27 September 2023 : Daily Current Affair
Daily Current Affairs
27-September-2023
Daily Current Affairs For UPSC ,Daily Current affairs of The hIndu and Indian Express.
1. Punjab govt. commits to 50% reduction in stubble burning cases this year.
Topic: GS3 – environmental pollution.
Context:
- The Punjab government has pledged to decrease paddy stubble burning incidents by at least 50% compared to the previous year.
- Stubble burning is a significant issue in northern states during October-November, contributing to air pollution in Delhi and nearby regions.
Issues with Stubble Burning in Northern India:
- Air Pollution: Stubble burning releases pollutants and particulate matter into the air, leading to poor air quality. Smoke from burning fields contributes to severe pollution.
- Health Impacts: The smoke and pollutants can harm respiratory health, exacerbate asthma, and increase the risk of heart conditions, posing health risks to residents.
- Visibility and Road Safety: Thick smoke reduces visibility on roads, increasing the risk of accidents for drivers and pedestrians.
- ontribution to Smog: Stubble burning contributes to winter smog, disrupting daily life, outdoor activities, and even causing flight delays.
- Environmental Damage: It depletes soil nutrients, contributes to soil degradation, and reduces biodiversity in affected areas.
- Economic Impact: Stubble burning leads to soil fertility loss, reducing crop yields and increasing input costs, affecting farmers economically.
Possible solutions:
- Promotion of Mechanized Farming: Encourage farmers to adopt modern machinery for crop residue management, such as straw balers and shredders, which can help incorporate stubble into the soil without burning.
- Crop Diversification: Promote crop diversification by incentivizing the cultivation of crops that do not generate as much crop residue, reducing the need for stubble burning.
- Financial Incentives: Provide financial incentives to farmers who adopt sustainable practices and refrain from stubble burning.
- Subsidized Farm Machinery: Offer subsidies or loans for the purchase of farm machinery that can manage crop residue effectively, making it more accessible to small and marginal farmers.
- Biomass Energy: Encourage the use of crop residue for biomass energy production, creating an additional source of income for farmers and reducing the need for burning.
- Awareness Campaigns: Conduct awareness campaigns to educate farmers about the harmful effects of stubble burning and the benefits of alternative practices.
2. Balsams in full bloom add to visual treat in Munnar
Topic: GS3 – environmental diversity.
Context:
- Balsams (genus Impatiens) are currently in full bloom in Munnar, known locally as Kasithumba and Onappovu, offering a visual treat to tourists.
- These small, pink flowers are a major attraction along the Devikulam stretch of the Kochi-Dhanushkodi National Highway.
About Balsams:
- Balsams (genus Impatiens) are flowering plants known for their vibrant, small, pink flowers.
- They are commonly referred to as “touch-me-not” due to their unique seed distribution mechanism, where mature seeds burst open upon touch, scattering them for propagation.
- Balsams are found in various regions, including Munnar in Kerala, India.
- In Munnar, they are known as Kasithumba and Onappovu, and their blooming season typically occurs from June to December.
- The Munnar region is renowned for its rich diversity of balsams, with over 46 different species discovered in the area.
- The Western Ghats, particularly the high ranges like Anamudi, harbor a significant variety of wild balsams, some of which are endemic to these high-altitude areas.
- These plants usually thrive in humid habitats and have a life cycle closely tied to the rainy season.
- Balsams serve as a valuable indicator species for monitoring climate change, as shifts in their populations can reflect environmental changes.
3. Indo-Pacific region a web of interdependencies: Army chief
Topic: GS2 – International relations.
Context:
- The Indo-Pacific region is characterized by its intricate interdependencies among nations, according to India’s Army Chief, General Manoj Pande, emphasizing that it extends beyond a mere collection of countries.
- While addressing the 13th Indo-Pacific Army Chiefs Conference, General Pande highlighted the security and humanitarian concerns that span not only the maritime domain but also the land, alluding to the South China Sea territorial disputes without direct naming.
Additional information about the news:
- Key challenges in the region include territorial disputes, artificial island expansions for military purposes, transnational terrorism, the impact of climate change on coastal areas, and natural disasters.
- General Pande emphasized that these challenges are collective threats that affect multiple nations, highlighting the necessity of cooperation among land forces to formulate a unified response.
- General Randy George, the Chief of Staff of the U.S. Army, stressed the importance of unity and collective commitment to address regional security challenges, acknowledging the region’s critical significance for the U.S.
Key challenges in the region:
- Territorial Disputes: The Indo-Pacific region witnesses various territorial disputes over land masses and maritime boundaries, often leading to tensions and conflicts among neighboring nations. These disputes can involve competing claims over islands, exclusive economic zones (EEZs), and other strategic areas.
- Artificial Island Expansion: Some countries have engaged in land reclamation and artificial island-building activities, especially in the South China Sea. These activities are primarily aimed at expanding their territorial claims and establishing military bases, which has raised concerns and led to regional tensions.
- Transnational Terrorism: The region faces threats from transnational terrorist organizations operating in multiple countries. These groups exploit porous borders and regional instabilities, posing security challenges to nations in the Indo-Pacific.
- Climate Change Impacts: The consequences of climate change, such as rising sea levels and extreme weather events, disproportionately affect coastal areas and inhabited islands in the region. These changes can lead to displacement, loss of livelihoods, and increased vulnerabilities.
- Natural Calamities: The Indo-Pacific is prone to natural disasters like earthquakes, tsunamis, cyclones, and typhoons. These disasters can cause widespread destruction, disrupt infrastructure, and require coordinated disaster response efforts.
- Piracy: Maritime piracy remains a concern in certain parts of the Indo-Pacific, particularly in waters with heavy shipping traffic. Piracy incidents can impact trade, maritime security, and the safety of seafarers.
- Boundary Disputes: Along with territorial disputes, some countries in the region have unresolved boundary issues, leading to occasional tensions and conflicts along land borders.
4. 95% of components used in Indian rockets indigenous, says ISRO chief at CSIR event.
Topic: GS3 – Science and technology
ISRO’s Indigenous Rocket Components:
