19 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs
Daily Current Affairs
19-April -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Indigenously built cruise missile successfully tested
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology – Achievements of Indian S&T.
The successful test highlights India’s progress in indigenous defence technology, relevant for UPSC exams on defence and strategic affairs. |
| Context |
| ● The DRDO conducted a successful flight test of a long-range subsonic cruise missile, demonstrating waypoint navigation and sea-skimming flight off the coast of Odisha. |
Additional information on this news:
- DRDO successfully conducted a flight test of a long-range subsonic cruise missile from the Integrated Test Range in Chandipur, Odisha.
- The missile demonstrated waypoint navigation and very low altitude sea-skimming flight, following the desired path.
- All subsystems performed as expected during the test, according to DRDO’s statement.
- Although the specific details or specifications of the missile were not disclosed, it bears resemblance to the Nirbhay subsonic cruise missile.
- The test signifies a significant advancement in indigenous cruise missile technology and showcases India’s growing capabilities in defense research and development.
| What is a subsonic cruise missile? |
| ● A subsonic cruise missile is a type of missile that travels at speeds slower than the speed of sound (approximately 343 meters per second at sea level).
● These missiles typically fly at subsonic speeds, often ranging from around 0.8 to 0.9 times the speed of sound. ● Subsonic cruise missiles are designed for long-range precision strikes against ground targets, naval vessels, or other specific targets. ● They are characterized by their ability to fly at low altitudes, often skimming the terrain or sea surface, which helps them evade enemy radar detection. ● These missiles are powered by turbofan engines, providing sustained propulsion during flight. ●Subsonic cruise missiles can carry various types of warheads, including high-explosive, penetrating, or submunitions, depending on the intended target and mission requirements. ● They are equipped with advanced navigation systems, including GPS, inertial navigation, and terrain contour mapping, to ensure accurate targeting. ● Subsonic cruise missiles offer several advantages, including long-range capabilities, stealthy flight profiles, and the ability to engage targets with precision, making them valuable assets in modern warfare scenarios. |
| PYQ:
With reference to Agni-IV Missile, which of the following statements is/are correct? 1. It is a surface-to-surface missile. 2. It is fuelled by liquid propellant only. 3. It can deliver one-tonne nuclear warheads about 7500 km away. Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only Ans: Option A (UPSC civil services prelims 2014) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the recent DRDO test of a long-range subsonic cruise missile in bolstering India’s defence capabilities. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. WHO defines pathogens that transmit through air
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health, GS3 – Science and Technology
Understanding standardised terminology for airborne pathogen transmission aids global health communication and preparedness, relevant for UPSC exams. |
| Context |
| ● The World Health Organization (WHO) has introduced the term “infectious respiratory particles” (IRPs) to standardise communication on airborne pathogen transmission. |
Additional information on this news:
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has introduced the term “infectious respiratory particles” (IRPs) to describe pathogens transmitted through the air.
- This move addresses the lack of a common terminology for such transmission, which posed challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The announcement follows extensive consultations conducted by the WHO between 2021 and 2023.
- Varying terminologies previously used for airborne pathogen transmission hindered effective public communication and efforts to control the spread of diseases.
- The term IRPs encompasses a wide range of pathogens that can spread through respiratory droplets or aerosols.
- Examples of infectious respiratory particles include viruses like influenza, SARS-CoV-2 (responsible for COVID-19), and bacteria like Mycobacterium tuberculosis (causing tuberculosis).
- The adoption of a standardised term facilitates clearer communication among healthcare professionals, policymakers, and the public regarding preventive measures and transmission risks.
- This initiative reflects WHO’s commitment to enhancing global health preparedness and response strategies against infectious diseases.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the World Health Organization’s introduction of the term ‘infectious respiratory particles’ (IRPs) in standardising communication on airborne pathogen transmission. (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. Why have private investments dropped?
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Issues related to growth.
Understanding the dynamics of private investment in India is vital for UPSC exams covering economic policies and growth strategies. |
| Context |
| ● The news highlights the persistent decline in private investment in India, despite government efforts, impacting economic growth and requiring structural reforms. |
Introduction: Private Investment in India
- Private investment, measured by Private Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) as a percentage of Gross Domestic Product (GDP), has been a crucial issue in India’s economic landscape.
