use them judiciously and can follow the 3-R rule: Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle.
- Some more tips include the following:
- Choose organic clothing (not synthetic)
- Hand wash and air-dry clothes
- Avoid single-use plastics
- Use microplastic-free cosmetics
- Limit shellfish consumption
- Use public transportation
- Keep your home clean by regular dusting and vacuum cleaning.
- Avoid storing drinking water in plastic bottles
Way forward:
- Although microplastics may not be the most toxic environmental contaminant on their own, the trend of increasing plastic contamination in natural environments globally is consistent across the past, present, and future. Hence, personal initiatives such as zero-waste trips, shunning disposable and using own utensils etc., can
- Governments, research institutions and industries need to work collaboratively on redesigning products, and rethink their usage and disposal, in order to reduce microplastic waste from pellets, synthetic textiles and
Article 8: Soil to soil -In the true spirit of a circular economy
Biochar from rice husks can benefit Indian farmers by conserving resources and nutrients and improving profitability in rice cultivation.

Figure: Traditional 3S-cookstove and biochar cook stove (photograph taken in Vietnam, June 2014) and Rice husk biochar produced in Vietnam by Pacific Biochar Company
Introduction:
- Rice is a staple food for millions worldwide, with India as the second largest producer. India produces over 110 million tonnes of rice paddy annually, which is a significant income source for many farmers. West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, and Punjab account for almost 40% of total
- Rice harvest produces 20% organic waste, like rice husk. For every 110 million tonnes of rice, 22 million tonnes of husk need to be
Dealing with the husk:
- Rice husk in India has many uses, including cattle feeding, fueling kilns and furnaces, and as a raw material for chemicals. It can also be used in metalworking and building materials.
- Burning rice husk is harmful and wasteful. It should be viewed as a valuable resource instead of being disposed of in landfills or
- Rice husk has low nutritional value for cattle but can be repurposed for energy, wastewater treatment, and the adsorption of
- Theoretically, 22 million tonnes of rice husk can generate 25 TWh of electricity annually and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Back to soil option:
- Biochar improves soil, reduces fertiliser and water usage, and increases crop productivity. It’s made from organic waste heated in an oxygen-limited environment. Its effectiveness depends on soil type, biomass, climate, crop species, and pyrolysis
- Biochar production can reduce indoor air pollution and improve fuel efficiency by producing biochar and heat energy for cooking on small or large
- Reducing LPG use and deforestation can improve social sustainability. Research shows 25% less cooking time benefits mothers and women, giving them more time for family, community, education, and income.
- Biochar reduces methane emissions in rice fields by creating unfavourable conditions for methane-producing bacteria, improving soil aeration, and increasing the oxidation of methane to biogenic carbon
- Biochar in composting boosts aeration, nutrient retention, and Mixing biochar in a 1:4 ratio with poultry litter compost can reduce nitrogen losses.
- Adding biochar to soil can be expensive, but mixing it with composted manure or minerals can still provide benefits, according to research in Vietnam.
- To adopt biochar, consider its impact on the environment, health, society, and economy. In North Vietnam, biochar production costs around US $118 per ton, which farmers find beneficial.
- Replace forestry residues with crop residues to support small farmers and save money. Biochar can boost rice production in
New and promising:
Biochar production from rice residues has many benefits over open burning. It generates renewable energy, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, and enhances crop productivity, among others. Introducing this technology in India could be valuable.
Article 9: Ingenious Traditional Water Harvesting System Used in Jharkhand
Context:
India’s water demand will exceed water supply by 2030. Depletion of groundwater levels is a significant concern that requires immediate attention for future water security.

Figure1: Gada Daadi method of water purification by tribes from Jharkhand (Gada-river, Dead-water collecting site)
What is Water Harvesting?
Water harvesting is collecting and storing water from natural or artificial surfaces that prevent it from soaking in. Factors affecting the amount collected include rainfall, surface properties, water needs, and recharge capability.
