21 September 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
1. SC asks govt. to explain delay in the appointment of judges
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 3)
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Polity – Judiciary |
| Context |
|
Concerns Raised by the Supreme Court:
- Delay in Appointments: The Supreme Court expressed concern over the government’s inaction on Collegium-recommended names, some pending for months or years.
- Undermining Judicial Independence: The court stressed that ignoring reiterated names undermines the independence of the judiciary as outlined in the Second Judges case.
- Collegium Status: The Supreme Court clarified that the Collegium cannot be treated as a mere “search committee” whose recommendations can be selectively accepted or ignored.
- Pending High Court Vacancies: Multiple High Courts are functioning under Acting Chief Justices, which the court noted is affecting the administration of justice.
Potential Harms:
- Judicial Delays: Prolonged vacancies in High Courts lead to delays in case hearings, burdening an already overloaded judiciary.
- Erosion of Trust: Continuous government inaction on appointments may erode public trust in the judicial appointment process and weaken judicial independence.
- Administrative Inefficiency: The absence of permanent Chief Justices hampers the efficient functioning of High Courts.
- Impact on Justice Delivery: Vacancies contribute to increasing case backlogs, slowing down justice delivery across courts.
- Diminished Collegium Authority: Ignoring reiterated names weakens the authority of the Collegium, a body mandated for judicial appointments.
Way Forward:
- Time-Bound Process: The government should adhere to a time-bound process for clearing or responding to Collegium recommendations, ensuring timely judicial appointments.
- Transparent Mechanism: Establishing clear communication and transparency between the government and the Apex court can resolve the stalemate.
- Deemed Acceptance: If the government fails to act on a recommendation within a specified period (e.g., six weeks), the recommendation should be deemed accepted.
- Permanent Chief Justices: The government should prioritise filling vacancies in High Courts, particularly appointing permanent Chief Justices to ensure efficient judicial administration.
| PYQ: Constitutionally guaranteed judicial independence is a prerequisite of democracy. Comment. (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2023) |
| Practice Question: Examine the implications of delays in judicial appointments by the executive on the independence of the judiciary and the overall functioning of the judicial system. Suggest measures to ensure timely appointments in line with the Collegium system. (250 Words /15 marks) |
2. Indigenous heavy water reactor attains criticality
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 5)
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
|
Pressurised Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR):
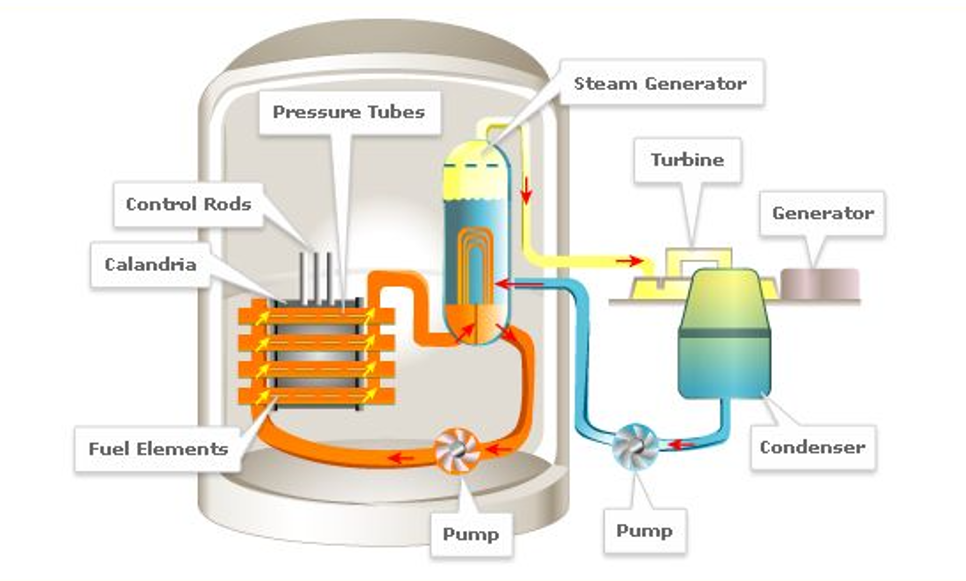
- Definition: A Pressurised Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR) uses heavy water (D2O) as both a coolant and a neutron moderator.
