23 February 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC
PIB Summary for UPSC
23 February -2024
1. With a focus on promotion of organic exports, APEDA forms dedicated organic promotion division
| Topic: GS3 – Agriculture – Storage, transport and marketing of agricultural produce Enhancing organic exports vital for agricultural growth in India. UPSC may focus on policies, sustainability, and global alignment in questions. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) has established a dedicated organic promotion division to boost India’s organic export sector.
- APEDA is strategically focusing on Uttarakhand to enhance its organic sector by improving farming practices, streamlining certification procedures, and identifying key export products.
- In Sikkim, where it is already India’s first fully organic state, APEDA is formulating a roadmap to diversify exports and strengthen sustainable practices.
- APEDA envisions replicating successful strategies in more states to create a network of thriving organic export hubs across India.
- The National Programme for Organic Production (NPOP) is undergoing significant updates to enhance the accessibility of organic products in international markets, aligning with global regulations and standards.
- The NPOP overhaul includes modernizing its IT infrastructure to provide resilient oversight, focusing on geo-tagging of farms and geo-location of inspection visits.
| Organic Exports from India |
Potential:
Challenges:
Way Forward:
By addressing these challenges and leveraging its potential, India can become a leading player in the global organic export market. |
| PYQ: Sikkim is the first ‘Organic State’ in India. What are the ecological and economic benefits of Organic State? (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2018) |
| Practice Question: Critically examine the potential of India’s organic exports, highlighting the key challenges and suggesting measures to overcome them. (250 words/15 m) |
2. Government meets academia and industry to steer R&D projects under National Green Hydrogen Mission
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies – Interventions for development in various sectors GS3 – Indian Economy – Infrastructure – Energy Critical for UPSC: National Green Hydrogen Mission focuses on research, collaboration, and efficiency improvement in renewable energy, aligning with national goals. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- Union Power and New & Renewable Energy Minister chair a meeting on Green Hydrogen R&D Scheme in New Delhi.
- Emphasis on identifying primary areas for research, supporting research institutions, and bringing technologies to fruition.
- Collaboration among institutions with diverse expertise is stressed for effective research efforts.
- Increasing efficiency of electrolyzers is highlighted to reduce the cost of Green Hydrogen.
- Exploration of cost-effective alternatives for production and transportation of Green Hydrogen is encouraged.
- Sea-water electrolysis is recognized as a promising area to lower production costs and enhance scalability.
- Formation of consortiums suggested for research across the Green Hydrogen value chain.
- R&D projects under National Green Hydrogen Mission include Mission Mode, Grand Challenge, Blue Sky projects, and support for Centres of Excellence.
| Green Hydrogen Mission |
○ Achieve 5 million metric tonnes (MMT) per annum green hydrogen production capacity by 2030. ○ Reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels. ○ Create export opportunities for green hydrogen and its derivatives. ○ Develop indigenous manufacturing capabilities. ○ Decarbonize industrial, mobility, and energy sectors.
○ Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) programme: Provides financial and other incentives for electrolyser manufacturing, green hydrogen production, and R&D. ○ Pilot projects: Supports demonstration projects for green hydrogen production, storage, and utilization. ○ R&D activities: Focuses on developing new technologies and improving efficiency in green hydrogen production and utilization. ○ Other mission components: Include skill development, capacity building, and awareness creation. Benefits:
Overall, the Green Hydrogen Mission is a significant initiative with the potential to transform India’s energy landscape and contribute to a sustainable future. |
| PYQ: Clean energy is the order of the day. Describe briefly India’s changing policy towards climate change in various international fora in the context of geopolitics. (250 words/15 m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2022) |
| Practice Question: Critically evaluate the Green Hydrogen Mission, assessing its potential to achieve its stated objectives and suggesting measures to address any potential challenges. (150 words/10 m) |
For Enquiry

23 February 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC

23 Feb 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis
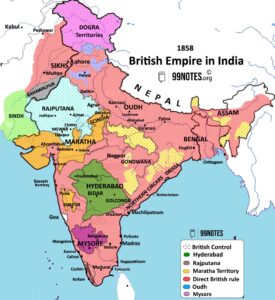
Annexation of Sindh & Punjab by British- Complete Notes for UPSC

Debate on future strategy after Civil Disobedience Movement

Early Political Activities: 1858-1905 [Complete Notes for UPSC]

Peasant Movements in India- Complete Notes for UPSC
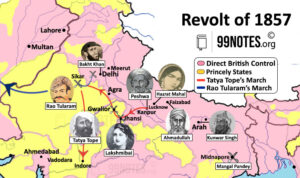
Revolt of 1857

Economic Impact of British Rule in India- Complete Notes for UPSC

Revolutionary Nationalism 2.0

Revolutionary Movement in India
feb 2024 PIB 23 February 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
22-February -2024
1. Cabinet approves amendment in the Foreign Direct Investment…
Indian Express 23 Feb 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
23-February-2024
1. A long institutional road
Topic: GS2 – Polity…
Modern India Annexation of Sindh & Punjab by British- Complete Notes for UPSC Annexation of Sindh & Punjab by British
By 1818, the entire Indian subcontinent, except Punjab and…
Modern India Debate on future strategy after Civil Disobedience Movement Debate on future strategy after civil Disobedience movement
In the Aftermath of the withdrawal of the…
Modern India Early Political Activities: 1858-1905 [Complete Notes for UPSC] Early Political Activities: 1858-1905
The revolt of 1857 was the first major large-scale revolt against…
Modern India Peasant Movements in India- Complete Notes for UPSC Peasant Movements in India
Peasant movements in India have been pivotal in shaping the socio-political…
Modern India Revolt of 1857 The Revolt of 1857 was one of the most significant watershed moments during British rule. During this…
Modern India Economic Impact of British Rule in India- Complete Notes for UPSC Economic Impact of British Rule in India
The British Empire in India was highly organized administratively….
Modern India Revolutionary Nationalism 2.0 Revolutionary Nationalism 2.0
Revolutionary Nationalism 2.0 in India marks a pivotal shift towards radical…
Modern India Revolutionary Movement in India The First Phase of the Revolutionary Movement in India (1907-17)
With the decline of the mass phase of…