Rainwater harvesting systems include several components:
- Catchment – used to collect and store
- Conveyance system – transports harvested water from the catchment to the recharge
- Flush – eliminates the first spell of
- Filter – removes pollutants and filters collected
- Tanks and recharge structures – store the filtered water for later
Significance of rainwater harvesting:
Rainwater harvesting is crucial for food security in India, as 60% of farmland relies on rainwater. Harvesting rainwater helps control runoff and evaporation, providing a decentralised water source that reduces the burden on women living in remote and dry areas.
- Reduces evaporation losses: as water is stored either below ground or in tanks.
- Prevents water from getting polluted: pollution of surface water with fertilisers, pesticides, metals and other sediments are filtered out.
- Sustainable Use: Promotes both water and energy conservation.
- Easy to operate: The cost of recharge to sub-surface reservoirs is lower than surface reservoirs. This technology is relatively simple, easy to install and operate.
- Reduces runoff challenges: It reduces soil erosion, storm-water runoff, and flooding.
- Mitigates probability of agricultural drought due to rise in groundwater and stored water.
- Food security: reduced floods, recharged aquifers and storages lead to lesser agricultural droughts.
- Social Impact: Women do not have to walk for miles to get water.
- Cheap storage: It can be used as a water reserve. No land is wasted for storage purposes, and no population displacement is involved.
- Productivity: It increases the productivity of the aquifer.
Some traditional water harvesting techniques:
For centuries, India has used successful and sustainable traditional methods for water management, such as Johads, Jhalars, Kulhs, Baolis, Sars, Bandhas, Talavs, Tals, and Tonks.
Traditional water harvesting system used in Jharkhand:
- Daadi, a traditional water conservation method used in Jharkhand, India, has proven effective in combating water scarcity, pollution, and depletion of water bodies. This sustainable and low-cost approach is helping to protect rural
- Small cylindrical holes called Daadis are constructed or carved out near the riverbank, typically 2-5 feet in size. They are strategically dug out to a depth of 1-2 feet to collect sufficient water. Each season, multiple Daadis can be dug on the river (Shown in the above figure1)
- The holes in Daadis work in two ways:
- The horizontal movement of water from the adjacent river into these holes through the sand deposited on the shore;
- Capillary movement of water due to the potential difference between the Gada (river) and Daadi (the collecting hole) in the Tribal people dig holes around their land edges to collect water from the riverbed, which acts as a natural filter.
- Water can be collected using household containers or by digging up to 20 feet with modern tools. No need for pumps or power tools; women can do it
- Locals use water for irrigation, cattle, and chores without They filter it for drinking and use plants to improve the quality of cooking.
Way ahead:
To improve water security, reduce reliance on groundwater by replenishing natural and artificial water sources, recycling treated wastewater, and installing rainwater harvesting systems. Governments and local authorities should implement sustainable policies and comprehensive water management strategies.
Conclusion:
Rainwater harvesting is a sustainable water management method that can lead to economic opportunities and empowerment at the grassroots level. Combining traditional methods with modern techniques could solve India’s water scarcity issues. The tribals in Jharkhand have a sustainable water harvesting technique that provides valuable lessons.
Article 10: Paul Berg
Context: Paul Berg, a pioneer in genetic engineering, has passed away.

What is Genetic Engineering?
Genetic engineering modifies DNA to introduce new traits. It’s used in food production, medicine, and the creation of gene-edited organisms. Paul Berg discovered it in 1971. It’s led to therapies for diseases, including Covid-19 vaccines.
About Paul Berg:
- Berg was a US Navy veteran with a keen interest in Biochemistry.
- He earned his PhD in biochemistry from Case Western Reserve University in 1952 and completed postdoctoral studies in Copenhagen and Bethesda after his PhD.
Contributions of Paul Berg:
- Paul Berg discovered the importance of vitamin B12 and folic acid in one- carbon mechanism in Human Metabolism. He increased our understanding of how foodstuff converts to cellular material.