- Despite government measures, private investment has not picked up pace, posing challenges to economic growth.
What is GFCF and its Significance?
- GFCF indicates the growth in the size of fixed capital in an economy, including investments in buildings and machinery.
- It serves as an indicator of private sector willingness to invest, crucial for economic growth and living standards.
- Developed economies like the U.S. have higher per capita fixed capital compared to developing economies like India.
Trends in Private Investment in India
- Historically, private investment in India remained below or slightly above 10% of GDP until economic liberalisation in the late 1980s.
- Public investment surpassed private investment in the early 1980s but declined post-liberalization, with private investment taking the lead.
- Private investment rose significantly until the global financial crisis of 2007-08 but declined thereafter, hitting a low of 19.6% of GDP in 2020-21.
Reasons for Decline in Private Investment
- Economists attribute the decline to low private consumption expenditure, which impacts business confidence in future demand.
- Despite historical evidence of a negative correlation between consumption and investment, consumption has risen while private investment has fallen since 2011-12.
- Structural problems such as unfavourable government policies and policy uncertainty also deter private investment.
Impact of Low Private Investment
- Low private investment leads to slower economic growth due to inadequate expansion of fixed capital.
- Government efforts to boost public investment may crowd out private investment and potentially lead to wasteful spending.
- Private investors are considered better allocators of capital compared to public officials, and taxes for public spending can hamper economic growth.
Conclusion: Addressing the Challenges
- India faces significant challenges in reviving private investment, requiring structural reforms and policy stability.
- Balancing public and private investment while ensuring efficient allocation of resources is crucial for sustainable economic growth.
| Significance of private investment: |
| Impact of Lack of Private Investment:
● Slow Economic Growth: Insufficient private investment leads to sluggish economic growth, stagnation, and missed opportunities for job creation, wealth generation, and poverty reduction. ●Infrastructure Deficit: Lack of private investment results in inadequate infrastructure development, hindering connectivity, mobility, and access to essential services, and impeding overall economic development. ● Technological Stagnation: Without private investment, countries may lag behind in adopting and developing cutting-edge technologies, limiting innovation, and competitiveness in the global economy. ●Unemployment: Insufficient private investment exacerbates unemployment and underemployment, particularly among youth and marginalized populations, fueling social unrest and inequality. ● Fiscal Strain: Governments may face fiscal constraints and budgetary pressures in funding public investments, social programs, and essential services in the absence of robust private investment. Way Forward: ● Policy Reforms: Implement pro-business policies, regulatory reforms, and investment incentives to attract private capital, foster investor confidence, and create a conducive business environment. ● Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Promote PPPs to leverage private sector expertise, resources, and efficiency in financing and delivering infrastructure projects, addressing gaps in public investment. ● Investment Promotion: Launch targeted marketing campaigns, investment summits, and business forums to showcase investment opportunities, attract foreign investors, and facilitate capital inflows. ●Capacity Building: Enhance institutional capacity, governance, and transparency to ensure effective project planning, implementation, and risk management in collaboration with private investors. ● Innovation Ecosystem: Foster an innovation-friendly ecosystem by investing in research and development, supporting startups, and facilitating technology transfer and commercialization to spur private investment in innovation-driven industries. |
| PYQ: Explain the meaning of investment in an economy in terms of capital formation. Discuss the factors to be considered while designing a concession agreement between a public enSty and a private enSty. (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2020) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the factors contributing to the decline in private investment in India and suggest policy measures to revitalise it. (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. Carbon price fall deprives Europe’s green funds of billions of euros
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations.
Understanding the economic implications of carbon pricing and its effects on green technology funding is relevant for UPSC exams. |
| Context |
| ● The news discusses the impact of a drop in the European Union’s carbon price on a major green technology fund, risking low-carbon projects. |
EU Carbon Price Dip Impacting Green Technology Fund
- The drop in the European Union’s (EU) carbon price may reduce the size of a major fund for green technologies, risking low-carbon projects.
- EU carbon permit prices plummeted from over €100 per tonne of CO2 in 2023 to nearly half by February 2024 due to reduced emissions.
Losses in Potential Revenues
- The decline has resulted in a €4.1 billion loss in potential revenues for Europe’s low-carbon investment budget in 2024.
