6 November 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. On India-Canada diplomatic relations
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 10)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral Relations |
| Context |
|

Background and Recent Developments
- Canada and India expelled their top diplomats following Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau’s allegation of a possible link between Indian intelligence and the killing of Hardeep Singh Nijjar, a Canadian citizen categorised by India as a Khalistani terrorist.
- Nijjar faced no criminal charges in Canada, though he was placed on a no-fly list, and his accounts were frozen.
- The diplomatic fallout has heightened Hindu-Sikh tensions in Canada.
Historical Context of India-Canada Khalistan Relations
- India has long criticised Canada as a safe haven for Khalistani separatists, expressing frustration over Canada’s handling of the 1985 Air India bombing, orchestrated by Canada-based Khalistani extremists.
- The bombing, which killed 329 people, remains Canada’s deadliest act of terrorism, yet Canadian authorities were slow in acknowledging it as a “Canadian tragedy” due to racial biases.
The Sikh Community’s Political Influence in Canada
- While Sikhs make up only 2% of Canada’s population, their political influence is strong due to geographic concentration and representation, particularly within Trudeau’s Liberal Party.
- Despite allegations from India, surveys indicate that the majority of Canadian Sikhs do not uniformly support Trudeau’s party or Khalistani sympathisers.
- Canada’s political landscape has seen gestures like dropping “Sikh” and “Khalistani” terms from terrorism reports, and leaders attending Sikh events where pro-Khalistan figures were honoured.
Canadian Cultural and Legal Frameworks
- Canadians view vote bank politics differently than in India, and Canadian politicians have not explicitly supported Khalistani extremism.
- Canadian independence in law enforcement and high standards of evidence for extradition often hinder India’s requests, especially given Western concerns over human rights in India.
- Canada’s emphasis on freedom of speech allows Khalistan referendums and non-violent advocacy for separatism, while hate speech laws remain relatively stringent but open to further scrutiny.
Legal Complexities in Extradition and Anti-Terror Efforts
- India’s extradition requests are often declined due to differences in legal standards and human rights concerns.
- Between 2002-2020, Canada extradited only six individuals to India, reflecting Western reluctance to engage with nations where political dissent may lead to arbitrary imprisonment.
- Legal obstacles include insufficient evidence based on Canadian standards and the inadmissibility of Indian intelligence evidence.
Media’s Role in Shaping Public Perception
- Canadian media has questioned its government’s handling of Khalistani activism and criticised Trudeau for political grandstanding, while maintaining balanced coverage by presenting India’s perspective.
- Indian media, however, has pushed a one-sided narrative, with disinformation about the case, inflaming public sentiment without critical analysis.
| Practice Question: Discuss the factors contributing to the recent diplomatic tensions between India and Canada. How do these issues impact bilateral relations and diaspora politics? (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. State has no right to acquire every private property, asserts SC
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 4)
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity – Judiciary |
| Context |
|
Key Judgement and Background
- A nine-judge Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court, led by Chief Justice D.Y. Chandrachud – ruled that not all private property can be classified as “material resources of the community” for the state to use for the “common good.”
- This judgement dismissed the idea that private resources could be broadly controlled by the state, deeming this perspective as part of an outdated “rigid economic dogma.”
- The majority opinion argued that India’s economic system has evolved from a public investment model to a mix of public and private investments.
| Justice V.R. Krishna Iyer’s Doctrine and its Influence |
|
Shift in Economic Policy Interpretation
- Chief Justice Chandrachud’s majority opinion highlighted India’s shift from socialism to a more market-based, liberalised economy.
- The judgement observed that India’s democratic process allows the electorate to choose different economic policies, supporting diverse development strategies.
- The court emphasised that India’s high growth rate and global economic position result from the flexibility provided by this constitutional framework.
Differing Opinions on Justice Iyer’s Approach
- Chief Justice Chandrachud’s majority judgement suggested that the rigid “Krishna Iyer Doctrine” no longer aligns with India’s current economic and constitutional stance.
- Justices B.V. Nagarathna and Sudhanshu Dhulia expressed reservations about the Chief Justice’s assessment of Justice Iyer.
