9 Oct 2023 : Indian Express
Indian Express
9-October-2023
1) Israel-Palestine Conflict
Context:
- On the morning of Saturday, October 7, the Palestinian group Hamas carried out a surprise attack on Israel on an unprecedented scale: firing thousands of rockets, infiltrating militants into Israeli territory, and taking an unknown number of hostages.
- This article will discuss the reasons for the age-old Israel Palestine conflict.
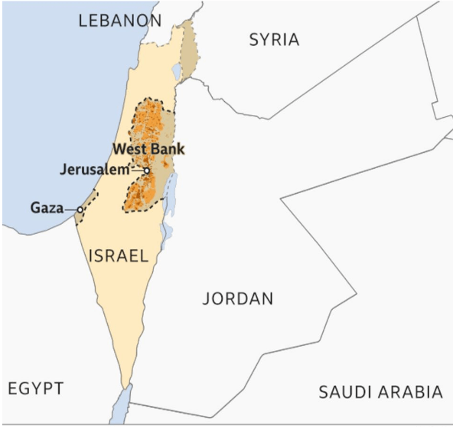
What is the Israel-Palestine conflict?
- Jews and Arabs have been at odds over a plot of land between the Jordan and Mediterranean rivers for more than a century.
- The UN decided in 1947 to divide Palestine into Jewish and Arab governments, with Jerusalem becoming a global metropolis.
- Jewish authorities agreed to the proposal, but the Arab side opposed it and it was never put into action.
More Details:
- First off, Israel, which is situated just east of the Mediterranean Sea, is the only Jewish state in the world. Arab residents of the area call it Palestine, and they desire to create a state called Palestine on all or a portion of that region.
- Second, the Israeli-Palestinian conflict centres on the ownership and management of land.
- Thirdly, the current political battle started in the early 20th century, despite the fact that Jews and Arab Muslims both date their claims to the country back several thousand years.
- Fourthly, Jews who were escaping persecution in Europe yearned to establish a national homeland in a region with a predominance of Arab and Muslim people. The Ottoman Empire and, later, the British Empire both included this region.
- Fifth, the Arabs opposed, believing they had a claim to the country. Both sides have since fought numerous wars over the land.
About Hamas and Fatah:
- The Palestine Liberation Organization’s largest group, Fatah, is intimately associated with Yasser Arafat’s leadership.
- Hamas on the other hand is a fundamentalist Sunni-Islamic group in Palestine.
- Fatah lost its majority in the Palestinian parliament to Hamas in the 2006 legislative elections.
- As a result, a struggle erupted between Fatah and Hamas, with the former controlling the Palestinian National Authority in the West Bank and the latter ruling Gaza.
- Both parties have vowed to put all of Palestine back under Islamic governance.
- Their main point of contention is how to best accomplish this shared goal; while Fatah favours a nonviolent approach, Hamas prefers to use violence.
Potential Remedies for Israel Arab-Israeli conflict
There are primarily two methods for solving the issue:
- Two-state solution:
- It would first establish independent Israel and Palestine. Gaza and the majority of the West Bank would be turned up to Palestine as an independent state, leaving Israel to control the remaining territory.
- Since the 1947 UN Partition Plan, it has been the objective of the international community.
- It would specify the Green Line, a demarcation line that divided Israeli and Palestinian territory in 1967. Jerusalem would also be split between the two states.
One-state solution:
- Israel, the West Bank, and the Gaza Strip would all be combined into one huge nation.
- There are two variations of it. One would establish a solitary democratic nation, which is supported by certain leftists and Palestinians. Jews would be outnumbered by Arab Muslims, eliminating Israel’s identity as a Jewish state.
- The alternative proposal, which is supported by some right-leaning Israelis, calls for Israel to annex the West Bank and forcibly remove or deny voting rights to Palestinians.
Why hasn’t the problem been fixed yet?
- Jerusalem: The Palestinians and Israel both have conflicting claims to the city. Israel considers the entirety of Jerusalem to be its capital and took control of the formerly Jordanian-held eastern portion in 1967.
- Palestinian Statehood: PLO and Israeli authorities have yet to reach an agreement on the issue of the Palestinian Statehood. Israel further claims that any peace agreement must call for Palestinian acknowledgment of it as the “nation-state of the Jewish people”.
- Borders: The positions of the prospective borders of a Palestinian state are fundamentally disputed by both parties. Palestinians demand borders based on the 1949–1967 ceasefire lines that divided Israel from East Jerusalem, the West Bank, and Gaza. Israel, meanwhile, has requested an expansion of its eastern boundary all the way to the Jordan River.
- Settlements: In the occupied West Bank and East Jerusalem since 1967, Israel has constructed around 140 settlements which the majority of the international community views them as illegal. For a viable Palestinian state, according to the Palestinians, all settlements must be razed.
- Refugees:5 million Palestinian refugees are reportedly supported by UN agencies in the Middle East. This covers the offspring of those who left or were driven from their homes by Jewish forces during the 1948–1949 conflict. Israel claims that the Palestinians do not have the right to return to their previous homes, despite the Palestinians’ insistence.
- Political Division: Palestinians are still divided politically between Fatah and Hamas, making it impossible for them to engage in joint negotiations. Israel also doesn’t want to talk to the terrorist organisation Hamas.
Conclusion
- The international community must make an effort to bring the two states together in peace.
- A successful peace initiative would also need to address the four main problems that have hampered the peace process: Israeli security, Palestinian refugees, West Bank borders and settlements, and Jerusalem.
2) The Rise of Services
Context:
- India has been performing quite well in two sectors viz. the fast-evolving services exports to the rest of the world while the other is the rapid transformation of domestic services.
- This article will discuss the various reasons for this leap and also the possible steps that should be taken to grow on a large scale.
The services export sector:
This sector now generates $60 billion more in annual revenues than they did three years ago, on a net basis.
Reasons for growth:
- IT services received a boost during the pandemic period.
- The demand for tech expertise surged as more people chose to work from home.
- India has advanced up the value chain and is now selling a wide range of professional services, including business development, design, and R&D in addition to accounting, law, and HR and the list is growing.
- Large IT companies are not the sole sources of growth, even if they continue to expand. Mid-sized IT companies have been expanding their markets, while consulting companies are expanding their service export books.
India can now boast the world’s largest share in Global Capability Centres (GCCs)
What are GCCs?
- Global capability centres, or GCCs are overseas divisions of multinational firms with operations all over the world. These centres are in charge of offering their parent organisations a range of support services, including IT, finance, human resources, and analytics. In the past, these divisions were mostly created to offshore back-office functions, but that is no longer the case. Today’s GCCs manage more complicated line items throughout the value chain of the firm. They have evolved into hubs for product creation, operational excellence, and innovation.
- In2022- 23, around 1,600 GCCs made up a market of $46 billion, employing 1.7 million. These facilities have significantly aided India’s economic development by generating high-quality employment opportunities and raising the GDP of the nation.
- These GCCs, which stand in for international corporations in India, cover a wide range of industries, including engineering, consulting, and technology. In reality, a number of these innovation centres have chosen India as their preferred location due to the nation’s enormous pool of creative and trained workers, cost-effectiveness, and supporting government regulations.
Possible reasons which may help maintain this growth:
- There is a seemingly permanent change in attitude about getting more work done from “home”.
- India can provide a talent set that can create a variety of services, from engineering to design. This has been made possible by impressive internet penetration, young and digitally savvy demographics, and rising educational attainment.
- India offers cost-competitiveness. For instance, in value terms, Indian IT services exports make up 18 per cent of global trade, but in volume terms, this doubles to 36 per cent.
- Many multinationals are increasing their footprint in India. Those which started with producing services, for instance via GCCs, are increasing the range of services and some, especially in sectors such as medical equipment, electronics, and precision manufacturing, are even crossing over into manufacturing.
The Domestic Services Sector:
- India has a remarkable public digital infrastructure.
- It has been tapped into by numerous tech start-ups employing a range of business models.
- The majority are concentrated in the services industry, but if they get more ambitious, they may transition to manufacturing and agriculture.
- In a sense, they may take up the challenge of raising “old India” up rather than being limited to building “new India.”
How can growth be achieved in this sector?
Manufacturing sector
- Many of the everyday issues faced by small manufacturers can be resolved using digital infrastructure.
- Small businesses may benefit from start-ups if they want to access formal funding, cheaper raw materials, larger final markets, better warehousing and logistics, and improved quality controls.
- By enabling small manufacturers to gain the advantages larger ones benefit as they are incentivised to expand.
- We are already finding evidence of the “new” domestic services sector companies, for instance in the transport services, procurement support, and ecommerce sectors, making forays into manufacturing.
Why is growth of this sector important?
- Slow-moving low- and medium-tech manufacturing is the root of India’s employment issue.
- Too many manufacturing companies fail to take advantage of economies of scale or produce enough jobs because they stay too small for too long.
- India requires a raft of reforms to get rid of many of the obstacles that manufacturers encounter.
Way Forward:
- An increase in contemporary services can boost manufacturing.
- Therefore, it is encouraging to see examples of global corporations switching over to manufacturing goods in India.
- It is also encouraging to observe how domestic service startups are branching out into manufacturing.
- This may signal the beginning of a pattern that spurs economic expansion and employment creation.
For Enquiry