- Indigenous Rocket Components: Approximately 95% of the components used in rockets, including those for the Chandrayaan-3 mission, were manufactured in India. This achievement was the result of several years of collaboration between the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Indian industries, laboratories, and defense institutions.
- Collaborations and Research: The development of these components involved collaborations with various agencies, including Indian laboratories, national labs, defense labs, and the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR). The focus was on material indigenization, technology capabilities, and research.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: ISRO developed its lithium-ion batteries for space applications and is in the process of transferring this technology to industry. These batteries are essential for powering spacecraft and missions.
- Semi-Conductor Laboratory (SCL): Chandigarh’s Semi-Conductor Laboratory played a significant role in producing key components for space missions. Only about 5% of high-end electronics were imported for these missions.
- Indigenous Industry: ISRO’s efforts have resulted in the creation of an industry capable of producing critical components for space missions, including battery systems, storage, and solar cells.
- Contribution to Socio-Economic Growth: The Indian space program is not only aligned with national aspirations but also contributes to socio-economic growth by developing advanced technologies and fostering collaboration between scientific institutions and industry.
5. NHRC seeks action taken report on welfare of transpersons from govt.
Topic: GS2 – International relations.
Context:
- The NHRC has issued an advisory to the Centre, State governments, and Union Territory administrations regarding the welfare of transgender persons.
- The advisory includes provisions for separate toilets, free sex reassignment surgery, pension rights, and inheritance rights for transgender individuals.
More information about the news:
- Despite legal reforms, transgender individuals in India continue to face discrimination, resulting in employment disparities, limited access to healthcare, and exclusion from social circles.
- The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019, aims to protect and uphold the rights of transgender individuals.
- The NHRC has requested the implementation of its recommendations and action-taken reports within two months from relevant authorities.
NHRC’s Powers to seek a report from the government:
The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) in India has the authority to seek a report from the government or any relevant authority regarding human rights violations or issues of public interest. This power is derived from the Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993, which established the NHRC.
Under Section 12 of the Protection of Human Rights Act, the NHRC has the following powers:
- To inquire, suo motu or based on a complaint, into complaints of human rights violations or negligence in the prevention of such violations by a public servant.
- To visit and inspect any jail or other institution under the control of the State government where persons are detained or lodged for purposes of treatment, reformation, or protection to study the living conditions and make recommendations.
- To review the safeguards provided under various laws for the protection of human rights and recommend measures for their effective implementation.
- To undertake and promote research and educational programs on human rights.
- To encourage the efforts of non-governmental organizations and institutions working in the field of human rights.
6. Centre softens angel tax rules.
Topic: GS3 – Indian economy.
Context:
- The Indian government has eased certain provisions of the angel tax introduced in the recent Budget, specifically targeting investments into startups by non-resident investors at a premium over their fair market value.
What is angel tax:
- Angel tax refers to the taxation of capital raised by unlisted companies, primarily startups, through the issuance of shares at a premium over their fair market value.
- The tax authorities in India have been concerned about startups issuing shares at a premium that exceeds their fair value, viewing such premiums as taxable income for the startups.
- This taxation practice has led to disputes and challenges for startups and investors, as valuing early-stage companies can be subjective and complex.
- To address this issue, the Indian government has introduced various measures and changes to the angel tax regulations over the years.
- These measures aim to provide relief to startups and investors by raising the threshold for exemptions and introducing valuation guidelines to reduce tax disputes.
- The goal is to create a more favorable environment for startup growth and investment, making it easier for innovative companies to raise capital without facing heavy taxation.
7. Nepal says ‘no’ to China’s Security Initiative
Topic: GS2 – International relations.
Context:
- Nepal has indicated its reluctance to join China’s Global Security Initiative (GSI) during Prime Minister Prachanda’s visit to Beijing.
- While Nepal expressed support for China’s Global Development Initiative (GDI), it stopped short of endorsing the GSI, a key security cooperation initiative proposed by President Xi Jinping.
What are China’s Global Security Initiative (GSI) and Global Development Initiative (GDI):
- China’s Global Security Initiative (GSI) and Global Development Initiative (GDI) are two ambitious foreign policy initiatives that were first proposed by President Xi Jinping in 2021.
- The GSI is a proposal for a new global security order that is based on the principles of common, comprehensive, cooperative, and sustainable security. It emphasizes the importance of multilateralism and cooperation in addressing global security challenges. The GSI also calls for a more balanced and inclusive approach to global security, one that takes into account the interests of all countries, regardless of size or power.
- The GDI is a proposal for a new global development agenda that is focused on promoting sustainable development and common prosperity for all. It calls for a more inclusive and equitable approach to development, one that is based on the principles of multilateralism, sustainable development, innovation, and green development.
- Both the GSI and the GDI have been met with mixed reactions from the international community. Some countries have welcomed the initiatives as a positive step towards addressing global challenges, while others have expressed concerns about China’s motives and the potential impact of the initiatives on the existing global order.
8. China refuses to expand CPEC terms with Pak
Topic: GS2-IR
Context:
- China has refused to further expand cooperation in the areas of energy, water management, and climate change under the multibillion dollar China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), signalling a strain in the friendship between the two all-weather allies.
Details:
- Cash-strapped Pakistan also gave up its opposition to setting up a new imported coal-fired power plant in Gwadar in Balochistan province and agreed to a number of Chinese demands to address Beijing’s concerns.
About China–Pakistan Economic Corridor
