18 July 2023 : Daily Current Affairs
DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS
18-July-2023
Daily Current Affairs For UPSC ,Daily Current affairs of The hIndu and Indian Express.
1. NITI Aayog report says 13.5-cr. people lifted out of multidimensional poverty.
Topic: GS3 – poverty alleviation.
Context:
- Steep decline in multidimensional poverty: The number of multidimensionally poor individuals in India decreased from 24.85% to 14.96% between 2015-16 and 2019-21.
- Rural areas witness fastest decline: Poverty in rural areas showed the fastest decline, decreasing from 32.59% to 19.28%.
- Progress towards SDG Target 1.2: India is on track to achieve Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) Target 1.2, which aims to reduce poverty, well ahead of the 2030 deadline.
- Improvements in all 12 MPI indicators: Significant improvements were observed across all 12 indicators of the Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI).
What is multidimensional poverty?
- Multidimensional poverty refers to a concept that goes beyond traditional income-based measures of poverty and considers multiple dimensions of deprivation that individuals may experience simultaneously. It recognizes that poverty is not solely defined by lack of income but also encompasses various interconnected factors that affect people’s well-being.
- In multidimensional poverty measurement, indicators are used to capture different dimensions of deprivation, such as education, health, living standards, access to basic services, nutrition, sanitation, housing, and more. These indicators are selected based on their relevance and impact on people’s quality of life.
- The Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) is one commonly used framework to measure multidimensional poverty. It assesses poverty by identifying individuals who are deprived in multiple dimensions simultaneously, providing a more comprehensive understanding of poverty beyond income alone.
- The MPI looks at various indicators within each dimension and assigns a deprivation cutoff for each indicator. Individuals are classified as multidimensionally poor if they experience deprivation in a certain number or combination of dimensions. The index considers the intensity and severity of deprivation, providing a nuanced view of poverty by distinguishing between those who experience severe deprivation and those who experience fewer deprivations.
Multidimensional poverty measurement helps policymakers and development practitioners identify and address the specific deprivations that individuals face, enabling more targeted and comprehensive poverty reduction strategies. By considering multiple dimensions of poverty, it aims to capture the complex and interconnected nature of poverty and promote holistic approaches to improving people’s lives.
2. Injured tigress dies in M.P.’s Bandhavgarh tiger reserve
Topic: GS3 – Environment conservation.
Context:
- An injured tigress undergoing treatment at Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve (BTR) in Madhya Pradesh’s Umaria district has died.
- The tigress was found injured near Madhau village and was rescued by a patrolling team from the reserve.
About Bandhavgarh tiger reserve:
Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve is a prominent wildlife sanctuary located in the Umaria district of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is renowned for its rich biodiversity and serves as a crucial habitat for the Royal Bengal Tigers.
- Tiger Population: The reserve is recognized for its high tiger density and is home to a significant population of Royal Bengal Tigers. It has played a crucial role in the conservation efforts of this endangered species.
- Geographical Features: Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve spans an area of approximately 1,536 square kilometers. It comprises a diverse landscape with undulating terrains, steep cliffs, rocky hills, forests, and meandering streams.
- Flora and Fauna: The reserve boasts a diverse range of flora and fauna. It is covered with mixed forests consisting of sal trees, bamboo, and various other plant species. Besides tigers, the reserve is also inhabited by other wildlife species like leopards, Indian bison (gaur), sloth bears, sambar deer, spotted deer, wild boars, and several species of birds.
- Bandhavgarh Fort: Within the reserve, there is an ancient fort known as the Bandhavgarh Fort, which dates back to the 2nd century. It holds historical and archaeological significance and offers panoramic views of the surrounding landscape.
- Cultural Significance: Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve is also known for its cultural heritage. The area surrounding the reserve is inhabited by indigenous tribes, and their unique customs and traditions add to the cultural richness of the region.