- Fuel Type: Typically utilises natural uranium as fuel, which allows for more efficient fission reactions without the need for enrichment.
- Sustainability: PHWRs can use a variety of fuels, including thorium, enhancing long-term fuel sustainability.
- Operation Principle: The reactor maintains high pressure to prevent heavy water from boiling, enabling effective heat transfer to the steam generators.
- Efficiency: PHWRs are known for their fuel efficiency and capability to operate for longer durations between refuelling.
- Design Features: They have a robust design that enhances safety, including multiple barriers to prevent the release of radioactive materials.
| What is the criticality of a nuclear reactor? |
|
Key Differences Between PHWRs, LWRs, and BWRs:
| Feature | Pressurised Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR) | Light Water Reactor (LWR) | Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) |
| Moderator | Heavy water (D2O) | Light water (H2O) | Light water (H2O) |
| Fuel Type | Natural uranium | Enriched uranium | Enriched uranium |
| Pressure System | High pressure, preventing water from boiling | Low pressure, water boils in core | Low pressure, water boils directly in the core |
| Cooling Method | Separate steam generators | Direct cooling in core | Steam produced from the reactor core used for cooling |
| Efficiency | High fuel efficiency due to natural uranium use | Lower efficiency due to enrichment needs | Moderate efficiency with a simpler design |
| Safety Features | Robust safety design with multiple barriers | Requires active safety systems | Relies on passive safety systems |
| PYQ: With growing energy needs should India keep on expanding its nuclear energy programme? Discuss the facts and fears associated with nuclear energy. (250 words/15m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2018) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the advantages of heavy water reactors (PHWRs) over light water reactors in the context of India’s nuclear energy strategy. How do these advantages contribute to energy security and sustainability? (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. Closed doors at affluent gated communities dent official data
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 11)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
What is the issue?
- Data Collection Challenges: High-income groups in gated communities are increasingly refusing to participate in official surveys conducted by the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO), leading to a significant data gap.
- Representation Skew: The non-response from affluent households skews the socio-economic representation in survey samples, distorting the overall understanding of the population and economy.
- Impact on Policy: Officials express concern that guessing the data of non-responders undermines effective policymaking, as accurate data is essential for informed decisions.
- Rising Non-Response Rates: There has been a noticeable increase in non-response rates among affluent households, with many openly declining to share information or allow enumerators entry into their residences.
- Criticism and Irony: Although these affluent groups often critique policies on social media, their reluctance to provide necessary data hampers the formation of effective policies, revealing a disconnect between public criticism and active participation in governance.
Way Forward:
- Awareness Campaigns: Launch targeted awareness campaigns to educate affluent households about the importance of survey participation for effective policymaking and resource allocation.
- Engagement with Resident Welfare Associations: Collaborate with resident welfare associations to encourage participation and build trust within gated communities.
- Simplifying Processes: Streamline the survey process to make it less intrusive and more user-friendly, encouraging higher response rates.
- Confidentiality Assurance: Emphasise data confidentiality and privacy to alleviate concerns about sharing personal information.
- Feedback Mechanism: Establish a feedback mechanism where participants can see the impact of their contributions on policy decisions, fostering a sense of ownership.
- Incentives for Participation: Consider offering incentives or rewards for participation, for example – gift vouchers or access to public services.
