24 February 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC
PIB Summary for UPSC
24 February -2024
1. President’s greetings on the eve of birth anniversary of Guru Ravidasji
| Topic: GS1 – History – Indian culture – Significant personalities UPSC may focus on Guru Ravidasji’s legacy, his role in social reform, and contributions for social awakening and upliftment. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- President of India, Smt. Droupadi Murmu, extends warm greetings on Guru Ravidasji’s birth anniversary.
- Sant Ravidas exemplified spiritual wisdom and dedicated his life to serving humanity.
- He fought against caste-based discrimination and worked for social harmony.
- Guru Ravidasji promoted peace, tolerance, and brotherhood through devotional practices.
- President urges citizens to adopt his teachings for national development.
| More about Sant Ravidas |
|
| PYQ: The Bhakti movement received a remarkable re-orientation with the advent of Sri Chaitanya Mahaprabhu. Discuss. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-1 2018) |
| Practice Question: Examine Sant Ravidas’ role in promoting social equality and religious harmony in medieval India, and highlight the lasting impact of his teachings on Indian society. (250 words/15 m) |
2. If India succeeds, SDGs will succeed. And if the SDGs are to succeed, India has to succeed: Hardeep S Puri at UNGCNI’s 18th National Convention
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government Policies Critical for UPSC as it addresses India’s role in global sustainability, poverty alleviation, and inclusive growth, aligning with SDGs. |
| Context |
|
Additional information on this news:
- Shri Hardeep Singh Puri, Minister of Petroleum & Natural Gas and Housing & Urban Affairs, emphasized India’s crucial role in the success of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) during his address at the UN Global Compact Network India’s 18th National Convention.
- India’s significant population, fifth-largest and fastest-growing economy, and increasing status as a preferred investment destination make its outcomes pivotal for the world.
- The convention, themed “Advancing Sustainable India: Driving Change with Forward Faster 2030,” focused on topics such as climate change action, water resilience, sustainable finance, and economic empowerment through living wages.
- India showcased remarkable progress in achieving SDGs, with over 250 million people lifted out of multidimensional poverty in the last decade, reflecting the nation’s commitment to inclusive growth.
- Missions like Swachh Bharat and AMRUT transformed the water and sanitation landscape, achieving open defecation-free status, supported by rigorous third-party verification.
- Despite global challenges, India’s sustainable development approach shines, particularly in addressing water and sanitation issues and mobilizing resources to bridge financing gaps.
- Government efforts toward women empowerment include a shift to women-led schemes, exemplified by the historic Women’s Reservation Bill introduced last year.
- India’s progress on sustainability targets includes advancements in ethanol blending, building an enabling ecosystem for emerging technologies, and a net-zero target of 2070.
- Acknowledging the role of the private sector, Shri Puri emphasized combining purpose with profit, linking business reputations to SDG commitments, and integrating sustainability into core operations.
- He praised impactful Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives but stressed the need for businesses to incorporate sustainability in their operations for meaningful change.
| Role India can play in the success of SDGs worldwide |
Through these multifaceted contributions, India can play a transformative role in the worldwide success of the SDGs, fostering a more sustainable and equitable future for all. |
| PYQ: Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2018) |
| Practice Question: Examine India’s role in achieving Sustainable Development Goals, citing specific initiatives and outcomes, and discuss the global significance of its efforts. (250 words/15 m) |
For Enquiry

24 February 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC

23 Feb 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

23 Feb 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

23 Feb 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

23 February 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

23 February 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC

23 Feb 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis
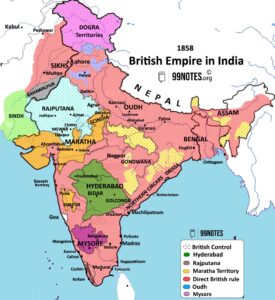
Annexation of Sindh & Punjab by British- Complete Notes for UPSC

Debate on future strategy after Civil Disobedience Movement

Early Political Activities: 1858-1905 [Complete Notes for UPSC]
feb 2024 PIB 24 February 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
23 February -2024
1. With a focus on promotion of organic exports, APEDA forms dedicated…
Daily Quiz 23 Feb 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 23 Feb 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 23 Feb 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
23-February-2024
Q1) Though President of India is the constitutional head of the…
Daily Current Affairs 23 Feb 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
23-February-2024- Top News of the Day
1. Escalating Farmer Protests: Challenges…
Feb 2024 The Hindu 23 February 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu Editorial
23-February-2024
1. The government must keep the regulatory environment of space…
feb 2024 PIB 23 February 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
23 February -2024
1. With a focus on promotion of organic exports, APEDA forms…
Indian Express 23 Feb 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
23-February-2024
1. A long institutional road
Topic: GS2 – Polity…
Modern India Annexation of Sindh & Punjab by British- Complete Notes for UPSC Annexation of Sindh & Punjab by British
By 1818, the entire Indian subcontinent, except Punjab and…
Modern India Debate on future strategy after Civil Disobedience Movement Debate on future strategy after civil Disobedience movement
In the Aftermath of the withdrawal of the…
Modern India Early Political Activities: 1858-1905 [Complete Notes for UPSC] Early Political Activities: 1858-1905
The revolt of 1857 was the first major large-scale revolt against…