3. The risk of small states’ heavy reliance on the Union government
Topic: GS2, GS3 – Indian polity, economy.
What is the issue?
- Small States in India, with a population of less than 1 crore, face unique challenges in revenue mobilization and are heavily dependent on the Union government for financial support.
- While revenue receipts have increased for small States, the growth is primarily driven by Union transfers rather than the States’ own revenues, indicating a continued dependence on the Union.
- The share of Union transfers in revenue receipts is high for small States, with most of them having the Union’s share above 60%, and for some, it reaches around 90%.
- Small States struggle to raise their own taxes, with limited capacity for revenue generation due to their distinctive characteristics and restricted economic activity.
- The ability of small States to mobilize taxes has not shown significant improvement over time, fluctuating at best and performing poorly compared to the all-State average.
- The heavy dependence on the Union government exposes small States to vulnerabilities, including reliance on political goodwill, limited fiscal freedom, and weakened state capacity to deliver essential services.
Possible way forward:
- To address these challenges, small States need to identify new sources of tax revenue and improve tax administration to enhance resource mobilization.
- States can also revise charges and rates for services, improve administrative revenue collection efficiency, and revitalize or corporatize state public sector enterprises to boost revenue performance.
- Mitigating vulnerabilities and strengthening revenue mobilization in small States is crucial for their development and national security, given their international border locations.
Model question: “Explain the fiscal challenges faced by small states in India due to their heavy dependence on the Union government for revenue. Discuss the vulnerabilities arising from this dependence and propose measures to enhance revenue mobilization and reduce reliance on the Union government.”
4. U.S. hands over 105 antiquities to India following agreement
Topic: GS1 – Indian art and culture.
Challenges of repatriation of looted items::
- Ownership disputes:Determining the rightful owners of looted items can be complex. Over time, ownership may have changed hands multiple times, making it difficult to establish clear ownership claims. Disputes may arise between the countries from which the items were looted and the current possessors, often museums or private collectors.
- International laws and regulations:Legal frameworks surrounding the repatriation of cultural artefacts can be intricate. International laws, such as UNESCO conventions, provide guidelines for the return of stolen cultural property. However, not all countries have ratified these conventions, which can impede the legal basis for repatriation.
- Preservation and conservation concerns:Cultural artefacts often require specialized care and preservation techniques. Concerns about the ability of the original homeland to adequately preserve and protect the items may arise, especially if there are insufficient resources or infrastructure in place.
- Lack of documentation:In some cases, the documentation related to the looting of cultural artefacts may be incomplete or lost. Without proper documentation, establishing a solid case for repatriation becomes challenging, as it may be difficult to prove the origins and ownership history of the items.
- Cultural significance and access:Museums and institutions in possession of looted items often argue that they provide wider access and appreciation of the artefacts. They contend that returning these items to their original homelands may limit access and appreciation for a broader audience.
- Repatriation precedent:The return of looted items sets a precedent for other claims, potentially leading to an overwhelming number of requests for repatriation. This can create concerns for museums and institutions about the potential loss of significant portions of their collections.
Model question: Should colonial countries return cultural artefacts and precious objects acquired during the colonial period to their original homelands? Discuss the moral implications and potential impact on bilateral relations, considering the importance of historical responsibility, symbolic value, and true atonement. (250 Words)
5. Rupee-dirham deal is bilateral: envoy
Topic: GS3 – Indian economy.
Context:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Central Bank of the UAE have agreed to establish a framework for using the Indian rupee and UAE dirham for cross-border transactions.
- The aim is to reduce dependence on a third country’s currency, such as the US dollar, and promote the bilateral use of local currencies.
- Current account payments, including those involving exporters, importers, and certain capital account transactions, can be settled using either the rupee or the dirham.
More information about the news:
- A Local Currency Settlement System will be put in place, and the payments messaging systems of the two banks may be interlinked in the future.