9 Oct 2023 : Indian Express

9 Oct 2023 : PIB

9 October 2023 : Daily Current Affair

9 October 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF

7 Oct 2023 : Daily Quiz

7 Oct 2023 : Daily Answer Writing

7 Oct 2023 : Indian Express

7 Oct 2023 : PIB

7 October 2023 : Daily Current Affair

7 October 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF
Indian Express 9 Oct 2023 : Indian Express Indian Express
7-October-2023
1) RBI’s MPC Meet
Context:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has released…
October 2023 PIB 9 Oct 2023 : PIB PRESS INFORMATION BUREAU
9-Oct -2023
1. Government of India has taken several steps to strengthen all…
Daily Current Affairs 9 October 2023 : Daily Current Affair Daily Current Affairs
9-October-2023
1. Israeli air strikes pound Gaza as death toll climbs.
Topic:…
October 2023 The Hindu 9 October 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu Editorial
9-October-2023
1. A census for a new deal.
Topic: GS2 – Indian polity
Context:
Caste…
Daily Quiz 7 Oct 2023 : Daily Quiz 7 Oct 2023 : Daily Quiz…
mains answer writing 7 Oct 2023 : Daily Answer Writing Mains Answer Writing
7-october-2023
Q1) The collective strength of BRICS nations allows for meaningful…
Indian Express 7 Oct 2023 : Indian Express Indian Express
7-October-2023
1) RBI’s MPC Meet
Context:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has released…
October 2023 PIB 7 Oct 2023 : PIB PRESS INFORMATION BUREAU
7-Oct -2023
1. Bureau of Indian Standards conducts 1176 exposure visits for…
Daily Current Affairs 7 October 2023 : Daily Current Affair Daily Current Affairs
7-October-2023
1. Nobel Peace Prize 2023 goes to jailed Iranian activist Narges…
October 2023 The Hindu 7 October 2023 : The Hindu Editorial Notes PDF The Hindu Editorial
7-October-2023
1. Aligning higher education with the United Nations SDGs
Topic:…





