Kalinga Architecture: India’s Ancient Temple Architecture
Kalinga Architecture | Kalinga Temple Architecture
Kalinga architecture, renowned for its distinctive style, represents a significant chapter in the history of Indian temple architecture. Originating in ancient Odisha, it is celebrated for its intricate artistry, sophisticated construction techniques, and the symbolic significance embedded within its structures. Kalinga temple architecture, with its iconic Jagannath Temple in Puri, epitomizes the zenith of this architectural tradition, reflecting a profound spiritual ethos and advanced engineering prowess.
The Kalinga style of temple architecture developed in ancient Kalinga. It is a regional style of the Nagara style of temple architecture that reached its mature phase around the 10th to 12th century CE. This architectural style span from the 4th century BCE to the 17th century CE.
-
Three distinct types of temples within Kalinga temple architecture are:
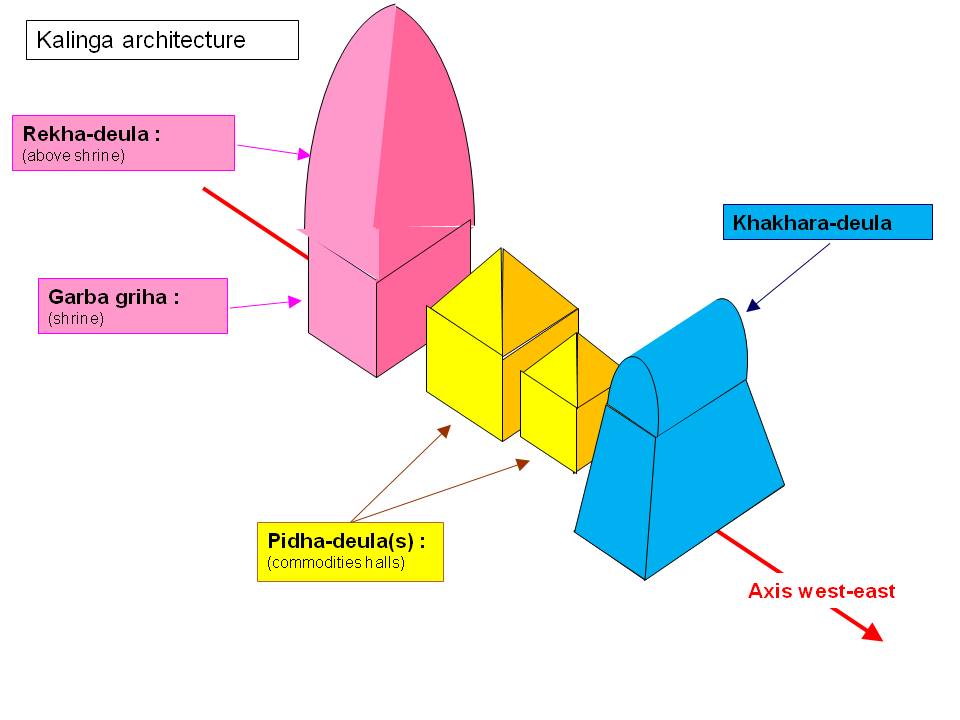
Type ➜
Rekha Deula
Pidha Deula
Khakhara Deula
Principal deities
Vishnu, Surya and Shiva
Chamunda and Durga
Purpose
Houses sanctum-sanctorum
Outer dancing and offering halls.
Houses sanctum-sanctorum
Ground plan
Square
Square
Rectangular
Shikhara
The Shikhara is above the sanctum sanctorum. The shikhara is curvilinear; it goes straight to the top and abruptly bends inwards. As a result, these temples are called “curvilinear temples“.
Lines around the Shikhara run from the temple’s base to the superstructure’s topmost part.
Shikhara here is like a stepped but compressed pyramid. It has a series of flat platforms placed one over the other, in diminishing order, each one representing a storey. An Amalaka tops it as a rule. As a result, these temples are called “flat seat temples.”
It is an elongated, barrel-roof-shaped shrine, a Kalingan adaptation of the Valabhi shrines.