| Practice Question: Discuss the implications of the increasing non-response rates from affluent households in official surveys on data collection. What measures can be taken to ensure better participation from these socio-economic groups to enhance the quality of national statistics? (250 Words /15 marks) |
4. Bombay High Court Strikes Down IT Rules Provision Empowering Government’s Fact-Check Unit, Citing Violation of Free Speech
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 13)
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Issues arising out of design and implementation |
| Context: |
|
Analysis of News:
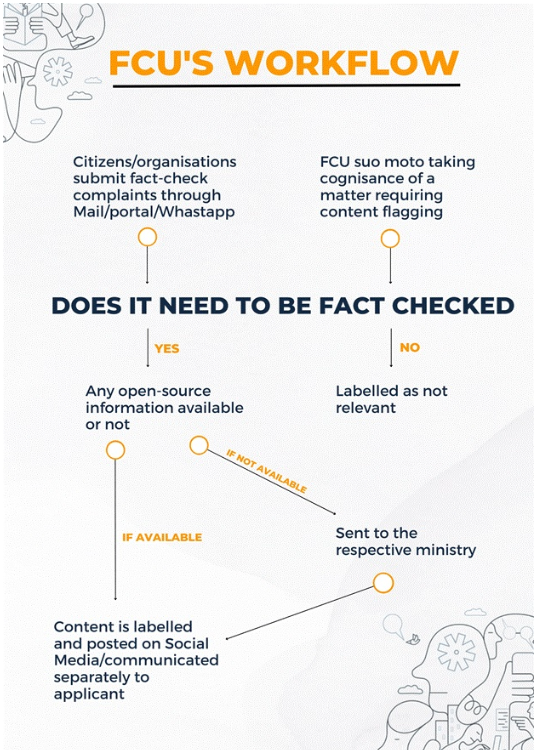
What is the Fact Checking Unit and Amended IT Rules 2023?
- Fact Checking Unit: The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, designated the FCU as a statutory body under the Press Information Bureau (PIB) as per the amendment made to Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021 in 2023.
- FCU has been tasked with flagging content deemed to be false information related to the central government and its agencies on social media platforms.
- Key Provisions of IT Rules, 2023 Regarding Fake News:
- Online intermediaries, such as social media platforms like Facebook, YouTube, and Twitter, along with internet service providers like Airtel, Jio, and Vodafone Idea, are required to ensure they do not disseminate inaccurate information about the Government of India.
- Additionally, these platforms must make reasonable attempts to avoid hosting content related to the Central Government that has been flagged as false or misleading by a fact-checking unit.
- If the fact-checking unit identifies any information as false, online intermediaries will be obligated to remove it.
- Failing to do so could result in the loss of their safe harbour protection, which shields them from legal action regarding third-party content.
Provision in Question
- IT Rules Amendment (2023): Expanded Rule 3(1)(b)(v) of the IT Rules, 2021, to include “fake news” about government business.
- FCU’s Role: The FCU could flag posts containing fake or misleading information about the government, compelling social media platforms to remove such content to retain their “safe harbor” protection (legal immunity for third-party content).
Key Arguments
- Petitioners: Stand-up comedian Kunal Kamra, Editors’ Guild of India, and others argued that the rules violated fundamental rights, were arbitrary, and gave the government excessive power over free speech.
- Government’s Defense: The rules targeted only misinformation about government business, not opinions or satire, and sought to ensure that misleading facts were curbed.
High Court Rulings
Justice Atul S Chandurkar’s Decision:
- Agreed with the earlier opinion of Justice Gautam S Patel, ruling the amendment unconstitutional.
- Violation of Articles 14, 19(1)(a), and 19(1)(g): The rules infringed upon equality before law, free speech, and the right to practice a profession.
- Vagueness: The terms “fake, false, or misleading” were too broad, creating an overreach into citizens’ rights.
- Chilling Effect: The threat of losing safe harbor status imposed a chilling effect on free speech.
Justice Patel’s Earlier Opinion:
- Criticized the FCU for creating censorship, classifying speech as true or false, and curbing free expression.
- Noted the FCU had excessive power with no adequate checks.
Dissenting Opinion (Justice Neela Gokhale):
- Defended the rules, claiming they did not penalize intermediaries directly and did not impose a chilling effect.
- Argued that access to authentic information is essential for democracy, and concerns about the FCU were premature.
Implications
- Impact on FCUs: This ruling affects both central and state-level FCUs, like those in Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, potentially limiting their ability to flag misinformation.
- Further Legal Steps: The decision could be appealed to the Supreme Court. Similar cases are pending before other courts, including in Delhi and Madras.