- The establishment of the settlement mechanism would facilitate the development of a rupee-dirham foreign exchange market, enabling pricing of the two currencies independent of their exchange rates with other major currencies.
Positive outcomes of inter-country currency settlement mechanism:
The establishment of an inter-country currency settlement mechanism, such as the one between India and the UAE, can bring about several positive outcomes, including:
- Reduced reliance on third-country currencies: The use of local currencies for cross-border transactions reduces dependence on a third country’s currency, such as the US dollar. This enhances financial sovereignty and reduces exposure to currency risks associated with third-country exchange rates.
- Enhanced bilateral trade: The availability of a local currency settlement system improves the ease of doing business between the two countries. It eliminates exchange rate risks for businesses and facilitates smoother trade transactions, thereby boosting bilateral trade volumes.
- Increased efficiency and cost savings: Settlements in local currencies eliminate the need for multiple conversions, reducing transaction costs and increasing efficiency in cross-border payments. This can lead to cost savings for businesses engaged in international trade.
- Development of local currency markets: The establishment of a settlement mechanism promotes the development of local currency markets. It can create a market for the exchange and pricing of the respective currencies, allowing for more accurate valuation independent of major global currencies.
- Opportunities for investment and capital flow: The availability of local currency settlement encourages investment between the two countries. It provides avenues for businesses to deploy potential flows of the respective currencies, fostering investment and economic cooperation.
- Precursor for currency internationalization: Inter-country currency settlement mechanisms can act as important initial steps towards the internationalization of a currency. It increases the visibility and usage of the local currency in international transactions, potentially leading to broader acceptance and usage in the global market.
- Strengthened economic ties: The use of local currencies in cross-border transactions strengthens economic ties between the countries involved. It fosters closer economic cooperation, facilitates trade agreements, and encourages bilateral investment, contributing to deeper bilateral relations.
Challenges Associated:
- Adoption and acceptance: The success of a currency settlement mechanism relies on the widespread adoption and acceptance of using local currencies for cross-border transactions. Businesses, financial institutions, and individuals need to be willing to embrace and use the local currencies, which may require significant efforts in terms of awareness, education, and incentivization.
- Currency risks: Despite using local currencies, there can still be risks associated with exchange rate fluctuations between the two countries. Volatility in exchange rates can impact the value of transactions and create uncertainties for businesses involved in cross-border trade.
- Infrastructure and compatibility: Establishing a seamless settlement mechanism requires robust infrastructure and compatible payment systems between the participating countries. This includes the development of payment messaging systems, interoperability of banking systems, and efficient clearing and settlement mechanisms.
- Regulatory and legal framework: Creating a conducive regulatory and legal framework for inter-country currency settlements is crucial. This involves addressing regulatory barriers, ensuring compliance with international standards, and establishing legal mechanisms to protect the rights and interests of parties involved in the transactions.
- Market liquidity: Adequate market liquidity in both currencies is essential for smooth and efficient settlements. Sufficient liquidity ensures that transactions can be executed at fair prices without significant slippage. It may take time for a robust market for the settlement currency to develop, which could initially pose liquidity challenges.
- Market depth and accessibility: The depth and accessibility of the market for the settlement currency can impact its usability. A well-developed market with a broad range of participants, including banks, financial institutions, and businesses, enhances liquidity and facilitates smoother transactions.
- Monitoring and oversight: Effective monitoring and oversight are necessary to prevent misuse, ensure compliance with regulations, and mitigate risks associated with inter-country currency settlements. Regular assessments, audits, and surveillance mechanisms should be in place to maintain the integrity and stability of the settlement system.