- Paul switched to studying mammal viruses and discovered how to create hybrid viruses using SV40 and bacterial viruses in the
- In 1971, Berg created the first recombinant DNA by combining genetic material from the lambda bacterial virus and the simian virus through a process of cutting and reconnecting DNA using enzymes. This breakthrough paved the way for genetic engineering and the biotechnology
- Berg won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1980 for his work on nucleic acids and recombinant DNA research.
DNA Exchange Mechanism
- Dr Berg delayed introducing rDNA into another organism due to concerns about potential hazards and ethical considerations regarding interference with the natural order.
- Exchanging DNA carries potential risks, such as harmful genes spreading and causing disease or environmental disasters. Caution and careful consideration are
- In 1974, Dr Berg and a team of researchers warned about the risks of combining virus and bacteria DNA. They urged scientists to take precautions when creating recombinant DNA.
- Berg co-founded DNAX in 1980 to design unique immunoglobulins using DNA. After the acquisition by Schering-Plough, research shifted to producing interleukins using Berg’s cloning system. DNAX is now a leading immunology research
- Berg was a renowned scientist who won numerous awards, including the Eli Lilly Award and the National Medal of Science. He was also a respected teacher, receiving the Henry J Kaiser Award
- Berg supported science education and postdoctoral researchers, emphasising their creativity and potential for success.
Conclusion:
Paul Berg’s passing is a great loss to the scientific community. He established and managed the Beckman Centre, raised funds, and promoted research sharing. Berg believed in following passions and exploring new frontiers.
Article11: Phytosemiotics-Decoding the Secret Language of Plants
To learn about “Phytosemiotics“ and how it helps decode the secret language of plants.
Discussion in brief:
- Petrichor is the scent after the first rainfall, caused by plant oils, geosmin, and ozone from the
- Freshly cut grass has a sweet smell similar to petrichor, but it’s actually a distress signal. The scent comes from Green Leaf Volatiles, which help stimulate wound healing and have antibacterial
- Green Leaf Volatiles(GLVs) attract predators to caterpillars but also
cause urban smog and reduced visibility in North India.
- Scientists study plant communication through phytosemiotics, focusing on petrichor and GLVS. The idea of “W-waves” as a language of trees has been dismissed as pseudoscience.
- Jagadish Chandra Bose found that plants react to stimuli with electrical impulses, similar to animals. Recent studies support this
- Plants release ethylene when injured and can attract helpful species through VOCs, revealing a hidden language of plants facilitated by glutamate. This area of research sheds light on nature’s intricate
- Plants use geosmin and sound to communicate with insects and share nutrients with neighbouring trees. Human activities can impact plant communication, but scientists are working on strategies to reintroduce lost genes and use plants to detect
Conclusion:
Plant communication reveals hidden aspects of nature through low-frequency clicks and fragrances. Decoding chemical signals is like deciphering codes or searching for signs of extraterrestrial life. It’s a fascinating field that inspires scientists to learn about plant behaviour.
Article 12: Bats Are Helpful Too
Context: Bats and humans have lived together for a long time, but people often don’t realise the benefits that bats bring to the environment. Recent worries about viruses carried by bats have increased because of COVID-19.
About Bats-
Bats are the only flying mammals with elongated fingers and a thumb connected by skin. They can change direction quickly and catch mosquitoes while in flight.
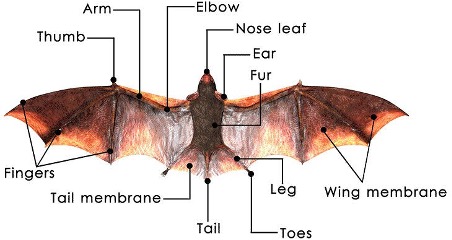
Diagram Of Bat Anatomy With Labeled Parts (totalwildlifecontrol.com)
Classification of bats-
| Microbats | Megabats |
 |  |
| Small in size | Large in size |
| Feed on insects | Feed on fruit |
| Have large ears relative to their
body size | Have small ears relative to their
body size |
| Use echolocation to find food | Use a sight to find food |
| Vampire bats are a type of microbat that feeds on blood, but they prefer cattle and horses to humans. There are also a number of microbats that eat fruit and are valuable pollinators as well. | Megabats are mainly herbivorous. There are some exceptions to this, like (Myotis Vivesi) which is known as the Fishing Bat, and not surprisingly; it eats fish. |
Indian Flying Fox:
The Great Indian Fruit Bats, also known as Indian flying foxes, are giant bats worldwide. However, they can carry diseases like the lethal Nipah Virus, which can spread to humans.