Future Considerations
- Other Pending Guidelines: Beyond this ruling, other IT guidelines from 2021, such as mandates for social media platforms to establish grievance redress mechanisms, remain under judicial review across various courts.
| What is the Press Information Bureau (PIB)? |
|
| Practice Question: How does the Bombay High Court’s ruling against the amended Information Technology Rules, 2021, reflect the balance between government regulation of misinformation and the protection of free speech rights in India? (250 words/15 m) |
5. India Launches White Revolution 2.0: Aiming for 50% Increase in Dairy Cooperative Milk Procurement by 2028
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 13)
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy |
| Context: |
| The Indian government has launched White Revolution 2.0 to strengthen dairy cooperatives, increase milk procurement, and expand coverage, aiming for a significant boost in milk production by 2028. |
Analysis of News:
Operation Flood and the White Revolution
- Background
Operation Flood, launched in 1970, transformed India’s dairy sector, ushering in the “White Revolution.” This initiative, led by dairy cooperatives, expanded milk production and empowered rural farmers. - The National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) played a pivotal role, and India’s milk production surged, making the country the world’s top producer.
White Revolution 2.0
- Objective
Announced by Union Home and Cooperation Minister Amit Shah, White Revolution 2.0 aims to enhance the cooperative model established during Operation Flood. - Its goal is to increase milk procurement by dairy cooperatives by 50%, from 660 lakh kg/day in 2023-24 to 1,007 lakh kg/day by 2028-29.
- This will provide better market access to farmers in uncovered areas and expand the cooperative network.
Key Strategies
- Cooperative Network Expansion: The NDDB plans to establish 56,000 new dairy cooperative societies (DCSs) and strengthen 46,000 existing ones in key states such as Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, Rajasthan, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Infrastructure and Capacity Building: Investments in milk procurement systems, chilling facilities, and training will enhance operational efficiency.
- Inclusion of Uncovered Areas: A pilot project in districts like Jind, Indore, and Chikmagalur has already established 79 DCSs, procuring 15,000 liters of milk daily.
India’s Dairy Sector Overview
Current
- India is the world’s largest milk producer, with a production of 230.58 million tonnes in 2022-23.
- The average national milk yield is 8.55 kg/day for exotic breeds, and 3.44 kg/day for indigenous animals.
- The per capita availability is 459 grams/day, surpassing the global average of 323 grams/day.
Key Contributors
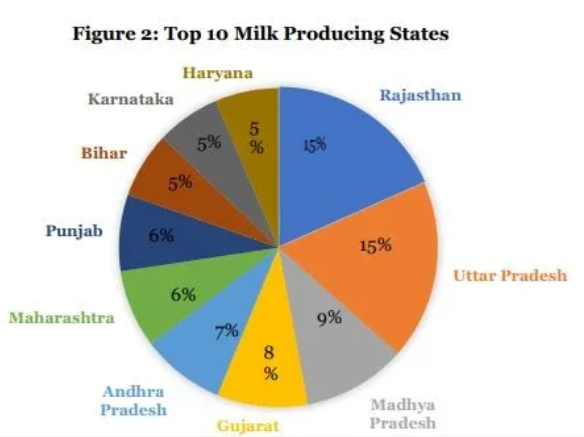
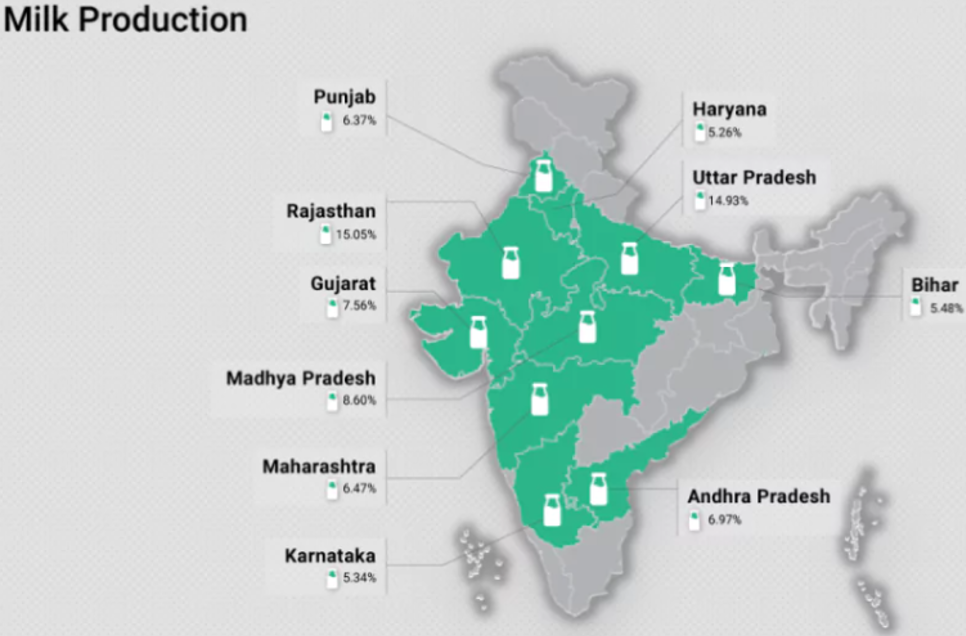
- The top milk-producing states are Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh, contributing over 53% of the country’s total milk production.