- Justice Nagarathna argued that past judges should not be criticised for their views, given the context and economic realities of their time. She warned against devaluing historical judicial wisdom.
Justice Dhulia’s Dissent
- Justice Dhulia authored the lone dissent, defending Justice Iyer’s approach, which he viewed as based on principles of “fairness and equity.”
- He acknowledged the lasting impact of Justice Iyer’s humanist philosophy, which placed people at the centre of judicial decision-making.
Broader Implications
- The judgement underscores the Supreme Court’s stance that it should not interfere with economic policy decisions, allowing elected governments to navigate the country’s economic path.
- It also highlights a need for the judiciary to balance respecting past judicial doctrines while adapting to modern realities without disregarding former judges’ contributions.
Broader Implications
- This decision marks a pivotal shift in interpreting the state’s powers over private property.
- It reinforces a market-driven approach aligned with constitutional democracy and the evolving economic landscape.
| Practice Question: Critically examine the evolving role of the Indian judiciary in economic policy, considering the Supreme Court’s recent stance on state control over private resources. Discuss the implications of this shift for India’s economic trajectory and democratic governance. (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. Towards a TB-Free India: Achievements, Challenges and the Way Forward
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2070942®=3&lang=1 )
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health |
| Context |
|
India’s Journey Towards Tuberculosis (TB) Elimination
- India achieved a 17.7% decline in TB incidence from 2015 to 2023, which is more than twice the global average decline of 8.3%, according to the WHO Global Tuberculosis Report 2024.
- This success is attributed to the National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP), aimed at eliminating TB by 2025.
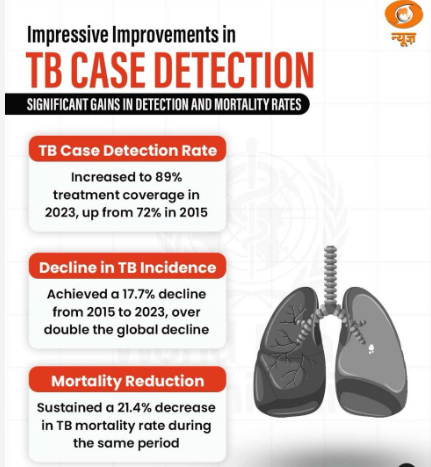
Strategies and Goals for Ending Tuberculosis in India
- SDG Target 3.3:
- Aims to end epidemics of tuberculosis by 2030.
- India targets to meet the End TB goal by 2025, five years ahead of the SDG deadline.
- Key Indicators for India’s TB elimination target:
- 80% reduction in TB incidence (compared to 2015 levels).
- 90% reduction in TB mortality (compared to 2015 levels).
- Zero TB-affected households experiencing catastrophic expenses due to TB.
- Political Commitment:
- The Indian government first announced the commitment to end TB at the End TB Summit in 2018.
- Reaffirmed at the One World TB Summit in Varanasi on World TB Day 2023.
- India is a signatory to the Gandhinagar Declaration to accelerate TB elimination by 2030 in the South-East Asia region.
India’s Approach: National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP)
- Post-COVID-19 Efforts:
- Intensified focus on TB elimination under NTEP, aligned with the National Strategic Plan (NSP) 2017-2025.
- In 2023, around 1.89 crore sputum smear tests and 68.3 lakh nucleic acid amplification tests were conducted.
- Comprehensive Care:
- Introduced shorter oral regimens for drug-resistant TB (DR-TB).
- Decentralised services to reduce treatment delays.
- Focused on addressing coexisting health conditions like malnutrition, diabetes, HIV, and substance abuse.