Distribution of bats-
- Megabats live in Africa, Asia, Australia, and the Pacific
- Microbats are found all across the world except for Antarctica and the Arctic.
- All bats can be traced back to one ancient species. India is one of the world’s mega-biodiversity hotspots.
- India has around 100 species of bats, including 12 types of fruit bats that eat fruits or nectar.
Role of bats in disease spread such as Corona, Ebola-
- Bats can transmit rabies and cause new conditions, so studying them is essential.
- Bats carry harmful viruses such as Nipah, Hendra, Ebola, Marburg, and
- Bats can pass diseases to humans through direct contact or contact with infected animals, known as ““
Reasons for spillover of diseases from bats to humans-
- Human activity and consumption of bushmeat are causing increased zoonotic disease
- Human activities like deforestation, agriculture, and infrastructure building disrupt bat roosts, causing them to seek new homes.
- Scientists say that mining and quarrying can harm bats’ natural cave structures, leading to stress and virus shedding.
Significance of bats:
Bats are often associated with negative superstitions. They were also linked to the COVID-19 virus. But bats have also contributed positively to society. Let’s explore their benefits.
- Seed dispersal: Bats rely on plants for food, with fruit-eating bats consuming flowers and fruits. They play a crucial role in seed dispersal and forest regeneration, with research indicating better germination rates and growth from seeds dispersed by
- Pollination: Bats are crucial for pollinating plants and protecting crops, especially fruit bats for big nectar-filled flowers and mangrove species important for coastal ecosystems and
- Production boost: Insects can harm crops, costing $470B and affecting 26% of global production. Bats are insects’ ingesters, i.e., they eat so many insects. Insectivorous bats eat pests and rodents, enhancing crop productivity and boosting the
- Soil fertility: Bats are essential for maintaining soil fertility and nutrient distribution. Their droppings enrich the soil and improve agricultural productivity without harming human
- Health benefits: Bats can improve human health by eating disease-carrying insects like mosquitoes. They can consume up to 5,000 mosquitoes in one night, making them a great natural solution for controlling insect populations.
- Human Helpers: They are human helpers as one of the bats, called the vampire bat, has some anticoagulant in its saliva, which scientists have discovered can treat heart patients in future.
Precautions related to interaction with bats:
- Avoid handling or consuming bats, and don’t eat fruits bitten by bats or contaminated by bat fluids.
- This will gradually reduce the disease
- In the long term, we must focus on limiting and reversing land use practices that increase our interaction with bats.
Reasons for the decline of Bats:
- Ongoing obliteration of natural habitats
- Hunting and killing for sport and food
- The growing use of wind turbine energy
- Spread of harmful and baseless myths about bats etc
Conserving Bats:
According to IUCN, 5% of bat species are in danger of becoming
extinct, while 11% have insufficient information about their status. Unfortunately, fruit bats are considered pests under the Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1973, Schedule 5, making conservation efforts difficult due to legal barriers.
Conclusion-
Protecting biodiversity and habitats is crucial in stopping pandemics. Illegal hunting, wildlife trade, and habitat destruction raise the risk of viruses jumping from animals to humans. Even the absence of bats can significantly affect our daily lives.
Article13: Kleptoparasitic Birds The “Winged Pirates of the Avian World”
Context: Have you heard of Kleptoparasitic Birds? They’re known as the “Winged Pirates of the Avian World” and have intriguing strategies for obtaining food and resources.