- Lower emissions indicate progress towards climate goals but reduce revenue for EU green transition funds and member states’ climate efforts.
EU Innovation Fund and Revenue Shortfall
- The EU Innovation Fund, aimed at fostering nascent technologies like hydrogen and carbon capture, may fall short of its €40 billion target this decade due to lower-than-expected carbon prices.
- Current prices averaging around €70 per tonne fall below the needed €75/t to meet the fund’s goals.
Impact on Energy Transition and Industries
- Reduced carbon revenues affect the support for energy transition projects, impacting industries striving for green transformation.
- European industries, facing competitiveness challenges, may shift investments to regions like the U.S. with cleaner technology subsidies.
Industry Perspectives and Innovation Fund’s Role
- Companies like Holcim credit the Innovation Fund for spurring low-carbon investments, citing projects across Europe.
- Uncertainty in funding threatens projects deemed risky by investors but crucial for climate goals.
Market Outlook and Analyst Forecasts
- Analysts expect carbon prices to rebound despite short-term dampening factors, anticipating a gradual rise this decade.
- However, forecasts have been revised downwards, indicating market uncertainty.
Short-term Factors and EU Policy Implications
- Recent EU actions, such as additional carbon permit sales to fund transitions away from Russian gas, contribute to price dampening.
- The European Commission maintains its €75/t carbon price estimate for the Innovation Fund despite market fluctuations.
Funding Challenges and Project Viability
- The Innovation Fund supports projects lacking private investment due to perceived risks, crucial for scaling up low-carbon technologies.
- Funding uncertainties prompt projects to target EU support amidst oversubscription, delaying essential investments.
Conclusion:
- Companies like Heatrix aim to continue decarbonization efforts despite price dips, though investments in emissions-saving projects may be postponed.
- The hope remains for a temporary market state and eventual price recovery to support sustainable investments.
| What is a carbon price? |
| ● Carbon price refers to the monetary value assigned to the emission of carbon dioxide (CO2) or other greenhouse gases.
● It is implemented through mechanisms such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems. ● Carbon pricing aims to internalise the external costs of greenhouse gas emissions into the market, encouraging polluters to reduce emissions. ● In a carbon tax system, emitters pay a set price for each tonne of CO2 they release into the atmosphere. ● Cap-and-trade systems set a limit or cap on total emissions and issue permits, each representing the right to emit a certain amount of CO2. ● Emitters can buy and sell these permits in a regulated market, creating a price for carbon. ● The carbon price provides a financial incentive for industries to invest in cleaner technologies and practices. ● It also generates revenue that can be used for climate mitigation and adaptation efforts. ● Carbon pricing is considered a key policy tool for addressing climate change and transitioning to a low-carbon economy. ● Many countries and regions, including the India, have implemented carbon pricing mechanisms as part of their climate strategies. |
| PYQ: Should the pursuit of carbon credit and clean development mechanism set up under UNFCCC be maintained even through there has been a massive slide in the value of carbon credit? Discuss with respect to India’s energy needs for economic growth. (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-3 2014) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of carbon pricing as a policy tool for mitigating climate change and transitioning to a low-carbon economy. (250 Words /15 marks) |
5. India must invest more in education, health to tap demographic dividend: IMF
| Topic: GS2 – Indian Economy – Issues relating to development and employment.
Understanding IMF’s recommendation on investing in education and health for India’s demographic dividend is crucial for UPSC aspirants. |
| Context |
| ● The news emphasises the IMF’s recommendation for India to prioritise heavy investments in education and health to ensure adequate employment for its growing young population. |
Additional information on this news:
- The IMF suggests that India should heavily invest in education and health to ensure adequate employment for its growing, young population.
- The World Bank previously warned that India and other South Asian countries were not utilising their demographic dividend effectively.
- With 15 million people being added to the labour force annually, investment in education and health is crucial for India to benefit from its young workforce.
- According to Krishna Srinivasan of the IMF, prioritising education and health spending is essential, especially with 65% of Indians being under the age of 35.
- The labour force needs to acquire the right skills to compete with challenges such as artificial intelligence (AI).
- Despite high youth unemployment, projected economic growth for India in FY25 is 6.8%.