Model question: Discuss the significance and challenges associated with the establishment of inter-country currency settlement mechanisms for cross-border transactions. How can such mechanisms promote bilateral trade, economic cooperation, and currency internationalization? What measures should be taken to address the challenges and ensure the effective functioning of these settlement mechanisms? ( 20 Marks)
6. Amid doubts, Government sets up panel to review conduct of surveys
Prelims: Indian Polity <Parliamentary Committees>
Mains: GS-II, Indian Constitution < Parliamentary Committees>
Context:
- The Standing Committee on Economic Statistics (SCES) formed in December 2019 as Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS) with objective
- to review the existing data framework and issues related to all surveys, the government has renamed and expanded the scope of coverage of the Standing Committee on Economic Statistics (SCES).
- This committee will be headed by former Chief Statistician Pronab Sen, who was also the head of the earlier SCE.
Parliamentary committees
- Parliamentary committees are act as Parliament’s ‘Watch Dogs’ over the Executive.
- A Parliamentary Committee is a panel of MPs that is appointed or elected by the House or nominated by the Speaker/Chairman in the Indian Parliament.
- The committee works under thedirection of the Speaker/Chairman and it presents its report to the House or to the Speaker/Chairman.
- They draw their authority from Article 105 and Article 118 of the Indian constitution.
- Article 105, deals with the privileges of MPs.
- Article 118, gives Parliament authority to make rules to regulate its procedure and conduct of business.
- Parliamentary committees can be differentiated on the basis of their work, their membership and the length of their tenure,
- However, broadly there are two types of Parliamentary Committees; Standing Committees and Ad Hoc Committees.
- Standing Committees are permanent in nature which are formed every year or on a regular basis and function on a continual basis.
- While the Ad Hoc Committees are temporary and cease to exist on completion of the task assigned to them.
- Standing committees can be classified into the following six categories:
- Financial Committees
- Departmental Standing Committees
- Committees to Inquire
- Committees to Scrutinise and Control
- Committees Relating to the Day-to-Day Business of the House
- House-Keeping Committees or Service Committees
7. PUBLIC SHAMING AND ASSEST SEIZURES OF DRUG TRAFFICKERS
Prelims: National Plan for Drug Demand Reduction
Mains: GS- I < Society> // GS-III < Security Challenges>
Context:
- Home Minister Amit Shah at a regional conference on ‘Drug Trafficking and National Security’
- pitched for harsher punishment, including confiscation of assets of those involved in drug trade and their public shaming, such action will act as a strong deterrent.
What are the issues?
- It is a social problem that harms youth and families and the money it generates is diverted for disruptive activities that have bearings on national security.
- Criminal networks traffic a range of drugs including cannabis, cocaine, heroin and methamphetamine.
- Methamphetamine (meth) is an addictive drug and can cause considerable health adversities that can sometimes result in death.
- USA has recently witnessed a new zombie drug (Fentanyl) gripping its population.
- It can cause raw wounds on the user’s skin that can spread rapidly with repeated exposure.
- It starts with ulcers, hardens to dead skin called eschar, and if left untreated can result in amputation.
Challenges Related: Drug smuggling and National Security
- Drug trafficking is often associated with other forms of crime, such as terrorism, money launderingor corruption.
- Trafficking routes can also be used by criminal networks to transport other illicit products.
- The global drug trade is a major problem that has put security and law enforcement agencies on high alert worldwide, including in India.
- India has been seen as sandwiched between the Death (Golden) Crescent and Death (Golden) Triangle and is being flooded with drugs, especially heroin and methamphetamine, from these two regions by drug lords indirectly supported by intelligence setups.
- “Earlier the main area of drug smuggling was called ‘Golden Triangle’ and ‘Golden Crescent’ but the government of India has proposed inter nationally that it should be named as ‘Death Triangle’ and ‘Death Crescent’.