Strengthening Patient Care Through Supportive Services
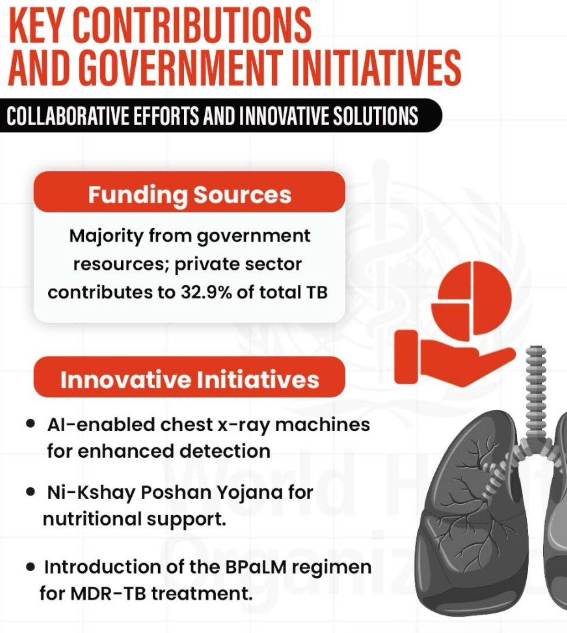
- Financial Support:
- Under Ni-kshay Poshan Yojana, Rs. 2,781 crores were disbursed to nearly 1 crore beneficiaries for nutritional support to TB patients.
- Community Engagement:
- Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan (PMTBMBA) launched in 2022, strengthening community participation.
- Over 1.5 lakh Ni-kshay Mitras committed to supporting TB patients through awareness and advocacy.
- Incentives for Treatment Supporters:
- Initiatives like TB Vijeta (TB champions) and ASHA workers were incentivized to support patients.
The Way Forward
- Future Interventions:
- Conduct studies on adult BCG vaccination.
- Rapidly scale up Tuberculosis Preventive Therapy (TPT), including shorter regimens.
- Increase access to molecular diagnostic testing for all suspected TB cases.
- Decentralise TB service delivery through “Ayushman Arogya Mandirs”.
- Strengthen community-based patient support systems through PMTBMBA.
Conclusion
- India’s approach to TB elimination is showing positive results with a decline in TB incidence and a strengthened healthcare response.
- By emphasising cross-sector partnerships, innovative care solutions, and community engagement, India is well-positioned to meet its TB-free nation goal by 2025.
| Practice Question: Discuss the strategies adopted under the National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP) in India to achieve the goal of TB elimination by 2025. (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. US Presidential Race 2024: Kamala Harris vs. Donald Trump – Implications for India’s Trade and Economic Relations
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations |
| Context: |
| The US presidential race between Kamala Harris and Donald Trump holds significant implications for India’s trade policies, with potential shifts toward protectionism and economic impacts on key Indian exports. |
Analysis of News:
Impact of US Presidential Election on Trade Relations
- The 2024 US presidential race between Kamala Harris and Donald Trump has significant implications for India, particularly in trade policy.
- Harris’s win could lead to policy continuity with the Biden administration, but Trump’s victory may revive trade tensions and a protectionist stance, which would directly impact over $75 billion of Indian exports to the US.
- Trump’s rhetoric suggests he may impose higher tariffs on Indian goods, creating potential economic strain.
Trump’s Past Protectionist Policies
- During Trump’s first term, the US leaned towards trade isolationism, blocking WTO functions and invoking national security to raise tariffs on imports from allies, including India. His administration also ended India’s duty-free benefits under the Generalised System of Preferences (GSP), impacting $5.7 billion in exports.
- A potential Trump return could revive these measures, leading to renewed tariff pressures on India and affecting sectors like pharmaceuticals and IT due to expected visa restrictions.
India’s Dependence on US Trade
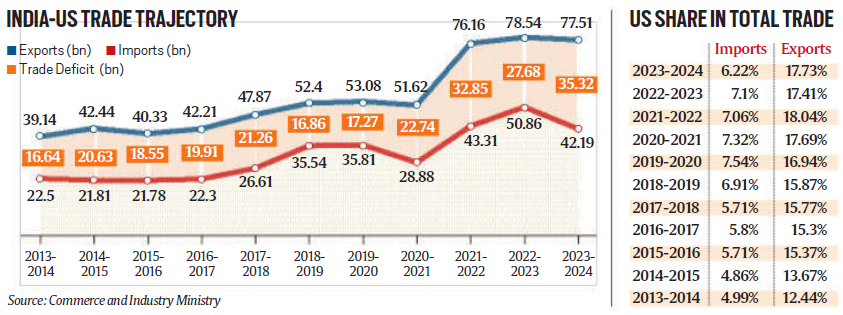
- India relies heavily on the US as a trade partner, with bilateral trade reaching $120 billion in FY24. India’s exports to the US account for 18% of its total exports, significantly up from a decade ago, making the US a crucial source of foreign exchange.