- Public investment and private consumption are driving India’s growth, but the IMF questions whether public spending is crowding in private investment.
- However, there has been a recent uptick in private investment, signalling a positive outlook for the future, alongside an increase in consumption linked to a deceleration in inflation.
| Demographic Dividend Of India: An Overview |
| ● Demographic Profile: India is home to a large and youthful population, with over 65% of its citizens below the age of 35, making it one of the youngest countries in the world.
● Demographic Dividend: The demographic dividend refers to the economic growth potential that can result from shifts in a population’s age structure, particularly when the working-age population (15-64 years) surpasses the dependent population (under 15 and over 65 years). ●Economic Opportunities: India’s demographic dividend presents significant economic opportunities, including a growing labour force, increased productivity, higher savings and investment rates, and greater potential for innovation and entrepreneurship. ● Consumption Boom: The youthful demographic profile contributes to a consumption boom, with rising demand for goods and services across various sectors, including retail, housing, healthcare, education, and entertainment. ● Human Capital Development: Realising the full potential of the demographic dividend requires investments in human capital development, including education, skills training, healthcare, and employment generation, to equip the youth with the necessary knowledge, skills, and capabilities to contribute to the economy. ● Employment Challenges: Despite the demographic dividend, India faces significant employment challenges, including underemployment, informal sector dominance, skill mismatches, gender disparities, and rural-urban migration, which need to be addressed through targeted policies and interventions. ● Policy Interventions: Policy interventions aimed at harnessing the demographic dividend include skill development initiatives, vocational training programs, entrepreneurship promotion, labour market reforms, investment in education and healthcare, and infrastructure development to create employment opportunities and enhance productivity. ● Sustainable Development: Leveraging the demographic dividend for sustainable development requires a holistic approach that balances economic growth with social inclusion, environmental sustainability, and equitable distribution of benefits to ensure that no segment of the population is left behind. ● Global Competitiveness: India’s ability to leverage its demographic dividend will determine its global competitiveness and position in the 21st-century knowledge-based economy, making it imperative for policymakers to prioritise investments in youth empowerment and human capital development. |
| PYQ: “Demographic Dividend in India will remain only theoretical unless our manpower becomes more educated, aware, skilled and creative.” What measures have been taken by the government to enhance the capacity of our population to be more productive and employable? (200 words/12.5m) (UPSC CSE (M) GS-2 2016) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the IMF’s recommendation for India to prioritise investments in education and health to harness its demographic dividend. (150 Words /10 marks) |
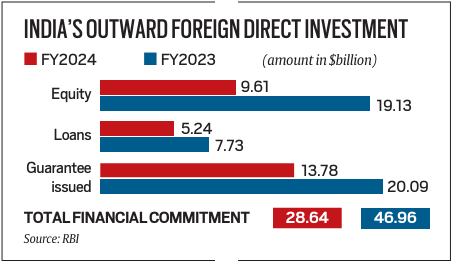
6. India’s Outward Foreign Direct Investment (OFDI) Plummets by 39% to $28.64 Billion Amid Global Economic Uncertainties
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy –
This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains in the context of understanding the trends and factors affecting India’s outward FDI. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Comparative Analysis with Previous Years:
- In contrast, the previous fiscal year ending March 2023 witnessed a higher outward FDI of $46.96 billion, reflecting a notable decrease in OFDI commitments in the following year.
- The decline in OFDI commitments is evident both under the automatic route and the approval route, indicating a broad-based reduction in overseas investment activities.
Composition of Outward FDI Commitments:
- The breakdown of outward FDI commitments reveals a notable decline in equity investments, which stood at $9.62 billion in fiscal year 2024 compared to $19.13 billion in fiscal year 2023.
- Equity contributions constituted approximately 34 percent of the total financial commitments made in fiscal year 2024, highlighting a significant reduction in equity-based overseas investments by Indian companies.
- Similarly, loan commitments also witnessed a decline from $7.73 billion in fiscal year 2023 to $5.24 billion in fiscal year 2024.
- This decrease in loan commitments reflects a cautious approach towards leveraging external financing for overseas ventures amidst prevailing economic uncertainties.