Example
-
Lingaraja Temple (Bhubaneswar, 13th century),
-
Jagannath Temple (Puri, 13th century)
-
Konark temple, Konark (11th century)
-
Baitala deula, Bhubneshwar
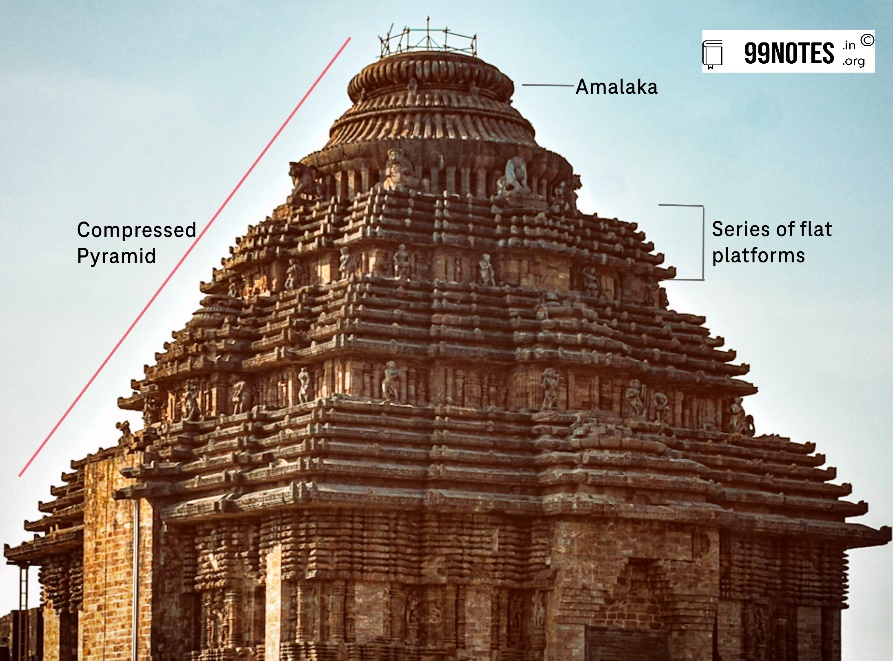
Fig: Sikhara of Konark Temple (Source: Wikipedia)
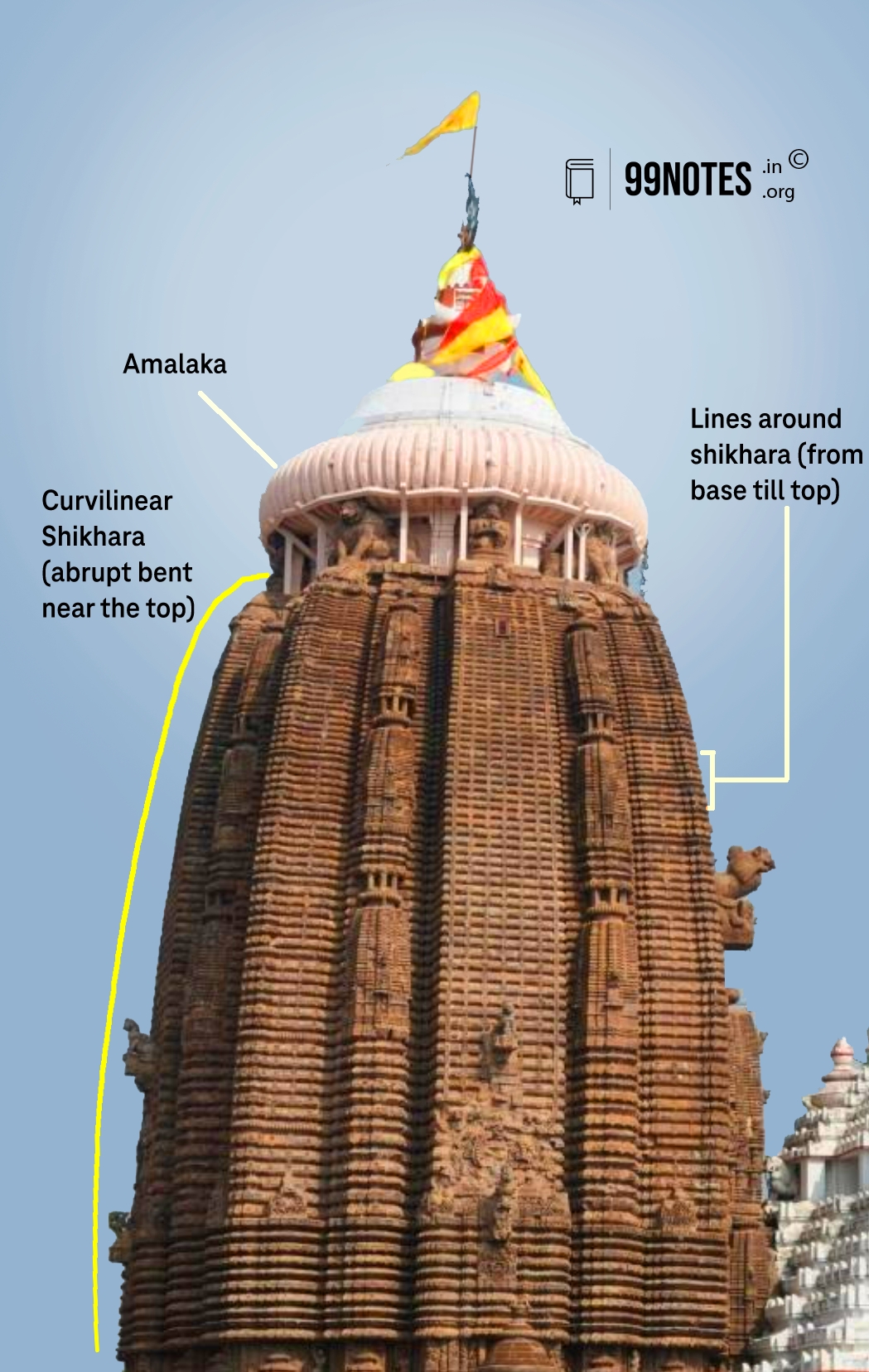
Fig: Sikhara of Jagannath Temple (Source: Wikipedia)

Fig: Shikahra of Baitala Deula Temple in Bhubaneshwar
-
-
Some of the important patrons of this architectural style were:
-
Somavanshi king Yayati I (r. 1025-1040) – Lingaraj temple.
-
Anantavarman Chodaganga (r. 1077-1150), the first king of the Eastern Ganga dynasty – Jagannath temple of Puri.
-
Narasimhadeva I of the Eastern Ganga dynasty (r. 1238–1264 CE) – Konark Sun temple.
-


![Panchayatana Style Of Temple Architecture [Complete Upsc Notes] | Updated November 21, 2024 Panchayatana Style Of Temple Architecture [Complete Upsc Notes]](https://99notes.in/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/panchayatan-style-99notes-upsc-768x512.webp)