- It is a 3000 km Chinese infrastructure network project undertaken in Pakistan.
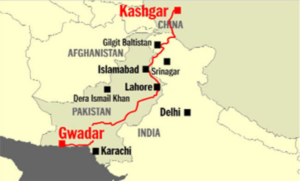
Features
- After the proposal from Chinese President Li Keqiang in 2013, the preliminary study on this project was done in 2014 which acknowledged the hostile environment and complicated geographic conditions but prioritized the importance of having a China-run port near the Gulf of Oman.
- Post this corridor is functional, existing 12,000 km journey of oil transportation to China will be reduced to just 2,395 km.
- This is estimated to save China $2 billion per year.
- China had already acquired control of Gwadar Port in 2013.
- Originally valued at $46 billion, the value of CPEC projects was worth $62 billion as of 2020.
- China refers to this project as revival of the Silk Road.
Indian objections
- India’s objections to Chinese activity in Pakistan-administered Kashmir dates back to the 1970s, when the People’s Liberation Army built the Karakoram Highway that linked China’s far-western province of Xinjiang with northern Pakistan.
- The GoI, which shares tense relations with Pakistan, objects to the CPEC project as upgrade works to the Karakoram Highway are taking place in Gilgit-Baltistan, territory that India claims as its own.
9. Law Commission readies report on simultaneous elections
Topic: GS2-Polity
Context:
- The Law Commission of India is set to submit a report recommending simultaneous elections in the country.
- The Commission is likely to frame tentative timelines for simultaneous polls for the 2024 and 2029 cycles.
Details:
- The report by the 22nd Law Commission, which will be submitted to the Law Ministry, will be one of three — the other two reports are on the minimum age of consent under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, and recommendation of a law to provide for online filing of First Information Reports.
- The Commission’s report is set to be submitted days after the government, citing “national interest”, formed a high-level committee headed by former President Ram Nath Kovind to “examine and make recommendations for holding simultaneous elections” to Lok Sabha, state Assemblies, municipalities and panchayats.
One nation, one election
About
- “One nation, one election” is a concept aimed at synchronizing the timing of elections for various tiers of government in India, primarily the Lok Sabha (national parliament) and state legislative assemblies. The idea behind this concept is to streamline the electoral process, reduce election-related expenses, and ensure continuity in governance.
10.Grameen Samvaad Yatra
Topic: Prelims
Context:
- Ahead of the Lok Sabha elections next year, the BJP-led government at the Centre is planning a ‘Grameen Samvaad Yatra’ which would be a mega outreach programme with the dual purpose of showcasing its achievements as well as enroling new beneficiaries to ensure “saturation coverage” of Central schemes.
Details:
- Besides being equipped with GPS and drones, the specially-designed raths will have LED display screens and preloaded audio-visual content to highlight the major Central schemes and demonstrate innovations and new technologies.
- Conceptualised on the “whole of government approach”, it is expected to be a two-month-long exercise.
- While the launch date is yet to be finalised, it is learnt that the yatra may begin in October-November.
11. Anti-drone system along International Border soon: Home minister
Topic: GS3-Internal Security
Context:
- Union home Minister Amit Shah said anti-drone system will be deployed along the international border for strengthening security.
Details:
- Smuggling of arms, ammunition and narcotics from across the international border to Punjab and Jammu and Kashmir has been a major problem confronting the border guarding forces.
How anti drone system works?
- Unwanted drones and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are detected and/or intercepted using anti-drone devices.
- The proliferation of low-cost UAVs has increased the number of hostile drone occurrences. These incidents may involve the use of hostile drones to drop explosives, smuggle drugs, or gather intelligence on valuable assets.
- Large public spaces including stadiums, key infrastructure, airports, military installations, and battleground locations are all protected by anti-drone equipment.
- Based on their visual and thermal characteristics, respectively, electro-optical (EO) and infrared (IR) sensors can be used to find drones in the air.
- These sensors might need to be combined with artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques to lessen the possibility of false positives and false negatives.
- There are multi-camera EO/IR gimbals for anti-drone systems that can be mounted on stationary objects or moving vehicles.
- Acoustic Counter-Unmanned Aircraft System (CUAS) detection systems compare drone propulsion system noise to a sound database. Other nearby sounds can have an impact on their accuracy.
- The System has already been shown to the military and other internal security organizations.
12. Home Ministry extends disturbed area status in parts of Arunachal and Nagaland by six months
Topic: GS3-Internal security
Context:
- The Union Home Ministry extended for another six months the disturbed area status in parts of Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland under the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act,1958.
Details:
- The decisions have been taken after review of the law-and-order situation in both the states.
- The central government had declared the Tirap, Changlang and Longding districts in Arunachal Pradesh and the areas falling within the jurisdiction of Namsai and Mahadevpur police stations in Namsai district of Arunachal Pradesh, bordering the state of Assam as ‘disturbed area’ on March24, 2023.
About Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)
- The Army, Air Force, and Central paramilitary forces are given exceptional authority and immunity to uphold public order in “disturbed areas” under a statute passed by the Parliament in 1958.
When can it be used?
- It can only be used when a region has been designated as “disturbed” in accordance with section 2 of the legislation.
What is a disturbed area?
- Disagreements between various castes, communities, or religious, ethnic, linguistic, or regional groups might be regarded as causing disturbance in a certain area.
- A “disturbed area” is defined by Section 3 of the AFSPA as a state or a region that has been officially declared as such by the governor of the state or Union territory.
- The center then has the option of sending in armed forces in response.
The ‘special powers’ of armed forces under Section 4 are:
Under Section 4, the armed forces have the following “special powers”:
- the ability to use deadly force, destroy ammunition and weapon dumps, and fortifications and covert locations.
- authority to make arrests without a warrant.
- Without a warrant or a reason, you have the right to search and seize.
- It demands that people who have been detained and seized property be sent as quickly as possible to the local police station.
- Unless the Union Government gives the prosecuting agency permission, certain armed forces are free from prosecution.
For Enquiry