Factors Influencing Outward FDI Trends:
- Economists and experts attribute the decline in outward FDI to the limited availability of investment opportunities for Indian companies amidst the global economic flux.
- The uncertain economic environment may have deterred Indian companies from pursuing large-scale overseas acquisitions, contributing to the overall decline in outward FDI commitments.
Month-wise Trends and Observations:
- March 2024 marked the highest outward FDI for the fiscal year, with commitments amounting to $3.92 billion.
- Equity commitments in March 2024 reached $2.03 billion, the highest recorded for the year.
- Additionally, loan commitments in March amounted to $1.05 billion, with guarantees issued standing at $839.17 million, indicating a surge in overseas investment activities towards the end of the fiscal year.
Conclusion:
- The decline in India’s outward FDI underscores the impact of global economic uncertainties on cross-border investment decisions.
- As Indian companies navigate through volatile market conditions, the cautious approach towards overseas investments reflects the need for strategic evaluation of investment opportunities and risk management strategies in the international arena.
| What is Foreign Direct Investment? |
About:
|
| PYQ: Consider the following: (2021)
1) Foreign currency convertible bonds 2) Foreign institutional investment with certain conditions 3) Global depository receipts 4) Non-resident external deposits Which of the above can be included in Foreign Direct Investments? (a) 1, 2 and 3 (b) 3 only (c) 2 and 4 (d) 1 and 4 Ans: (a) |
| Practice Question: Explain the recent trends in India’s outward foreign direct investment (OFDI) and discuss the factors influencing its decline in the fiscal year ending March 2024. How can India encourage overseas investment by its companies amidst global economic uncertainties? (250 words/15 m) |
7. Election Season Alert: Rise of Deepfake Videos Sparks Concerns Over Manipulated Media
| Topic: GS2 – Governance – Government policies – Interventions for development in various sectors
GS3 – Science & Technology – This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains as the issue of disinformation and manipulated media online raises questions about the role of governance in regulating digital spaces and ensuring the integrity of democratic processes. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Manipulated Videos of Actors Aamir Khan and Ranveer Singh:
- Two manipulated videos of actor Aamir Khan went viral recently, one portraying him as explicitly supporting the Congress party and the other featuring him speaking about “nyay” (justice), a key Congress talking point.
- Similarly, actor Ranveer Singh became a victim of deepfake technology when a manipulated video of him criticizing Prime Minister Narendra Modi on issues like unemployment and inflation circulated widely.
- However, the original clip revealed Singh actually praising the Prime Minister.
Voice Swap Technology and its Application:
- Deepfake videos are created using sophisticated techniques like voice swap technology.
- Platforms like ai, developed in collaboration with IIT Jodhpur, demonstrate how voice swap technology is used to alter or mimic an individual’s voice, including accent, tone, pitch, and speech patterns.
- This technology allows creators to make the manipulated videos appear more realistic by modifying various characteristics of the voice.
Spotting Deepfakes:
- Detecting deepfake videos can be challenging, but there are several strategies to identify them.
- Verifying sources is crucial, especially for controversial or sensational content. Listening for anomalies in audio, such as unnatural tonality or robotic speech, can also indicate manipulation.
- Scrutinizing visual content for inconsistencies, such as lips not syncing with speech, is another method.
- Staying informed about current events helps individuals recognize the risks associated with deepfakes.
- Additionally, using AI voice detectors can assist in determining the authenticity of suspicious audio or video content.
Conclusion:
- The proliferation of deepfake videos poses a significant challenge during election periods, where misinformation can influence public opinion.
- Understanding the techniques used to create deepfakes and employing strategies to identify them are essential steps in combating the spread of false narratives and ensuring the integrity of democratic processes.
| What are Deepfakes? |
About:
|
| PYQ: With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
1) Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units 2) Create meaningful short stories and songs 3) Disease diagnosis 4) Text-to-Speech Conversion 5) Wireless transmission of electrical energy Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only (b) 1, 3 and 4 only (c) 2, 4 and 5 only (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 Ans: (b) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the proliferation of deepfake videos during elections and their implications for democratic processes. Evaluate the challenges posed by manipulated media in influencing public opinion and electoral outcomes. Suggest strategies to mitigate the spread of disinformation and safeguard the integrity of electoral processes in the digital age.. (250 words/15 m) |
8. Report Reveals Discrepancy in Sugar Content of Nestlé Baby Foods Across Regions
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice – Health
This topic is relevant for both Prelims and Mains as the analysis sheds light on the impact of added sugars in baby food on infant nutrition and health. |
| Context: |
|
More about the news:
Dominance of Nestlé in the Baby Food Market:
- Nestlé, the world’s largest packaged food company, reportedly controls 20% of the baby food market, valued at nearly $70 billion.