Want to learn more?
- Some birds steal food from others instead of searching for it, which is called Kleptoparasitism. They are known as “the winged pirates of the avian world”.
- Kleptoparasitism is common in birds like skuas and frigate birds. They steal food from other animals as a foraging strategy, but the exact reasons for this behaviour remain
- Many bird species use this technique, including Golden Eagles, Bald Eagles, Corvids, Gulls, Boobies, and Gannets. Seagulls can be seen snatching food from people’s
- Falcons and hawks are called pirates because they steal. Red-tailed hawks take from other hawks, like Rough-legged and Northern
- Some birds use different tactics to steal food from other birds, like chasing prey in flight, diving, imitating alarm calls, and crabbing. Examples include Aleptoparasitic birds, Golden eagles, and Peregrine
- Birds scavenge for food in city garbage dumps, but Carrion crows may attack other birds for scraps.
- The Bald eagle was chosen as the national symbol of the USA because of its habit of stealing prey from other birds, but Benjamin Franklin was concerned it might give a negative impression of America as it appeared lazy and unwilling to hunt for
Conclusion:
Birds that engage in Kleptoparasitism are significant contributors to the ecosystem and have even been showcased on various stamps across the globe.
Article 14: Waterbirds Bio-indicators of the Ecosystem
Context: The presence and abundance of waterbirds serve as important indicators of the overall health and well-being of the ecosystem.
Want to learn more?
- Monitoring the health of an ecosystem is crucial but expensive and time-consuming. Bio-indicators help assess ecosystem health by providing data on species and substances, aiding conservation and research efforts.
- Birds, particularly waterbirds, are often used as bio-indicators since they are sensitive to environmental contaminants. Wading birds are at risk due to decreasing numbers worldwide and face increasing threats.
- Waterbirds indicate the health of coastal ecosystems and need monitoring to detect threats early.
- Birds are valuable indicators for monitoring habitat health and quality because of their long lifespan, role as top predators, diverse diet and habitat utilisation, and reliance on local resources during migration and breeding. This approach has been used for a considerable time to evaluate environmental health.
- Factors that affect waterbird abundance include population processes, migration, and local habitat characteristics such as water depth and physical and chemical conditions. Wetlands with high nutrient levels tend to have more birds and species diversity.
- Waterbirds provide valuable data for population studies. Population management should consider factors like density, environment, and competition.
- Waterbirds are important indicators of environmental health, especially coastal birds. Improving their habitat can attract more birds and help monitor the local food web.
Importance of Wetlands for Waterbirds:
- Wetlands are diverse areas between land and water, with two types: coastal and inland. Coastal wetlands are affected by tides, which can limit species diversity. Examples include mudflats and sandy flats.
- Inland wetlands near bodies of water provide habitats for waterbirds, such as marshes and wet meadows. Environmental factors impact waterbird populations, including climate changes that can affect nesting and foraging behaviour.
- Climate change can indirectly impact waterbird populations by altering their available habitat. Waterbirds are valuable bio-indicators for seasonal and climatic changes and can alert us to various changes, such as the loss of wetlands, increased salinity, and reduced breeding habitats. Monitoring waterbirds can help us take swift action to minimise the impacts of climate variations.
Conclusion:
Accurate information on waterbirds is crucial for conservation efforts, but there have been few studies in India. Encouraging young scientists and prioritising funding and planning are important in the country’s conservation effort.
Article15: Bird Migration and Quantum Physics
Context: The phenomenon of bird migration is fascinating and complex, presenting ongoing challenges for scientific understanding.

Introduction:
- Some animals, including sea turtles, sharks, and migratory birds, use the Earth’s magnetic field for navigation. This is known as avian magnetoreception for birds, and it provides them with a unique ‘compass’.