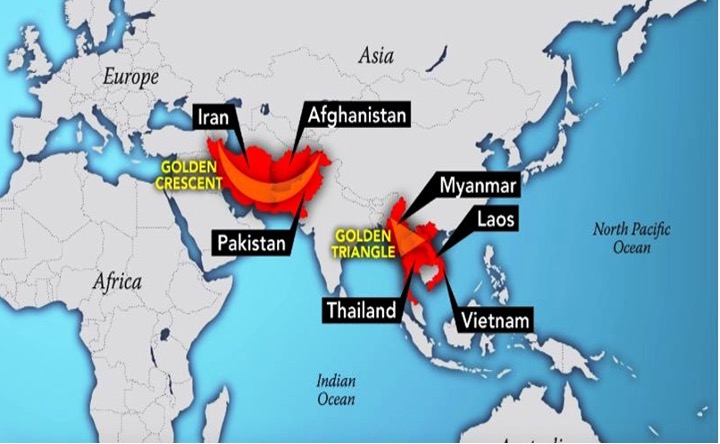
-
- Threats from Death (Golden) Crescent: Includes Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan, parts of Pakistan adjoining Afghanistan are also used by Pakistani drug traffickers to convert Afghan opium to heroin and then sent to India.
- Threats from Death (Golden) Triangle: Compromise of Vietnam, Thailand, Laos and Myanmar, the Shan and Kachin provinces of Myanmar bordering China also pose challenges.
- India had the third-highest amount of morphine confiscated in the same year, at 0.7 tonnes, and the fourth-largest amount of opium, at 5.2 tonnes, according to the World Drug Report 2022.
- The Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB)’s most recent annual report estimates that over 70% of all illegal drugs transported into India enter the country via sea routes in the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
8. GLOBAL ECONOMIC GROWTH REMIANS UNEVEN
Prelims: Economic Development
Mains: GS-III < Global Economy, Indian Economy >
Context:
- Finance ministers and central bank chiefs of G20 countries began talks on debt restructuring, multilateral bank reforms, and finance to tackle climate change.
- Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman called for “coordinated international efforts” to a navigate a challenging period of “uneven and below- average growth”.
What are the reasons of Uneven Growth of Global Economy?
- Countries are emerging from the crisis with different challenges, often reflecting their pre-COVID 19 strengths and weaknesses, and their policy approaches during the pandemic.
- Even in the countries where output or employment have recovered to their pre-pandemic levels, the recovery is incomplete, with jobs and incomes still short of the levels expected before the pandemic.
- Renewed outbreaks of the virus are forcing some countries to restrict activities, resulting in bottlenecks and adding to supply shortages.
- Large differences in vaccination rates between countries are adding to the unevenness of the recovery.
- There is a marked variation in the outlook for inflation, which has risen sharply in the US and some emerging market economies but remains relatively low in many other advanced economies, particularly in the euro area.
- A rapid increase in demand as economies reopen has pushed up prices in key commodities such as oil and metals as well as food, which has a stronger effect on inflation in emerging markets.
- The disruption to supply chains caused by the pandemic has added to cost pressures. At the same time, shipping costs have increased sharply.
- Higher likelihood among poor households to adopt strategies to cope with income losses that reduce their productivity over time mostly in the developing countries.
- the economic impacts reinforced preexisting inequality patterns.
9. Indian and French Connection Rooted in Trust and time, Now Aiming for New Peaks
Prelims: International Relations
Mains: GS-II < International Relation>
CONTEXT:
- Prime Minster Narendra Modi has completed a successful visit to France, India’s oldest strategic partner, even though the two countries could not close the deal on the “procurement of Scorpene submarines and the joint development of a combat aircraft engine” in time for their joint statement.
India and France Relation
Strategic Dialogue:
- After our 1998 nuclear tests, France was the first country with whom we began a Strategic Dialogue because it declined to put bilateral sanctions on us and showed a far higher understanding of India’s security imperatives than other counties.
Trade between the both Countries:
- The last ten years have seen a steady increase in bilateral commerce with France, which is expected to reach USD 10.75 billion in 2020. The two parties agreed that it was critical to move the trade and investment negotiations between India and the EU along quickly.
- At the business summit, contracts worth around $16 billion were signed. Over a hundred Indian enterprises have established operations in France, compared to roughly 1,000 French companies.