- However, Trump’s approach to tariffs, even if mainly targeting China, could still harm India’s economy by causing trade disruptions and potentially drawing American attention to India’s own tariff policies.
Challenges with Tariff Policies
- India’s average tariffs have increased, aimed at protecting and encouraging domestic manufacturing through policies like the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes.
- While India’s approach mirrors early economic protectionism seen globally, high tariffs have also led to competitiveness issues compared to countries with lower tariff regimes.
- Trump’s criticism of India as a “tariff king” underscores a potential source of conflict in trade negotiations if he returns to office.
Potential Economic Consequences of US Protectionism
- Trump’s policies, according to the Peterson Institute for International Economics, could drive up inflation in the US, adversely affecting India’s exports in labor-intensive sectors such as textiles and gems.
- As nearly 20% of Indian exports are US-bound, higher US inflation could reduce demand, impacting employment in export-oriented Indian industries.
- If inflation rises to the projected 6-9.3%, it could significantly disrupt India’s economic stability and export growth.
Prospects for India in a Changing Trade Environment
- If Trump’s policies focus on China, India could benefit from a “China-plus-one” strategy, which encourages diversification of supply chains.
- However, gains may be limited by increased US tariffs on Indian products, impacting sectors like pharmaceuticals, where regulatory hurdles could stifle profits.
- India may need to balance its protective economic measures with global competitiveness to navigate potential shifts in US trade policy effectively.
| Highlights |
 |
| PYQ: “What introduces friction into the ties between India and the United States is that Washington is still unable to find for India a position in its global strategy, which would satisfy India’s National self- esteem and ambitions” Explain with suitable examples. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2019) |
| Practice Question: Analyze the potential impact of a Donald Trump presidency on India’s trade relations with the United States. How can India mitigate the challenges posed by protectionist policies while leveraging potential opportunities in the changing trade landscape? (250 words/15 m) |
5. Supreme Court Upholds Constitutional Validity of UP Madarsa Education Act, Balances Secularism and Religious Education
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 17)
| Context: |
| The Supreme Court upheld the constitutional validity of the Uttar Pradesh Madarsa Education Act, 2004, balancing religious education with secular principles. |
Analysis of News:
Analysis of the UP Madarsa Education Act Ruling: Key Points and Implications
1. Background of the UP Madarsa Act (2004)
- The UP Madarsa Education Act, 2004, was established to provide a legal framework for madarsa education in Uttar Pradesh. Under this act, the UP Madarsa Board was formed to oversee madarsa education, incorporating both NCERT curriculum subjects and religious studies specific to Islam.
- The board is responsible for setting course content, conducting exams, and awarding degrees up to the master’s level.
2. Allahabad High Court’s Ruling
In March 2023, the Allahabad High Court struck down the Madarsa Act, citing three main grounds:
- Secularism: The HC argued that secularism mandates equal treatment for all religions by the state. It held that requiring madarsa students to study Islamic teachings conflicted with the government’s duty to provide secular education.
- Right to Education (RTE): Article 21A requires the state to provide free, quality education to children. The HC asserted that the Act’s focus on religious teachings over modern subjects failed to meet this standard.
- Conflict with Central Law: The HC ruled that the madarsa board granting degrees conflicted with the UGC Act, which reserves this authority for universities or deemed institutions.
3. Supreme Court’s Examination
The Supreme Court, under CJI D Y Chandrachud, reviewed the HC’s ruling and upheld the constitutionality of the Madarsa Act. Key issues discussed included:
- Religious Education vs. Religious Instruction: The SC differentiated between “religious instruction” (compulsory worship, prohibited in state-recognized institutions) and “religious education” (teaching about religions for awareness). The SC leaned toward allowing regulated religious education without mandating instruction.