Challenges
- Despite increased production, the annual growth rate of milk output has slowed from 6.47% to 3.83% between 2018-19 and 2022-23.
- Additionally, the sector faces regional disparities in milk yields and per capita availability.
Government’s New Initiative
Funding and Support
- The National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD) 2.0 will finance White Revolution 2.0, focusing on setting up village-level cooperatives, improving milk testing infrastructure, and building chilling facilities.
- Financial assistance will be provided to Multipurpose Primary Agricultural Credit Cooperative Societies (MPACS) to support procurement systems.
Social Impact
- The initiative is expected to create employment opportunities and contribute to the economic empowerment of rural women, who constitute a majority of dairy workers.
Conclusion
- White Revolution 2.0 aims to expand India’s dairy sector by strengthening cooperatives, improving infrastructure, and extending coverage to underserved areas.
- This initiative is positioned to further enhance rural livelihoods while boosting milk production.
| Government Initiatives for the Promotion of Dairy Sector |
|
Rashtriya Gokul Mission: It was launched in 2014, to conserve and develop indigenous cattle breeds. Aim: To enhance the productivity and genetic improvement of indigenous cattle. National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD): NPDD has been in place since 2014 and aims to build or strengthen infrastructure for the production of high-quality milk as well as for the procurement, processing, and marketing of milk and milk products through the State Cooperative Dairy Federation. Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme (DEDS): DEDS is being implemented by the Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying, and Fisheries to create self-employment opportunities in the dairy industry.It provides financial assistance to individuals for setting up small to medium-scale dairy ventures.The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development is carrying out the programme. National Animal Disease Control Programme (NADCP): It is a flagship scheme launched in 2019 for control of Foot & Mouth Disease and Brucellosis by vaccinating 100% cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat and pig population. National Livestock Mission (NLM): The NLM, launched by the Ministry of Agriculture, aims to ensure sustainable development of the livestock sector, including dairy farming.It focuses on increasing the productivity of livestock, improving their health, and providing support for fodder and feed resources. |
| PYQ: Explain various types of revolutions, took place in Agriculture after Independence in India. How these revolutions have helped in poverty alleviation and food security in India? (150 words/10m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2017) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of White Revolution 2.0 in enhancing the dairy sector in India, with a focus on cooperative societies. How does the initiative aim to address the regional disparities in milk production and procurement? (250 words/15 m) |
Prelims Facts
1. Exploding devices in Lebanon trigger a nation that has been on edge for years
(Source – The Hindu, International Edition – Page No. – 13)
| Context |
|
Key Issues In Lebanon Amid Ongoing Crisis:
- Economic Collapse: Lebanon is facing a severe economic crisis, exacerbated by the 2020 Beirut port blast and ongoing financial instability.
- Political Paralysis: The country has been without a functioning government or president for over two years, leading to governance challenges.
- Security Threats: Continuous hostilities between Israel and Hezbollah, including recent attacks targeting civilian areas, increase fear and uncertainty.
- Mental Health Crisis: The population suffers from psychological trauma due to past explosions and ongoing violence, with many experiencing heightened anxiety and paranoia.
- Public Safety Concerns: Recent explosions from devices have led to widespread fear, prompting parents to keep children away from schools and communities to take safety precautions.