Defense:
- France was the second largest defense supplier for India in 2017- 2021.
- Induction of six French Scorpene submarines and Rafale fighter jets
- Joint military exercises like Varuna (navy), Garuda (air force), and Shakti (army).
- Joint manufacturing with the Tata Group tied up with Airbus to manufacture C-295 tactical transport aircraft in Vadodara, Gujarat.
Economic Cooperation:
- With annual trade of USD 12.42 billion in 2021–2022, France has emerged as a significant commercial partner of India.
- With a total investment of USD 10.31 billion made between April 2000 and June 2022, or 1.70% of all FDI into India.
- France emerged as the 11th largest foreign investor in that country.
Maritime cooperation:
- Combined Strategic Vision of France and India an outline for a tightening of links is provided by regional cooperation in the Indian Ocean.
- India’s intention to increase its presence in the Indian Ocean by cooperating with like-minded allies is signalled by French and Indian combined patrolling in the region.
- As both nations have expressed their shared goal for a free, just, and open Indo-Pacific, maritime security has gained pace.
- In September 2022, France and India decided to create an Indo-Pacific Trilateral Development Cooperation Fund to foster innovative sustainable solutions for nations in the Indo-Pacific region.
- The India, France, and UAE Trilateral Initiative aims to promote marine security and domain awareness from the east coast of Africa to the far reaches of the Pacific.
Space cooperation:
- Earlier France assisted India to set up the Sriharikota launch site.
- ISRO-CNES Joint Working Group: To deepen their cooperation in the realm of space, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the French National Centre for Space Studies (CNES) created a Joint Working Group in 2020.
- Collaborative Mars Mission: In 2020, ISRO and CNES said they would work together to develop a cooperative Mars mission soon.
- Space agencies of India and France inked an agreement for cooperation for the country’s first human space mission Gaganyaan.
- Collaboration on Space Debris: France and India have also been collaborating on finding solutions for the problem of space debris.
- Joint Earth Observation Mission: In 2021, ISRO and CNES stated they would work together to create a satellite to investigate the Earth’s atmosphere and climate.
What are the Challenges in India-France Relations?
- Free Trade Agreement (FTA): France and India don’t have a free trade agreement (FTA), notwithstanding their cordial relations.
- France has criticised India for failing to appropriately protect intellectual property rights, which has had an impact on French companies doing business in India.
- India and France are both concerned about China’s growing influence in the Indian Ocean, which has the potential to disturb the balance of power and jeopardise regional stability and security.
10. US Hands over 105 Antiquities, Will Reach INDIA Soon
Prelims: Ancient History and Art and Culture
Mains: GS-I < Indian Heritage and Culture>
Context:
- 105 trafficked antiquities have been returned to India to the United States and will be back in India soon.
- A repatriation ceremony for these objects’ consulate at the Indian Consulate in New York on Monday.
Impotence of Artefacts:
- These artefacts represent a wide geographical spread in terms of their origin in India.
- Around 50 artefacts relate to religious subjects (Hinduism, Jainism and Islam).
- The objects to return as part of this batch span a period of 1,600 years – from the 1st century BC to the 15th century AD, and hold significant historical.
- These include:
- a terracotta Yakshi plaque belonging to the 1st century BC, which was stolen from ‘eastern India’;
- a red sand- stone Dancing Ganesha from the 9th century, with its provenance in central India;
- a 10th century Kubera, also belonging to central India, and several other valuable antiquities and objects in mediums such as marble, terracotta and sandstone.
11. CRIMEA BRIDGE ATTACK
Prelims: Geography Maps
- The bridge is the only direct link be- tween the transport network of the country and Crimean Peninsula.
- It was inaugurated in 2018, four years after Russia’s annexation of Crimea.