- Scope of Judicial Review: The SC questioned the necessity of striking down the entire Act rather than addressing specific provisions, indicating a preference for preserving the Act while ensuring that education becomes more secular.
4. Implications of the Supreme Court’s Decision
The SC ruling primarily affects UP but has broader implications:
- Religious Education Across India: CJI Chandrachud’s comments suggest that other religious educational institutions (e.g., gurukuls, convent schools) might also need to balance secular and religious curricula.
- State Power in Regulating Religious Education: The ruling confirms that state governments can set guidelines to ensure that institutions like madarsas incorporate secular subjects, aligning with RTE principles.
5. Conclusion
- The SC’s decision emphasizes the need for a balanced approach in religious education. While upholding the Madarsa Act’s validity, it paves the way for further dialogue on how secularism and religious education can coexist in India’s educational landscape, impacting future cases involving religious institutions.
| Practice Question: Critically analyze the Supreme Court’s verdict on the constitutional validity of the Uttar Pradesh Madarsa Education Act, 2004. How does the decision address the balance between secularism and religious education in India? (250 words/15 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. Does the sun rotate?
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 7)
| Context |
|
Rotation of the Sun
- Unlike Earth, the Sun exhibits differential rotation, where different parts rotate at different speeds.
- Near the equator, the rotation period is about 26.5 days, while at the poles, it extends to 31.1 days.
- This differential rotation is observed through daily photographs of sunspots and other solar features across various latitudes.
- Observing sunspots and calculating sidereal rotation periods aid in understanding this complex rotation.
Unsolved Mystery
- The cause of the Sun’s differential rotation remains an ongoing puzzle for solar physicists.
Temperature and State
- The Sun has an intense core temperature of 15 million K and a surface temperature of 6,000 K.
- Due to these extreme temperatures, the Sun exists in a plasma state, a high-pressure gaseous form of matter.
2. India to Launch European Union’s Solar Observatory Satellite Proba-3 in December.
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2070865®=3&lang=1 )
| Context |
|

European Union’s Proba-3 satellite:
- Purpose: Aimed at observing the Sun, focusing on solar corona dynamics.
- Mission Collaboration: Joint effort between India and the European Union.
- Previous Missions: Proba-3 is India’s third launch for the EU, following the successful launches of Proba-1 and Proba-2.
- Technological Significance: Proba-3 will enhance scientific knowledge of the Sun, contributing to the study of solar activities and their impact on space weather.
- Scientific Impact: Aims to provide valuable data for solar research and space weather predictions.
- India’s Role: The launch underscores India’s growing leadership in space exploration, particularly through ISRO’s capabilities.
3. India Launches “Chalo India” Campaign at WTM London to Boost Tourism with Free Visas for Friends of OCI Holders
(Source: Indian Express; Section: The Second Page; Page: 02)
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
Key Feature: Free Visas for “Friends” of OCI Holders
- The campaign is a first-of-its-kind approach, offering free e-visas to foreign friends nominated by Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) cardholders.
- Through a dedicated portal, OCI cardholders can nominate up to five people, with a total cap of 100,000 free e-visas available. Upon registration and verification, nominees will receive a special code to redeem the free visa.
Target Audience and Significance
- With around five million OCI cardholders globally, this initiative seeks to leverage the Indian diaspora’s network, particularly in the UK, which has the third-largest source market of inbound tourists to India, representing nearly 1.9 million people.
- The campaign thus builds on Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s call to overseas Indians to promote India as a tourism destination.
India’s Pavilion at WTM London
- India’s presence at WTM London includes a delegation of 50 stakeholders, encompassing state governments, airlines, hoteliers, and tour operators.
- The India pavilion highlights India’s cultural diversity, focusing on specific themes such as MICE (Meetings, Incentives, Conferences, and Exhibitions), Mahakhumbh, and wedding tourism.
- A mock “Mandapam” representing traditional Indian weddings was set up to provide visitors with an immersive experience.
Expected Impact and Future Prospects
- The “Chalo India” campaign, with its focus on diasporic engagement, could significantly increase tourist inflow and promote India’s image internationally.