27 September 2023 : Daily Current Affair

27 September 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

26 September 2023 : Daily Quiz

26 September 2023 : Daily Answer Writing

26 September 2023 : Indian Express

26 September 2023 : PIB

26 September 2023 : Daily Current Affair

26 September 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

25 September 2023 : Daily Quiz

25 September 2023 : Daily Answer Writing
Daily Current Affairs 27 September 2023 : Daily Current Affair Daily Current Affairs
27-September-2023
Daily Current Affairs For UPSC ,Daily Current affairs of The…
September- The Hindu Editorial 27 September 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu Editorial
27-September-2023
Daily Current Affairs For UPSC ,The Hindu Editorial Summary
Facebook-f
Twitter
Youtube
1. With…
Daily Quiz 26 September 2023 : Daily Quiz 26 Sep 2023 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 26 September 2023 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
One of the key components of these exams is the written test, which consists of…
Indian Express 26 September 2023 : Indian Express Indian Express
26-September-2023
The Indian Express, CSE candidates can stay informed about current…
PIB 26 September 2023 : PIB PRESS INFORMATION BUREAU
26-September -2023
Daily Current Affairs For UPSC ,The PIB ( Press Information…
Daily Current Affairs 26 September 2023 : Daily Current Affair Daily Current Affairs
26-September-2023
Daily Current Affairs For UPSC ,Daily Current affairs of The…
September- The Hindu Editorial 26 September 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu Editorial
26-September-2023
Daily Current Affairs For UPSC ,The Hindu Editorial Summary
Facebook-f
Twitter
Youtube
1. On…
Daily Quiz 25 September 2023 : Daily Quiz 25 Sep 2023 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 25 September 2023 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
One of the key components of these exams is the written test, which consists of…