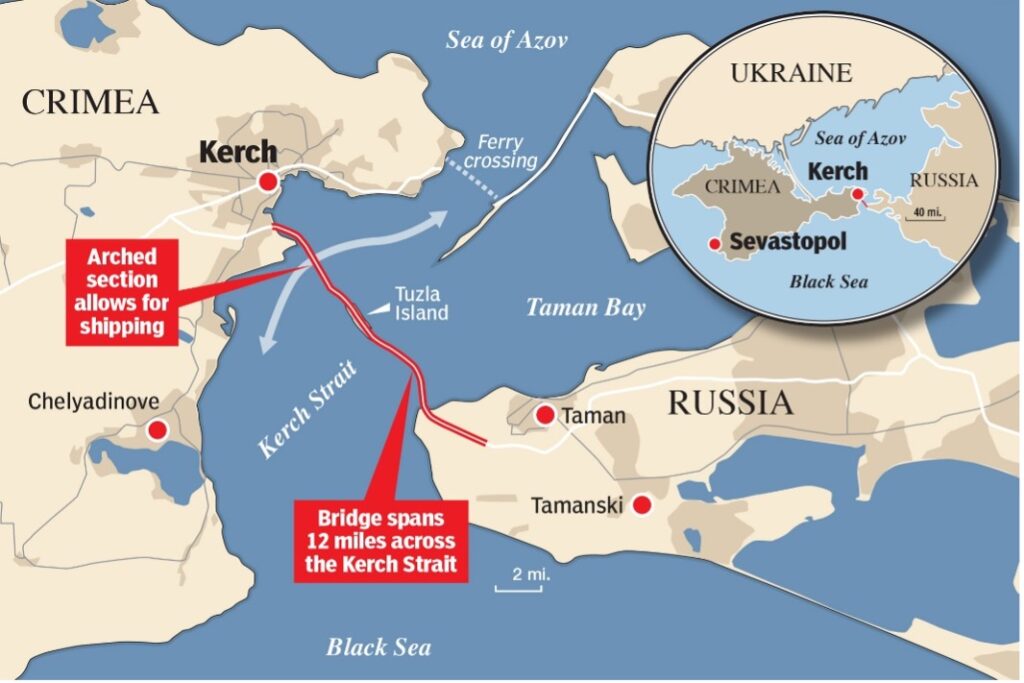
- It is a part of the route that supplies fuel, food and other products to the region, where the port of Sevastopol is the historic home base of Russia’s Black Sea Fleet, Reuters reported.
- After the war broke out, Russian convoys, carrying weapons, vehicle and fuel, use the route to reach Ukrainian territories, especially Kherson region and some of the adjoining Zaporizhzhia province.
For Enquiry

26 Mar 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

26 Mar 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

26 March 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC

26 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

26 March 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis

26 March 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

23 Mar 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

23 Mar 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

23 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

23 March 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC
Daily Quiz 26 Mar 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 26 Mar 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 26 Mar 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
26-March-2024
Q1) The Jal Jeevan Mission needs meticulous coordination and collaboration…
March 2024 PIB 26 March 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
26-March -2024
1. Payroll Data: EPFO adds 16.02 lakh net members during January…
Daily Current Affairs 26 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
26-March -2024- Top News of the Day
1. EU probe into tech giants for ‘violation’…
Indian Express 26 March 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
26-March-2024
1. WTO’S EXISTENTIAL CRISIS
Topic: GS2 – International…
March – The Hindu Editorial 26 March 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu EDITORIAL
26-March-2024
1. China, a ‘want-to-be’ superpower
Topic: GS2 – International…
Daily Quiz 23 Mar 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 23 Mar 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 23 Mar 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
23-March-2024
Q1) The enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of health is…
Daily Current Affairs 23 March 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
23-March -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Delhi Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal Arrested…
March 2024 PIB 23 March 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
23-March -2024
1. Ministry of Earth Sciences hosts Inter-Ministerial Joint Workshop…