- Healthcare Strain: The healthcare system is overwhelmed and unprepared for a potential large-scale conflict, complicating emergency responses.
2. Starlink Satellites Disrupt Radio Astronomy: Study Calls for Urgent Regulations on Electromagnetic Emissions
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Explained; Page: 13)
| Context: |
| Elon Musk’s Starlink satellites, part of a constellation delivering high-speed internet globally, are causing significant disruptions to radio astronomers due to unintended electromagnetic radiation (UEMR). |
Analysis of News:

Starlink Project:
- It is a SpaceX project, launched in 2019, to build a broadband network with a cluster of thousands of orbiting satellites.
- The goal of the project is to create a low-cost, satellite-based broadband network that can provide global internet access.
- The Starlink satellites are placed in an altitude range between 350 km and 1,200 km in Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
- Reduced latency between a user seeking data and the server transmitting that data is the key benefit of placing satellites in LEO for space-based Internet.
Radio Noise and Its Effect on Astronomy
Radio Astronomy
- Radio astronomy observes celestial objects using radio waves rather than visible light.
- However, UEMR from satellites like Starlink creates “radio noise,” blinding telescopes and obstructing scientific observations, akin to being overwhelmed by bright headlights while trying to see faint stars.
Increased Interference
- The study found that Starlink’s second-generation satellites emit UEMR 32 times brighter than the first generation, worsening the issue despite efforts to reduce interference in older models.
The Need for Regulation
Growing Satellite Numbers
- With satellite launches becoming cheaper, experts predict up to 100,000 satellites in orbit by 2030, escalating the issue of UEMR.
- This signals the urgent need for regulations to minimize radio pollution from satellites, similar to existing controls on ground-based electronic sources.
Current Approach
- Currently, astronomers rely on informal agreements with satellite operators like Starlink, but regulatory frameworks are necessary to control electromagnetic leakage and protect astronomical research.
3. India Joins International Big Cat Alliance to Boost Global Conservation Efforts for Big Cats
(Source: Indian Express; Section: Express Network; Page: 09)
| Context: |
| India, after receiving Union Cabinet approval, has officially joined the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA), which it launched in 2023 to protect big cats globally. |
Analysis of News:

International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)
- It was launched by the Indian Prime Minister in Mysuru on April 9, 2023, at an event commemorating 50 years of Project Tiger in India.
- Objective: Strengthen global cooperation and efforts for conservation of seven big cat species (tiger, lion, leopard, snow leopard, cheetah, jaguar and puma) and their habitats.
- Out of the seven big cats, five — tiger, lion, leopard, snow leopard, and cheetah — are found in India.
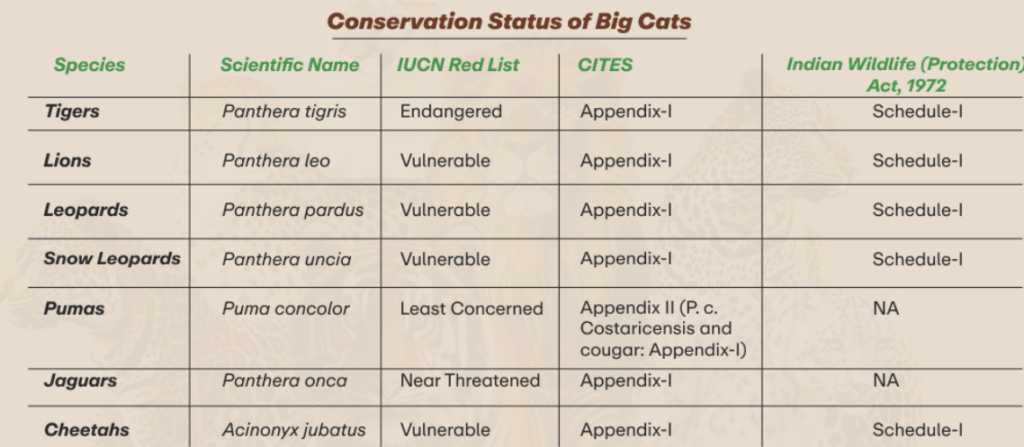
- The alliance aims to reach out to 97 range countries covering the natural habitats of the seven big cats.