- With 9.5 million foreign visitors in 2023, including 0.92 million from the UK alone, this campaign is set to strengthen India’s global tourism footprint.
4. India’s 2024 Kharif Season Sees Record Rice Production Amid Strong Monsoon, Decline in Pulses and Cotton
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Govt & Politics; Page: 06)
| Context: |
| India’s 2024-25 kharif season records a surge in rice production due to favorable monsoon, while pulses, sugarcane, and cotton see a decline. |
Analysis of News:
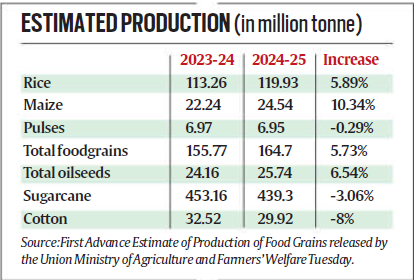
Record High in Rice Production
- India’s rice production for the 2024-25 kharif season is projected to reach a record 119.93 million tonnes, up 5.89% from last year.
- This increase, driven by favorable monsoon conditions, has resulted in a substantial rise in the area under paddy cultivation, particularly in states like Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and West Bengal.
- The southwest monsoon season brought 108% of the long period average (LPA) rainfall, boosting production.
Overall Kharif Foodgrain Production
- Total kharif foodgrain production is estimated at 164.70 million tonnes, 5.73% higher than the previous season’s 155.77 million tonnes.
- The abundance of rice has led to a significant stockpile in government reserves, with the Central pool holding 31.06 million tonnes of rice as of October 1—well above the buffer requirement of 10.25 million tonnes.
Decline in Pulses, Sugarcane, and Cotton Production
- Despite increased sowing areas, kharif pulses production is expected to be slightly lower than last year at 6.95 million tonnes. Sugarcane and cotton outputs are also predicted to decrease.
- Among coarse cereals, however, maize and jowar production are expected to rise, while bajra is anticipated to see a slight drop.
Digital Crop Survey Initiative
- For the first time, area estimates were prepared using the Digital Crop Survey (DCS) under the Digital Agriculture Mission, replacing the traditional Girdawari method.
- The DCS covered all districts in states like Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh, leading to more accurate data and contributing to the recorded increase in rice area, particularly in Uttar Pradesh.
5. Uttar Pradesh Introduces New Rules for Independent, Transparent Selection of Police Chief
(Source: Indian Express; Section: The Cover Page; Page: 01)
| Context: |
| Uttar Pradesh establishes a new, independent selection process for its police chief to enhance transparency and reduce political influence. |
Analysis of News:

New Rules for Selection of Uttar Pradesh’s Police Chief
- The Uttar Pradesh government has introduced new rules for selecting the Director General of Police (DGP) through a nomination committee led by a retired High Court judge.
- This marks a shift from the previous practice, where the state forwarded a list of candidates to the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) for selection.
- The change is formalized under the ‘Director General of Police, Uttar Pradesh Selection and Appointment Rules, 2024.’
Aim of the New Selection Process
- The revised rules aim to create an independent and transparent process for appointing the DGP, free from political and executive interference.
- This approach aligns with a Supreme Court directive from 2006, which urged state governments to enact legislation ensuring a police force independent from external pressures, dedicated to upholding citizen rights and the rule of law.
Composition of the Nomination Committee
- The selection committee for the DGP will be chaired by a retired High Court judge and will include senior officials such as the Chief Secretary, a UPSC nominee, the chairperson (or nominee) of the Uttar Pradesh Public Service Commission, the Additional Chief Secretary (or Principal Secretary) of the Home Department, and a retired DGP.
- The committee will shortlist candidates based on merit, selecting officers with at least six months of service remaining before the vacancy arises.
Fixed Tenure and Grounds for Early Removal
- Under the new rules, the DGP will have a fixed minimum tenure of two years to ensure continuity in leadership.
- However, the state government may remove the DGP before the two-year term if any criminal or corruption charges are filed against him or if he fails to perform his duties adequately. This clause aligns with Supreme Court guidelines on DGP removal.