- The report points out that all 15 products under Nestlé’s Cerelac brand in India, designed for babies aged 6 months and older, contain an average of 7 grams of added sugar per serving.
Corporate Response and Regulatory Scrutiny:
- A spokesperson for Nestlé India acknowledged the issue, stating that the reduction of added sugars is a priority, with a reduction of up to 30% achieved over the past five years.
- However, regulatory bodies like the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) are yet to comment on the report.
- Government officials have indicated that lab reports of the samples from India will be sought and examined by the FSSAI’s subject expert committee.
Understanding Added Sugars and their Impact:
- Added sugars, as defined by the American Heart Association (AHA), are sweetening agents added to processed foods and beverages.
- Unlike naturally occurring sugars found in fruits and milk, added sugars are considered more harmful, contributing to health issues such as obesity and chronic diseases.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) advises against the introduction of added sugars in baby food before the age of 2, citing risks of developing addictive eating habits and long-term health consequences.
Lack of Clear Regulations in India:
- The report underscores the absence of upper limits for added sugars in Indian regulations governing infant nutrition.
- While the regulations outline requirements for macronutrients and micronutrients, they do not specify limits for added sugars.
- Moreover, the regulations permit the use of certain sweeteners in cereal-based infant food, further complicating the issue of sugar content in baby products.
Conclusion:
- The discrepancy in sugar content across regions in Nestlé’s baby food products raises concerns about the adequacy of regulatory oversight and the potential health implications for infants.
- As public scrutiny intensifies and regulatory bodies delve deeper into the matter, there is a pressing need to establish clearer guidelines and standards to ensure the safety and nutritional quality of baby food products in India.
| Challenges Related to Food Processing Sector: |
|
| PYQ: With what purpose is the Government of India promoting the concept of “Mega Food Parks”? (2011)
1) To provide good infrastructure facilities for the food processing industry. 2) To increase the processing of perishable items and reduce wastage. 3) To provide emerging and eco-friendly food processing technologies to entrepreneurs. Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (b) |
| Practice Question: Discuss the concerns raised by the recent report on Nestlé’s baby food products regarding their sugar content in different regions. Evaluate the potential health implications of added sugar in infant nutrition and suggest measures to address this issue. (250 words/15 m) |
For Enquiry

19 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

19 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

19 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

19 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC

19 April 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

19 April 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis

18 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz

18 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing

18 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs

18 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC
Daily Quiz 19 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 19- April 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 19 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
19-April-2024
Q1) Critically evaluate the performance of Goods and Services Tax…
April 2024 Daily Current Affairs 19 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
19-April -2024- Top News of the Day
1. Indigenously built cruise missile successfully…
April 2024 PIB 19 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
19-April-2024
1. IREDA’s GIFT City office to boost Green Hydrogen and Renewable…
April 2024 The Hindu Editorial 19 April 2024 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu EDITORIAL
19-April-2024
1. A world in disarray, a concern about the future
Topic: GS2…
April 2024 Indian Express 19 April 2024 : Indian Express Editorial Analysis Indian Express Editorial Analysis
19-April-2024
1. Clash of aspirations
Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy
This…
Daily Quiz 18 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Quiz 18- April 2024 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 18 April 2024 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
18-April-2024
Q1) Limiting the country’s fiscal deficit is a cherished goal, but…
April 2024 Daily Current Affairs 18 April 2024 : Daily Current Affairs Daily Current Affairs
18-April -2024- Top News of the Day
1. ICMR Initiates Study to Address Maternal…
April 2024 PIB 18 April 2024 : PIB Summary for UPSC PIB Summary for UPSC
18-April-2024
1. SPACE, a premier testing & evaluation hub for sonar systems…