- IBCA has been conceived as a multi-country, multi-agency coalition to strengthen global cooperation and mobilise financial and technical resources to support the entire ecosystem associated with the conservation of these species and their habitats.
- It will serve as an evolving platform for convergence of knowledge and best practices, supporting existing specific inter-governmental platforms, while also providing direct support to recovery efforts in potential range habitats.
- IBCA would have a multi-pronged approach in broad-basing and establishing linkages in several areas and help in knowledge-sharing, capacity-building, networking, advocacy, finance, and resource support.
- IBCA governance consists of an assembly of members, a standing committee, and a secretariat with its headquarters in India.
- IBCA has secured the Government of India’s initial support of Rs. 150 crore for five years (2023-24 to 2027-28).
Member Nations
- Currently, India, Nicaragua, Eswatini, and Somalia have joined IBCA, collaborating to address common conservation challenges and protect big cats and their landscapes.
4. India Achieves Tier 1 Status in Global Cybersecurity Index 2024
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2057035 )
| Context |
| India’s top-tier achievement in the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2024 reflects its growing global leadership in cybersecurity.Published by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), the GCI assesses national cybersecurity efforts.India’s high score signifies robust legal, technical, and organisational measures, alongside international cooperation and education initiatives promoting cyber resilience. |

Global Cybersecurity Index 2024:
- India achieved Tier 1 status in the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2024, published by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
- India scored 98.49 out of 100, joining the ranks of ‘role-modelling’ countries.
- The index evaluates national cybersecurity efforts across five pillars: legal, technical, organisational, capacity development, and cooperation.
- A comprehensive questionnaire with 83 questions is used, covering 20 indicators, 64 sub-indicators, and 28 micro-indicators.
- Countries are classified into tiers based on their performance, with Tier 1 representing role-model countries.
- The index emphasises the importance of legal frameworks to combat cybercrime and strengthen cybersecurity standards.
- It recognizes efforts in establishing sectoral Computer Incident Response Teams (CSIRTs) to address cyber incidents.
- Capacity development focuses on enhancing skills, promoting cybersecurity education, and research.
- Cooperation is assessed through bilateral and multilateral collaborations and information-sharing initiatives.
- The GCI promotes international benchmarks for cybersecurity preparedness and highlights global best practices.
5. NPS Vatsalya: A Groundbreaking Pension Scheme for Minors
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2056918 )
| Context |
|
NPS Vatsalya scheme:
- The NPS Vatsalya scheme, launched in 2024 by the central government, is a pension scheme exclusively for children below 18 years of age.

- Managed by the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA), it promotes early financial planning and savings habits.
- Parents can contribute a minimum of ₹1,000 per month, with no upper limit.
- The account is managed by the guardian until the child turns 18, at which point it seamlessly transitions to the minor’s control.
- Upon reaching adulthood, the account converts into an NPS Tier-I or other non-NPS scheme.
- The scheme emphasises long-term wealth accumulation through compounding, ensuring a secure financial future for minors.
- Account creation can be done through Points of Presence (PoPs) or online via the eNPS platform.
- Required documents include proof of birth for the minor and KYC of the guardian.
5. IndiaAI Innovation Challenge launched to foster impactful AI Solutions inviting applications to build AI Solutions for critical sectors
(Source – https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=2056991 )
| Context |
|


More About IndiaAI Mission:
- The IndiaAI Mission is an initiative under the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), implemented by the IndiaAI Independent Business Division (IBD) of the Digital India Corporation (DIC).
- It aims to democratise the benefits of AI across all sectors of Indian society, fostering inclusive growth.
- IndiaAI Innovation Challenge is part of this mission, encouraging Indian innovators, startups, students, and organisations to develop impactful AI solutions.
- Key focus areas include AI-driven healthcare improvements, better governance through language technologies, AI-assisted agriculture, support for learning disabilities, and AI-powered climate and disaster management solutions.
- The mission also emphasises technological self-reliance and ensures ethical and responsible AI use, aligning with India’s vision of global leadership in AI.