- Researchers study migratory birds in a chamber with manipulated magnetic fields to understand how they sense direction during
The following characteristics have been observed in these behavioural experiments:
- Light activation: Birds need a light with a specific frequency to detect the Earth’s magnetic field. Studies indicate that they can use UV to green light for their compass, but yellow and red lights can confuse and disorient
- Inclination-only compass: Migratory birds use an inclination-only compass that is sensitive to the tilt of the magnetic field but not the
- Functional window: Birds can sense a narrow range of magnetic fields centred around their local geomagnetic field. If exposed to a new intensity for a few hours, their sensing window adjusts to the new value.
- RE disruption: Radiofrequency (RF) fields in the Megahertz(MHz) range can disrupt birds’ magnetic senses and affect their compass
Some more discussion:
- Birds’ navigational abilities are due to the protein cryptochrome in their retinas, which creates a radical pair when interacting with This allows them to sense the Earth’s magnetic field.
- Radicals are molecules or ions with unpaired electrons. They can have a net spin of 0 or 1. Spin 0 is a singlet state, while spin 1 is a triplet state. Singlet state radicals combine to produce the same products, while triplet state produces a different product.
- Birds use quantum mechanics to navigate by relying on the percentage of radical pairs in the triplet state, which is influenced by the surrounding nuclei and the local geomagnetic field.
- Birds use quantum principles for their visual system and navigation, like the avian compass and Chiral-Induced Spin Selectivity.
- Chirality is important for biomolecules, including proteins, and affects the avian compass for migration. It also plays a role in maintaining quantum coherence in radicals. Understanding bird navigation may require examining physics
Conclusion:
Throughout millions of years of evolution, nature has developed the ability to utilise quantum mechanics far more effectively than humans. As a result, scientists require a thorough understanding of mathematics and interdisciplinary knowledge to comprehend and analyse natural processes.
Article 16: Transparent Glass Frogs An Act of Camouflage
Context: Glass frogs increase transparency by concealing the RBCs uniquely in their reflecting liver.
Introduction:
Aquatic creatures like glass octopuses, crocodile icefish, salps, and jellyfish can achieve transparency, but it’s harder on land because of RBCs.
Glass frogs conceal their RBCs in their liver to achieve transparency.
Some more discussion:
- Glass frogs are small, nocturnal creatures found in Central and South American forests. They have translucent bodies, inhabit tree branches above water, and can jump up to 10 feet in a single
- What makes them amazing is the visibility of their inner organs without any X-ray or ultrasound. To see this wonderful view, you have to just flip the frog, and you can see the beating heart, bones and food moving through the gut — and hence the name Glass Frog!
- Glass frogs use a unique camouflage technique to become more transparent and avoid predators. Researchers have observed this without harming the frogs.
Conclusion:
An interesting discovery has been made about glass frogs. It turns out that they can regulate the flow and spread of red blood cells without any risk of clotting. This finding could hold significant value for research into blood clotting.
What’s New:
1. Fireproof and Durable Oxygen-ion Battery:
- Vienna researchers made an efficient, fireproof oxygen-ion
· It uses ceramic materials, so no rare elements are needed.
- Best of all, it can be charged through atmospheric oxygen and doesn’t degrade with usage. Published in Advanced Energy
2. Highly Efficient Spintronics-based Neuromorphic Hardware:
- Experts from IIT Delhi and IIT Bombay have developed neuromorphic hardware that uses magnetic materials to store data even when power is off.
- This breakthrough can address data loss and reduce power consumption. The details were published in ACS Applied Electronic
3. Thought-controlled Biosensor Technology operates robots & machines:
- University of Technology Sydney (UTS) created a biosensor using brain waves to control devices hands-free and without voice commands.
- It can process nine commands in two seconds and has practical applications in science, industry, and healthcare, as well as aiding those with disabilities. The study has been published in ACS Applied
4. IIT Madras researchers develop a database on Coronavirus Antibodies:
- IIT Madras researchers made a free online antibody database called “Ah-CoV.“ It has info on the source, recognition, and 3D models.
- Researchers can use it to study immune escape and binding affinity. It was announced in a scientific



